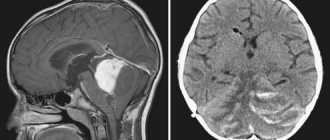
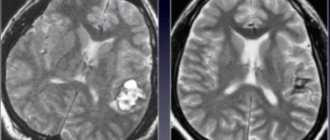
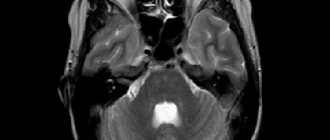
The cerebellum is one of the most important, fundamental parts of the brain. The coordination of a person’s movements, his ability to navigate in space, and respond to external mechanical or temperature stimuli depend on how well it works. A cyst of the cerebellum of the brain can not only disrupt all the functions of this department, but also become a background for the development of many other complications.
Causes of pathology
A cyst in the cerebellum of the brain develops under the influence of primary and secondary factors. The primary ones are disturbances during the intrauterine development of the baby. If a child suffocates during childbirth, this becomes the cause of tissue necrosis and cyst development .
Secondary reasons are:
- Brain hematomas, which are accompanied by hemorrhages;
- Multiple sclerosis;
- Hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke;
- Viral tissue lesions;
- Circulatory disorders in the vessels of the brain.
The disease is diagnosed in patients after brain surgery. The pathology develops against the background of traumatic brain injuries, which are moderate to severe.
If the brain has pockets of dead tissue against the background of impaired blood circulation, this leads to the development of the disease. It is diagnosed in people with neuroinfections and parasitic lesions. If cerebral cells are replaced by cystic tissue, this leads to disease.
A cerebellar cyst develops in a patient due to exposure to various unfavorable factors and diseases that occur in the patient’s body.
Signs of the disease
Depending on the location and severity, cerebellar cysts share a variety of disease symptoms. With pathology, patients complain of pulsating movements in the head of a bursting nature.
A headache occurs that cannot be eliminated with the use of analgesic medications. With a long course of the disease, the patient's hearing and vision deteriorate. It is accompanied by disturbances in sleep and daily routine.
The disease causes noise and ringing in the ears. A common symptom of the pathology is fainting. Patients complain of cramps and trembling in the fingers. If the disease is not treated in a timely manner, partial paralysis of the upper and lower extremities is diagnosed.
The patient cannot control the movements of his arms and legs. The disease is accompanied by nausea and vomiting, which does not bring relief. The patient's orientation in space and coordination of movements becomes impaired. Patients complain of weakness and increased tension in the muscles.
Some patients limp during the course of the disease. The skin of patients is characterized by reduced sensitivity. Patients' gait and handwriting change. In newborns with the disease, the fontanel pulsates and excessive regurgitation is observed.
A cyst of the cerebellum of the brain is accompanied by a large number of symptoms. If several of them appear, it is recommended to consult a specialist who, after diagnosis, will prescribe effective treatment.
Diagnostic measures
After the patient contacts a specialist, he is examined and anamnesis is collected. This allows the doctor to make a preliminary diagnosis. To confirm it, it is recommended to use instrumental research methods:
- Ultrasound examination and magnetic resonance imaging . These diagnostic methods make it possible to determine the location of the cyst in the cerebellum, its size and pressure level. Magnetic resonance imaging is used to determine the quality of treatment.
- Neurosonography . The diagnostic procedure is recommended for children under 2 years of age. This examination is characterized by safety and provides the opportunity to obtain detailed information about the condition of the brain and the location of the cyst.
- Electroencephalograms . Provides the opportunity to determine convulsive readiness and the possible outcome of therapy.
If necessary, the doctor will prescribe additional research methods. It is recommended to conduct a blood test , which can be used to determine diseases of an infectious and autoimmune nature.
Benign and malignant tumors are distinguished using histological examinations. The inflammatory or infectious process is determined by analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid.
Comprehensive diagnostics makes it possible to determine how much the cerebellum is affected by the tumor process and to develop an effective treatment regimen.
Complications
If the disease is not treated in a timely manner, patients are diagnosed with the development of undesirable effects. The hollow structure, in the absence of proper therapy, degenerates into a tumor process. A common consequence of the pathology is encephalitis. If the disease develops in a newborn, then his mental and physical development becomes insufficient.
