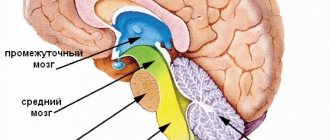
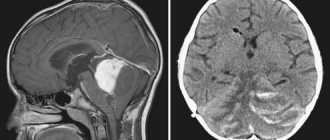
Pineoblastoma is a fairly rare type of neoplasm that originates in or near the pineal gland. This tumor is a rare cerebral tumor. Pineoblastoma of the brain occurs most often in children; boys are usually affected by this pathology, although precise data on gender distribution is not available.
Morphology
The parenchyma cells of the pineal gland - pinealocytes or pineocytes - have a polygonal shape. There are also glial cells - gliocytes. Recently, 4 more types of cells have been discovered:
- interstitial endocrinocytes;
- perivascular phagocytes;
- neurons;
- peptidergic neuron-like cells.
The full significance of the gland has not yet been clarified; this is explained by its small size, depth and complexity of location. Very little is known exactly about its effect on the functioning of internal organs.
Risks and forecasts
The main risk factor for the formation of a benign formation in the pineal gland should be considered the increased likelihood of hydrocephalus. Formations in this segment of the brain increase extremely rarely. In this regard, the formed cyst in no way affects the functioning of the pineal gland and the brain as a whole.
Periodic checks of the tumor will make it possible to avoid its subsequent growth. A serious risk when cysts are detected in the pineal gland is an incorrect diagnosis and inappropriate therapy (including resection).
Functions of the pineal gland
Its full purpose is unknown. The pineal gland produces hormones: melatonin, serotonin, pinealin, adrenoglomerulotropin, dimethyltryptamine.
Melatonin is formed from serotonin; it synchronizes circadian rhythms, i.e. sleep and wakefulness. 80% of melatonin is formed in the pineal gland.
Melatonin is a product of serotonin; inhibits the development of gonads (human sex glands - ovaries and testes). Melatonin is produced in complete darkness; when the slightest light source appears, its amount decreases and it ceases to be synthesized.
This occurs because the pineal gland receives information from the retina, being part of the photoneuroendocrine system. After puberty, melanin production decreases.
The pineal gland helps in the regulation of electrolyte metabolism, at an early age it affects the complex of other endocrine glands: the thyroid gland, the pituitary gland, the adrenal cortical layer. Takes part in growth and puberty; has functional connections with other parts of the brain. Directly affects the ovaries and testicles; in children it slows down their work.
The following functions of the pineal gland have been accurately identified: reduces the release of growth hormone, inhibits puberty, the development of tumors, and is responsible for orientation in time and space.
Serotonin is the hormone of happiness, responsible for the emotional background, creating a good mood. Adrenoglomerulotropin - regulates the synthesis of adrenal hormones responsible for electrolyte balance.
The pineal gland regulates the exchange of P, K, Ca, and magnesium. Has a great influence on gonadotropic hormone.
Pinealin is less studied than others. All that is known about it is that it lowers blood sugar.
Dimethyltryptamine (DMT) – Some researchers suggest that it is responsible for dreaming and clairvoyance, near-death experiences.
Causes
Germinoma of the brain occurs against the background of a disorder of embryonic development.
Despite the fact that the dysontogenetic theory of the occurrence of brain germinomas has not yet been officially proven, the young age of the patients is indirect evidence of its validity. According to this theory, brain germinoma is formed as a result of a disorder of tissue differentiation and tissue migration in the initial stages of embryonic development. Factors that contribute to the development of embryonic disorders include various adverse effects that affect the fetus directly through the mother’s body. For example, radiation exposure, intoxication, carcinogenic substances, infectious diseases that a woman suffered during gestation can create favorable conditions for the development of this neoplasm.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcopyrightru
Germinoma of the brain is a dysontogenetic tumor, the cause of its occurrence is various disorders of embryonic development. According to the dysontogenetic theory of germinoma, it appears as a result of disruption of tissue differentiation and tissue migration at the initial stages of embryonic development.
Factors such as radiation exposure, intoxication, contact with carcinogens, various infectious diseases (herpes, measles, severe influenza, etc.) can be factors affecting the fetus and causing various embryonic disorders.
Mythology
The pineal gland is precisely the gland that was studied last. Due to the fact that the pineal gland is located too deeply and is so unclear, it has become overgrown with various speculations and myths, like everything unknown. For centuries, the pineal gland was considered the seat of the soul, as they said
Rene Descartes and Leonardo da Vinci, this is the “saddle of the soul.” Also, the pineal gland was considered the third eye because it is stimulated by light - impulses coming from the retina.
In addition, rotational movements similar to those of the eyeball are possible for the pineal gland. The structure of the gland has a resemblance to a lens and some receptors that resemble the eyeball, but are underdeveloped. Yogis call the pineal gland the sixth chakra, and if you develop it, you can achieve beyond your abilities and become clairvoyant.
