Cerebral ischemia in a newborn: degrees, symptoms and causes, treatment and reviews
Cerebral ischemia occurs in infants for several reasons.
This condition is quite serious and requires constant medical supervision. The kids are in the hospital for a full examination and treatment. The disease occurs due to insufficient blood supply to the brain due to blockage of blood vessels. This disease has several other names: perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage and hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE).
There are 3 degrees of cerebral ischemia. Each of these degrees is characterized by its own clinical manifestations. In the first degree they manifest themselves weakly, in the second and third they have a pronounced character. Grade 1 cerebral ischemia in a newborn is mild and does not require hospitalization. With the second and third HIE, the baby requires hospital treatment. And the sooner it begins, the fewer health complications the child will experience in the future.
Treatment of ischemia in newborns
Despite significant advances in the treatment of ischemia in newborns, there are still no effective means of eliminating the disease.
The main goal of treatment is to restore blood circulation to the blood vessels to ensure normal functioning of the damaged areas of the brain. In the mild stage of the disease, the treatment method is very simple and accessible to everyone - it is a regular massage without the use of any medications. In the case of more complex stages of the disease, therapy is selected according to individual characteristics and always according to the indications of a medical specialist. Usually, medications are prescribed to stimulate brain function, normalize the circulatory system, and medications to restore and strengthen the child’s body’s defenses. Folk remedies are widely used in the treatment of cerebral ischemia, and they must be combined with basic medications. Traditional methods can relieve the symptoms of the disease well, but only medications and surgery can eliminate the cause. Traditional methods of treatment are not used for newborn babies.
The main symptoms of convulsive syndrome in children are well described in this article. You will learn how to help your child during an attack and how to avoid it in the future. You can find out Dr. Komarovsky’s opinion on intracranial pressure in infants here. Is hand tremors dangerous in newborns, what causes them and how to prevent them
Classification of pathology
Experts distinguish two forms of the disease:
- Cerebral ischemia in newborns is a congenital pathology; its signs appear in the first days of a child’s life. And in 70 out of 100 infants it starts at the time of birth or in the later stages of gestation.
- The chronic form of coronary artery disease is diagnosed in patients of older, often retirement age.
According to the time of appearance there are:
- Ischemia of the central nervous system in newborns, which appears during embryonic and natal development. Clinical signs appear in the first few days of life. In 70% of cases, the appearance of symptoms is observed during childbirth or gestation, especially characteristic in the last stages.
- The chronic type appears in adults and older people. It occurs especially often among pensioners. May lead to ischemic stroke.
Ischemic diseases of newborns are divided into 3 stages. Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy grade 1 is the mildest form of neurological disease of the central nervous system. It is characterized by mild symptoms that appear 3-5 days after birth.
The most characteristic manifestations:
- severe nervous excitement or depression;
- the muscular system is constantly tense;
- tendon reflexes are strengthened.
With this form, it is not necessary to place the patient in a hospital. The disease goes away with time.
Cerebral ischemia of the 2nd degree in a newborn manifests itself in the first day of the child’s life. Symptoms usually appear within a month. Obligatory requirement is supervision by a doctor. During your stay in the hospital, therapeutic measures are required. If the pathological condition of the central nervous system is caused by blockage of blood vessels with a blood clot, surgical intervention may be required.
Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy grade 3 in newborns is considered the most severe. Characteristic manifestations:
- lack of reflex activity;
- coma;
- problems with heart rhythm;
- severe hypertension;
- impossibility of normal functioning of the respiratory system;
- problems with oculomotor function.
Upon consultation with a specialist, the presence of severe symptoms can be determined within a few minutes after birth. The patient is necessarily sent to intensive care. If the baby has problems with independent breathing, then connection to an artificial life support apparatus is required. The phenomena are often observed in prematurity.
Degree of disease in newborns
There are three degrees of ischemia in children:
- Mild degree ( grade 1 ) - when the child is overly excited or depressed during the first 4-7 days of his life. Treatment is carried out in the maternity ward, after which the child is observed by a neurologist at home.
- With a moderate degree ( grade 2 ), the child experiences seizures and a number of neurological disorders occur. The child is being treated in hospital.
