When a child has a brain cyst, medication is prescribed to eliminate the problem that led to the anomaly. If such a diagnosis is made in a child in the first days of life, the question arises: what will be the further prognosis, and whether the child can be cured. Timely detection of pathology and its treatment will help to avoid many neurosurgical problems.
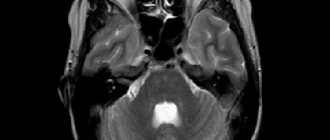
A cyst is a formation in hollow areas that looks like a capsule and has fluid inside. Pathology is detected by MRI. It can be located in any part of the brain, in a single instance or have several formations. Sometimes it can be diagnosed in the prenatal state, but in many cases it disappears on its own. This is considered normal during certain periods of pregnancy.
Causes
A cyst in a child’s brain is often detected before birth during perinatal screening. During this period, the woman will undergo an ultrasound, with the help of which early developmental disorders are determined. The cause of the tumor-like process is a disorder of the nervous system. Congenital brain cysts in a child almost never degenerate into an oncological formation, but they need to be monitored.
Against the background of what factors is pathology detected?
- Complications during pregnancy (preeclampsia).
- Compression of the head during passage through the birth canal.
- Oxygen starvation in the fetus or hypoxia (anemia, maternal asthma, insufficient placental blood flow, Rh factor incompatibility).
- Viral infections.
- Uncontrolled use of medications.
- Head injuries with damage to brain tissue.
- Inflammatory processes (encephalitis, meningitis).
Symptoms of cystosis
Pathology can affect any part of the brain. Depending on which area is damaged, certain symptoms occur. If the cystic cavity is localized:
- In the occipital zone, the child’s vision suffers.
- In the cerebellum there is a violation of stability and coordination of movements. The baby begins to walk later, has difficulty moving, and suffers from attacks of severe dizziness.
- As the child grows older, hormonal disruptions will begin near the pituitary gland
Important! The rapid growth of a cystic tumor is always accompanied by high intracranial pressure. In this case, the patient begins to complain of bursting pain in the head, morning sickness, and weakness. Intensive growth of the formation can cause separation of the bone sutures on the skull, so treatment should not be delayed.
Children with a cyst in the brain constantly experience headaches that cannot be relieved by painkillers. Due to the pronounced signs of the disease, they cannot develop according to age. In severe cases, patients suffer from epileptic seizures. Some groups of cystic formations are prone to rupture, which can be fatal.
Types of cysts in the brain of a child
Benign tumors form in different parts of the brain, some of which do not affect the development of the baby.
Vascular plexus cysts
There are no nerve cells in the vascular epithelial tissue of the brain; they are the main source of saturation of the brain through the cerebrospinal fluid. With rapid cell division, cerebral substance accumulates in the space between the plexuses. Education does not change the functioning of the brain. The cyst can be discovered in a small child or in adolescence.
This diagnosis is not uncommon in pediatric practice, but mental and mental development remains at a natural level, so it does not require conservative or surgical correction. In the fetus, cavities usually disappear on their own by week 28. If this does not happen before the baby is born, there is a high probability that this will happen within a year after the birth.
Retrocerebellar cyst
A rare pathology that can develop deep in any part of the child’s brain. The reason for the formation of the retrocerebellar capsule is the death of gray matter cells, which in itself is a dangerous phenomenon. Gradually, the capsule fills, increasing in size, and leads to severe compression of neighboring areas of the organ. The specificity of the tumor is its rapid growth with disruption of blood flow in the brain.
Pathology in a child is manifested by multiple symptoms - deviations in the mental state, impaired body movement, unstable coordination, headache, hydrocephalus and paralysis. In aggravated dynamics, the retrocerebellar cyst reaches 11-12 cm, and the thickness of its walls can be up to 2 cm. The most dangerous forms of opuoli occur after meningitis and do not respond to conservative therapy.
Aranoid cyst
A hollow formation filled with fluid grows on the surface of the child’s cerebral cortex, where the arachnoid membranes are located. The walls of the aranoid capsule are formed from arachnoid cells or scarred collagen. Primary pathology is characterized by abnormal development of the meninges in the embryo. The secondary type is an acquired pathology caused by infectious and inflammatory processes in the brain. Often in children, aranoid cysts form due to mechanical damage, trauma to the back of the head and bruise.
Dermoid cyst
Dermoid or mature teratomas are formed when germinal elements are displaced under the skin. As a result, the cavity contains derivatives of the dermis - follicles, hair, sebaceous glands, cartilage tissue and even tooth enamel. Dermoid cysts in the head of a child are a disorder during embryonic development, which is determined by the lines of parts of the fetus, in the embryonic joints and folds. The structure of the areas allows the germ layers to accumulate.
The appearance of a dermoid capsule in the head is rare; almost all cases of pathology are seen in the ventricle of the organ. Large sizes of the formation negatively affect the course of labor and interfere with the normal development of the child. The largest cysts reach 15 cm, have 1 chamber, and grow very slowly. About 8% of teratomas are prone to malignancy—the production of malignant cells.
Cerebral cyst
Another type of tumor formed deep in the brain. A cerebral cyst can form during the development of the nervous system, including dead neurons and cerebral substance. Stagnant processes lead to the formation of walls, the capsule grows and compresses the cells.
The consequences of such a tumor for a child without treatment are varied. In some cases, there are no symptoms, but they suddenly appear if the size of the cyst becomes critical.
