15267
0
—>
Oncological diseases can be diagnosed in the early stages of cancer development if you pay attention to the slightest conditions in your body. The brain tumor process is not similar in characteristics to other types of cancer processes and is diagnosed in approximately 2% of all cancer diseases. Symptoms of a brain tumor in the early stages in an adult are usually nonspecific, which is why the pathology goes undetected for a long time.
Brain cancer is most often discovered at a late stage, when it can no longer be cured, and the future prognosis is extremely poor. Therefore, it is very important to know how the disease manifests itself at the initial stage of development in order to promptly diagnose the problem and remove the benign formation, stopping the uncontrolled division of brain cells.
Classification and types of tumors
To begin with, it is worth saying a few words about the most common ways of typing pathological structures. All tumors of cerebral localization are divided into two types.
Benign
They differ in a number of factors from their more dangerous “brothers”.
- They grow relatively slowly. By a few millimeters over a couple of years. And then, this is considered a very rapid development of an anomalous structure. In reality, the situation is often different.
- These tumors do not grow through healthy brain tissue. Thus, they do not destroy them, they are well delimited from other cells, therefore they can be completely removed relatively simply and without difficulty.
- Benign structures do not metastasize. That is, they do not create secondary foci of neoplastic lesions.
Of course, it is impossible to say that they are safe. The space inside the skull is limited. If the tumor is large enough, compression of cerebral structures, dysfunction and death will begin. It is very dangerous.
Malignant
They are characterized by rapid growth, infiltrative spread (affect healthy tissue), and metastasis. They pose a fatal threat.
Cells are characterized by atypia of varying severity: from minor deviations to critical changes. When tissues are unrecognizable, they are so transformed.
The second basis for classification: the origin of neoplasia. In this case, the following are distinguished:
- Primary structures. Which developed virtually from scratch.
- Secondary. So-called metastases. Digging a little from the topic, it is worth saying that in this localization you can find lesions originating from the lungs, mammary glands, and intestines, oddly enough.
Finally, there is a more specific classification that takes into account the origin of neoplasia and its cellular structure. In this case, we need to talk about the following new formations:
Tumors from the membrane
So-called meningiomas. They belong to benign tumors. These are very common neoplasias from hard tissue of the brain.
Theoretically, they can appear in any part of the cerebral structures. They grow relatively slowly.
There are atypical forms that are rapidly increasing, interfering with normal life activities and posing a real danger to patients. But this is rather an exception to the rule.
Formations from nerve tissue
Neuromas. Most often they are not prone to malignancy and degeneration into conventional cancer. Therefore, from the point of view of mass effect, brain compression does not pose a great danger. The problem is different.
They affect certain cranial nerves. It is these structures that are responsible for important functions: hearing, eye movement and much more.
Attention:
Treatment should be started as early as possible. If everything is done on time, there is every chance of maintaining nervous activity.
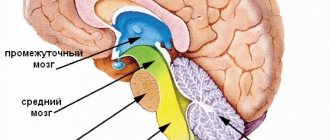
Pituitary tumors
They develop very often. They are in second place in terms of prevalence among all intracranial formations.
Statistics show that neoplasia of this location and origin occurs in almost every fifth person on the planet.
Only they are so small that they do not cause any discomfort. The phenomenon is discovered accidentally during a post-mortem autopsy.
Pituitary tumors can be divided into three types:
- Adenomas. Structures that grow and develop from the front of an organ. They can produce different types of hormones. And in some cases, they do not release any substances and simply compress the tissues around them. If large enough, removal is required.
- Tumors of the neurohypophysis. Its posterior lobe. They are extremely rare. But mostly these are formations of low malignancy.
- Neoplasia of the infundibulum, organ pedicles. Develop in isolated cases. There are currently less than 50 documented situations described throughout the world.
Real casuistry. Here so-called pituicytomas are formed. Technically, they are malignant. In fact, they are well demarcated and grow very rarely. For decades.
Pituitary tumors are most often not dangerous. At least in the initial stages. But they still need to be watched.
Germ cell neoplasia
Tumors that grow from those tissues that were formed in the prenatal period, in its first stages.
Their characteristic feature is their tendency to share quickly and aggressively. Moreover, a very small amount of biomaterial is enough.
These include the following types of tumors:
- Germinomas. Actually, the most common morphological form. These are malignant structures that grow rather slowly. They are very sensitive to radiation, which is what doctors use.
- Teratomas of varying degrees of maturity. Accumulations of fat, hair, teeth, nails and other primary tissues from which a person could potentially form.
- Craniopharyngiomas. Tumors of Rathke's pouch. They are localized close to the pituitary gland, which is why they are often confused with adenomas. A sufficiently large neoplasia can compress the chiasma (optic chiasm), the brain, and other structures and provoke complications. Although craniophyrangioma itself is not malignant.
