Brain contusion is a local disorder of brain activity that occurs due to severe mechanical damage to the head. The pathological condition causes a number of negative symptoms - from severe headache, nausea and short-term fainting to massive hemorrhages, paralysis of the limbs and deep coma. If not treated promptly, a head contusion can lead to disability or death.
Concussion is a brain disorder that usually occurs as a result of head trauma.
Brain contusion: consequences, symptoms, treatment
Concussion is one of the types of damage to the entire body or parts of it that appears from the sudden impact of a blast wave or impacts from a fall. In severe cases, extensive bruising is accompanied by damage (rupture) of internal organs.
Contusion is classified according to the severity and location of the lesion. It is accompanied by a number of symptoms, the main of which is loss of consciousness.
Over time, its consequences appear, which cause painful sensations and psycho-emotional discomfort to the affected person.
Types of concussion
Depending on the strength of the mechanical impact, two types of contusion are distinguished:
- General (mild) contusion is the result of extensive traumatic injury to the entire body or most of its parts. The cause of general concussion can be a fall from a height, a blow to water or a hard surface, or pressure on the body from heavy masses resulting from rubble. Associated symptoms of mild contusion are loss of consciousness and memory, severe dizziness.
- Severe contusion is a severe injury to the body, aggravated by serious damage to tissues and internal organs (rupture of the liver or spleen, broken bones, hemorrhages in the brain). As a result, the work of the main systems and vital organs is disrupted, which leads to unpredictable consequences.
Depending on the location of the focus, the following traumatic injuries are distinguished:
- Eye contusion - occurs due to direct or indirect mechanical effects on the organs of vision. In the first case, the bruise appears from a blow to the visual organ, in the second - as an aggravating factor against the background of a general contusion.
- Brain contusion is a severe head injury that provokes pathological disorders in brain activity. As a result, the person may remain disabled or die.
Also, contusions of the brain and eyes are classified according to the severity of the symptoms that appear. Depending on the complexity of the bruise, specialists diagnose mild, moderate or severe contusion.
Signs of a brain contusion are pathological in nature, and the intensity of their manifestation depends on the severity of the injury.
With a mild , the patient experiences:
- short-term fainting (up to 10 minutes);
- “ringing” headache accompanied by dizziness;
- attack of nausea and intense vomiting;
- memory loss regarding the injury;
- rapid pulse and heartbeat;
- increased blood pressure.
With a moderate , the described symptoms are supplemented by other pathological signs:
- amnesia, affecting not only the incident with the trauma, but also the events preceding it;
- excruciating headaches;
- decreased sensitivity of the skin and olfactory organs;
- failure of important vital systems.
Severe contusion has more pronounced and life-threatening symptoms:
- loss of consciousness lasting from several days to 3 weeks, coma;
- disruptions in the functioning of systems and internal organs due to their mechanical damage;
- psychoneurological disorders;
- tachycardia;
- epilepsy attacks;
- impairment of visual functions and speech;
- temporary numbness of the limbs;
- profuse hemorrhages in the brain tissue.
Brain contusion is quite often accompanied by eye contusion, the symptoms of which also have pathological manifestations:
- mild degree – retinal clouding, decreased vision, corneal swelling, erosion;
- medium degree - hemorrhages in the tissue of the visual organs, decreased vision up to its loss, deep damage to the cornea by erosion, rupture of the eye muscle responsible for changing the size of the pupil;
- severe degree - a pronounced decrease or increase in eye pressure, rupture of the sclera (white membrane), swelling and severe enlargement of the eye.
If there are obvious signs of contusion, the patient must be given priority assistance and immediately taken to a medical facility to diagnose the degree of injury and prescribe treatment.
Consequences of cerebral concussion
Depending on the location of the affected tissues in the acute phase of the contusion, the patient should be prescribed effective treatment to reduce the likelihood of consequences in the future. However, this cannot be avoided in all cases.
The consequences of a brain contusion resulting from exposure to a shock wave, in most cases, appear months after the incident. The patient begins to experience the following symptoms at regular intervals:
- intense headaches;
- shortness of breath, tachycardia;
- intolerance to loud sounds;
- dizziness;
- speech disturbance during excitement (stuttering).
