Cerebral hemorrhage in more than half of all cases is a complicated consequence of stable blood pressure. Hemorrhagic stroke (the medical name for cerebral hemorrhage) is more often considered a consequence of degeneration of the small arteries of the brain, protrusion of their walls due to stretching or thinning, which can be caused by high pressure of a persistent nature.
The frequency of hemorrhages will depend on how pronounced and intense the blood pressure is. Intracerebral hemorrhage occurs due to the breakthrough of deformed arteries. When there is a breakthrough in the vascular system inside the skull, the bleeding into the brain will not stop until the area of damage to the artery is blocked. This may take from a few minutes to several hours.
As a result of hemorrhage in the brain, cerebral circulation is significantly impaired, the nerve tissues of the brain become saturated with blood or a hematoma is formed. Damage to the brain substance causes serious neurological pathology: the ability to move and feel is lost, the swallowing and breathing reflex is significantly impaired, and speech is distorted. Hemorrhagic stroke quite often causes the death of the victim; most patients who have suffered this disease acquire a certain group of disabilities.
It's unfortunate, but strokes affect an incredibly large number of people today, most of them young. Such statistics indicate another deviation in human health: impaired blood circulation in the brain is often observed, and there can be many reasons for this. As a consequence, necrosis or ischemic stroke occurs (in other words, cerebral infarction). But most often there is an outpouring of blood into the brain tissue: a hemorrhagic stroke is diagnosed.
Mechanism of formation
The development of the disorder is based on one factor or several pathogenetic factors at once. What exactly can affect the likelihood of a violation:
- Cardiovascular diseases. Represented by a wide group of diagnoses. In the vast majority of cases, hemorrhagic stroke develops as a complication of long-term and untreated hypertension. That is, a stable and pronounced increase in blood pressure.
Statistics show that the mechanism accounts for up to 85% of the total number of hemorrhages. This is the absolute majority. The only way to prevent an emergency condition is to undergo high-quality treatment of the underlying pathology.
- Metabolic disorders. Basically, deviation of lipid movement. That is, a disorder in which the rate of deposition and elimination of fats significantly deviates from the conventional norm.
The pathological process leads to another problem - atherosclerosis. When cholesterol deposits form on the walls of blood vessels, which interfere with blood flow. The result is that the likelihood of hemorrhagic stroke and death from complications increases significantly.
- Hormonal imbalance. We are talking about a variety of disorders: from changes in the quality and intensity of the synthesis of sex substances to problems with the production of insulin and compounds of the adrenal cortex.
- Hereditary causes. The mechanism is associated with a not yet fully understood method of transferring risks from parents to children. The disease itself, of course, is not transmitted.
If a mother, father, grandmother, grandfather has a hemorrhagic stroke, this does not mean that the same thing will happen to a descendant. But the likelihood is growing. Apparently - by several tens of percent. The topic has not been fully studied, research continues.
- Toxic damage to the body. Poisoning by vapors of non-metals, some medications. The risk of hemorrhagic stroke increases with the systematic use of antiplatelet agents, anticoagulants, and hormonal agents.
- Some forms of anemia, blood diseases. Changes in the rheological properties of connective tissue lead to disruption of the speed and quality of trophic systems and an increase in blood pressure. In some cases, vascular permeability increases. The result is an increased risk of cerebral hemorrhage.
Mechanisms exist in isolation or are combined with each other. This question needs to be clarified, since the therapy strategy and its essence depend on the origin of the pathological process.
Urgent Care
Quick help for this disease is very important. We need to urgently call a doctor. Then create an environment for the patient in which further development of hemorrhage will be stopped.
For this:
- the patient must be placed horizontally on something solid, the head must be elevated,
- The head must be turned to the side. This is done so that the patient can breathe easier,
- Such patients need fresh air,
- When transporting a patient, he must lie horizontally and motionless,
- You need to measure blood pressure and temperature.
Classification
The condition is divided according to three bases. The first criterion is the localization of the violation. The most common variants of the disorder are:
- Lateral.
- Lobar.
- Subcortical or subcortical.
- Thalamic.
- Cerebellar.
- Mixed.
- Stem.
Most likely, this terminology will mean nothing to a patient without special knowledge. The point is different. Depending on the location of the pathological change, the symptoms will be one or another. Plus, prognoses are determined by the essence of the disorder and its location. You need to clearly know where the hemorrhage occurred.