These tumors are different in nature; it is impossible to give them a single assessment.
Neuroepithelial structures
The most common type of pathological formations. They make up almost 80% of the total number of cases.
Among the varieties:
- Astrocytomas.
- Oligodendrogliomas.
- Ependymomas.
All these structures have a common name - gliomas. Studies show that all gliomas are malignant, although to an unequal extent.
It is possible to assess what the situation is in each specific case only with the help of histological examination.
These structures are classified into several more types. According to the generally accepted methodology, there are 4 degrees of malignancy (in English spelling - grade).
- I. Pilocytic astrocytomas, subependymomas and other varieties. They do not pose a major health hazard. Occurs mainly in young patients and children. They are well demarcated from surrounding tissues, which means they can be removed without problems. If such a structure has developed, it is incredible luck. Life forecasts are favorable.
- II. Fibrillary tumors. They grow faster and behave more aggressively. Sooner or later they move to the next stage. The chances of a cure are quite small, although they still exist. The main thing is not to start the pathological process.
- III. Anaplastic gliomas. Very dangerous. Cellular atypia is significant, although the tissues still recognize some features of the structures from which the neoplasia arose. It is no longer possible to recover from such a problem. All that remains is to delay the transition to a new stage.
- IV. Glioblastomas. Critically dangerous structures. The patient is killed in a matter of months.
Unfortunately, the likelihood of curing glioma depends not so much on the moment of initiation of therapy, but on the type of tumor itself.
Therefore, it’s more a question of luck (if in such a situation it’s even appropriate to talk about luck).
Tumors of the pineal gland or pineal gland
Pinealomas and pineoblastomas. Quite rare, but no less dangerous.
Due to the extremely complex localization, surgery is almost impossible or carries such risks that the treatment becomes worse than the disease itself.
Attention:
Basically, a pathology of this kind is accompanied by disturbances in circadian rhythms. It is impossible to sleep at night or work during the day.
The named types exhaust the list of neoplasias almost completely. And this is not counting metastatic lesions.
Classification
A brain tumor is a pathology characterized by the uncontrolled division of brain cells, which ultimately leads to the growth of a large amount of tissue. The tumor grows at an accelerated pace, capturing an increasing amount of new tissue. There can be two types:
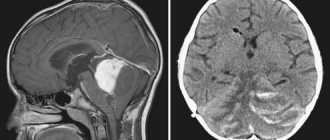
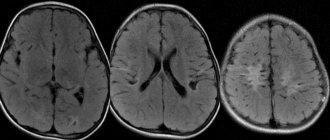
- Benign. The peculiarity is that they do not invade neighboring tissues, having their own clearly defined growth boundaries, which can be easily seen on MRI and CT. The exact cause of their occurrence is unknown; various diseases, radiation, and prolonged exposure to chemicals can trigger the appearance of neoplasms. The disease can occur in men, women, children of all ages, and even cats or dogs. The danger of a benign brain tumor lies in the compression of neighboring tissues during development, which can lead to the appearance of cancer.
- Malignant. A rapidly growing neoplasm that does not have clearly defined boundaries and spreads to neighboring tissues is called a malignant tumor. It leads to tissue necrosis, bleeding and is inoperable, as a result of which the patient dies in a short period of time. Malignant tumors are primary (glioma, which is formed from nerve cells) and secondary (occurs due to metastatic tumors of other tissues). Brain glioma develops in several stages, the most dangerous of which is stage 4 glioblastoma. You can see what it looks like in photographs of patients.
It is very difficult to determine the first signs of a tumor in the initial stages in men and women, but you should know what they look like in order to diagnose the disease in a timely manner. Depending on the type of tumor, treatment is selected, which consists of removal using various techniques. Only an experienced specialist can decide which treatment method is most suitable.
Focal symptoms
The clinical picture depends on the exact localization of the pathological formation. If we look at the issue in more detail:
Frontal lobe
Responsible for behavior, movement, and the creative component of thinking. Therefore, the signs of the pathological process are very severe. And almost from the very beginning of the development of neoplasia.
Among the symptoms:
- Epileptic seizures. Both weak and high intensity with all that it entails: loss of consciousness, convulsions, etc.
- Unsteady gait. Uncertainty when moving.
- Aggressiveness, increased irritability. Out of the blue, with no apparent reason for such a pathological condition.
- Weakening of thinking. Gradual degeneration of the intellectual sphere in principle.
- Decreased concentration and memory.
- Weakness, muscle rigidity.
- Speech disorders. Because this is where the so-called Broca’s center is located, which is responsible for the formation of the ability to speak, formulate one’s thoughts and objectify them.
Symptoms of a tumor in the head, when localized in the frontal structures, are accompanied by behavioral disorders, disorders of the intellectual, cognitive sphere, as well as motor and motor functions.