- Severe degree ( grade 3 ) of ischemia involves serious disorders in which the baby is admitted to the intensive care unit. After discharge, the baby will have a long rehabilitation period.
The first two degrees of brain disease are in rare cases considered to be a consequence of the development of neurological pathologies. And, if adequate therapy is carried out on time, the functional symptoms of the disease disappear completely. Severe ischemic dysfunction of the brain contributes to the development of abnormalities in the nervous system.
This leads to dysfunction of the central nervous system, as a result of which the child develops poorly, has seizures, and hears and sees worse.
If you are looking for a rehabilitation center for recovery, we recommend the rehabilitation center, where rehabilitation after neurological diseases is carried out using the most modern equipment.
How does it manifest?
Clinical manifestations of central ischemia can be noticed from the first days of a child’s life. The degree of their severity depends on the stage of the disease. Most often, children with this diagnosis experience the following changes in their condition:
- decreased muscle tone;
- excitability of the nervous system, which manifests itself as shudders during sleep, trembling of the jaw and limbs;
- weakening of sucking reflexes;
- lethargy, decreased activity;
- lethargy of the child;
- asymmetry of facial muscle movements;
- convulsions;
- increase in head volume.
1st degree
Cerebral ischemia in a newborn of the first degree manifests itself with mild symptoms. At this stage of development of the disease, the child may experience headaches and a feeling of heaviness in the head. At the same time, the baby becomes lethargic, eats and sleeps poorly.
During sleep, you may notice frequent shuddering, and after strong crying, trembling of the lower jaw and limbs, which do not disappear for a long time after the baby has calmed down. The last sign is very important, because When crying and normally, many children's chin may tremble.
Cerebral ischemia in a child of the first degree is relatively easy to treat. As a rule, therapy is carried out on an outpatient basis.
2nd degree
Cerebral ischemia of the 2nd degree in newborns is characterized by local lesions in children's brain and requires hospitalization of the child. Symptoms at this stage of the disease become more pronounced.
The child experiences frequent dizziness, instability and spontaneity of movements. There is a decrease in motor activity, involuntary muscle contractions and cramps. Tremors during sleep become more frequent, and the duration of trembling of the jaw and limbs increases.
In addition, the baby exhibits symptoms of intracranial hypertension and autonomic-visceral disorders. That is, the skin becomes pale and becomes “marbled.” At the same time, the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract organs is disrupted - defecation disorders, flatulence, etc.
3rd degree
Cerebral ischemia of the 3rd degree in children develops against the background of perinatal asphyxia or prolonged intrauterine oxygen starvation. As it develops, the newborn experiences a rapid decrease in cerebral activity. There are cases when babies even fall into a coma. Next, there is a short-term increase in activity, then again its sharp inhibition.
With grade 3 cerebral ischemia, newborns experience repeated seizures. Brain stem cells almost completely stop functioning, which leads to disruption of the breathing process and oculomotor disorders.
Symptoms of autonomic-visceral disorders and increased intracranial pressure also occur. In cases where extensive brain damage occurs, the child changes in appearance. His body lengthens due to the maximally reduced muscle tone, internal rotation syndrome is observed on the limbs, and frequent rolling of the eyes and dilation of the pupils occur.
In severe forms of cerebral ischemia, comatose syndrome may occur. It is characterized by symptoms such as infrequent blinking, “floating” eyeballs,” muscle atony and disorders of the urinary system.
Treatment of the disease
Cerebral vascular ischemia diagnosed in newborns has varying degrees of impact on the child’s body. Accordingly, the treatment itself will depend on the stage of the disease, as well as the symptoms observed in the baby.
Cerebral ischemia in newborns causes various consequences, therefore treatment should begin immediately. As a result of the course of this disease, certain areas of the brain are affected. Modern medicine, despite all its achievements, simply cannot restore those brain cells that have already died. There are no miracle drugs or special procedures that could restore them. However, not everything is as bad as it might seem at first glance. There are certain methods that can stop the development of the disease, preventing it from becoming severe. They also contribute to the speedy rehabilitation of the child so that he can feel full.