During this period, the receptors and neurons of the damaged areas of the brain begin to recover, which causes a number of additional signs of a psychogenic nature in a shell-shocked person:
- hysteria;
- epilepsy attacks;
- heavy sweating;
- emotional sensitivity, manifested in the form of depression, tearfulness, fatigue, feelings of uselessness and frequent mood swings.
After a shell shock, it is difficult for a person to adequately perceive life’s difficulties; with frequent hysterics, he tries to attract the attention of loved ones.
Such conditions, if left untreated, become protracted and then become chronic. To prevent this from happening, it is necessary to periodically undergo treatment, including drug therapy and a range of health procedures.
Treatment of concussion
A person suffering from a concussion needs urgent hospitalization. Depending on the severity of the brain injury, the patient may be prescribed the following types of treatment:
- cold compress on the head;
- peace and quiet during the acute phase;
- stopping bleeding if present;
- drug therapy with the administration of antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, vascular drugs, vitamins;
- surgery for life-threatening conditions;
- physiotherapy;
- immunotherapy;
- help from a psychologist and psychotherapist;
- classes to restore speech in case of speech impairment.
During the recovery period, the patient is prescribed sanatorium treatment, massage sessions, soothing baths with extracts of pine needles, motherwort, and valerian. After a concussion, it is undesirable for a person to be in the sun or in stuffy rooms. There are also restrictions on working in noisy areas.
Source: https://progolovy.ru/golovnoj-mozg/kontuziya-golovnogo-mozga
Rehabilitation
If a brain injury occurs, the recovery period will be long. With severe bruises, complete recovery cannot be achieved, but the quality of life of the victim can be improved.
For closed TBI, the recovery period ranges from six months to 2 years. Sets of exercises selected by a doctor are aimed at restoring lost skills; training is carried out regularly without fatigue. At the same time, medications are prescribed to improve tissue metabolism and restore the number of neurons to an optimal level.
Treatment methods such as massage, acupuncture, electrosleep, medicinal electrophoresis on the collar area, and exercise therapy will help speed up the rehabilitation period. With intracranial hypertension, exercise is approached with the utmost caution. For amnesia, they work with a psychotherapist. If amnesia is persistent, conditions are created for the socialization of the patient.
Brain contusion and its consequences
Brain contusion is a type of traumatic brain injury caused as a result of indirect exposure to the body of a blast wave or pressure from heavy masses. In the victim, this condition is expressed in a disorder in the functioning of the nervous system, which manifests itself in the appearance of neurological disorders: memory loss, muteness, hearing loss, and in the worst case, coma.
In the absence of the correct approach to providing first aid, a subsequent brain contusion can cause disability or even death.
What is cerebral contusion
Literally, the term “Contusio” is translated from Latin as bruise. However, these two concepts are not equivalent, since a concussion is a consequence of the impact of some energy on the victim’s head, for example a blast wave, while a bruise or concussion is a consequence of hitting the head on a hard surface.
The main characteristic of this type of brain injury is the formation of multiple lesions of the nervous tissue, which ultimately leads to partial or total organ dysfunction. This is evidenced by the loss of consciousness or comatose state of the victim.
After he comes to his senses, other consequences of disorganization of the central nervous system structures develop: muteness, partial deafness, clouding of consciousness, psychosis or amnesia.
What provokes such changes in the functioning of the central nervous system? As is known, under the influence of a shock wave in the skull, displacement and damage to brain structures occurs. Moreover, first, the main zone of damage to the brain substance appears, which is located directly in the area of impact, and then the brain, moving from behind, hits the bones of the skull, forming a counter-impact zone.
In this way, several foci of contusion are formed at once, as evidenced by multiple disorders in the functioning of the central nervous system.
For example, if the focus of damage to the brain substance is located in the temporal zones of the terminal region, then the victim has problems with speech, if it is localized on the anterior or posterior central sulcus of the left hemisphere, paralysis develops and loss of sensitivity occurs.
When the corpus callosum is damaged, mental abnormalities develop.
Symptoms of concussion
The international classification ICD 10 classifies brain contusion as an intracranial injury and is classified depending on the type of brain injury under the code S06.3 “Focal brain injury” or S06.2 “Diffuse brain injury.”