A person becomes deeply disabled almost at the initial stage of the pathological process.
Temporal lobes
Signs of the disorder include:
- Auditory hallucinations and even pseudohallucinatory images. In the first case, the patient is sure that everyone around him perceives the stimulus. In the second, he knows that all sounds exist only in his own mind. Criticism of the state continues. This is the key difference between damage to the temporal lobe from schizophrenia and any other psychopathology.
- Epileptic seizures.
- Memory impairment. Retrograde amnesia is very common. When a person is unable to remember what happened to him before.
- Feeling of deja vu. It is as if the patient has already experienced the situation in which he is here and now. A typical manifestation of a pathological process.
Symptoms of a temporal brain tumor include hearing loss, verbal hallucinations, seizures, and memory problems.
The severity of the clinical manifestations depends on the size of the neoplasia and the rate of its destructive growth.
Parietal lobes
Changing the functional activity of this area gives very interesting signs:
- A person forgets how to read, write, and count.
- The ability to navigate in space suffers. Including the abstract. For example, the patient cannot show on a map where a particular country is located.
- Tactile hallucinations appear. It seems to a person that someone is touching him, licking him, pinching him. This is an extremely painful experience, according to the patients themselves.
- Impaired perception of objects. They become impossible to recognize by touch. Moreover, even very well-known, familiar ones.
- Sensory disturbances. Numbness of fingers, toes.
- Inability to navigate your own body. A person may claim that he does not have a limb. He refuses her, is unable to control his movements.
A volumetric formation in the brain, in the parietal lobe, gives tactile symptoms, hallucinations, plus disturbances in orientation in real and abstract space.
Occipital lobes
Mainly responsible for visual images. Therefore, the clinical picture will be specific:
- Impaired vision. Up to complete blindness. In some cases, a person denies his dysfunction and cannot perceive it realistically.
- Signs of a tumor of the occipital lobe of the brain in adults are hallucinations. From dots flickering in the sky to complex paintings that appear to exist.
- Illusions. It is impossible to normally determine the distance to an object, its size, shape.
- In difficult cases, a person does not recognize the faces of relatives, things that he perceived and saw a hundred times before.
The condition is extremely serious. And it only gets worse as the pathological process develops.
Extrapyramidal system
Represented by the cerebellum. Specific manifestations:
- Disorders of orientation in space.
- Clumsiness of gait.
- A lot of unnecessary movements, because the body is not able to compensate for the disorder.
Signs of a brain tumor and damage to the extrapyramidal system are disturbances in motor activity, dizziness, weakness, nausea, vomiting and the inability to navigate normally in space.
Pituitary
It all depends on whether the structure produces hormones or not. In total, several varieties of neoplasia of this type can be named.
- Prolactinomas. The most common and widespread form. Produces a substance of the same name. It prevents women from conceiving and disrupts the menstrual cycle. It “knocks out” all masculinity from men, making them feminine-like. The breasts grow, the size of the testicles decreases, impotence develops, and the person becomes obese.
- Thyrotropinomas. They produce TSH, which encourages the thyroid gland to work more actively. Thyrotoxicosis develops with all the ensuing consequences: increased blood pressure, temperature, weakness, tachycardia and other issues.
- Corticotropinomas. Synthesize cortisol. As a result, such a severe pathology as Itsenko-Cushing's disease develops. The bones cannot support the weight of the skeleton, the person quickly gains weight and suffers from hypertension. Urgent treatment is needed.
- Somatotropinoma. Produces a special hormone that is responsible for the continued growth of individual parts of the body even after growing up. Mainly the cartilage increases: nose, ears. This disease is called acromegaly.
There are also functionally inactive structures. They are dangerous because they can create a mass effect and compress tissue.
Brain Cancer: Signs and Symptoms in the Early Stages – AskADoctor
Most types of cancer develop gradually, but despite this, the first symptoms of the disease are quite difficult to identify on your own.
The brain is precisely the system that, when affected, the tumor often develops quickly, without specific manifestations in the first stages.
Unfortunately, many patients come to the clinic already with stages III-IV of the oncological process. We’ll talk about what signs should be a reason to see a doctor in the article.
The article was checked by doctor Victoria Druzhikina
Neurologist, Therapist
Oncologists cannot give a definite answer about the causes of the development of malignant tumors in the brain. But there are individual factors that contribute to the appearance of primary tumor cells.
Separately, it is necessary to highlight the risk groups whose representatives encounter this disease most often:
- Cases of cancer and other diseases in the family history, for example, Li-Fraumeni syndrome, Turcotte syndrome, Gorlin syndrome, von Hippel-Lindau disease.
- Irradiation of the brain stem or cerebellum. Unfortunately, treatment for one type of cancer, such as leukemia, provokes another form of the disease. Living in a region with high radiation levels also increases the risk of brain tumors.
