Experts refer to the interhemispheric fissure as the gap between the hemispheres of the human brain. Newborn children with timely development do not have problems with well-being and adaptation to the world around them. Timely diagnosis of abnormalities and competent treatment are of great importance for children.
For young patients, ultrasound often checks the size of the interhemispheric fissure.
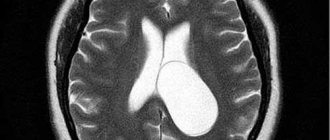
What is the interhemispheric fissure
In the process of studying the child’s brain using ultrasound, tomogram, and neurography, specialists can detect pathological changes, and the parameters of the interhemispheric fissure are also assessed. The gap should not be more than 3 mm - this is a normal anatomical characteristic of the child.
In newborn children, the gap between the hemispheres of the brain can exceed standard values for the following reasons:
- Accumulation of fluid between the hemispheres.
- Illness of a woman during pregnancy.
- Obstetrics by caesarean section.
Expansion of the subarachnoid space and its causes
Changes in size and pressure in the subarachnoid space are often a sign of an inflammatory process or tumor.
The mechanism for the development of such changes is quite simple. The inflammatory process (usually arachnoiditis or meningitis) increases the production of cerebrospinal fluid, which gradually stretches the subarachnoid space. During the tumor process, a mechanical barrier is created to the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, which is a consequence of a local increase in pressure and the formation of expansions in a certain area of the ventricular system of the brain. However, other options are possible that can lead to expansion of the subarachnoid space. In particular, a temporary change in the size of the cerebrospinal fluid circulatory system is possible with reactive cerebral edema and a decrease in intracranial space due to a hematoma or abscess.
How is its size estimated?
It must be emphasized that the distance between the hemispheres of the human brain, which does not exceed standard values, does not relate to pathology - this is an anatomical characteristic of a particular child.
The interhemispheric fissure can have different sizes
To identify deviations in the dimensions of the interhemispheric fissure, neurosonography is performed. In the diagnostic process, ultrasound sensors are used, the study is carried out through the temporal region, anterior or posterior fontanel. Modern diagnostic testing is indicated for children under one year of age. During the examination, echographic visualization of the brain is clearly monitored.
Read also: how you can check a child’s brain using ultrasound diagnostics.
Transparent septum of the brain: description, purpose, norm, pathology and treatment
The brain is the most important human organ, on whose work the functioning of the entire organism directly depends. This is a complex structure consisting of several departments, each of which performs clearly defined functions. This article discusses what the septum pellucidum of the brain is.
Definition of the term
In the telencephalon there are two plates of brain tissue located parallel to each other. These plates are called a transparent partition. Between them there is a cavity filled with cerebrospinal fluid. This structure is located in the space between the anterior part of the brain and the corpus callosum.
The septum is normal
When the human embryo is at the developmental stage, this cavity is always present, but approximately six months after birth it closes. In approximately 15% of cases, the cavity of the septum pellucida normally remains.
This structure is not so well studied, however, experts conclude that non-closure of the cavity occurs due to the effect of alcohol on the fetus during pregnancy. An unfilled cavity, as a rule, does not have a significant clinical effect on the functioning of the body.
The cavity can be of varying sizes, in some cases it reaches 45 millimeters. Due to the complete isolation of this formation from the ventricles of the brain, in some cases the cavity is called the fifth ventricle, but this definition cannot be considered completely correct.
Pathologies of the septum
Sometimes there are cases of pathological formations of the transparent septum, as well as various types of developmental defects, when a condition occurs that threatens health.
These types of pathologies include:
- septal cavity cyst;
- agenesis of the septum.
As is the case with other diseases of brain tissue, it is necessary to pay close attention to such disorders and be promptly observed by doctors in order to prevent serious complications.
Cyst: symptoms and diagnosis
The diagnosis of cyst of the cavity of the transparent septum of the brain is made after an MRI of the brain and is observed in approximately a quarter of patients. The cyst can be either congenital or acquired.
