Causes
Scientists currently cannot name the exact causes of the disease. However, experts identify some possible factors for the development of cerebral hemangioma in adult patients:
- hereditary disorders, genetic predisposition to diseases of the vascular system;
- arterial hypertension and increased intracranial pressure;
- extensive, serious traumatic brain injuries of the head;
- long-term exposure to large doses of radiation on the body. The risk increases in patients who are exposed to ionizing radiation. And also to radiation caused by the influence of an atomic bomb, man-made disasters with the formation of radioactive radiation. Factors such as radiation from mobile phones, electromagnetic fields of power lines remain unproven;
- exposure to chemical or carcinogenic substances. There is a risk of developing brain hemangioma among employees working in enterprises whose specific activity is the production or use of chemicals;
- constant nervous tension, severe stressful situations;
- wrong lifestyle. This includes both low physical activity and the use of alcoholic beverages, drugs, and nicotine.
Causes
It is impossible to establish reliably what exactly caused the development of vascular tumors. However, it is generally accepted that some isolated causes, when combined, can still create optimal conditions for the formation of a neoplasm:
- Genetic predisposition;
- Pregnancy period in women after 35 years of age;
- Presence of cardiovascular diseases;
- Previous infectious diseases of the brain;
- Increased tendency to develop cerebral stroke;
- Chronic anemia, in which brain cells experience oxygen starvation;
- Congenital brain pathologies;
- Epilepsy and nervous shocks provoking acute spasm of cerebral vessels;
- Chronic fatigue syndrome, in which a person sleeps less than 4 hours a day;
- Frequent head injuries that resolve on their own without proper diagnosis and recommendations from a specialist.
All these reasons can cause the development of hemangioma, so if some of them are present, unscheduled diagnosis will not harm.
If a person is at risk, he is recommended to undergo an annual medical examination if there are no complaints, and also seek qualified help if he has severe headaches, constant dizziness and acute reactions to light and sound.
Symptoms
Often in adults, cerebral hemangioma occurs unnoticed over a fairly long period of time. Often a patient learns about his problem by chance during an examination. However, there are common symptoms of cerebral hemangioma in adults that make you think about the existence of the disease. These include:
- regular headaches of varying duration, disturbing for unknown reasons;
- violation of movement coordination;
- vision problems, weakened sense of taste, hearing, decreased sense of smell;
- constant dizziness, vomiting, nausea;
- fainting conditions;
- epileptic seizures;
- convulsions;
- intellectual disability;
- impaired memory, concentration;
- muscle weakness.
Brain hemangioma is divided into 2 types:
- Sluggish (torpid). Sluggish hemangioma is characterized by headaches, cramps, nervous disorders and insomnia. Convulsions occur against the background of a headache and can manifest themselves both locally and in several places at once.
- Prone to bleeding (hemorrhagic). A symptom of the hemorrhagic type of hemangioma is high blood pressure.
Stages and symptoms
There are three stages of vascular disease, the manifestation of which has its own distinct symptoms:
The initial stage is marked by the presence of a small neoplasm (up to 1 cm in diameter), which does not have any effect on the blood vessels of the brain.
People can live for years and not know about the presence of a tumor in the head, since in the initial stage it is asymptomatic and does not bother its owner.
The progressive stage is characterized by a rapid increase in tumor size, which may be accompanied by clinical manifestations such as:
- In the frontal lobe: severe compressive migraine-type headache, nausea, dizziness, visual disturbances.
- In the occipital lobe: memory problems, hearing impairment, tinnitus, acute reaction to light, dizziness, speech impairment, mental disorders.
- In the cerebellar region: impaired coordination of movements, paresis.
- Medulla oblongata: decreased manifestations of unconditioned reflexes.
Long-term compression of brain vessels by a tumor leads to disruption of nutrition of entire sections, which entails dangerous consequences that, if delayed, can cost a person his life.