- Viral blood invasions.
- Previous brain injuries, concussions.
- The influence of an electromagnetic pulse has a negative effect.
- A secondary tumor may develop as a consequence of a malignancy in another part of the body.
- Working in chemical production or processing plants increases the risk.
- Even bad habits, such as excessive use of tobacco and alcohol, can cause cancer.
Brain cancer is curable only at an early stage and only with a three-step approach to treatment: surgery, radiation and a course of chemotherapy.
The symptoms listed below are characteristic not only of malignant tumors that have developed in brain tissue, but also of various tumors of the bone, muscle and nervous systems. Therefore, any of these signs should be a reason to consult a specialist to make a diagnosis.
The first manifestations of brain cancer depend on the size of the tumor and its location.
Symptoms of early stages of brain cancer are usually classified into:
- focal - occurring in only one location of the brain;
- cerebral - when symptoms appear in all areas of the brain without exception.
Primary and secondary tumors have virtually no significant symptomatic differences.
General signs of malignant tumors in the brain:
- Periodic headaches without clear localization. Discomfort increases when trying to change the angle or position of the head, while swallowing, sneezing, or speaking. Particularly vivid attacks occur after waking up. Antispasmodics and analgesics bring virtually no relief.
- Excessive chronic fatigue, which does not allow you to lead an active lifestyle. The patient is excessively sleepy, irritable, and forgetful. Short amnesic attacks occur when a person is unable to name the names of loved ones or perform a habitual action. There is a lack of attention and concentration.
- Fainting and frequent dizziness. An attack of sudden nausea can occur for no reason: during sleep, while walking, at rest or after eating.
- The larger the tumor, the greater the risk that the patient will experience visual, tactile, taste and auditory hallucinations. Photophobia appears. In 12-15% of the total number of cases, epileptic seizures of unknown etiology are observed.
- Impaired spatial orientation and coordination. Sometimes short-term paralysis develops.
As the tumor grows and metastasizes, the symptoms worsen and become more obvious.
Clinical symptoms of brain cancer depending on the current stage:
| Stage | Symptoms |
| Stage I | It is characterized by a slow course with little damage to brain tissue. If surgical removal of the tumor is performed at this stage, the prognosis for cure becomes quite favorable. Symptoms are mild:
Diagnosis of brain cancer at an early stage is carried out in conjunction with the differentiation of oncological tumors with neurological lesions. |
| Stage II | Most tumors still grow very slowly, but malignancy affects nearby healthy tissue. There is still the possibility of an operation that gives a chance for a full cure. The symptoms are more pronounced, and the following are added to the signs listed above:
|
| Stage III | The tumor grows rapidly and the process of metastasis begins. The operation will no longer give the expected result; the patient needs drug treatment, chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Most tumors are considered inoperable. This is a severe form of brain cancer, accompanied by the following symptoms:
|
| IV stage | The most dangerous, inoperable stage. The prognosis is clear and unfavorable. The rapid growth of the tumor is almost impossible to stop; metastases affect vital centers of the brain. If the tumor is localized in one lobe, then surgery can increase the chance of survival, accompanied by courses of chemotherapy or radiation therapy. In all other cases, excision of part of the tumor can slow down the progression, but will not improve the prognosis. All the symptoms described above are accompanied by the failure of most of the life-supporting systems of the body. The patient's condition is alleviated with the help of potent drugs, but there is no treatment. Symptoms preceding death: unconsciousness, coma, lung failure. |
This division into stages and symptoms is very arbitrary. It all depends on the localization of education. The presence of hallucinations or loss of balance does not necessarily mean metastasis or extensive growth of the tumor.
If the situation allows, tumors are often removed with a CyberKnife or Gamma Knife. These are special installations that allow manipulation with minimal risks. It is based on a stream of radioactive rays directed pointwise.
Both adults and children are operated on.
Neurologist, Therapist
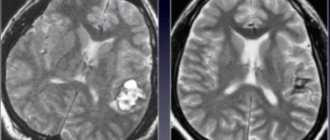
For diagnostic purposes, MRI, CT, angiography, neurological examination methods, radioisotope methods for studying the tumor, stereotactic biopsy and ventriculoscopy are used. To confirm an oncological diagnosis, a lumbar puncture is often used.
It happens that a large tumor is completely asymptomatic, and a formation several millimeters in size has obvious and typical symptoms.
It is almost impossible to independently detect the disease based on its symptoms, since the tumor is localized deep inside the skull.
Brain tumors are dangerous not only because of their malignancy, but also because of their location. It is quite difficult to remove a formation that develops in the closed space of the skull without affecting the vital centers. But not all tumors need to be considered fatal.