As mentioned earlier, each degree of contusion in a victim is characterized by the appearance of certain symptoms of disruption of the central nervous system, caused by the appearance of several foci of destruction of brain matter.
Some of the most common consequences of this type of injury include:
- short-term loss of consciousness (up to 10 minutes); prolonged headache;
- dizziness;
- nausea, vomiting;
- noise in ears;
- increased heart rate, respiration, blood pressure;
- clouding of consciousness;
- muscle hypertonicity;
- “veil before the eyes”;
- decreased performance of the sense of touch.
- loss of consciousness for a long period of time (10 minutes or more);
- retrograde amnesia;
- severe headaches;
- nose and ear bleeding;
- dizziness;
- changes in consciousness, up to the development of psychosis;
- vomit;
- increased blood pressure, heavy breathing, increased heart rate.
- coma or prolonged loss of consciousness for a period of time up to 3 weeks;
- disruption of life support systems due to damage to the structures of the reticular formation;
- mental disorders;
- paralysis;
- severe tachycardia;
- epileptic seizures;
- hemorrhages in the brain and subarachnoid space.
Often, even after receiving a mild concussion, the victim can change his behavioral habits, and his character changes not for the better, which is noticeable to others.
Therefore, to prevent the development of complications, such patients should remain under the supervision of specialists.
Causes
What is a head contusion, and what injuries cause it? The main causes of cerebral contusion include serious bruises and strong blows to the head, which provoke a concussion. People get injured in fights, road accidents, or from blows when falling from a height.
The following can contribute to the development of concussion:
- High blood pressure . At the same time, vessels that are under constant tension are especially vulnerable and vulnerable. A strong blow, for example, associated with heavy objects falling on the head, can cause internal bleeding, which is extremely dangerous for the life and health of the victim.
- Blast wave . Soldiers serving in hot spots are well familiar with this phenomenon. Moreover, a bruise or contusion of the head in such cases can be obtained without mechanical trauma to the skull.
- A powerful sound wave produced by an explosion or artillery shell. It creates a sound impulse that disables the human tactile system. As a result, the victim loses consciousness and is temporarily destabilized.
You can get a concussion due to strong vibration, sudden changes in atmospheric pressure, or disturbances in the composition of the cerebrospinal fluid caused by severe brain diseases.
Kinds
Experts divide tissue and organ injuries resulting from concussion into the following degrees of severity:
- Easy . Characterized by dizziness, loss of consciousness, cephalalgia, tinnitus, rapid heartbeat, and a sharp increase in blood pressure. All unpleasant symptoms often disappear in the near future without serious consequences for the victim.
- Average . Severe headaches, impaired heat exchange, convulsions, nose or ear bleeding, intense breathing that exceeds the body's oxygen needs, and retrograde memory loss are observed. In such cases, the symptoms last for several weeks, and often lead to a malfunction of the patient’s important organs and systems.
- Heavy . Here you can observe such deviations as: prolonged loss of consciousness (up to falling into a coma), convulsions, dysfunction of the body (involuntary urination, problems with heart rhythm), partial or complete amnesia, loss of vision and hearing.
Symptoms
In order to adequately treat a concussion, in addition to assessing the degree of its severity, the organs most affected by the injuries are identified. There may be contusion of the head, eyes, ear (acoustic), spine, heart.
Each such damage has specific symptoms. A contusion (or bruise) of the brain develops when it hits the inner base of the skull.
Blood vessels burst, hemorrhage occurs, tissues swell and compress neighboring structures.
Depending on the severity of a head contusion, the following are observed:
- Loss of consciousness.
- Sensation preceding vomiting.
- Acute cephalalgia.
- Head spinning.
- Paralysis of limbs.
- Temporary memory loss.
- Muscle hypertonicity.
- Cramps.
- Speech impairment.
- Hypotonicity of the occipital muscles.
Consequences of concussion
If we talk about what consequences can develop after a head concussion, and when they appear, we need to take into account the severity of the injury. For example, the first consequences resulting from exposure to a blast wave appear several months after the incident. Basically, the victim begins to worry about:
- Severe attacks of headache.
