Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of a brain cyst do not always appear. In some cases, this disease is completely asymptomatic. This happens when the cysts are small. Large tumors compress the membranes of the brain. The consequence of this exposure is the following symptoms of a brain cyst:
- severe headaches;
- deterioration of vision and hearing;
- disturbances in coordination of movements and sleep;
- hypo- or hypertonicity of muscles;
- noise and pulsation in the head;
- loss of consciousness, epileptic convulsions, trembling (tremor) of the limbs;
- children experience regurgitation and vomiting;
- swelling and noticeable pulsation occurs in the area of the fontanel.
The clinical picture of the disease depends on where the cyst is located. The appearance of certain symptoms is influenced by the pressure of the cyst on individual areas of the brain.
Cyst in the brain
General information about the disease
A porencephalic cyst is a benign tumor containing cerebrospinal fluid.
On this topic
- central nervous system
How does a headache with a brain tumor hurt?
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 3, 2020
The tumor forms in the brain tissue. Its appearance is similar to a ball. Education is innate.
The cyst size ranges from 1 to 5 centimeters in diameter. The disease is diagnosed mainly in children under one year of age. But most often the disease is detected during an ultrasound examination during pregnancy.
A porencephalic cyst is also found in adults, but such a pathology is detected in exceptional cases.
Types of brain cysts
There are several types of brain cysts. The most common are the following:
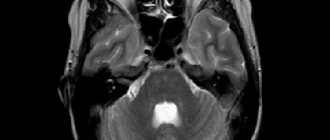
1. Cyst of the pineal gland of the brain. Most often, it is discovered accidentally during an MRI scan for other reasons. A pineal cyst of the brain in this gland can be provoked by a violation of the outflow of melatonin and the presence of echinococcus. After blockage of the excretory duct, secretions and gland cells accumulate in the cyst. In this case, lining tissue is formed, which, with further intake of the hormone, promotes its growth. Penetration of echinococcus into the pineal gland also contributes to the formation of a cyst. This disease is accompanied by the following symptoms: headache, double vision, inability to roll the eyes up, difficulty walking.
Pineal cyst
An asymptomatic pineal cyst of the brain, which is not accompanied by a tumor and when discovered by chance, does not cause trouble. Despite this, doctors recommend undergoing an annual examination by a neurosurgeon who will monitor the dynamics of its development. A pineal cyst that has been treated with medication will not go away, but the causes of its occurrence will be eliminated. If there is frequent pain and there is suspicion of the growth of this neoplasm, it must be removed through surgery.
2. An arachnoid cyst of the brain develops on the arachnoid membrane of the brain. It is filled with cerebrospinal fluid. Arachnoid cysts are most common in boys and adolescents. Its formation is most often caused by injuries. If the pressure in the arachnoid cyst exceeds the intracranial pressure, it will compress the cerebral cortex and cause pain. Doctors also identify a retrocerebellar arachnoid cyst of the brain. It resembles a bubble of liquid. This formation is benign, but if the cyst is formed by cerebrospinal fluid, then it forms on dead areas of gray matter. This cyst is often a consequence of encephalitis or stroke, as well as insufficient cerebral circulation. Most often, this disease is asymptomatic. A retrocerebellar cyst often leads to brain destruction, so it always requires treatment.
Treatment of arachnoid cysts of the brain is surgical (surgical). Burst cysts accompanied by fluid accumulation are removed. Most often, such neoplasms cause epilepsy attacks. Today, surgical intervention is performed in 3 ways:
- performing endoscopic surgery;
- use of microsurgery;
- shunting.
3. A pineal cyst of the brain is formed in the pineal gland. Most often it is small in size. It causes disruption of metabolic processes. It affects the functions of vision and coordination. It can cause hydrocephalus and encephalitis.
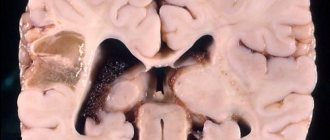
4. A dermoid cyst appears during fetal development. Hair and fat can be found in its cavity. It grows quickly during childhood, often compressing various structures. Most often it is removed surgically.
Dermoid cyst
Other types of brain cysts
The following types of cysts are also common:
- Cyst of the epiphysis of the brain, the symptoms of which are severe headaches, drowsiness, disorientation, double vision. It also makes walking difficult. At the initial stage of the disease, drug treatment is used. A neglected cyst that increases in size is removed surgically.
- Vascular plexus cyst is a benign neoplasm that manifests itself at certain stages of fetal development in the womb. Such a brain cyst in a child most often resolves on its own. In some cases, a brain cyst in a newborn occurs as a result of complications during pregnancy and childbirth. Infectious infection of the fetus can also lead to it. In rare cases, this formation leads to pathological changes in other body systems. A congenital brain cyst is determined using a procedure called neurography. It is absolutely harmless to the child's health. Diagnosis of such a cyst in adults is made using ultrasound examination.
- Pseudocyst of the brain in newborns occurs in 1% of premature infants. It is detected by ultrasound in the first 24 hours of a child’s life. This fetal brain cyst occurs as a result of hemorrhage of the germinal matrix. It can be unilateral or bilateral. Pseudocysts are the safest health consequence of childbirth. They do not require special treatment. As a rule, by the first year of a child’s life they completely resolve.