A congenital cyst is characterized by the fact that it appears as a result of a genetic predisposition or developmental disorders of the fetus during pregnancy.
The causes of an acquired cyst can be previous infectious diseases of the meninges, hemorrhages and even serious mental trauma. The most common cause is meningitis.
In premature babies, this formation is almost always observed and, as a rule, does not require treatment, but goes away on its own.
According to some reports, the area of the cavity of the transparent septum is one of the safest places for a cyst to occur in the brain. However, this does not mean that this diagnosis should be ignored. In any case, you need to consult a neurologist who will recommend the necessary therapy.
If the septal cyst is congenital, then it does not require any special therapy; it is enough to undergo regular preventive examinations with a neurologist or neurosurgeon.
With an acquired cyst, the following symptoms are observed:
- headache, periodically worsening;
- the appearance of tinnitus;
- unpleasant pressing sensation inside the head.
To establish a diagnosis, a complex of measures is carried out, including MRI, ultrasound, as well as blood tests and blood pressure checks.
Cyst therapy
Often, a cyst of the transparent septum of the brain does not require special therapy; only careful observation and control of its growth are carried out. Sometimes the size of the cyst becomes so large that it begins to put pressure on nearby parts of the brain and interferes with their normal functioning. Then the neurologist prescribes treatment.
In most cases, the doctor determines the cause of the accelerated growth of the cyst and prescribes therapy for the original disease, then the growth of the formation stops, and the cyst of the cavity of the transparent septum ceases to pose a danger. Usually a set of measures is performed to stimulate blood circulation in the brain and reduce ICP.
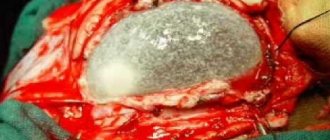
If conservative treatment does not bring results, they resort to surgical treatment - using a special probe, holes are created in the walls of the cyst through which fluid comes out, and the formation cavity is reduced.
Septal agenesis: symptoms
Agenesis of the septum pellucidum is a serious congenital pathology of brain development caused by improper development of the corpus callosum in the fetus.
This is a very rare anomaly of the central nervous system, caused mainly by hereditary factors, genetic mutations and insufficient supply of nutrients to the embryo.
Another reason may be toxic drugs that a woman takes during pregnancy.
At birth, children with this pathology are practically no different from healthy ones; clinical signs begin to appear at the age of 2-3 months.
The main symptoms of agenesis of the cavity of the transparent septum include:
- formation of cystic cavities in brain tissue;
- atrophy of the auditory and optic nerves;
- fits and seizures;
- microencephaly.
As a rule, this malformation of brain development is preliminarily diagnosed in the second trimester of pregnancy (after 18 weeks) and is confirmed by a set of diagnostic measures after birth. An ultrasound examination of the newborn's brain, CT scan of the head, and, if necessary, MRI and neurosonography are performed.
Therapy and prognosis of agenesis of the cerebral septum
Conservative treatment is carried out, mainly with anticonvulsants and corticosteroid hormones. Therapy is aimed at eliminating serious and dangerous symptoms that pose a danger to the child. There are no specific means of correcting the absence of a septum.
If agenesis is not complicated by concomitant brain defects, then the child’s development proceeds normally or with minor neurological impairments. However, in cases where there are complications in the form of other malformations of the brain, there may be consequences in the form of mental retardation, decreased learning ability and other serious abnormalities.
Conclusion
Congenital pathologies of the transparent septum of the brain are usually genetically determined and require regular monitoring by a neurologist or neurosurgeon. As a preventive measure for septal pathologies acquired during life, it is recommended to avoid complications on the brain after infectious diseases, injuries and concussions, and mental shocks.
Source: https://FB.ru/article/431509/prozrachnaya-peregorodka-golovnogo-mozga-opisanie-naznachenie-norma-patologiya-i-lechenie
How is the procedure performed?