The advanced stage is characterized by the presence of large tumors that compress large areas of the brain, which is manifested by symptoms such as:
- impairment of speech perception and reproduction;
- problems with memory, especially short-term;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- seizures of the epilepsy type;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- an increase in blood vessels leading to the brain, which is noticeable visually;
- decreased manifestation of some reflexes;
- paralysis of individual parts of the body;
- constant tinnitus, in which a person develops irritability.
Additional classification
There is an additional classification, taking into account the type of vessels that form them:
- Capillary (telangiectasia) is the most common brain tumor that is localized to the skin. Hemangioma of cerebral vessels in children and adults rises above the skin, but does not affect the epidermis, so bleeding occurs extremely rarely. The structure of a capillary neoplasm is a network of densely intertwined capillaries. Their walls can grow together and turn into a lump of vascular tissue.
- Venous hemangioma of the brain - a neoplasm puts pressure on the brain, causing the appearance of neurological disorders. If it appears in the crown area, symptoms may be noted that correspond to the capabilities of this area. The patient has a headache, fever, coordination is impaired, it is difficult for him to recognize symbols and signs, and there is also a disorder of touch. Due to its structure, venous hemangioma is considered the most dangerous - there is a risk of vein rupture and hemorrhage.
- Arteriovenous (mixed) hemangioma is usually localized in the internal organs. But with a superficial location, it can take the form of tortuous and branched arteries, veins and bundles, which are located under atrophied, altered skin and its fiber. In most cases, the tumor is located in the neck or head.
- Cavernous hemangioma of the brain - neoplasms of this type feed large arterial vessels. Most often they are localized in the skin. This type of tumor is the rarest. Cavernous hemangioma of the brain spreads quite quickly. With internal localization, parenchymal structures with a rich vascular network are affected.
The question often arises: why are small cavernous hemangiomas of the brain dangerous in adults? They are dangerous due to the possibility of extensive bleeding.
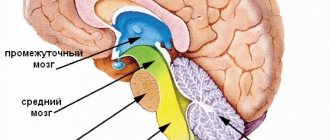
Localization and symptoms
Most often, venous angiomas are located in the white matter of the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres, near the walls of the ventricles. The temporal lobes are very rarely affected.
In the human body, angiomas can be single or multiple (from 2 to 9% of all cases), then they speak of the angiomatous type of structure of the venous system. The larger the tumor, the more pronounced the symptoms of the disease.
Neurological symptoms that appear over a long period of time and cannot be relieved “help” in making a diagnosis.
A patient with an angioma periodically experiences headaches, non-food nausea, sensory disturbances, and fainting. Depending on which part of the brain the neoplasm is localized and what its nature is (veins, capillaries, or caverns are involved), specific symptoms will appear:
- Venous angioma of the occipital lobe:
- spasmodic sensations in the muscles of the back of the head;
- visual hallucinations (the appearance of long-term images and short-term sparkling).
- Venous angioma of the right temporal lobe:
- Damage to the left temporal lobe, just like the right, disrupts speech and the ability to perceive it. Strong emotional surges are added for no apparent external reasons.
- Venous angioma of the right parietal lobe:
- lack of “right-left” distinction when exposed to stimuli;
- unconscious paralysis.
- Damage to the left parietal lobe leads to loss of orientation not relative to one’s body, but in space (inability to determine distances or read a map).
- Venous angioma of the right frontal lobe:
- emotional instability;
- inability to control your actions;
- euphoric mood;
- loss of the ability to competently construct sentences of any length.
- With a tumor of the left frontal lobe, the patient cannot move on to the verbal formulation of thoughts (he thinks, but cannot speak), and has little control over his own behavior.
In general, capillary angiomas can occur in any part of the brain, and venous angiomas mainly in the cerebellum, the white matter of the brain.
The prognosis depends on the size of the tumor, its benign or malignant quality, and location. Most formations are treatable.