- Shortness of breath, arrhythmia.
- Noise phobia.
- Frequent increases in blood pressure.
- Dizziness.
- Logoneurosis (stuttering).
At this time, receptors of damaged brain structures are restored, which causes additional signs of psychogenic genesis:
- Attacks of hysteria.
- Seizures.
- Obsessive thoughts.
- Increased sweating.
- Tearfulness.
- Nervousness.
- Unreasonable irritability and aggression.
- Sudden change of mood.
After a shell shock, it is difficult for the victim to cope with life’s problems; his character changes, which close people cannot help but notice. If treatment is not started, this condition will progress to the chronic stage. To prevent complications, you should periodically undergo special therapy and health courses.
Diagnostic methods
To clarify the diagnosis of a possible brain contusion, the doctor:
- Finds out the causes of injury.
- Collects anamnesis.
- Interviews witnesses to the incident (if the patient is unconscious).
- Conducts a general examination and evaluates the functioning of important organs and systems.
These actions are carried out at the scene of injury or after the person is transported to the hospital.
In the future, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- X-ray , which reveals violations of the integrity of the bones of the skull (severe head injury is a mandatory indication for this examination).
- Electroencephalography , which allows you to study the brain by recording its bioelectrical activity.
- Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging will help to accurately determine the severity and location of injuries received, even in the deep structures of the brain.
Having established the extent of the damage and identified possible hemorrhage, the specialist prescribes appropriate treatment. It should be noted that during the period of therapy and rehabilitation, the patient will have to be periodically examined so that the recovery process can be monitored over time.
Treatment
Brain damage caused by a concussion, contusion, or head injury causes serious consequences and leads to neurological problems. Therefore, the main therapy is aimed at restoring brain function.
Patients are prescribed:
- Analgesics and antispasmodics: Spazmalgon, Baralgin, Andipal.
- Antipyretics: Nurofen, Paracetamol, Ibuprofen.
- Antiemetics: Metoclopramide, Metukal, Perinorm.
- Nootropics: Noofen, Citimax.
- Diuretics: Furosemide.
It is recommended to use cool compresses in the first 24 hours after a concussion to relieve inflammation. If necessary, surgical intervention is performed.
During the rehabilitation process, the patient must monitor his health, eat right, and completely avoid alcohol consumption. He is prescribed sanatorium treatment, courses of therapeutic exercises, soothing herbal baths, massage, and ozone therapy. A psychiatrist or psychologist communicates with the victim; this will help avoid depression.
First aid
If a concussion is accompanied by damage to tissues and organs, then the injured person needs competent assistance. To alleviate the condition of the victim until the medical team arrives, assistance for concussion is provided as follows:
- Lay the victim on a flat surface face up.
- Unclench your teeth and cleanse your mouth of possible contaminants.
- When vomiting, hold the head on the side so that the person does not choke on the vomit.
- Check your breathing. If it is difficult, do mouth-to-mouth breathing.
- Cardiac massage cannot be performed in such cases, since contusion in most people is characterized by damage to the tissues of the entire body, especially the chest. Pressing can make the situation worse.
- If you have a nosebleed or ear bleed, roll up a piece of tissue and try to stop it.
Even in a mild stage, concussion leaves an imprint on a person’s mental and physical health. Therefore, it is important to promptly seek qualified medical help, not refuse treatment and follow all doctor’s recommendations.
(1 5,00 of 5) Loading...
Source: https://BolitGolova.info/mozg/kontuziya-golovnogo-mozga-posledstviya.html
Brain contusion: causes, treatment, consequences
Brain contusion occurs as a result of brain injury due to contusion of the entire body caused by mechanical force, such as a blast wave or impact with the surface of water.
It can be expressed by such symptoms as temporary loss of consciousness, sometimes reaching coma, headaches, dizziness and others such as:
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Temporary loss of vision and hearing.
- Breathing problems: shortness of breath, suffocation, hyperventilation.
- Bleeding from the nose and ears.
- Loss of coordination.
- Motor retardation.
- Disorders of the vestibular apparatus.