If the child does not take his first breath after a couple of minutes from the moment of birth, then doctors begin certain resuscitation actions. For this, artificial ventilation is used, after which, if everything is normal, the child and the mother are transferred to the ward. If the condition is still serious, then he is sent to the intensive care unit, where he is given the closest care and monitoring.
A symptom that is characteristic of this disease is limb cramps. To get rid of them, phenobarbital or phenytoin is used, which also prevent further brain damage.
In addition to the negative consequences for the head, ischemia is also dangerous for the heart. In particular, there are frequent cases when transient myocardial ischemia develops in newborns. To normalize its work, dobutamine, dopamine and other drugs of this type are prescribed.
It is worth noting that medications are prescribed only for obvious damaging factors. In general, it is not recommended to give newborns any strong medications, so if they have a mild form of the disease, then a therapeutic massage can be prescribed, the purpose of which is to normalize blood circulation. Only after it becomes clear that massage procedures are ineffective does the doctor decide to prescribe medications.
Causes of the disease
Cerebral ischemia in a child is not considered an independent pathological condition. Most often these are consequences of cerebral hypoxia. With the development of oxygen deficiency, the rate of metabolic processes decreases significantly and starvation of the nervous tissue occurs. Neurons are unable to remain without oxygen for a long time.
The most common causes of the disease include:
- Intrauterine oxygen starvation in the fetus. This happens quite often. It is a common cause of the disease. Most often it appears if there are disturbances in the flow or outflow of blood from the placenta.
- Suffocation. This cause can occur both intranatally and postnatally. Asphyxia can occur during complicated passage of the birth canal, or in the first few minutes after birth.
- Respiratory distress syndrome, which is a severe pathological condition of the respiratory tract. Occurs for third-party reasons not related to the functional abilities of blood pumping of the cardiovascular system. Characterized by pulmonary edema, followed by disruption of the breathing process.
- Apnea. Paroxysmal respiratory rhythm disturbances are also observed in children. Especially during sleep. At the same time, due to delays in breathing, the volume of oxygen supplied to the tissues is significantly reduced. Nervous tissues suffer from this, as they are most susceptible to starvation.
- Heart defects. With functional disorders of the cardiovascular system, oxygen deficiency occurs. In premature babies, patent ductus arteriosus is most common.
- Acute disturbances in the blood circulation system. It causes severe hypotension, after which the blood flow rate decreases significantly. All parts of the body suffer from this phenomenon, but the brain is most affected.
In addition, some pathological conditions and processes in the mother’s body during the natal development of the fetus can contribute to the development of oxygen starvation.
These include:
- Viral diseases of the respiratory tract accompanied by intoxication.
- A decrease in the level of respiratory pigment in the blood, which is often observed in anemia due to iron deficiency.
- Diabetes mellitus and elevated plasma sugar levels.
- Poor nutrition, especially associated with a lack of nutrients, vitamins and microelements in food.
- Bad habits, smoking, excessive consumption of alcohol, drugs and more.
- Age category. The older the woman, the higher the likelihood of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. The likelihood of a pathological process increases significantly.
Also, there is periventricular ischemia, which is caused by premature birth. Premature babies are susceptible to diseases. Hypoxia mainly affects the ventricles.
Causes of cerebral ischemia
Cerebral ischemia can occur due to various factors. Again, if you believe the statistics, the cause of this disease may even be the mother’s age.
For example, it has been found that most often ischemia can be detected:
- in women who gave birth before 20 years of age;
- in women who gave birth after 35 years.
This is due to impaired blood circulation in the placenta.
Also, the threat can be identified in those women who suffer from chronic diseases, most often these are:
- diabetes;
- vascular hypertension.
However, even healthy women who do not fall into statistically dangerous age categories can be susceptible to this disease (as a result of which the newborn will be diagnosed with “cerebral ischemia”).
The reasons may be:
- manifestation of toxicosis in the last months of pregnancy;
- twins, triplets (multiple pregnancy);
- frequent changes in blood pressure (especially increases);
- post-term baby (the fetus risks not receiving enough nutrition from the mother in the womb);
- premature baby;
- entwining the baby with the umbilical cord (regardless of when this phenomenon occurred: during pregnancy or during childbirth);
- rapid birth (birth of a child in less than 6 or 4 hours in primiparas and multiparas, respectively);
- long labor (here ischemia is caused due to hypoxia or asphyxia).