Once the neurosurgeon determines the boundaries, size and exact location of the tumor, it will become clear how the patient should be treated. If there is even the slightest chance of a successful outcome of the operation, then histology of the malignant tissue will be required, if such a procedure is possible and does not complicate the patient’s condition.
Doctor's advice
Brain surgery is not as scary as it seems. If there is a choice to do or not to do, then refusal means a pessimistic forecast, while consent gives a chance, and not a small one. After treatment with modern devices, in most cases, long rehabilitation is not required, the patient returns to his normal life.
During this period, he needs to be supported morally, helped with usual household chores and childcare. Students can read the curriculum little by little, this will help them get into a familiar rhythm. If you have panic attacks, neurosis, or depression that develops as a result of an illness, you need to consult a psychologist.
All this is very important for recovery.
Treatment is always complex. At an early stage of cancer, all available methods are used: radiosurgery, cryosurgery, radiation and chemotherapy, surgery, symptomatic therapy. The goal is not only to cure cancer; first, it is necessary to relieve pain, alleviate the general condition and prevent swelling of the brain.
The survival prognosis for people with early stage brain cancer depends on two factors: the accuracy and timeliness of diagnosis.
If treatment is started immediately, about 82% of patients survive after five years. With late presentation, the five-year survival rate is only 31%. The prognosis largely depends on the type, aggressiveness and growth rate of the tumor.
Brain tumors are strikingly different from other malignant tumors and occur in approximately 3% of all recorded cases of oncology. They are located so inconveniently that the symptoms of the disease are difficult to differentiate, and this significantly complicates treatment.
The basis for referral to an oncology clinic is sudden development and increasing neurological symptoms. However, modern medicine has hardware diagnostic tools that can not only detect cancer at an early stage, but also identify predisposition to it.
For more information about the symptoms of a brain tumor, watch the video:
Useful articles on the topic: Why women may feel dizzy: common causes Tension headaches: causes, types of pathology, symptoms and effective treatments
Source: //sprosivracha.com/articles/health/114-rak-golovnogo-mozga-simptomy-na-rannih-stadiyah-i-prognoz-izlecheniya
General signs
There are also general clinical signs that do not depend on the location of the pathological process.
- Moderate headaches, the main symptoms of a brain tumor in the early stages. Then, as the tumor grows, it becomes much worse: the drainage system suffers, the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) stagnates. Intracranial pressure increases.
This leads to the development of unbearable pain. They can only be stopped with very powerful drugs. Including drugs.
- Dizziness, weakness.
- Nausea, vomiting. Especially in the later stages of the pathological process. Other symptoms also occur.
The described localizations do not exhaust the entire possible list. Thus, damage to the limbic system leads to loss of the ability to learn.
And if the brain stem is involved, this is an almost guaranteed immediate death, because respiratory and cardiovascular functions suffer.
You need to figure it out on the spot, but you absolutely cannot procrastinate.
Diagnosis of brain cancer
If you have chronic, ever-increasing headaches associated with the symptoms mentioned above in the article, it is important to immediately consult a therapist. If brain cancer is suspected, a biochemical blood test is performed. There is a high probability that the pathology will be detected at the first stage by an ophthalmologist after examining the fundus. To make an accurate diagnosis, a comprehensive study is necessary, the main stages of which will be:
- CT scan
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the head (MRI)
- Vascular angiography
- Taking cerebrospinal fluid (puncture)
- Carrying out electroencephalography
Causes
Factors in the development of the pathological process are poorly understood. At least for now. There are several assumptions about where the violation comes from. But these are just theoretical calculations.
What are we talking about:
- Radiation. Ionizing radiation. You can meet him in a number of cases. Banal x-rays, service at a nuclear power plant, work in a uranium mine, undergoing radiation therapy for cancer of any location. Even living in an area with increased radiation pollution.
Attention:
The dependence of the pathological process on this factor has been studied and proven in some detail.
- Toxic effects. Poisons, pesticides, organic fertilizers that penetrate the plant tissue. Basically, we are talking about poisoning the nutritional plan. It is difficult to say how quickly a tumor will develop or whether it will form at all. But such risks exist and are quite real.
The main recommendation is to give up nitrate vegetables, fruits, dangerous fast food and other potentially harmful products based on vegetable fats, trans fats, etc.
- Unfavorable environmental conditions. Found all over the planet. In Russia, this is almost ¾ of the entire country. The same can be said about Ukraine and all territories of the former Union, where ecology was given, at best, 10th place. Living in such regions is potentially dangerous.
- Immunity disorders. The main cause of a brain tumor is the inability of the defense forces to stop the abnormal process of cell division and their abnormal proliferation. This is what lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell, are responsible for. This happens, for example, after a severe illness or taking immunosuppressants, or heavy consumption of glucocorticoids. And not only.