Classification
There are several degrees of severity of concussion:
First (mild) severity : characterized by temporary loss of consciousness (about 10 minutes), headache and dizziness, tinnitus, increased blood pressure (blood pressure), tachycardia (rapid heartbeat), bradycardia. Usually all these symptoms go away within a few days and without any special consequences for the body.
Second (moderate) severity : characterized by severe headaches, impaired skin and temperature sensitivity, bleeding from the nose and ears, convulsions, hyperventilation, retrograde amnesia (the patient does not remember the period before the injury), disorders of other organ systems. Symptoms in this case usually last from one to several weeks, and often cause complications.
Third (severe) degree of severity : characterized by prolonged loss of consciousness (up to coma), neurological symptoms (eye nystagmus, tics, etc.
), disorders of various organ systems (urinary disorder, damage to the heart muscle, bradycardia, tachycardia, arrhythmia, etc.
), motor disorders (paralysis of the limbs), convulsions (up to epileptic seizures), temporary or complete loss of hearing and vision, speech disorders (aphasia, alalia), partial or complete amnesia, hemorrhages, mental disorders, etc.
Consequences
Sometimes the consequences of an injury may not appear immediately, but after several days, months or even years. Even some time after treatment, various symptoms may occur: dizziness, headaches, shortness of breath, high/low blood pressure, stuttering, depression, neuroses, phobias.
Often, even a mild form of contusion leads to delayed consequences in various areas of human health. One of the most common disorders are psychological disorders due to concussion.
Under normal conditions, it is almost impossible to get a cerebral contusion. Most often, the cause of concussion itself is psychologically traumatic for a person . For example, if it was received during military operations, then first of all one should expect such changes in human behavior as the appearance of aggression, depression, apathy, and an increased level of anxiety.
As a result of hemorrhage, cerebral edema, epilepsy, or even brain death may occur; in this case, a person’s life can be maintained artificially, but, in fact, he will already be dead.
If damage occurs to the base of the skull or midbrain, this usually means instant death, because in that part of the brain the centers of instinctive regulation of the body are localized.
A person will simply stop breathing or his heart will no longer beat, because signals from the brain will not arrive.
One of the most common conditions after a concussion is asthenic syndrome . It manifests itself in chronic fatigue and drowsiness. Along with this, symptoms such as irritability, tearfulness, fatigue, and problems with concentration are observed.
Contusion is also characterized by the appearance of hysterical syndrome. Such patients are demonstrative, tearful, capricious, hypochondriacal, suspicious, react sharply and emotionally to any life difficulties, and are selfish.
Such patients are usually afraid of loud noises or places similar to the one where they were injured for the rest of their lives.
Diagnostic measures
Considering what a contusion is and its consequences, you can understand how dangerous the injury is. Therefore, it is very important to visit a doctor on time to make a diagnosis. Diagnostic measures include the following:
- A physical examination of a person to evaluate the condition.
- Consultation with a neurologist. The specialist determines the reaction of the pupils to light and conducts diagnostics using the Glasgow scale.
- CT. The procedure helps determine the presence of fractures, hematomas, and hemorrhages. This is the most accurate method that helps to determine any changes in the substance of the brain.
- MRI. It is not used very often, since advance preparation is necessary.
If the listed methods are not enough, then secondary ones, such as lumbar puncture, etc., may be prescribed.
Brain contusion
Brain contusion is a local disorder of brain activity that occurs due to severe mechanical damage to the head.
The pathological condition causes a number of negative symptoms - from severe headache, nausea and short-term fainting to massive hemorrhages, paralysis of the limbs and deep coma.
If not treated promptly, a head contusion can lead to disability or death.
Concussion is a brain disorder that usually occurs as a result of head trauma.
Causes of cerebral contusion
A contusion (contusion) of the brain is a traumatic brain injury, which results in the formation of irreversible destruction of the brain substance - contusion foci.
This pathology is provoked by serious factors:
- head injuries from explosions during emergencies, in war, from a strong blow during car or natural disasters;
- sudden and severe changes in atmospheric pressure;
- finding a person in difficult conditions associated with blockages of sand, avalanches, and stones;
- inflammatory processes in the meninges;
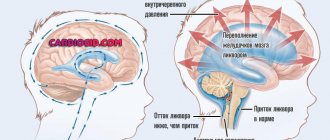
- a sharp increase in intracranial pressure as a result of pathological changes in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Degrees and their symptoms
Signs of a head concussion depend on the severity of the injuries received and manifest themselves in different ways.