Another basis for classification is the type of lesion.
Highlight:
- Actually parenchymal process. When blood enters the brain tissue and permeates it. It is considered a very dangerous type of disorder. Potentially more lethal than the second one.
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage. Liquid connective tissue extends into the space between the cerebral membranes. The main pathological effect concerns compression of the brain, as a result of increased intracranial pressure.
However, the risks are less. Since there are not as many factors of damage as in the first case.
The third basis for classification is the severity of the pathological process.
These options are called:
- Mild degree. If the amount of bleeding into the brain is minimal. Happens quite often. In some cases, the patient does not understand at all what happened until neurological disorders increase. The outlook for recovery is good.
- Average degree. There is a pronounced clinical picture. Everything is noticeable from the very first second of the pathological process. Deviation requires urgent hospitalization and treatment in an intensive care unit. Even in this case, the chances of recovery are rather dim.
- Severe form. Doesn't bode well for the patient. In more than 80% of cases, a person dies from massive death of brain tissue. In 20% of situations he remains deeply disabled for the same reasons. There is almost no chance of restoring at least the basic functions of cerebral structures and ensuring adequate life activity.
These classifications are actively used in medical practice to describe the pathological process, its essence and dynamics.
First aid
First aid for the development of this disease includes the following:
- Call a doctor, and before his arrival, administer medications to the patient to normalize blood pressure.
- The patient must be transported in a supine position with his head elevated.
- To eliminate edema, diuretics should be administered.
Further drug therapy is carried out after diagnostic procedures have been carried out and the advanced stage of the disease has been determined. If necessary, urgent surgery may also be prescribed.
Read how a major stroke manifests itself and what consequences arise for a person.
How does a stroke on the left side manifest: manifestations, treatment, recovery.
What does an increase in temperature after a stroke indicate: treatment and prevention.
Causes
Development factors have already been named earlier; it is worth specifying the described mechanisms and identifying the exact provocateurs. Among them:
Hypertension
Stable increase in blood pressure. It is considered an independent cardiovascular disease. It occurs frequently, especially in patients of the older age group. Almost in 90% of cases, albeit to varying degrees of severity.
The higher the blood pressure level, the more serious the risks. Since the vessels are in a state of constant increased load, they wear out faster. At a certain point, they simply cannot stand it and burst. Which leads to an emergency.
The cause of cerebral hemorrhage is an excessive impact on the internal lining of the artery, its muscle layer, dystrophy and, as the final result, a sharp rupture and leakage of liquid connective tissue.
Diabetes
An endocrine disease that stands apart. It is characterized by a stable, regular increase in blood sugar levels.
In addition, the pathology poses a danger to all tissues of the body. First of all, it is the blood vessels that suffer. A pathological narrowing of the lumen of the arteries develops. The tissues do not receive enough nutrition.
In addition, the phenomena of degeneration of the internal lining and muscle layer are increasing. The result is the same as in the previous case.
The disease cannot be treated as such, so the likelihood of encountering a hemorrhagic stroke is enormous and is growing every year.
By the way, this is one of the main factors in the death of patients with diabetes.
Smoking
Subjective reason. The problem is not only and not so much with nicotine, but with other toxic substances. The quality of vessels is affected by cadmium, arsenic vapors, sulfur structures, carbon compounds and other chemicals.
If you smoke regularly, the likelihood of a stroke increases. Because the vessels quickly wear out and narrow.
Alcohol consumption
About the same thing happens, only the poisons are different. When ethanol is processed, acetaldehyde and acetic acid are produced. They are dangerous for the heart and arteries. Which becomes the culprit that provokes hemorrhage.
Drug use
According to research, patients who love cocaine and synthetic stimulants are especially at risk.
The cause of intracerebral hemorrhage is thinning of the walls of blood vessels, increased pressure, and degeneration of the arteries. The result is obvious.
Arrhythmias
Oddly enough, the very nature of cardiac output determines the condition of the blood vessels. It turns out that the load on the arteries is distributed unevenly. Sometimes she is high, sometimes she is low. The pressure rises and falls.
In such an emergency mode, the body works constantly. This can't end well. The result of arrhythmias is cerebral hemorrhage. Provided that rhythm disturbances are not corrected in a timely manner.