As soon as the baby reaches 1 month of age, this procedure is carried out as part of screening diagnostics. Repeated examinations are carried out at 3 and 6 months of age.
There is no need to be afraid of such a diagnostic procedure. It does not pose any danger to the child; it does not take more than 10 minutes. The diagnostic examination is performed by a highly qualified doctor who is able to interpret the information received. In the conclusion, if necessary, a list of additional studies is prescribed.
During diagnosis, the child is not subjected to unpleasant or painful procedures, and there is no need for recovery after the procedure. Therefore, parents should not have any concerns about the diagnostic examination.
Cyst of the transparent septum of the brain - what it is and how to treat it - Nerves
Neoplasms that are localized in the brain can lead to dangerous complications. They try to remove benign tumors in rare cases, since interference with brain activity is unpredictable.
A cyst of the transparent septum of the brain, which is also called a Verge's cyst, is often found in completely healthy people. This pathology can resolve spontaneously and sometimes does not require treatment.
It is often found in completely healthy people.
Development mechanism and reasons
To understand what a neoplasm of this type is, you need to know the structure of the brain. It consists of several shells. A transparent septum separates the parts of the brain from each other. It consists of two plates containing brain tissue, which are separated by a small cavity.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c8dvuyulHck
Structure of the brain.
Cerebrospinal fluid also circulates between these two plates. If excess accumulation occurs, a capsule filled with contents is formed inside. Impaired fluid circulation is often accompanied by conditions such as Arnold's anomaly, disruption of the movement of nerve cells, etc.
Initially, a cyst in the brain can be congenital or acquired. If pathology of the transparent septum is discovered during pregnancy or after childbirth, this indicates disturbances in intrauterine development. The neoplasm almost certainly occurs in premature infants. The cyst can resolve spontaneously and is rarely accompanied by unpleasant symptoms.
The second type of benign tumor in the brain is acquired. The following reasons contribute to the appearance of compaction of the transparent septum:
May be a consequence of mechanical injuries.
- previously suffered infectious diseases;
- inflammatory processes in brain tissue;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- mechanical injuries (impacts, shocks, etc.);
- hemorrhages.
Most often, the cyst does not pose a threat to human life. Typically, the neoplasm of the transparent septum does not exceed a few millimeters in diameter. The maximum size of the brain thickening is several centimeters. In this case, unpleasant symptoms will arise, and the development of the process will lead to serious consequences.
Locations
In most cases, the cyst is located between the fornix of the corpus callosum and the front of the brain. Less common situations occur when it appears in the anterior part of the septum or in the cerebellum.
Signs
A neoplasm of small diameter does not have a significant effect on the human condition. As its size increases, the following symptoms appear:
Paroxysmal headache, feeling of constriction.
- paroxysmal headache, against which standard medications are powerless;
- the patient feels as if his head is being squeezed by a hoop;
- over time, problems with vision and hearing appear, extraneous noise is felt;
- pressure changes are observed, which affects well-being;
- Due to the strong pressure of the cyst in the cranial region, motor activity may be impaired. Trembling of the limbs appears and they go numb.
Possible complications of the disease
Unpleasant consequences are associated with the large size of the cyst. If it is actively growing, then soon the victim will experience pressure drops or his readings will significantly exceed the norm. The supply of oxygen to tissues and blood vessels is disrupted, which causes a malfunction of internal organs.
Over time, the neoplasm can transform into a malignant tumor. A dangerous complication is atrophy of brain tissue. In severe cases, this pathology causes paralysis. The next complication is dropsy, in which internal organs may fail. Another possible consequence is a stroke.
Modern diagnostic methods
If you suspect the formation of a cyst, you should immediately consult a doctor. To clarify the diagnosis, modern diagnostic methods are used, which will quickly determine the nature of the tumor:
- MRI is one of the most revealing ways to make a diagnosis. During the study, any pathological changes that occur in the transparent septum are identified. The location of the cyst, its diameter and structure are clarified; MRI is one of the most revealing ways of making a diagnosis.