Possible consequences
The consequences of cerebral ischemia can be very different. And most often they are severe. It is for this reason that treatment should begin immediately after the diagnosis is made.
The most common consequences of cerebral ischemia are the following conditions:
- frequent headaches;
- sleep disturbance;
- increased irritability;
- mental retardation;
- epilepsy.
Childhood ischemia of the first degree is easily treated and almost never leaves any consequences.
However, parents should understand that the longer they delay treatment, the more difficult it will be, and the risk of health complications increases.
How to prevent illness from occurring
- Hydrocephalic syndrome, in which the size of the head noticeably increases. Usually there is a noticeable enlargement of the fontanel, which occurs due to the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), a special fluid, in this part of the brain. Against this background, the pressure inside the skull increases several times;
- Convulsions, which manifest themselves as twitching of the limbs, head, and shuddering of the body;
- Decreased tone of various muscles, which occurs due to depression of the central nervous system. Because of this, there is a decrease in motor activity, the skills of sucking and swallowing are weakened, and sometimes even facial asymmetry and strabismus develop;
- Increased excitability, which refers to neuro-reflex disorders. In this case, you can observe symptoms from an extensive list: tremors of the hands, chin and legs, anxiety, poor sleep, shuddering, causeless crying, decreased or increased muscle tone;
- Comatose syndrome, indicating a very serious condition of the child. With it, he is completely unconscious, provided there is a complete absence of coordinating function on the part of the brain.
Diagnosis of cerebral ischemia in a newborn is carried out after the following examinations:
- Complete blood count (erythrocyte count and leukocyte formula).
- Urinalysis (protein content, leukocytes).
- Neurosonography is an ultrasound examination of the skull through the fontanelles, searching for asymmetrical parts of the brain, enlarged cavities and spaces, and formations.
- Ultrasound examination of blood vessels using Doppler methods. Additionally, acceleration or deceleration of blood flow through the main vessels is detected.
- EEG, which detects changes in the activity of the brain.
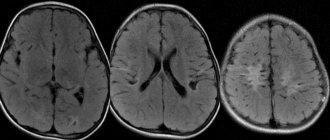
- Magnetic resonance imaging is rarely used due to the need for anesthesia. It is used only in cases of suspected brain developmental defects.
- Computed tomography, which is used if bleeding into the cranial cavity is possible.
The treatment method is chosen by the doctor based on the patient’s condition. In the acute period, methods are aimed at supporting life and include:
- artificial air circulation;
- maintaining blood salt balance;
- drugs against involuntary muscle contractions.
After the end of the acute period, the following groups of drugs are used:
- improving blood flow through vessels and intracellular metabolism.
- diuretics that lower blood pressure;
- restoration of the balance of metal ions;
- nootropics to improve the functioning of the central nervous system.
Also used:
- massage therapy;
- gymnastics;
- hydrotherapy;
- complex of physiotherapeutic measures.
Methods for preventing cerebral ischemia concern the mother of the child.
Activities include:
- increasing time spent in fresh air;
- getting rid of bad habits;
- avoiding stress and fatigue;
- adherence to the regime and consumption of foods containing vitamins;
- no need to overload the body with loads;
- monitor blood pressure;
- control the level of respiratory pigment;
- prevent obesity;
- prevent infections.
To prevent the development of cerebral ischemia in a child, it is necessary to minimize risk factors. When planning a pregnancy, you should:
- give up alcohol and smoking in advance;
- switch to a balanced diet and begin to observe a work-rest schedule;
- take daily walks in the fresh air;
- play sports with moderate exercise;
- normalize body weight and maintain it;
- protect yourself from infectious diseases;
- monitor hemoglobin levels and blood pressure;
- avoid stressful situations;
- be regularly examined by a doctor and follow all instructions;
- If you experience the slightest ailment, you should immediately go to the hospital.
By following these simple rules, you can give birth to a healthy baby. If the disease does appear, then it is necessary to contact a specialist as soon as possible and begin treatment. In this case, the chances of a full recovery increase.