Read more about the types of arrhythmias, possible risks and treatment here.
Atherosclerosis
Deposition of fatty compounds on the walls of blood vessels. Cholesterol plaques interfere with blood flow. The result is increased pressure as local resistance has to be overcome.
Gradually, the artery wears out, a wall protrusion of the vessel (aneurysm) is possible, then the likelihood of hemorrhage increases significantly. It makes sense to treat the disease at the earliest stage, while the chances of recovery are high enough.
Vascular defects
Congenital or acquired disorders. For example, too narrow a lumen or degeneration of the walls. Various options are possible. The bottom line is that they potentially increase the likelihood of a stroke.
If such a change is detected, you need to adhere to the rules of prevention: do not overexert yourself physically, eat right, etc. The treating specialist helps develop the strategy.
Heart defects
Also congenital or acquired. Most often, anatomical changes in the condition of the valves occur.
There are more dangerous variants of the pathological process, complex ones. Read more about the types of heart defects here.
Treatment is carried out by cardiology specialists and specialized surgeons.
Obesity
Increased body weight is associated with two disorders: increased blood pressure (hypertension) and changes in the nature of lipid metabolism (atherosclerosis).
Anemia
Basically, rare forms of the pathological process. The disorder is caused very rarely, in no more than 0.5% of cases.
Wrong lifestyle
A diet high in fat, carbohydrates, also sitting in one place, lack of mobility (so-called physical inactivity). They increase the risk, but do not themselves cause cerebral hemorrhage.
Hormonal imbalances
An increase in the concentration of substances in the adrenal cortex, pituitary gland or thyroid gland.
Use of certain drugs
To increase blood flow, oral contraceptives, and other medications.
These reasons need to be eliminated as quickly as possible. In the early stages, it is still possible to prevent the irreparable.
Causes of the disease
The main cause of hemorrhages is a rupture of one of the intracranial arteries, which caused insufficient nutrition and the supply of a small amount of oxygen to the brain tissue.
In addition, factors that increase the risk of bleeding in the skull may include:
- a wide range of different head injuries;
- high blood pressure;
- the formation of a growth in the brain that eventually fills with blood and bursts. Most often this is the cause of hemorrhage in babies, since neoplasms can be congenital;
- pathological structure of cerebral vessels;
- cancerous tumors;
- taking large quantities of medications aimed at thinning the blood;
- unhealthy lifestyle, abuse of nicotine, alcohol and drugs;
- accumulation of a large amount of specific amyloid protein in the walls of the brain;
- infectious diseases affecting blood circulation;
- diabetes;
- strong physical activity;
- harmful working conditions;
- living near factories that pollute the air;
- prolonged stress or depression;
- premature birth, the likelihood of hemorrhage in a newborn baby is especially high if the gestation period was less than thirty-two weeks. In addition, such a process can develop during the first week of a baby’s life - this is due to complicated childbirth, late toxicosis and a condition such as eclampsia.
Hemorrhagic stroke
Precursor symptoms
The preceding signs or so-called aura do not always develop. This is rather an exception to the rule, since in most cases the opposite is observed.
Hemorrhage occurs suddenly. If we talk about manifestations that will indicate the approach of an emergency condition, they can be as follows:
- Intense heat in the chest, flushing of the face. A sudden sensation that comes out of the blue. As a rule, there are no objective reasons.
- Numbness of half the face. In addition, tingling may occur. Paresthesias indicate sudden, acute ischemia. This is a very alarming sign, even if nothing followed after it. You need to pay close attention to such “calls” and urgently run to the doctor.
- Problems with speech perception. The native language that a person has spoken for many years suddenly turns out to be incomprehensible. This is the first sign of a malnutrition of the temporal lobes of the brain, into which blood may bleed.
- Problems with coordination of movements. Acute dizziness. May result in a fall and injury.
Attention:
Aura or precursors of a pathological process occur in only 5-10% of the total number of cases. Much more often, the disorder debuts directly from the main clinic.
All possible symptoms of pre-stroke in women are described in detail here.
Signs of hemorrhagic stroke
A person can recognize the symptoms of the disease in the first minutes of hemorrhage.
- Facial asymmetry : when trying to smile, the victim discovers uncontrollability of the facial muscles on the left or right (on the side of the affected hemisphere of the brain).