- Burdened heredity. An important etiological factor. In this case, we are not talking about direct transmission of the disease, but about the transfer of the probability of a pathological process.
You need to look at the medical history of direct line relatives: mother, father, grandmothers, grandfathers. If at least one loved one had a tumor, there is a 10 to 25% chance that a descendant will also have it.
Although this is just a statistical probability. It can be smoothed out if you avoid radiation, toxins, and maintain normal immunity.
When a collateral relative (brother, sister) is ill or is suffering, there are also risks, but many times lower: from 0.5 to 3-5%. This event should not be overlooked.
- Some forms of infection. It has been proven that the development of glioblastoma is influenced by the human papilloma virus. It triggers cellular atypia, changes in the cytological structure of structures and provokes conditional cancer.
It may well be that other anomalous agents have the same properties. But this is not known yet.
- Use of certain drugs. Hormonal agents, already mentioned immunosuppressants, corticosteroids. They can be accepted only when there is no other choice, and then in a very limited format.
- Features of embryogenesis. Violations of the formation of the embryo become the culprits in the development of germ cell tumors. But the pathology is discovered much later.
For now, this is all that can be said about development factors. The problem is that without knowing the exact causes, it is impossible to develop competent measures to prevent pathological processes.
For reference:
The named provocateurs apply equally to both benign and malignant neoplasias.
Classification of brain tumors
Doctors use two types of classification.
Differentiation by focus is based on the initial localization of the oncological process. Primary brain tumors develop directly from nerve and adjacent tissues. Secondary neoplasms are formed as a result of cancer metastasis from any other part of the body.
To assess the prognosis and plan treatment, a histological classification of pathology is used:
- Tumors of brain tissue, that is, neuroepithelial. These include gliomas and astrocytomas. The pathological process arises directly from the nerve fiber.
- Neoplasms of the membranes – meningiomas.
- Pituitary adenoma is a benign lesion in 70% of cases.
- Tumors of the cranial nerves – neuromas.
- Metastatic neoplasms occur when cells migrate from primary sites located outside the nervous system.
Different types of brain cancer should be treated differently. Some histological types respond well to chemotherapy and are quite easily curable, while others require surgical removal, which does not always help get rid of the disease.
Diagnostics
The examination is not particularly difficult. Oncologists and neurosurgeons work with patients. If we talk about methods, the following procedures are carried out:
- Questioning the patient.
- Collecting a life history.
- Survey MRI. To understand where the tumor is located. This is a kind of attempt to take aim.
- Contrast-enhanced tomography. A gadolinium-based agent is administered intravenously. It accumulates in altered tissues and increases the clarity of the image.
The doctor gets the opportunity to assess the size, structure, and exact location of the neoplasia. Assume the rate of cell division and the type of abnormal formation.
- Stereotactic biopsy. It is carried out only when there is a real suspicion that the tumor is malignant. It is a directed sampling of biomaterial particles. The procedure is not easy and quite risky.
- Histological and morphological assessment of the structure of neoplasia. Using these methods we can tell what kind of tumor it is, what it consists of and what type it is.
Diagnosis is carried out quickly so as not to delay therapy. There is not as much time as we would like.
Features of the oncological process in the brain
Malignant tumors consist of actively growing mutated cells that aggressively invade nearby tissues. Tumor cells require nutrients and oxygen for their growth and development. This problem is especially acute within the cranium, which is reflected in increased intracranial pressure, hypoxia and pressure on vital brain centers.
Another feature of brain oncology is the almost complete absence of metastasis. A malignant neoplasm develops in a confined space, causing local tissue destruction.
Treatment
Correction is extremely difficult. The room for maneuver is very wide. If we talk about approaches, they will differ. It all depends on the type of tumor.
Malignant formations
The abnormal tissue structure must be surgically removed. Whenever possible, we try to do this with microaccess.
Neoplasia larger than a centimeter in diameter often has to be treated openly. Through craniotomy. This does not add favorable prospects after the operation.
It is important to remove the structure as much as possible. Some cells will still remain, so radiation and chemotherapy are carried out.
Radiation is especially effective against germinal structures. They are often treated only in this way, without resorting to surgery.
There are also resistant forms of pathological structures that do not respond to such influence at all. The course of chemotherapy, its duration, and medications are selected by the doctor.
In the case of advanced forms of tumors, only palliative care remains.
Benign neoplasia
Until the structure grows, doctors choose a wait-and-see approach. Every 3 months, an MRI is performed to see how the abnormal accumulation of tissue behaves. And so on.
If there are no dynamics for a couple of years, they assume that everything is in order. Otherwise, the tumor is removed surgically. Fortunately, it is well demarcated and there are almost no problems with it.
Possible treatments
The tactics to combat brain cancer are determined based on the results of the examinations performed. The most effective is a combination of several methods. Unfortunately, this is not always possible due to the unstable condition of the patient.