Table “Degrees of brain contusion, their clinical manifestations”
| Degree | Characteristic symptoms |
| 1st degree – a mild form of traumatic injury, not life-threatening. Symptoms last no more than 4 weeks | Fainting lasting up to half an hour |
| Slow reactions to external stimuli, stupor, drowsiness | |
| Memory losses. In a shell-shocked person, memories are blocked before the injury, a short period after fainting, and the immediate moment of injury. Memory is fully restored within 1-3 days | |
| Severe headaches at the site of impact, in the frontal and occipital parts | |
| Dizziness, vomiting, nausea | |
| Pathological changes in heart rhythm - the pulse slows down or speeds up. Blood pressure increases, sometimes body temperature increases | |
| Muscle weakness, asymmetry of tendon reflexes | |
| Grade 2 – moderate form of brain tissue damage. Contusion is combined with skull fractures and hemorrhage in the subarachnoid area. Signs last from 3 weeks to 2 months | Fainting lasting up to 5 hours |
| Lethargy and feeling of stupor continue for another 1-3 days after the injury | |
| Memory impairment that recovers after 3-5 days | |
| Severe dizziness, headaches, prolonged disorientation and loss of balance when getting up from a place | |
| Severe nausea and repeated vomiting attacks | |
| Increased heart rate, increased blood pressure and body temperature | |
| Weakness in the limbs, changes in gait | |
| Grade 3 – severe form is life-threatening and can be fatal | Development of coma up to 3 weeks or more |
| Ruptures of internal organs, crushing of the brain matter | |
| Disturbances in the functioning of the heart and blood vessels - increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, disruption of normal blood circulation, cardiac arrest | |
| Stopping breathing | |
| Epileptic seizures | |
| Loss of hearing, speech, vision | |
| Severe bleeding in the brain |
The state of stupor can be attributed to concussion
During a concussion, a person suffers not only physically, but also mentally. Moderate and severe brain contusion is dangerous in the future for the psyche. A person experiences attacks of aggression, causeless panic, depression, and irritability.
Treatment of cerebral contusion
A shell-shocked person is unable to recover from injury on his own. Without proper treatment, there is a high probability of death of the patient or irreversible changes in the brain matter.
Medicines
Mild and moderate concussion should be treated in a hospital with the help of medications. Therapy is based on several groups of drugs at once.
- Nootropics - Nootropil, Dimanol, Pyritinol, Metadoxil - normalize blood circulation and nourish the brain with useful elements. Active components protect gray matter from lack of oxygen.
- Antioxidants – Mexidol, Emoxipin, Glycine, Glutamic acid – contribute to the body’s resistance in stressful situations and increase the ability to adapt to the external environment.
- Anticonvulsants - Epilim, Valparin, Diplecchis, Apilepsin - prevent the occurrence of convulsions and a strong increase in muscle tone. The drugs relieve pain and prevent the development of epileptic seizures. The drugs have a calming effect and improve the patient’s emotional state.
- Antihistamines - Suprastin, Tavegil, Diazolin - help normalize histamine production and prevent a negative reaction from the body.
- Analgesics and anti-inflammatory substances - Spazmolgon, Pentalgin, Farmadol, Diclofenac, Ibuprofen - anesthetize the lesion, relieve headaches, and produce an anti-inflammatory effect.
Pentalgin - an anti-inflammatory drug for head injuries
Diagnostics
In cases of concussion and contusion of the brain, CT is an informative diagnostic technique. The damage caused by a concussion and bruise is different. With a concussion, swelling and hemorrhage are usually absent. If there is a brain contusion, then separate lesions are visible on CT.
What else is the difference between a bruise and a concussion? There are no deviations in heart rate with mild trauma, while brain contusion is characterized by severe symptoms: asymmetry of tendon reflexes, partial amnesia. But these are not the only differences between a bruise and a concussion. When a bruise occurs, swelling occurs and the cerebrospinal fluid areas are reduced.