- Speech impairment : the patient cannot speak, his speech is slurred.
- Poor vision , symptoms of double vision or temporary blindness.
- Unbearable headache.
Signs of the acute phase
The complex of manifestations of the deviation is very bright and clearly visible, since the lesion is severe.
Hemorrhagic stroke is much more severe than its ischemic “brother”, since a whole group of factors accumulate that affect the functional activity of the brain.
Among them:
- Actually, an acute malnutrition of that part of the cerebral structures that received oxygen and nutrients through the destroyed vessel. As a rule, in the case of ischemic stroke, this is where it all ends. But not with cerebral hemorrhage.
- Inflammatory, necrotic processes in the very focus of trophic disturbances. They develop almost immediately. Pathological changes continue and complicate them. Both the main vessel itself and the nervous tissue at the local level suffer, which only aggravates the situation.
- Inflammation in the periphery. Changes in the structure of nerve tissue outside the lesion itself.
- Compression of the brain by a clot of accumulated blood. The space of the cranium is closed and does not change. Therefore, any deviations of this kind are potentially fatal and dangerous.
Liquid tissue puts pressure on nerve fibers and causes secondary ischemic processes, and then possible necrosis with the gradual development of neurological deficit.
Symptoms of hemorrhage in the brain are caused by the cumulative effect of various damaging factors, compression, necrosis at the source of the stroke, ischemia of tissues that do not receive nutrition and oxygen.
As for the clinical picture itself, the signs will be as follows:
- An acute headache, unbearable and very strong, is the first manifestation of hemorrhage in the structures of the brain. It occurs with lightning speed, suddenly and provokes forced body positions. The person tries to find a position in which the sensation will be less noticeable.
For reference:
The pain goes away gradually, as tissues die further and the pathological process worsens, which is quite remarkable.
- Dizziness. Changes in the perception of space, disturbances in orientation in the surrounding reality. The person also cannot coordinate his own actions. Forced to take a sitting or lying position. In the place where he was caught in an emergency.
- Speech disorders. Because the facial muscles and the entire articulatory apparatus are paralyzed. There may also be problems with the perception of other people's statements. Aphasia develops suddenly and lasts for many months.
Attention:
If the patient is lucky enough to survive and not remain a “vegetable,” speech function will have to be restored for at least a year.
Read more about the rehabilitation process after a stroke in this article.
- Nausea, vomiting. They develop just as suddenly. Moreover, it does not matter at all whether a person took food or not.
- Numbness of half the body. The result of paralysis or paresis. The disorder affects the side opposite the one where the cerebral hemorrhage occurred. Since the organization of nervous activity is mirror, cross. Gradually, sensitivity may be restored or only become stronger.
- Intolerance to sounds and smells. Everything that affects analyzers and sense organs. All such effects provoke an attack of severe headache, nausea and vomiting. All manifestations become more intense.
- Tachycardia. Increased heart rate. Reflex phenomenon. It usually does not pose a great danger, but creates additional discomfort for the patient.
- The simplest visual hallucinations. Signs of cerebral hemorrhage are flickering flies, lightning, bright dots before the eyes, the patient sees flashes of blue, golden color, black spots and geometric shapes. This is the result of poor nutrition of the occipital lobe of the brain. In the absence of a sufficient amount of oxygen, the cortex becomes excited and begins to produce non-existent images.
- Loss of consciousness. Fainting is a typical sign of cerebral hemorrhage and develops in 4 stages: from a feeling of unreality to the actual syncope episode. On average, it takes from 1 to 5 minutes for the state to fully develop. With extensive bleeding, coma is possible.
These are common signs of the disorder.
Diagnosis of cerebral hemorrhages
When a person with similar symptoms consults a doctor, a variety of tests are used to make a diagnosis. Some of them are urgent, others are used less frequently. But the most popular are the following:
- Survey. If the patient is conscious, the doctor asks questions about his well-being, the time of onset of symptoms, and intensity. Otherwise, your loved ones can provide the necessary information. It is important to collect anamnesis: the presence of diseases that provoke hemorrhage, hypertension, bad habits, lifestyle features, and so on.
- Testing simple nervous reflexes, sensitivity, limb mobility, vision, and so on.
- The simplest measurements: pulse, pressure, ECG. Often, a hemorrhagic stroke causes increased blood pressure, tachycardia and bradycardia, as well as some changes in the electrocardiogram.