Diagnostics
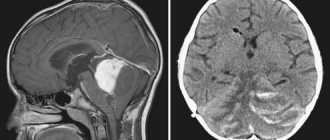
Brain hemangioma is detected only by computer technology; it is impossible to make such a diagnosis using other methods.
Contrast angiography was in great demand until recently, but since the method was dangerous for patients, it is now practically not used. How is angiography performed? A special contrast is injected into the patient's vascular system and then an X-ray of the brain is taken.
Superselective angiography - this method is more gentle for patients, it is less dangerous for the body. It is often prescribed to detect pathology in the vascular system. This diagnosis is carried out using this method: a special contrast is injected into a certain part of the brain where the hemangioma may presumably be located.
Computed tomography or CT is a safer method, as it does not violate the integrity of the tissue. This is a diagnostic method that uses X-rays of the brain. Special X-rays are produced in a tube and affect areas of the brain from different angles. The sensors receive data that is scanned layer by layer, the data is instantly processed and output to a computer. Therefore, the doctor immediately sees a detailed picture, detailed data of the entire brain.
Magnetic resonance imaging is a 100% effective examination. During diagnosis, it reveals hemangiomas of various sizes, from very small to large. And up to 98% detects the type of hemangioma. Also, basic computer diagnostics are supplemented by general analyzes and additional studies. This is a general blood test, biochemical analysis, ultrasound examination of cerebral vessels.
Treatment and diagnosis of cerebral angioma
In the initial stages, cerebral angiomas are usually asymptomatic and are detected incidentally during a brain examination for other diseases.
The doctor can suspect the presence of such tumors based on the patient’s complaints, which appear when the tumor increases in size and compresses the brain tissue. To make a diagnosis and determine treatment tactics, the following instrumental examination methods may be prescribed: MRI (with contrast); CT (with and without contrast); angiography. When a brain angioma is detected, the patient is almost always recommended to have it surgically removed. Before the intervention is performed, the patient is prescribed medications to eliminate various symptoms of the tumor: sedatives, painkillers and vascular drugs. Only in some cases, with venous angiomas that are asymptomatic and are not prone to rapid growth, the doctor can recommend the patient to follow-up the pathology.
If the tumor does not grow, surgery may not be performed. To remove angiomas, different types of surgical interventions can be performed: Removal of angioma - the operation is performed in the traditional way and consists of excision of vascular collections.
Embolization of a vascular tangle - this minimally invasive technique consists of introducing a platinum spiral or liquid embolisate through a catheter into the lumen of the tumor vessels, which, after injection, clog the pathological vessels and disconnect them from the general circulation.
Sclerosation of a vascular tangle - a sclerosant drug is injected into the lumen of tumor vessels through a catheter, and it “seals” the pathological vessels.
Gamma Knife is a non-invasive radiosurgery operation without opening the skull that is performed using a special device that obliterates a vascular tumor with beams of radio wave radiation. Cyberknife - this non-invasive radiosurgical technique is also performed using a special installation that affects tumor tissue with low-dose radiation beams at different angles.
Angioplasty is a minimally invasive intervention that involves the implantation of stents and balloons to restore normal cerebral circulation. The choice of one or another method of surgical treatment of brain angiomas is determined by the accessibility of the tumor and other clinical indications identified during examination of the patient.
Today, when treating such tumors, surgeons give preference to minimally invasive or radiosurgical techniques, because they allow minimal impact on surrounding tissues and significantly facilitate the patient’s rehabilitation after surgery. Stereotactic surgery methods – Gamma and Cyber Knife – deserve special attention in the treatment of brain angiomas.
Carrying out such interventions is non-invasive, possibly in the most inaccessible areas of the brain, and makes it possible to accurately influence tumor tissue, causing vascular obliteration. Brain angiomas are benign tumors.
However, their presence is not always harmless, since they can lead to significant compression of brain tissue, the appearance of symptoms that significantly worsen the patient’s quality of life, and cerebral hemorrhage.