In the later stages of the disease, the cystic capsule ruptures, which leads to paralysis of the limbs, general blood poisoning, internal bleeding and death of the patient. In certain areas of the brain, the disease is diagnosed with inadequate blood supply.
The disease is accompanied by hydrocephalus, in which irreversible impairment of various functions is diagnosed. Untimely treatment of the cyst leads to problems in motor activity . Undesirable effects manifest themselves in the form of disturbances in coordination. Patients experience frequent fainting.
The cyst may be accompanied by mental disorders. The disease is accompanied by hearing loss. Patients experience speech inhibition. In pathology, defective functioning of the visual organs is observed.
Classification of arachnoid cerebrospinal fluid cyst.
- Sylvian fissure arachnoid cyst 49% (the fissure formed by the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain), is sometimes called a temporal lobe arachnoid cyst.
- Arachnoid cyst of the cerebellopontine angle 11%.
- Arachnoid cyst of the craniovertebral junction 10% (junction between the skull and the spine).
- Arachnoid cyst of the cerebellar vermis (retrocerebellar) 9%.
- Arachnoid cyst sellar and parasellar 9%.
- Arachnoid cyst of the interhemispheric fissure 5%.
- Arachnoid cyst of the convexital surface of the cerebral hemispheres 4%.
- Arachnoid cyst of the clivus 3%.
Some retrocerebellar arachnoid cysts may mimic Dandy-Walker anomaly, but they do not have agenesis (a term meaning complete absence) of the cerebellar vermis and the cyst does not drain into the fourth ventricle of the brain.
Type 1: a small arachnoid cyst in the region of the pole of the temporal lobe, does not cause mass effect, drains into the subarachnoid space.
Type 2: includes the proximal and middle parts of the Sylvian fissure, has an almost rectangular shape, and partially drains into the subarachnoid space.
Type 3: includes the entire Sylvian fissure; with such a cyst, bone protrusion is possible (external protrusion of the scales of the temporal bone), minimal drainage into the subarachnoid space, surgical treatment often does not lead to straightening of the brain (transition to type 2 is possible).
It is worth highlighting separately in this article such congenital cysts as the cyst of the septum pellucidum, the Verge cyst and the cyst of the intermediate velum. There is no point in devoting a separate article to each of the cysts, since you can’t write much about them.
click on the image to enlarge
CT scan of the brain in the axial plane. The red arrow indicates a septum pellucida cyst. Author Hellerhoff, from Wikimedia Commons, click on the image to enlarge the MRI of the brain in the coronal plane. The red arrow indicates a septum pellucida cyst. By Hellerhoff, from Wikimedia Commons
A Verge's cyst or Verge's cavity is located immediately posterior to the cavity of the septum pellucidum and often communicates with it. Very rare.
The cyst or cavity of the intermediate velum is formed between the thalamus above the third ventricle as a result of separation of the crura of the fornix; in other words, it is located in the midline structures of the brain above the third ventricle. Present in 60% of children under 1 year of age and 30% between 1 and 10 years of age. As a rule, it does not cause any changes in the clinical condition, but a large cyst can lead to obstructive hydrocephalus. In most cases, no treatment is required.
Symptoms and treatment of cerebellar cysts
Cerebellar cyst (CSF cyst) is a formation that is a capsule filled with cerebrospinal fluid, cerebrospinal fluid. At the initial stage of the disease, the pathology does not manifest itself with the symptoms described below. But as such a tumor grows, it leads to compression of areas of the brain where they are located. As a result, educational growth processes affect neurological abnormalities.
The cerebellum regulates the coordination of movements, the body’s ability to maintain balance, and is responsible for reflex and neurotic reactions. Thus, changes in the cerebellum are fraught with failure of the functions described above and, of course, the inability to solve everyday problems, in other words, helplessness. In most cases, the formation is detected accidentally and does not carry serious consequences.
Folk remedies
Traditional recipes help curb tumor growth. However, they should not be used thoughtlessly. Before using any product, you must obtain the approval of your physician. Otherwise, you may not improve the condition, but only provoke the development of complications.
Traditional recipes can be used during the recovery period, but not in the acute stage. They are used only in combination with medications prescribed by a doctor. To slow down the growth of a tumor, the following means are used:
- spotted hemlock. It is used alone or in combination with elderberry and violet;
- tea from viburnum, rowan or horsetail helps stabilize blood pressure, which has a positive effect on the patient’s condition;
Features of a cerebellar cyst
When cysts are localized in areas of the cerebellum, formation occurs from the tissues that make up this organ. The cavity for fluid also acts as an anatomically located depression in the cerebellum.