- A blood test allows you to find out whether there are additional foci of inflammation, as well as other deviations from the norm. During the study, cholesterol levels are determined to exclude the presence of blood clots;
- An ECG is a standard procedure that evaluates cardiac activity;
- Ultrasound determines whether there are any abnormalities in vascular activity.
The doctor may prescribe additional tests if the need arises. Only after all diagnostic procedures are completed, individual treatment is selected.
Treatment
Quite often, a small cyst in the brain does not require any treatment at all. This occurs in cases where the tumor is safe for the patient and does not cause any discomfort. To monitor its size, regular MRI of the brain is prescribed. Sometimes the tumor resolves spontaneously.
Conservative treatment is also used. They resort to it when the thickening begins to grow. The patient may be prescribed the following types of medications:
Use drugs to improve blood circulation.
- nootropic medications;
- means for improving blood circulation in brain tissue;
- drugs for resolving blood clots;
- diuretics.
The medications prescribed by the doctor help remove excess fluid from the cavity and restore the normal functions of the transparent septum. With drug treatment, there is a high chance that the patient will no longer experience unpleasant symptoms.
If conservative therapy does not help, and the cyst has increased in size so much that it threatens the life and health of the patient, surgical intervention is chosen. It is aimed at restoring proper fluid circulation in the brain.
The operation is performed using the probing method. To do this, a probe is inserted into the area of the brain where fluid has accumulated. Then microscopic incisions are made through which the contents of the capsule are pumped out.
If the cyst had only one chamber, after the procedure the person will forget about the problem. But with cell proliferation and the formation of multiple cavities, there is a possibility of relapse.
In 20% of cases the tumor will manifest itself again.
The operation is performed using the probing method.
After surgery, the patient should undergo regular checks to eliminate the risk of cyst recurrence. You cannot use traditional medicine without the consent of your doctor and rely only on their effect. This type of neoplasm is dangerous because it provokes multiple complications.
A septum pellucida cyst does not always require treatment or surgery. Quite often it does not cause discomfort to a person and does not increase in size. If a benign tumor threatens health, drug therapy is used, and in the most severe cases, surgery is prescribed.
Source:
How dangerous is a cyst of the transparent septum of the brain?
Neoplasms in brain structures require monitoring and adequate treatment, since their presence disrupts the functioning of the central nervous system and creates a risk of death.
Cavities filled with liquid are also classified as neoplasms that tend to grow and can become both benign and malignant.
A cyst of the transparent septum of the brain is an abnormal phenomenon, the development of which begins in the early stages of fetal formation.
Description of the pathology
The transparent septum of the brain is brain tissue in the form of two thin plates. Between them there is a cavity shaped like a gap.
Its purpose is to delimit the spheres of the corpus callosum and the anterior part of the brain. The role of the septum in the overall functioning of the organ is not fully understood.
However, it is known that the absence of this element indicates various malformations of the brain.
Under normal conditions, cerebrospinal fluid is contained between the plates that form the transparent septum. If fluid accumulates in this cavity, then we are talking about the formation of a cyst or Verge's cavity.
This pathological phenomenon is a cavity formation, similar to a capsule, which contains liquid inside. The walls of the cyst are quite dense. When its size reaches certain values, the capsule will begin to put pressure on the surrounding tissues, which will cause compression of the vessels and an increase in intracranial pressure.
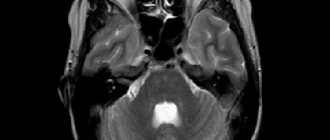
Image of a pathological disease on an MRI image
Cyst of the transparent septum of the brain is diagnosed in 60% of newborns. If a child is born premature, such an anomaly is sure to be present.
Often the deviation does not manifest itself in any way, so the cyst is discovered by chance, during comprehensive examinations. But sometimes the growth of a tumor provokes frequent pain in the head, memory loss, and visual impairment. According to statistics, the cyst resolves on its own in 85% of cases.