Such tumors can only be removed surgically. Sometimes, if the tumor is small and the risk of rupture is low, the patient may be offered clinical monitoring to monitor the growth of the tumor.
Source: doctor-cardiologist.ru
Treatment
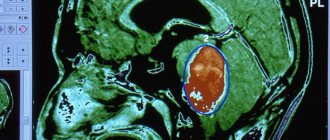
Under the influence of external factors, a tumor formed by the tissues of blood vessels in the structure of the brain can occur. A hemangioma looks like a red-blue node, the size of which can reach 2 cm. It contains tangled blood vessels with voids and clotted blood.
A mass in the head is very rare and difficult to remove. Most often, the tumor forms in females; in males it usually occurs less frequently, after 25 years. Hemangioma can be located in any part of the brain, but it is usually found in the cerebral hemispheres. They also occur on the surface of the skin, but they are not as dangerous as brain formations.
The danger lies primarily in hemorrhage, which can lead to a stroke. If left untreated, its progression will lead to death.
What happens in the body?
The formed neoplasm may consist of small or large vessels.
In the first case, the tumor is prone to growth. Cavernous hemangiomas usually do not increase in size until the conditions for this are created: trauma, hemorrhage, concussion. Small tumors can remain in the brain for a long time without characteristic symptoms, but as soon as their dimensions increase, compression occurs not only of the vessels and tissues of the localization site, but also of nearby tissues, which significantly expands the range of clinical manifestations.
Effective ways
There are several ways. Each of them contains certain means and the required sequence.
Doctors begin treatment of any disease and malformations based on three factors:
- location of the disease;
- size of the malformation;
- presence of possible hemorrhages.
Therefore, before getting rid of a nodular tumor, they undergo a consultation, after which individual treatment is prescribed.
Reasons for education
The causes of the pathology have not been established. It is believed that congenital forms, which are more common, develop against the background of previous intrauterine infections, chronic and acute intoxications of the mother. The hereditary factor plays a role in the process of formation of neoplasms. Other possible reasons:
- Birth injuries to the fetus.
- Pregnancy over 40 years of age.
- Injuries in the head area.
- Inflammatory diseases of the brain.
The development of pathology can be influenced by factors: bad habits, a decrease in the body’s own immune defense, living in an unfavorable ecological zone.
Surgical removal
For a small nodular formation, which is not located near the main part of the brain and is not so deep, removal occurs through open access surgery. To avoid any difficulties during the operation, it is performed after a hemorrhage that has occurred recently.
Hemangioma forms in different parts of the brain and skin. In the brain it can be located both on its surface and deep in it. If the tumor is located far from the surface of the skull, then any operations against it are very dangerous for the patient’s life. In this case, they try to avoid surgical intervention, because this can affect the functioning of certain brain structures.
What is venous angioma, how is it formed?
The blood vessels of the brain, with the participation of lymphatic tissue, can create “tangles” that impede blood flow and nutrition of brain cells. For example, blood from an artery immediately enters a vein, as a result, the tissues do not receive oxygen. Such vascular formations are called venous angiomas; they can be malignant or benign. Their main danger lies in compression of brain structures, possible rupture of vessel walls and hemorrhagic stroke.
Hemorrhage can occur due to the thinness of the tumor walls with a slight increase in pressure, trauma, or emotional stress. If a person did not know about the presence of such structures, then he can only rely on the experience of doctors in making an accurate diagnosis in case of sudden manifestations of the disease (paralysis, significant sensory disturbances, stroke).
With a small size, a brain angioma may not show itself in any way throughout life, which explains the difficulty of diagnosis.
Angiomas grow slowly, from the period of intrauterine development of a person. They are detected during unscheduled examinations, or suspicions of the presence of neoplasms of various natures in the brain.