During inflammatory processes, this cavity is filled with serous fluid, pus, and blood.
Signs of a cyst appear in 2 cases:
- When diagnosing chronic/congenital diseases of brain tissue.
- After a severe cerebellar disease of an inflammatory/bacterial nature.
In other situations, it can be detected after increasing to a critical size, using tomography or patient complaints about accompanying symptoms.
Causes
Due to their formation, they are divided into primary and secondary (acquired):
Primary: these are disorders that arose in the prenatal period and tissue necrosis (death of tissue in a living body) due to birth complications.
There are more secondary reasons:
- Past acute inflammatory process.
- Stroke.
- Brain surgeries.
- TBI.
- Parasitic diseases.
- Virus infection.
- Hematomas.
- Deterioration of blood circulation in the cerebral vessels.
- Replacement of cerebral cells with cystic tissue.
- Identifying the cause of the formation of the tumor is a primary task, since without its elimination, the cerebellar cyst will grow.
What is the danger?
Small seals do not pose a danger to human life and health. The problem is that in most cases they continue to grow and begin to put pressure on the brain tissue. This provokes the following complications:
- blood circulation deteriorates, insufficient oxygen reaches the cerebellum;
- irreversible processes occur that affect speech, vision, hearing, and coordination of movements;
- complete or partial paralysis cannot be ruled out, in which it is impossible to restore lost functions;
- in the most severe cases, the pathology leads to the death of the patient.
Sometimes spontaneous rupture of the capsule membranes occurs, which leads to sepsis and a purulent inflammatory process in the cerebrospinal fluid. There is also a risk of internal bleeding, paralysis and death.
A cerebellar cyst in a newborn child (if it does not resolve) causes developmental disorders and delays in many functions.
Types of cerebellar cysts.
The classification is based on the causes of disorders and tumor location.
The most commonly diagnosed types are:
- Changes in the right half of the cerebellum - manifested by dizziness, migraines, chronic fatigue. They develop as a result of an injury.
- Retrocerebellar cyst of the cerebellum is localized in areas of necrotization after head injury, surgery, inflammation and infectious lesions. Diagnosis requires examination of the cerebrospinal fluid to detect infection. When localized behind the cerebellum, severe migraines occur that are not relieved by analgesics, hallucinations, and mental disorders.
- Cyst-like expansion of the arachnoid space can be primary or acquired. Hydrocephalus often occurs as a result. In the case of a secondary nature, the most common cause is neuroinfection.
- An arachnoid cyst in the cerebellum forms in the area of adhesions, scars due to improper movement of cerebrospinal fluid.
- Cystic-atrophic formations are caused by prolonged disruption of the blood supply. Develop after injury or ischemic disease. It is difficult to treat.
- Lacunar cyst of the left hemisphere is an acquired neoplasm that arose against the background of a stroke. Characterized by the appearance of small single cysts.
- Cystic-glial formations of the left half appear after a stroke. Manifested by motor impairments, paralysis is possible. Speech disturbances are possible.
Symptoms and diagnosis.
Those acquired when they are small in size also do not cause symptoms.
Symptoms during growth:
- Throbbing in the head.
- Migraines, the intensity of which is not regulated by medications.
- Discoordination, disorientation in space.
- Tinnitus, hearing impairment.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Tremors, convulsions.
- Fainting, visual disturbances.
- Decrease/increase in muscle tone.
- Sleep disorders.
- Gait changes.
- The newborn has frequent regurgitation and pulsation of the fontanel.
The following methods are used in diagnosis:
- Magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasound - they make it possible to determine the location of the tumor, the size, and the degree of damage to nearby tissues.
- EEG - allows you to assess the potential of seizure activity in the brain
- Neurosonography is a diagnostic method used in examining young children.
The following are used as auxiliary research methods:
- Analysis of cerebrospinal fluid taken through puncture.
- Histology for differential diagnosis of benign from malignant neoplasms.
- Blood chemistry.
Which treatment should I choose?
Removal of the cyst can be done with medication or surgery. If the cyst is small and there are no symptoms, medications are used.
Conservative treatment of cysts.