Pathological phenomena
Diseases that can occur in the pineal zone are inflammation, tumors, circadian rhythm disorders; cysts, dystrophy and atrophy, circulatory disorders and congenital pathologies. More often than others, the rhythm of wakefulness and sleep occurs.
The reason for this lies in the reception of certain drugs, frequent use of cellular communications (smartphones, tablets) and laptops. All these technical innovations emit blue light, and the pineal gland works for a long time without rest. Sleep becomes superficial, a person cannot fall asleep for a long time. And during the day he is constantly sleepy.
Cysts occur when the epiphysis duct is blocked and the outflow of hormones becomes impossible. Very rarely, a cyst can be parasitic (echinococcus).
Pinealoma is a very rare lesion that occurs when the activity of the pineal gland increases. It's benign. With it, the balance of electrolytes is disturbed, drowsiness and cephalalgia appear. Inflammation of the pineal gland is usually secondary. They can be caused by TB, meningitis, sepsis, or brain abscess. Symptoms are most often from the underlying disease.
In case of TBI, hypertension, thromboembolism, blood flow in the pineal zone and general cerebral symptoms are possible.
Diabetes, cirrhosis of the liver, leukemia, severe infections, poisoning – cause dystrophy and atrophy of the gland.
Tumors of the pineal gland and infections can lead to the development of early macrogenitosomia - premature sexual and physical development. In girls it can be observed up to 9 years, in boys - up to 11 years. Accompanied by mental retardation.
The disease progresses very slowly; manifestations include daytime sleepiness, lethargy of the child, developed muscles with short stature and short limbs.
The genitals are also developed. ICH with nausea and vomiting is also present.
Classification of tumors by size and frequency of occurrence:
- A - location of the quadrigeminal cistern, diameter no more than 2.5 cm - 10% of occurrence;
- B - localization in the third ventricle in its posterior sections, diameter up to 2.5 cm - 12% of frequency;
- C - mixed version, diameter already up to 4 cm - 32%;
- D - the formation has completely taken over the quadrigeminal cistern and the posterior sections of the third ventricle, and can grow into one of the lateral ones; size 6-7 cm - 41%.
- E - gigantic sizes, sizes more than 7 cm -5%. It occupies the entire cavity of the third ventricle, part of the fourth ventricle and grows into both lateral ones.
Some types of tumors
The most common tumors of the pineal zone are germinomas (30%) and astrocytomas – 27%. Pineocytomas and teratomas – 6% each. The rest are even rarer.
Germinomas and teratomas arise from germ cells and are most often located in the pineal region - 56% of cases. In 3⁄4 cases the tumor is single, in a quarter it is multiple. Occurs between the ages of 10 and 20 years, more in men. In every fourth patient it is benign.
Germinoma noticeably disrupts the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, and all the symptoms of hydrocephalus predominate in the clinic. The headaches are bursting, there is a feeling of pressure in the eyes, and a feeling of nausea.
Visual disturbances are also noted: decreased visual acuity, diplopia, narrowing of visual fields. Boys with this tumor often experience early puberty.
Metastases usually pass through the CSF and cause damage to the spinal roots and myelopathy.; cerebellar disorders and endocrine disorders.
Metastasizes to adjacent brain structures. Brain tumors are commonly called “gliomas.”
Astrocytoma is a malignant tumor of glial cells that look like stars. Initially, these cells are designed to regulate the amount of intercellular fluid. Occurs at any age. The most common among neuroectodermal ones.
Teratoma of the brain of the head is rare, more often in boys 10-12 years old. Metastasizes in half of the cases. As it grows, it causes dizziness, cephalgia and nausea.
Tumors from germ cells are often malignant and can metastasize through the CSF and blood to other organ systems. All these tumors are divided into germinomas and non-germinomas.
The outcome of germinomas is better due to their differentiation.
Non-germinoma tumors:
- embryonal carcinoma;
- choriocarcinoma;
- teratoma.
Signs of a cyst
If the size of the cyst in the pineal region is no more than 1 cm, it does not manifest itself in any way and is not detected. Their diagnosis is most often random during studies for other reasons related to brain pathology and MRI.
The greatest danger is posed by growing cysts of the pineal region, which can cause circulatory problems in the surrounding tissues and lead to hydrocephalus.
Pineal cell tumors
Pineocytoma - develops from mature epithelial cells. It is also called benign pinealoma or adenoma. Occurs at any age, but more often from 25 to 40 years. Pineocytoma changes the functioning of the pineal gland and, with its growth, compresses neighboring brain structures.
Tumors of germ and pineal cells occur most often in youth and childhood. They cause ICH, cephalgia, nausea, paralysis of the eyeballs when they move up and down; coordination of movements is impaired; hand tremors, speech and handwriting disorders, constant drowsiness, weakness; weight changes and seizures.