Angiomas can be either congenital (95% of cases) or acquired (5%). The exact reasons have not yet been clarified. The most proven versions are:
- disruption of the intrauterine formation of the vascular system due to maternal illness, vitamin deficiency, pathological pregnancy;
- concomitant pathology of organs with a high risk of cancer (stomach, liver, mammary glands, lungs, uterus and prostate), this confirms the connection with liver cirrhosis;
- head injuries;
- infectious diseases suffered in early childhood.
It has been proven that children are more prone to the spread and growth of angiomas than adults. This is associated with the functional inferiority of various body systems and insufficient immunity.
Endovascular surgery
If the hemangioma is located in the deep tissues of the brain, endovascular surgery is used. With this type of intervention, a catheter is inserted into the problem area through the cerebral artery using radiographic instruments and a guide. In this way, an embolus is delivered to the brain, which can cause blockage of blood vessels.
After this, the patient is repeatedly subjected to an additional series of angiographic images. In this way, doctors can verify how successful the operation was. This method of combating brain hemangioma is one of the most advanced of all other treatment methods.
Types of disease
Pathology is classified according to histological structure and depending on location. The location of the tumor-like compaction determines the neurological symptoms. The most common are:
- Cavernous angiomas formed in the right temporal or left temporal lobe. Complications – hemianopsia (loss of visual fields), auditory hallucinations.
- Cerebellar cavernomas. They make up about 10% of all species. Complications of cerebellar angioma are a disorder of motor coordination and motor function in general.
- Cavernous angiomas arising in the left or right frontal lobe. Complications – mental disorders, loss of previously acquired practical skills, including labor, mental, and physical.
- Cavernous angiomas formed in the left or right parietal lobe. Complications – aphasia (speech impairment), problems with reading and performing simple arithmetic operations.
Tumor-like compaction in the area of the cerebral cortex is common and provokes epileptic seizures. In any localization, the development of the mental state of delirium is possible, which is accompanied by a disturbance of consciousness, a disorder of the functions of perception, attention, and thinking.
Radiosurgery
Another method of treating cerebral hemangioma is radiosurgery. In this case, all existing vascular clusters stick together due to the effect of radiation on them. This process gradually leads to the death of malformations. The most important advantage of this type of surgery is that the integrity of the brain tissue is not damaged in any way and there is no use of surgical knives. The accuracy of this method is maximum; the operation has virtually no side effects. The only disadvantage of radiosurgery is the long treatment period.
With such a disease, you need to get diagnosed in time so that there are no bad consequences.
Relationship between location and clinical manifestations
The presence of a malformation may not be noticed as long as it is small and does not affect adjacent tissues and brain structures. But in the future, when the size of the hemangioma increases, it will put pressure on the healthy tissues of the very section where it is located, which will certainly manifest itself with certain symptoms.
For example, a tumor in:
- The temporal lobe causes hearing loss and dizziness.
- The occipital part negatively affects visual acuity and causes hallucinations.
- The frontal lobe is characterized by disturbances in sleep, motor skills, speech, memory, and vision.
- The cerebellum leads to problems related to coordination of movements.
With hemangiomas formed in the deep tissues of the brain, patients often experience a buzzing in the ears. They often complain of sudden attacks of aching cephalgia.
Pathology is more often detected in young people with complaints of specific symptoms. In adult patients, hemangioma is detected during an examination of the head or the entire body associated with a preventive examination, since at this age the disease does not manifest itself in any way. Interestingly, clinical manifestations in men are more pronounced than in women. Often, in the weaker half of humanity, anxiety symptoms are more pronounced when carrying a child.
Prognosis and prevention
For timely detection of cerebral hemangioma, it is necessary to regularly conduct examinations: angiography, magnetic resonance and computed tomography. When the disease is diagnosed early, doctors often remove the tumor without damaging the tissue, especially if the tumor is located on the surface of the brain. If a tumor is detected in deeper layers, more complex operations are required, which can lead to negative consequences.