Medical therapy
The main goal of therapeutic therapy for cerebral ischemia is to normalize cerebral circulation and eliminate the consequences that arise due to oxygen starvation of the brain. Ischemia in children is treated individually. In this case, the gestational age, the degree of damage to the child’s brain, the presence of other health problems in the baby, etc. are taken into account.
Treatment of the first stage of cerebral ischemia does not require the use of any medications. At this stage, only therapeutic massage is used. During its implementation, muscle tone increases and blood circulation throughout the body improves, which has a beneficial effect on the overall well-being of the newborn. After the massage, the child’s sleep normalizes and his motor activity increases.
It is not recommended to massage yourself. In this case, you need to contact a specialist who knows all the intricacies. Massage should be carried out in courses. Their duration is selected individually, but most often it does not exceed 10 sessions. In total, you should undergo 3-4 massage courses per year. The interval between them should not exceed 3 months.
Even if first-degree cerebral ischemia in a child has been cured, the baby still needs constant monitoring by doctors.
Treatment of this disease at stages 2 and 3 in newborns is carried out using diuretics, nootropics and vasoconstrictors. The use of such medications must be under the strict supervision of a doctor, and therefore treatment must be carried out only in a hospital setting.
It is necessary to understand that cerebral ischemia is a very dangerous disease that can manifest itself with various symptoms. The first 2-3 months after the birth of a child, parents need to carefully monitor his behavior. And if something is bothering the child, he should be immediately shown to a pediatrician.
If the doctor, after examining the baby, reveals any abnormalities in him, then all tests must be taken immediately. And after confirming the diagnosis, carry out therapeutic therapy.
Basic principles of pathology treatment
Unfortunately, there are no treatment methods that can restore brain tissue cells damaged by oxygen starvation. However, there are techniques that allow you to normalize the supply of oxygen in the blood in the required quantity and help the body resume functionality after a lack of it.
Resuscitation methods for acute hypoxia
If within 1-2 minutes after birth the child does not begin to breathe on his own, the following resuscitation methods are used:
- Carrying out intubation and starting mechanical ventilation (artificial pulmonary ventilation) - with minor hypoxia, the baby can be transferred to the mother within 2-4 minutes after intubation. If necessary, the newborn is placed in the intensive care unit.
- Anticonvulsant therapy – stops convulsive manifestations and eliminates further damage to brain tissue.
- Maintaining the activity of the cardiovascular system.
- Hypothermia technique - in recent years, research has been conducted, according to which lowering the baby’s body temperature by 3-4 degrees can prevent the development of necrosis of brain cells during hypoxia. The technique has been used in clinics in our country since 2010 and gives good results.
Methods for eliminating the consequences of brain hypoxia
Ischemia of the second and third degrees usually results in changes in brain tissue that cannot be restored. They have varying degrees of severity and a very small range of treatment methods. Basically, you can have a positive impact on the consequences of ischemia only by regular activities with a sick child:
- For cerebral palsy you need:
- taking muscle relaxants;
- surgical treatment (if necessary);
- massage (it is better to entrust it to an experienced specialist).
There are many techniques that are used to restore children with cerebral palsy: from exercise therapy to exercises with horses and dolphins. They are selected strictly individually and may not give positive results.
- If seizures persist, anticonvulsant therapy is used.
- To restore speech, sessions with a speech therapist are prescribed.
- Correction of forced incorrect postures is carried out using splints, special furniture, and wheelchairs.
- For such a child to fully develop, he needs regular communication with peers and adults.
To prevent the development of hypoxia during pregnancy, the expectant mother should take all the doctor’s recommendations seriously, give up bad habits and closely monitor her health. If any complication of pregnancy develops, timely hospitalization is necessary.
Consequences of brain ischemia in children
Complications and consequences of cerebral ischemia in newborns are also distinguished by stages. With a mild course of the disease, changes are invisible. There may be no negative effects. There is no impact on development. With timely initiation of treatment, sleep problems, headaches, and epilepsy are possible.
The consequences of grade 2 cerebral ischemia in newborns can cause the following complications:
- Up to 10% of patients experience disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system associated with surges in blood pressure.
- Up to 50% of patients have developmental disorders.