Prognosis of pineocytoma
The prognosis of pineocytoma depends on several factors, such as the operability of the formation, its histological type, the presence of other pathologies and the age of the patient.
Extensive growth of even a benign node is extremely unfavorable for the patient.
According to statistics, a timely operation gives approximately 80% of patients a chance to live at least 5 years.
When pineoblastomas are detected, the prognosis is extremely unfavorable. These tumors grow rapidly, invade vital cerebral structures and impair their functioning.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of pineal gland tumors almost always fits into hydrocephalus with its characteristic symptoms:
- vomit;
- increased blood pressure;
- drowsiness;
- dysmnesia;
- visual impairment;
- abnormal increase in head volume in infants;
- convulsions.
Sylvian aqueduct syndrome or Parinaud syndrome manifests itself:
- partial loss of vision;
- cephalgia;
- mental impairment and changes in penetration.
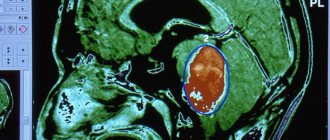
All neoplasms are diagnosed using MRI and CT. Treatment is radiotherapy and chemotherapy.
Pineal cyst - according to official data, it occurs in 2% of cases, but researchers believe that the % is much higher, it is simply not diagnosed due to the lack of growth of the cyst and its symptoms.
Pathology is most often discovered completely by chance during examinations for another reason. The reasons for its appearance are unknown. They are often congenital, but are more often diagnosed before the age of 45. It is only benign and never degenerates. Not progressing. Very often there are no symptoms at all. They can only appear if the formation is of impressive size. General manifestations: pressing and bursting headaches for no reason; analgesics are not relieved and can last for several days.
Visual impairment – diplopia, blurriness, pain when moving the eyeballs. Headaches can provoke noise in the head, nausea and vomiting, after which relief comes.
Difficulty in movement and precise movements. Disturbance of sleep and wakefulness: drowsiness during the day and insomnia at night.
If the cyst does not interfere with brain function, treatment is not carried out. Every six months you need to undergo an MRI. The operation is indicated only if the cyst grows and the cerebrospinal fluid in the skull increases.
Symptoms
90% of people who were diagnosed with a pineal gland cyst in the brain did not experience pronounced symptoms. However, some of them showed manifestations of a holistic nature characteristic of ailments of the penial segment:
- painful sensations in the head area that are not explained by other factors and occur without any system or apparent reason;
- problems with visual functions (patients indicate double vision, blurred images due to a large cyst in the epiphysis);
- problems with coordination of movements and gait;
- periodic attacks of nausea and diarrhea, which are provoked by attacks of sudden migraine;
- hydrocephalus (dropsy of the brain), which develops due to the fact that a cyst in the pineal gland compresses the ducts of the presented segment. There is a progressive disturbance of the outflow of subarachnoid fluid.
The severity of symptoms in benign formations in the penial segment entirely depends on the parameters of the cyst (from 1 cm or more). Another equally important factor is whether it puts pressure on other segments and glands of the brain. When the formation reaches excessive dimensions, it is able to 100% block the outflow of subarachnoid fluid. Thus, an enlarging cyst can have the most negative consequences for the body as a whole and for the brain in particular.
Severe and prolonged migraines are one of the signs indicating a specific cyst in the pineal gland, which is of parasitic origin. Symptoms will be supplemented by mental disorders. This refers to depression, dementia and aggressive delirium. Much less often, a pineal gland cyst, which has a parasitic origin, is accompanied by epileptic seizures.
With a rapidly enlarging epiphysis cyst, progression of focal symptoms and increased pressure inside the arteries are diagnosed.
Treatment of disorders
To normalize circadian rhythms, you need to follow a sleep and rest schedule. You need to go to bed no later than 11 pm; melatonin peaks at midnight. You need to sleep in complete darkness. Before going to bed, you should not play computer games, actively engage in sports after 19 hours, and do not watch action or horror films before bed. Your doctor may prescribe sedatives or artificial melatonin.
Cyst – there is usually no treatment. Only dynamic observation and MRI are required. Surgical treatment is indicated only for active cyst growth, migraines, fainting and visual impairment. Treatment of tumors still requires further study.
Prevention
Brain germinomas are characterized by relatively favorable prognoses after radiation therapy and surgical treatment. The five-year survival rate of patients reaches 95%, and the ten-year survival rate is 88%.
Prevention is aimed at eliminating various adverse effects on the mother’s body. Early registration and appropriate explanations from the obstetrician-gynecologist who is managing the pregnancy will help the woman protect herself from various teratogenic factors.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytdevru
Preventive measures that are aimed at preventing the occurrence of germinoma include eliminating the influence of various unfavorable factors on the woman’s body during the gestation stage.