The prognosis for cerebral hemangioma in adults is quite favorable. Since it is not a malignant tumor, in about a quarter of patients it does not affect a full lifestyle and does not manifest itself in any way. But complications are also possible that can cause serious damage to the patient. To avoid cerebral hemorrhages, you need to avoid any mechanical damage to the head, psychological stress, as well as sudden changes in blood pressure.
To prevent the appearance of a tumor, doctors recommend leading a healthy lifestyle: spending more time in the fresh air, playing sports and not abusing alcohol. If any symptoms of brain hemangioma are detected in children and adults, you should immediately contact an oncologist for further treatment.
What is cerebral angioma?
angioma of the brain
The prevalence of brain tumors is growing every year - this fact alarms doctors in different countries.
A benign tumor, which is a “tangle of blood vessels,” is a cerebral angioma. Externally, the pathology resembles a burgundy or red birthmark. The formation is observed on the mucous membranes and skin, and the main risk group is newborn girls. Most angiomas disappear by the age of ten, but this does not mean that there is no danger. The tumor can spread to internal organs, and this leads to a number of bad consequences. The main problem is damage to the brain - both the spinal cord and the brain. What are the causes of cerebral angioma and are there ways to cure it? Often the development of pathology is associated with traumatic brain injuries, various infectious infections and vascular anomalies. By the way, it is vascular anomalies that provoke the formation of angiomas in 95% of cases.
Tumors localized on the surface of the skin do not pose a significant danger. Much worse are the tangles affecting the brain area. An angioma that has affected the spinal cord can be recognized by numbness of the arms, legs and torso, dysfunction of the pelvic organs, pain in the limbs and back. The neoplasm is characterized by a compressive effect.
Here is a list of symptoms indicating a probable pathology: headache (intensity, character and frequency are variable), convulsions, epileptic seizures, paralysis of certain parts of the body, dizziness, nausea and vomiting, taste and speech disorders, noises in the head, aphasia (complete absence of speech ), disturbances in thought processes, memory loss, lack of attention.
Since the disease is closely associated with hemorrhages, it must be promptly diagnosed and treated. Otherwise, consequences in the form of strokes, brain disorders and seizures are possible.
Doctors distinguish capillary, cavernous and venous types of angiomas. Each of these types is dangerous in its own way. A capillary tumor affects a network of small capillaries. The cavernous type has the form of a cavernous purple formation, the blood flow inside of which is impaired.
The venous type is distinguished by a dark blue or brown color, while it can progress autonomously - this property can cause a stroke. Venous angioma of the brain is considered the most dangerous - the percentage of deaths here is especially high. The cavernous type leads to a number of pathological vascular changes.
Specific cavernomas are filled with blood and sometimes reach impressive sizes. Complications arise due to fragile vessel walls, which can lead to cerebral hemorrhage. Vascular cavities called caverns are the basis of this terrible pathology. Cavernous angioma of the brain is an extremely dangerous disease.
The walls of the cavity are separated by thin bridges, which are not very strong. The formation can rupture, leading to cerebral hemorrhage and death.
Here is a list of symptoms indicating the development of cavernoma: vomiting and nausea; increasing headache (medication does not help); tinnitus; thinking disorders, inattention; disturbances in the senses (taste, smell, vision); paralysis and paresis of the limbs, epileptic seizures.
Doctors call cavernous angioma a ticking time bomb. Hemorrhage can occur at any second - the fatal moment is difficult to predict. The advanced stage leads to numerous disorders of consciousness. Entire areas of the body may become paralyzed.
If convulsive attacks cannot be controlled with medication, this is another reason to think about your condition and conduct extensive diagnostics. This pathology puts continuous pressure on the brain and is often complicated by hemorrhages. The mortality rate is significantly higher than that of cavernomas.
The location of the angioma can influence the nature of the disorders. For example, a frontal tumor leads to a decrease in mental activity, and a parietal tumor is associated with a lack of pain and tactile sensitivity.