Combined treatment of the disease is effective. Preoperative irradiation of the affected area is used, followed by surgical removal of the reduced tumor. The effect is subsequently consolidated by chemotherapy to prevent recurrence of the process. Intraoperative administration of capsules with cytostatics into the cavity formed after extraction is also used.
Prognosis depending on tumor type
The prospects for recovery depend on the type of neoplasia. Here are just some calculations (the list is built on the principle of starting from the most favorable option to the less positive, from top to bottom):
- Pituitary adenomas, like tumors of the posterior lobe of the organ, or the legs, provide a survival rate of almost 100%. The same can be said about first-grade gliomas.
- Identical for meningiomas. Except for the atypical ones. There the probability of death is almost 15%.
- Germinomas and mature, highly differentiated teratomas also respond well to treatment. Survival rate is more than 75-85%.
- The situation is slightly worse with low-grade gliomas (starting with grade II). Chances of survival are about 65%.
- Anaplastic types of abnormal structures are associated with a prognosis of 45-50%.
- Patients with glioblastoma exceed the 5-year mark in 3-5% of cases. It's almost impossible. The months count down.
We need to start from neoplasia.
How to recognize a Brain Tumor in the Early Stages, First Signs of the Disease
The percentage of people living with AMS is quite high. Not everyone knows what the main symptoms are at the early stage of the disease. Unfortunately, in most cases it is possible to diagnose breast cancer only in the last stages, when the chances of survival are negligible, and some varieties are generally identified only posthumously, due to their rapid development.
Common symptoms of a malignant brain tumor:
- One of the most striking signs is a headache, which becomes more acute from any physical effort. But, by the way, in half of cancer patients it is completely absent at first.
- Dizziness can also be a symptom of a neoplasm if it occurs regardless of the patient’s position and does not go away for a long time. As a rule, it is explained by changes in the pituitary gland or an increase in intracranial pressure caused by the tumor.
- A feeling of “cottoniness” in the joints and limbs is also common. At the initial stage, this symptom usually manifests itself as weakness, but as the disease progresses, partial paresis or paralysis of the limbs may occur.
- Visual disturbances can also be considered as signs accompanying brain cancer.
In this case, they manifest themselves in the form of spots, floaters floating in front of the eyes, as well as pain in the optic nerve. Often at an early stage, nystagmus of the eyeball may also occur. - Hearing problems should also be a concern. They occur as ringing in the ears or unexplained one-sided deafness.
To all of the above, you can add causeless changes in pulse rate, pressure changes, pallor or the appearance of abundant spots on the skin, as well as sweating.
Treatment
Therapy will depend on how the disease manifests itself, the stage of development of the tumor and its location. The most effective treatment method today remains surgical removal.
But it is not always possible to remove a tumor, even in the initial stages. When localizing the formation in vital areas, a gamma knife or cyber knife is used.
The methods are based on irradiating the affected area with gamma rays.
Also, if it is impossible to perform a surgical operation, cryofreezing is practiced. The growth is frozen and carefully removed from the skull.
Neurological manifestations of cancer
The first signs of brain cancer can manifest as neurological and mental disorders, expressed by apathy, which can be replaced by short-term euphoria, causeless aggression and memory loss. They are often accompanied by confusion, disorientation in time and space, various manifestations of personality changes, as well as visual or auditory hallucinations.
And if the deep parts of the brain are damaged, rapidly increasing signs of complete disorganization of a person’s mental activity may be found.
Cost of operations
Previously, patients with a brain tumor sought to undergo treatment abroad due to the fact that it was impossible to carry out such operations at their place of residence due to the lack of necessary equipment. The situation has completely changed.
Most Russian clinics are equipped with the most modern equipment, which is not inferior to foreign ones. This allows you to receive quality treatment. In Russia there is the possibility of free treatment if you have health insurance.
The price for such operations in Moscow ranges from 50 to 500 thousand rubles, in Germany from 1,500 to 15,000 euros, in Israel from 8,000 to 18,000 dollars.
How do lesions in different lobes of the brain manifest?
Signs of brain cancer appear differently, depending on which part is affected. If the tumor affects the pituitary gland or the trunk, it usually causes a lack of coordination of movements.
The ability to concentrate noticeably decreases, in addition, the patient may experience distinct double vision.
Another sign is the inability to determine the distance to an object and unsteadiness in gait.
In some cases, brain cancer was manifested by painful sensations when swallowing, difficulty moving the tongue, as well as disturbances in the functioning of facial muscles or their paresis.
If the cerebellum is damaged, nausea, vomiting, spasms in the back of the head and nystagmus may be added to the symptoms listed above.