The medication course may include the following medications:
- Karipain. Longidaza. Designed to eliminate adhesions.
- Cerebrolysin. Encephabol. Nootropics - normalize blood flow, ensuring the supply of oxygen and nutrition to tissues.
- Simvastin. Regulates cholesterol concentration.
- Corinfar. Allows you to regulate blood pressure and ICP.
- Warfarin, Cardiomagnyl. To regulate blood clotting and fluidity.
- Antioxidants, antibiotics, immunomodulators.
Surgery.
The operation is performed in the following cases:
- The tumor provokes epileptic seizures.
- Hydrocephalus.
- Rapid growth of neoplasm.
- Brain hemorrhage.
- Hypertension.
- Malignant neoplasm.
An arachnoid cyst can be removed using methods such as:
- Endoscopy has low morbidity and the likelihood of complications.
- Bypass surgery - due to the prolonged presence of the catheter, the risk of infection increases.
- Microneurosurgery - there is a high risk of complications due to the opening of the skull.
3. Treatment of brain tumors
Among the treatment methods, the most popular is surgical
, especially in cases where complete removal of the tumor is possible.
If, due to a number of circumstances, radical surgery is not possible, partial removal of the tumor is performed, followed by chemotherapy and radiotherapy
.
Drug therapy can only be aimed at relieving the negative symptoms of the disease to reduce intracranial pressure and combat cerebral edema.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Cerebellar cyst
A lacunar cyst is a pathological benign cavity that contains fluid. Such a formation can occur in the brain. In the rarest cases, this problem can occur in the cerebellum. According to medical statistics, only 4% of the world's population suffers from lacunar cysts of the brain. Moreover, in the vast majority of cases it is diagnosed in representatives of the stronger sex. A person with such a serious problem needs urgent medical attention, since the severe consequences of this disease may be irreversible.
Traditional medicine for cyst formation
Traditional medicine methods help normalize the patient’s condition and reduce the intensity of factors - catalysts that provoke the development of education.
Herbal treatment includes the use of the following mixtures and tinctures:
- Herbs that resolve cysts. Spotted hemlock in combination with violet and black elderberry can help. Tinctures can only be used in cases of non-developing cysts.
- Herbs to normalize blood pressure. To maintain normal intracranial and blood pressure, chokeberry, viburnum, and horsetail are suitable. You should add plenty of asparagus and celery to your diet.
Treatment with folk remedies in combination with breathing exercises and yoga helps achieve amazing results. But the use of herbal medicine is possible only during the period of non-exacerbation.
“NEIRODOC.RU is medical information that is maximally accessible for assimilation without special education and created on the basis of the experience of a practicing physician.”
If you are looking for information on the topic “cyst in the brain” or an answer to the question “what is a cyst in the brain?”, then this article is for you. A cyst in the brain, or more precisely, an arachnoid cerebrospinal fluid cyst, is a congenital formation that arises during development as a result of splitting of the arachnoid (arachnoid) membrane of the brain. The cyst is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), a physiological fluid that washes the brain and spinal cord. True congenital arachnoid cysts should be distinguished from cysts that appear after damage to the brain due to traumatic brain injury, stroke, infection, or surgery.
Arachnoid cyst ICD10 code G93.0 (cerebral cyst), Q04.6 (congenital cerebral cysts).
Symptoms of a lacunar cyst
The disease can occur without causing discomfort to the patient. As a rule, it is possible to detect a problem at an early stage of development only during an examination. A cyst can manifest itself when it reaches a fairly large size. At the same time, it puts pressure on the membranes of the brain, thereby causing the appearance of:
- severe headaches;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- tinnitus;
- insomnia;
- pulsations in the head;
- sensory disturbances.
Causes of cerebellar cysts
The disease can be either congenital or acquired. In the first case, the cyst forms in the child during intrauterine development. Its appearance is associated with:
- gene mutation;
- the influence of alcohol and tobacco products consumed by the mother;
- taking psychotropic drugs by a pregnant woman;
- diseases suffered by the mother during pregnancy.
Acquired cysts occur against the background of other ailments. Every person has fluid between the parietal and temporal regions. After injuries or serious illnesses, it can collect in places of damage, thereby filling the place of dead cells. If too much of this fluid accumulates, a cyst occurs.