The first degree is considered safe for the baby. Possible slow growth or hyperactivity.
In the third degree, changes affect a specific part of the brain. Therefore, it depends on the department that was affected by the pathological condition. The patient remains paralyzed or dies. If you start treatment on time, the risk of irreparable changes is reduced.
Forecast:
- Up to 50% of patients die within a few days from infectious diseases.
- Mental development disorders, dementia, autism and others are possible.
- Up to 10% of patients remain with changes in mental development.
Children who have had ischemia are included in the risk group for diseases of the cardiovascular system and stroke.
Symptoms and signs
Symptoms of ischemic brain damage in a newborn appear immediately after birth or within a few days after it. Depending on the severity of functional damage to brain cells, 3 stages of the disease are distinguished, each of which has characteristic signs.
1st degree
This degree of the disease is the mildest. Its symptoms appear in the 1st week of a baby’s life and can go away without medical intervention. However, if grade 1 cerebral ischemia is diagnosed, the child should remain under the supervision of a specialist even after discharge from the maternity ward.
Manifestations of first degree encephalopathy include:
- severe headaches, as a result of which the child worries, cries, or sleeps poorly;
- depressed general condition of the newborn, which is determined visually by the pediatrician;
- hypertonicity of muscle tissue: they are very tense, resulting in a dense feel;
- increased reaction of the elbow and knee tendon reflexes, which are tested by lightly tapping the elbows and knees with your fingers.
It is extremely difficult to recognize grade 1 cerebral ischemia in newborns and infants in the early stages, and the later therapy begins, the lower the chances of full recovery.
2nd degree
Cerebral ischemia of the 2nd degree in newborns manifests itself already on the 1st day of the child’s life, and with timely and correct therapy, many of the signs disappear after 2-4 weeks. However, this stage of the disease is dangerous because in the future it can lead to the development of central nervous system pathologies of varying severity.
Pathology of the 2nd degree in a newborn manifests itself as:
- periodic cessation of breathing during sleep;
- holding your breath;
- slowing heart rate;
- blue lips;
- weakening of muscle tissue tone;
- weakening of innate reflexes: grasping and sucking;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- pallor or bluishness of the skin;
- fainting resulting from arterial hypertension and disruption of neural connections.
At this stage, the development of hydrocephalic syndrome is possible, in which due to the accumulation of fluid in the peri-cerebral space, an increase in the size of the head occurs. The child develops intracranial and arterial hypertension, accompanied by severe headaches.
At this stage of ischemic disease, brain tissue is formed with disturbances, as a result of which the most important reflexes do not develop correctly.
3rd degree
This degree of cerebral ischemia in newborns is the most severe. Against the background of changes occurring in the central nervous system, the risk of developing irreversible consequences increases. Due to insufficiency of cerebral circulation, part of the brain tissue dies and the performance of most vital functions becomes impossible. Stage 3 ischemia in a newborn can be detected already in the first hours of life. It appears as:
- complete absence of innate reflexes;
- damage to areas of the brain responsible for spontaneous breathing and food intake;
- disturbances of heart rhythm and light perception;
- difficulty supplying blood to the brain, resulting in increased intracranial pressure;
- loss of consciousness;
- periodic immersion in a coma;
- seizures;
- strabismus.
Stage 3 cerebral ischemia in a newborn is difficult to treat. Immediately after birth, infants with this diagnosis are placed in intensive care. In most cases, they require artificial ventilation. There is a high probability of death, and if treatment is successful, the child will subsequently be severely retarded in physical and mental development.
What happens to the child
Cerebral ischemia in newborns is a consequence of hypoxic manifestations during the period when the woman was pregnant and during childbirth. Cerebral ischemia in infants is a condition in which the brain is insufficiently supplied with blood. This brain damage in a child is rarely observed; for example, this condition is observed in heart failure.
A newborn is suspected of having cerebral ischemia if:
- He is crying for no reason and is shaking.
- The skin has a marbled color.
- The child's sleep is disturbed.
- His breastfeeding is weakened and he has trouble swallowing.
- There is weakened muscle tone, the child is lethargic.
- Enlarged head with fontanel.
- Respiratory function is impaired, convulsive seizures are noted.