Symptoms of hormone-producing pituitary adenomas
Pituitary adenomas account for 10 to 15% of the total number of neoplasms found in the brain. In 65% of cases, their development leads to an abnormal increase in the production (hypersecretion) of certain hormones, which is accompanied by characteristic clinical manifestations. Such tumors are called hormone-producing, and their diagnosis is usually not difficult.
Prolactinomas most often develop in the pituitary gland.
, i.e. tumors that produce the hormone prolactin. Its excess in women in 80-90% of cases leads to the appearance of:
- menstrual disorders (oligomenorrhea, amenorrhea) and infertility;
- decreased bone density (osteopenia);
- dryness of the vaginal walls and swelling;
- hirsutism (hair growth) and acne (pustules on the skin);
- decreased libido;
- abnormal discharge of colostrum from the mammary glands (galactorrhea).
Hypersecretion of prolactin in men manifests itself:
- often - decreased potency and libido, oligospermia with concomitant infertility, osteopenia;
- rarely – galactorrhea and enlarged mammary glands (gynecomastia).
Less commonly, formations that produce the hormone somatotropin appear in this part of the brain. Specific signs of hormonal dysfunction in somatotropinoma
become:
- change in facial features;
- enlargement of the feet and hands (acromegaly), tongue (macroglossia) and internal organs;
- cardiac dysfunction - left ventricular diastolic dysfunction, hypertension, arrhythmias, heart failure due to changes in the endothelium;
- breathing problems (ventilatory dysfunction) due to obstruction of the upper respiratory tract;
- metabolic disorders with the development of diabetes mellitus and hypertriglyceridemia.
The pituitary region can also develop:
- Thyrotropinomas.
Their appearance leads to an increase in the level of the hormone thyrotropin in the blood, which is accompanied by increased stimulation of the thyroid gland and causes exophthalmos, tachycardia, diarrhea, and increased body temperature. - Corticotropinomas.
Excess corticotropic hormone leads to the development of Itsenko-Cushing syndrome, including a characteristic type of obesity and the appearance of stretch marks (strichia) on the skin. The growth of formations of this type in women is also manifested by male-type hair growth, scanty periods or their absence. Children with corticotropinomas suffer from growth retardation, men – erectile dysfunction, oligospermia, and decreased libido.
If you need a second opinion to clarify your diagnosis or treatment plan, send us an application and documents for consultation, or schedule an in-person consultation by phone.
+7
Expert opinion
Brain cancer: symptoms and signs of damage to the temporal lobes
One or both temporal lobes affected by a cancerous tumor can cause auditory agnosia and mental impairment in the patient (the patient cannot understand what is said, write from dictation, read, and his speech is impaired). The presence of a tumor in these lobes also causes amnesia, causeless fear and anxiety. The patient may become depressed.
Signs of brain cancer in this case can manifest themselves as severe headaches, distortions of taste and olfactory sensations. The patient often suffers from causeless fainting.
Lesions of the medial sections in the temporal region can also manifest themselves in the form of affective disorders such as exaltation or causeless melancholy, as well as a state of “déjà vu”.
Types of tumor
Researchers have developed a fairly large classification of neoplasms depending on a variety of factors.
Histology
Histological, structural characteristics, and features of the course of the disease make it possible to distinguish two groups of neoplasms: benign and malignant.
Benign tumors are not capable of dividing, grow slowly, and do not penetrate other tissues. In their structure they resemble the cells from which they originated and partially retain their functions.
Such tumors can be removed through surgery, and recurrence is extremely rare. However, benign tumors in the brain are very dangerous.
They lead to compression of blood vessels, the appearance of edema, and stagnation of venous blood, while their location does not always make it possible to remove them.
Malignant neoplasms consist of cells that divide very quickly. Tumors grow rapidly, forming entire lesions and penetrating into neighboring tissues. Most often, malignant tumors do not have clear boundaries. They are difficult to treat, including surgery, and are prone to relapse.
Location
The location allows us to talk about 3 types of tumors. Intracerebral are found in the very substance of the brain. Extracerebral ones appear in the membrane and nerve tissues. Intraventricular - in the cerebral ventricles.
Source: //gb4miass74.ru/bolezni/rak-mozga.html
Symptoms of a tumor of the cerebellum of the brain
Cerebellar tumors are the most common of all, and also one of the most dangerous. Symptoms of such a tumor are of three types, namely: focal (in the cerebellum area), general cerebral, and also distant from the affected area. The most common ones are:
- Pain in the back of the head.
- Palsy of individual cranial nerves.
- When formed in the cerebellum area, seizures may occur.
- Balance disorders. With a cerebellar tumor, patients have poor posture or may experience abnormal positioning of the torso and head.
Having diagnosed a cerebellar tumor, the patient is indicated for immediate surgical intervention. Malignant transformation in the cerebellar region is cured in only 20% of cases.