Prevention
Many unfavorable factors lead to the occurrence of cystic formations. Since the abnormal process often begins during the development of the fetal nervous system, preventive measures mainly concern pregnant women. They need:
- Categorically give up bad habits.
- Do not abuse medications.
- Treat chronic diseases in a timely manner.
- Avoid contact with sick people.
- Regularly consult a gynecologist and follow his recommendations.
Sometimes injuries, including birth injuries, lead to the growth of cysts, so you need to take the choice of a clinic and a doctor who will deliver the baby very seriously in order to reduce all possible risks to nothing. Parents who do not ignore the first symptoms of the disease in their children and seek medical help in a timely manner can count on a successful treatment outcome. After all, the sooner the disease is detected, the better for the patient.
Symptoms
Clinical signs depend on the location of the cystic formation in the child. If it is complicated, then various signs may appear, including threatening conditions.
- Headache. The intensity of the symptom varies, but it usually appears after waking up. It is difficult to determine the presence of a headache in an unintelligent child. He changes in behavior, is capricious, sometimes cries for several hours.
- Deterioration of general condition. There is slowness in movement, changes in sleep and wakefulness. Appetite deteriorates significantly, sometimes complete refusal of breast or formula occurs.
- Head enlargement. This sign indicates a large size of the cyst in the child, but it rarely appears. Along with a change in the shape of the skull, pulsation in the area of the fontanelle and its protrusion are detected.
- Impaired coordination. The symptom is a consequence of the growth of the capsule in the cerebellar region. Additionally, visual disturbances are noted due to compression of the optic nerve - double vision, floaters, blurry pictures.
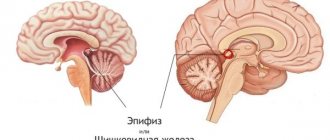
- Deviations in sexual development. They occur during adolescence when an opuole forms in the pineal gland. A hormonal imbalance occurs, which leads to early maturation or significant delay.
- Epileptic seizures. Excessive electrical impulses are provoked by a cyst located deep in the membranes of the brain and in its large furrows. Epilepsy is manifested by a convulsive state, rolling of the eyes, trembling of the eyelashes and loss of consciousness.
What to remember
- The symptoms of a cyst directly depend on its location and size.
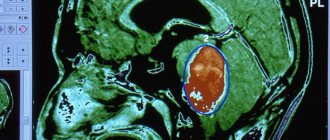
- The main diagnostic methods are tomography, MRI and ultrasound of the brain.
- A brain cyst is a serious diagnosis that requires medical treatment and regular medical supervision.
- Consequences of cysts include hydrocephalus, brain herniation, and sudden death.
- Drug treatment eliminates the causes of the appearance and growth of the cyst.
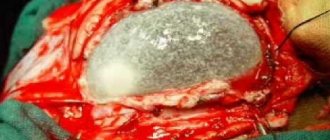
- Surgical treatment involves removal of the cyst and is carried out only as prescribed by the attending physician.
See you in the next article!
Share with your friends!
Treatment
Frozen cystic cavities without progression or cavities into the choroid plexus do not require special treatment and are monitored periodically. For dynamic formations, drug and surgical treatment is prescribed.
Drug treatment
Traditional therapy involves eliminating the cause of the pathology. Drugs may be prescribed to promote the resorption of the walls of the opuoli and adhesions. To restore blood circulation in the affected area, antihypertensive and antiplatelet drugs are prescribed. Nootropic and immunomodulatory drugs are widely used.
Diagnostic features
The disease can be diagnosed after the birth of a child using neurosonography. This ultrasound examination is carried out through the fontanel and provides reliable information without ionizing load on the body. Such a diagnosis can only be carried out on newborns and children up to the twelfth month of life, until the sutures of the skull finally fuse together.
Neurosonography is indicated for the following pathological conditions:
- Infant suffocation.
- Fetal hypoxia.
- C-section.
- Infectious diseases of the mother during pregnancy.
- Genetic abnormalities.
- Recession or bulging of the fontanel.
- Birth injuries.
- Lack of weight.
- Detection of pathology during intrauterine development.
- Profound prematurity.
- Prolonged labor.
Subsequently, MRI or CT is used for examination, which makes it possible to accurately determine the location of the cystic cavity, its size and shape. During these diagnostic measures, children under 6 years of age are in medicated sleep. Based on the results obtained, the doctor draws conclusions and determines further treatment tactics.
Types of cystic formations
A cyst is a benign neoplasm, which is a cavity with liquid contents inside. It often forms in a child in the womb due to the accumulation of fluid in places where dead brain cells accumulate.
No single cause has been identified that would lead to the development of pathology. The formation of a neoplasm can be influenced by a number of factors:
- Genetic abnormalities. This is influenced by poor ecology and the consumption of genetically modified products.
- Inflammatory process - genital herpes, toxoplasmosis.
- Past trauma. For example, a head injury during childbirth, a difficult pregnancy.
- Autoimmune processes, when the body perceives its own tissues as foreign and attacks them.
Cystic cavities can form in the white or gray matter of the brain, in the thickness of the meninges. There are three main types: arachnoid, subependymal and choroid plexus cysts.
How does the disease manifest itself?
In most cases, the disease is asymptomatic and is detected during ultrasound examination (ultrasound). Less commonly, clinical symptoms occur, which depend on the type of tumor, its location and size.
The clinical picture is often dominated by cerebral symptoms associated with cerebrospinal fluid hypertension. Focal symptoms occur less frequently, for example, when a cystic formation ruptures. At a later age, the child may experience delayed physical or mental development.