The formation of lacunar formations is greatly influenced by the immune system. According to research, most often a cerebellar cyst occurs due to:
- diabetes mellitus;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- arterial hypertension;
- meningitis;
- systemic connective tissue diseases.
In addition, diseases such as myocardial infarction, venereal and endocrinological diseases, and atherosclerosis can provoke the onset of the disease. It can also be caused by age-related changes that occur in the human brain.
How dangerous is an arachnoid cyst and is it possible to live with it?
Malignant and benign neoplasms can form in the human brain. Benign tumors include a type of neoplasm such as an arachnoid cyst (in some sources - an arachnoid cerebrospinal fluid cyst). We will discuss in detail the causes, symptoms and treatment of this disease in this article.
General information
So, what is a cerebrospinal fluid cyst? This is a spherical neoplasm that is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which is why the disease got its name.
Arachnoid space
It is arachnoid because it is located in the arachnoid membrane of the brain. In the place where the neoplasm is formed, the membrane thickens and divides into two petals, and liquid accumulates in the gap between these two petals.
The location of the cyst varies; it can be located in the fossa above the sella turcica or near the cerebellopontine angle.
In terms of prevalence, this disease is not rare, since approximately 3–4% of the world's population suffers from it. However, due to the small volume of the tumor, many do not even realize there is a problem.
Males are more susceptible to this disease than females.
Moreover, not only adults, but also children suffer from this disease. The development of such a cyst in a child follows the same scenario as in an adult.
The most dangerous thing about this disease is that it may not make itself felt for a long time and is discovered completely by accident, during a routine examination or during the diagnosis of another disease.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis for this disease, despite its seriousness, is very optimistic and life after the operation is quite normal. With timely treatment, the patient recovers completely. Naturally, if there is no treatment or it is of poor quality, certain consequences may occur, and in especially advanced cases, even death.
Normally, the patient recovers within several weeks.
As for preventive measures, there are no measures aimed at reducing the risk of cyst development. However, there are general recommendations that will help not only reduce the risk of arachnoid cyst formation, but also other tumors, including:
- all bad habits (especially smoking) are contraindicated for expectant mothers, as they can provoke oxygen starvation of the fetus, and this is not good;
- healthy eating;
- compliance with the work and rest regime;
- avoidance of stressful situations;
- maintain normal cholesterol levels;
- blood pressure control (upper and lower);
- timely and high-quality treatment of any inflammatory processes in the body;
- regular preventive examination by a doctor.
Which doctor should I contact?
This disease requires urgent treatment, since a lacunar cyst poses a real danger to human life. Help to cope with this illness:
At the first appointment, the doctor will carefully listen to all the patient’s complaints. After the examination, the doctor will ask the patient several clarifying questions:
- How long ago did the first symptoms of the disease appear?
- Have there been any traumatic brain injuries?
- Are there any chronic diseases?
- Have there been any illnesses affecting the brain?
- Is the patient taking any medications?
After this, the doctor will refer the patient for an examination, the results of which will allow an accurate diagnosis of the disease. First of all, the patient will be asked to undergo magnetic resonance imaging. This study will make it possible to detect the formation, find out its exact location, prevalence, size and shape.
Also, a cerebellar cyst can be diagnosed by computed tomography and morphological examination of a biopsy of brain tissue. This disease can only be dealt with through surgery.
The operation is prescribed after a complete examination of the patient. It includes a mandatory study of the state of the cardiovascular system. Urgent intervention is prescribed when:
- convulsive seizures;
- increased symptoms;
- rapid cyst growth.
Today, the disease can be managed using minimally invasive and endoscopic surgery. Previously, this disease was also dealt with using craniotomy and shunting, but today such methods are used extremely rarely. During endoscopy, the patient has the cyst removed using punctures. Such operations are low-traumatic, which significantly reduces the patient’s recovery time. However, this method is not always used. It has contraindications. For example, patients with severely impaired vision may be denied such an operation.
Recommendations
- At the first symptoms of the disease, immediately consult a neurologist.
- If a cyst is detected hypothermia and places with large crowds of people should be avoided to prevent the development of an infectious disease.
- Regularly be examined by a doctor and undergo all necessary examinations.
- Monitor your blood pressure and maintain cholesterol levels.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- During pregnancy, it is recommended to take vitamins, stress as little as possible, and eliminate bad habits from your life.