- A cerebrospinal fluid cyst is a neoplasm that arises between the meninges. Its formation is promoted by inflammatory processes (meningitis, stroke), trauma and surgery. It is diagnosed in adulthood, since in the early stages its symptoms are practically not expressed. Symptoms of a liquor cyst: nausea, vomiting, mental disorders, loss of coordination, convulsions, paralysis of the limbs.
- A subependymal cyst occurs in newborns after a cerebral circulatory disorder or during hypoxia (insufficient oxygen supply to the brain). This disease requires medical supervision.
- Porencephalic cyst of the brain is a formation that occurs in its tissues due to melting of the affected area. It leads to very serious consequences such as hydrocephalus and schizencephaly.
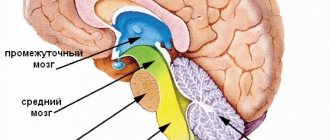
- A lacunar cyst forms in the area of the pons, in the cerebellum, subcortical ganglia, and optic thalamus. Most often it occurs as a result of age-related changes and atherosclerosis.
- Colloidal cyst is of congenital origin. It appears as a result of embiogenesis. A person can have it all his life, but it does not cause him any problems. It is believed that it is hereditary. This cyst blocks the flow of fluid. It is often accompanied by headache, epileptic seizures, weakness in the legs and high intracranial pressure. The symptoms of this disease manifest themselves most clearly in adulthood. Sometimes this disease causes hydrocephalus and cerebral hernia. In rare cases, it is fatal.
Colloidal cyst
Cysts of different parts of the brain
In some cases, doctors diagnose the following diseases:
- A pituitary cyst of the brain is a benign formation. It appears mainly in people aged 30-40 years. There are practically no pituitary cysts in children and adolescents. This disease is dangerous because the tumor affects the central nervous system. Most often, such a cyst is removed surgically.
- A cerebellar cyst can occur for a number of reasons. Most often, its treatment is aimed at resolving adhesions. If the cyst is formed as a result of autoimmune processes or infection, anti-inflammatory therapy will be needed. Surgical intervention is performed if there are signs of hemorrhage, convulsions, or loss of coordination of movement. In most cases, this disease is completely curable.
Reasons for appearance
Head injuries suffered during childbirth or injuries received during pregnancy affect the development of such a disease in a newborn child.
The causes of congenital abnormalities are not fully understood, and the opinions of neurologists differ. According to recent clinical studies, it has been found that the occurrence of a porencephalic cyst is influenced by a viral infection that a woman suffered during pregnancy. More often this refers to encephalitis and cytomegalovirus.
A tumor in the brain may not manifest itself in any way and the patient will not be aware of the pathology. And the progression of the disease and the appearance of the first symptoms are influenced by: a head injury or stress.
Symptoms
- Mental retardation;
- Disturbances in the functioning of the musculoskeletal system;
- Paralysis, convulsions;
- Decreased vision;
- The risk of death cannot be ruled out either.
Factors influencing symptoms and nature of formation:
- Education size;
- Number of cysts;
- The location of the anomaly and which brain organs will be compressed. (For example: nerves, choroid plexus, cerebellum, etc.).
- The root cause of its appearance.
Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis of brain cysts is made using ultrasound, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. During the study, the location and size of this neoplasm are determined. In this case, the doctor can make, for example, the following diagnosis: “cerebrospinal fluid cyst of the temporal lobe of the brain” or “arachnoid cyst of the left hemisphere of the brain.” In order not to confuse this formation with a tumor, a contrast agent is injected into it. Tumors accumulate it, but cysts do not.
Since the consequences of a brain cyst can be very different, it is necessary not only to detect in time, but also to prevent the appearance of new formations. Through various examinations, the reasons that led to the formation of the cyst are determined.
Forms
Experts distinguish two forms of cysts: true and false. They differ in location, appearance and other characteristics.
True
It is formed in close proximity to the outer cortex of the cerebral hemisphere, but rarely affects it. The neoplasm is capable of connecting to the ventricles of both hemispheres.
The size of the tumors varies from a few millimeters to 5 centimeters in diameter. In some cases, they are able to fill almost the entire space of the organ hemisphere.
The inner surface of cysts is always smooth and similar in appearance to the epindema layer. When connected to the ventricles, the formation contains cerebrospinal fluid. In other cases, the exudate is yellow in color and a large amount of protein is present.
When examined under a microscope, the surface of the cyst has altered areas, the appearance of which is caused by the incorrect structure of the cerebral cortex. The presence of hemorrhages and necrosis is established.
False
A porencephalic cyst is located in the tissues of the brain, but does not reach the cortex of the organ and does not connect to its ventricles.
Neoplasms are localized only in one hemisphere or in the white matter. A distinctive feature of false tumors is their ability to merge with each other. Single cysts are also detected.
With false neoplasms, deformation of the gyri does not occur, but scar tissue begins to form on the surface of the tumor.
Scientists have identified the bladder brain as a separate form. This is a condition in which the lesion affects both hemispheres at once, and the pathological process spreads to the brain stem.