Cystic formation does not pose an immediate danger to health. However, with its uncontrolled growth, irreversible changes in the structures of the brain can occur, which affects the person’s condition and the functioning of his body as a whole.
Read about methods for diagnosing and treating ICP here.
- The head of the neurosurgery department of the Rostov Clinical Hospital, Karen Airapetov, will talk about the reasons for the appearance of a cyst in the brain:
- A cyst of the transparent septum of the brain can be either congenital, formed in the fetus during intrauterine development, or acquired, which can be associated with injuries, concussions, or inflammatory processes.
- Typically, the maximum size of a cyst does not exceed 4 mm, although the risk of uncontrolled growth of the tumor cannot be excluded.
Doctors do not consider the described neoplasm a serious pathology that threatens the patient’s life, but classify it as a developmental anomaly.
Reasons that contribute to the formation of cysts
The appearance of cavities between brain tissues can be caused by the following factors:
- Traumatic brain injuries;
- Inflammatory processes spreading to the membranes of the brain;
- Past infectious diseases (especially meningococcal infection);
- Concussions and brain injuries;
- Brain hemorrhages.
In infants, the presence of a cyst is often associated with intrauterine infection.
Sometimes an anomaly of the transparent septum of the brain is combined with a number of abnormalities in the functioning of the nervous system. These include:
After the neoplasm acquires significant size, it begins to put pressure on nearby vessels and tissues. From time to time the cyst blocks the interventricular spaces.
In patients with Verge's cavity, severe symptoms appear if the cystic neoplasm progresses. In this case, the patient experiences:
- Regular headaches, the intensity of which increases when running or jumping;
- Noise or ringing in the ears that does not go away at night;
- A feeling of tightness in the area of the head where the cyst is located;
- Hearing impairment;
- Increased blood pressure;
- Deterioration of vision and memory.
Subsequently, with constant growth of the cyst, hydrocephalus of the brain may occur.
With the constant growth of the cyst, there is a risk of developing such consequences as:
- The formation of adhesions in the brain, which can compress the vessels supplying the brain;
- Stroke. This condition is caused by increased pressure in the cranial cavity, which disrupts blood circulation and the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid;
- Hydrocephalus. A similar pathology occurs when there are disturbances in the circulation and outflow of cerebrospinal fluid.
Source: https://gbuzrk-vpb.ru/diagnostika/kista-prozrachnoj-peregorodki-golovnogo-mozga-chto-eto-i-kak-lechit.html
What indicates deviations
If your child has the following symptoms, contact your doctor immediately:
- Restless and short sleep.
Strong crying and restless sleep can indicate problems
- Increased arousal.
- Sharp sounds provoke loud crying or screaming.
- When atmospheric pressure fluctuates, anxiety arises.
An increase in interhemispheric space is one of the possible signs of serious deviations. During the diagnostic examination, a relationship is established between this indicator and other clinical nervous manifestations.
Treatment of expansion of the subarachnoid space
Drug therapy is indicated for meningitis, encephalitis, trauma,... The complex includes diuretics (Lasix, Diacarb).
Indications for surgical intervention include:
- anomalies of skull development and SAP;
- benign and malignant neoplasms;
- intracerebral hemorrhage;
- brain abscess;
- adhesive process in arachnoiditis.
If it is impossible to radically eliminate the cause of hydrocephalus, then additional outflow pathways from the cranial cavity are created. Such operations are called bypass operations; they can also end with surgical treatment when removing a cyst or tumor, if the circulation of the cerebrospinal fluid is not restored at the main stage.
Expansion of the subarachnoid space occurs in congenital and acquired hydrocephalus
. Its causes are excessive formation of cerebrospinal fluid and/or disruption of its outflow. In adults, it manifests itself as severe headaches and psycho-emotional disorders, while in infants the head becomes enlarged and physical and intellectual development slows down. To find the causes, instrumental diagnostics are carried out. Treatment can be conservative or surgical.