After the formation of the choroid plexus, symptoms begin to appear. The matter is not limited to pain syndrome. Look for the following signs: loss of skin sensitivity; convulsions; dizziness; nausea, vomiting; epileptic seizures; lack of motivation; loss of speech control; decreased attention; distorted self-esteem.
The affected cerebellum is associated with pathologies of skeletal muscles, disorders of balance and coordination. The symptoms of the disease are very peculiar: variability in handwriting; motor tremor; chanted speech; slow movements. If an angioma is detected, doctors prescribe emergency treatment, the nature of which will depend on the type and location of the tumor.
Modern medicine, unfortunately, has not developed injections or tablets for angiomas. Any drug treatment is temporary and does not eliminate the causes of the disease. This means that once a tumor is diagnosed, surgery will have to be performed.
Before sending a patient for surgery, doctors perform extensive diagnostic tests, including a medical history, angiography and computed tomography. When identifying cavities, MRI diagnostics is used. To better plan the operation, surgeons also order tractography.
Having received a complete picture of what is happening, you may be prescribed one of three methods of surgical intervention: Removal. Used for superficial tumor localization. It is considered the most traumatic type of surgical treatment, therefore it is not used so often. Introduction of a plugging agent.
It is carried out through a vascular catheter directly into the angioma. Gamma Knife. The blood flow inside the angioma is stopped using radiation. Don't be fooled by the term "benign tumor." Any neoplasm that arises in the human brain poses a potential threat to health.
It is better to diagnose pathology at an early stage - if the tumor is small, the matter may not proceed to surgery; first, doctors will limit themselves to sclerotherapy. Special substances will help “clog” blood vessels and prevent further development of the disease. Take care of yourself and undergo comprehensive examinations more often!
Source: prososud.ru
Symptoms and forms
Cavernous angiomas can develop in various tissues, but the most complex, and also dangerous, form are those tumors that are localized in the brain. They quite often provoke hemorrhage and bleeding.
They are the first signs of these neoplasms. In addition, when a process of hemorrhage occurs in the brain or spinal trunk, this becomes the cause of extremely severe neurological problems, which can be quadriparesis and other pathologies.
Very often, such diseases occur completely asymptomatically. Such anomalies are detected in people under the age of 40. How exactly the formations will appear depends on where they are located. According to statistics, almost 80% of cases of cavernoma lesions occur in the upper parts of the brain, another about 8% in the cerebellum, and the rest are formed in the choroid plexuses.
Symptoms and diagnosis of the disease
The neoplasm is considered dangerous due to the rare manifestations of symptoms. Detection occurs by chance, during a computed tomography scan of the human head or similar examinations.
Depending on the type and type of malformation, symptomatic signs of the disease are distinguished:
- muscular dystrophy, manifested in weakness of the limbs;
- gastrointestinal problems - nausea and vomiting;
- epileptic seizures;
- dizziness;
- headache at the site of the tumor - distinguished by pressing, aching and throbbing pain;
- paralysis;
- ringing in the ears;
- speech disorder.
When a hemangioma is detected in a certain part of the brain, symptoms of visual impairment are noted, and coordination suffers. There is a possibility of hearing loss, there is also a decrease in intellectual abilities, and the likelihood of a stroke is high.
Torpid hemangioma is characterized by large sizes, because of this the patient suffers from headaches, sleeps poorly, exhibits convulsions and obvious hypertension.
Diagnostic methods for determining angioma and types of examination:
- Contrast angiography of the brain. It involves introducing a contrast agent into the circulatory system and taking an X-ray of the brain. In medicine of the 21st century, this type of examination will not be used due to the danger to the patient’s health and the possible consequences on the organ.
- Superselective angiography. A less dangerous type of recognition of hemangioma than the one presented above, since the substance is found in the expected localization of the formation.
- MRI and CT. A secure method for determining the location and type of angioma with a 100% guarantee.