- Lumbar puncture. In most cases of brain hemorrhage, blood elements leak into the cerebrospinal fluid and can be detected in a sample taken through a lumbar puncture. The presence of red blood cells in the cerebrospinal fluid sample confirms the preliminary diagnosis.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. This diagnostic method is considered the gold standard in such cases. It can be used to detect hematomas, displacement of brain lobes, tumors and other signs.
- Angiography. The study of the vascular network makes it possible to visualize possible signs of bleeding in the brain, as well as provoking factors: malformations, aneurysms. As a rule, this study is done during preparation for surgery.
The purpose of collecting information is to find the true cause of the hemorrhage and determine its volume and location.
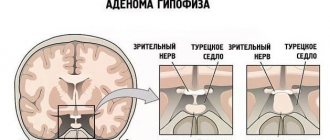
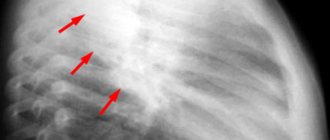
This is what a hemorrhagic stroke looks like on angiography
Focal manifestations
In this case, everything depends on the localization of the pathological process, which part of the cerebral structures does not receive enough nutrition and oxygen.
- If the frontal lobe is damaged, epileptic seizures, disturbances in behavior, thinking, and motor activity occur.
- Parietal region - disorders of smell, touch, loss of the ability to count and read.
- Temporal structures - auditory deceptions of perception, convulsive seizures, memory impairment.
- Occipital lobe - visual hallucinations, vision problems.
- Cerebellum and extrapyramidal system - loss of balance, movement coordination disorders, dizziness.
Attention:
In case of hemorrhage in the brain stem - dysfunction of breathing and cardiac activity. Patients die in 100% of cases.
The clinic urgently needs to stop, just like the primary pathological process.
Complications
The disease is dangerous due to the development of various complications. Sometimes the patient is accompanied until the end of his life by:
- speech disorders;
- discoordination of facial muscles;
- paralysis - complete or partial immobility.
In 50% of cases, hemorrhagic stroke is fatal.
Impaired motor skills and the general condition of the body directly depend on the size of the hematoma and the degree of brain damage.
Carrying out rehabilitation measures helps restore some body functions, but this requires patience and time.
If the patient is completely inactive, it is necessary to take measures aimed at preventing bedsores and caring for the skin.
Diagnostics
There is not much time for examination. It is necessary to urgently take the person to the hospital, study his general condition and begin action.
The emergency list of activities is as follows:
- Blood pressure measurement.
- Quickly interview the patient if he is conscious.
- Listening to heart sounds.
- Basic neurological examination. Checking reflexes.
Next, primary measures are taken to restore the functional activity of the body. Once the condition becomes stable, there is time to study the situation in more detail.
Special examinations are prescribed:
- Anamnesis collection.
- Doppler ultrasound of the brain. Duplex scanning of vessels of cerebral structures. To assess the quality of local blood flow.
- REG. In order to identify the electrical activity of nerve tissue.
- MRI. To assess the extent of damage and prospects for recovery. Develop treatment tactics.
- Hormone analysis, as well as blood biochemistry with an expanded picture of the lipid spectrum.
Diagnosis is carried out under the supervision of a neurologist. A cardiologist, neurosurgeon, and endocrinologist are also involved, if necessary.
Time is running out. The first few days and even months there is a real risk of relapse. No one survives a second hemorrhagic stroke.
Read the full algorithm for providing first aid for a stroke here.
How does massive hemorrhage occur?
The group of people over 50 years of age is most likely to experience stable blood pressure, a similar phenomenon observed throughout the world. Most of the representatives of this risk group are unaware of the likely presence of a dangerous pathology and its development, and do not notice the most important signals of their body. At the same time, irreparable transformations can occur inside the human body, affecting, first of all, the human vascular system. The main target in this case is the brain, but the kidneys, retina, adrenal glands, and heart become susceptible to damage.
Arteries, being under regular pressure, thicken, provoking pathological deformations, which causes local necrosis of the vascular walls. After a certain period, the fragility of the affected vessels increases, and partial protrusion of the walls occurs. In the event of a sharp hypertensive crisis, these areas are most prone to breakthroughs; here, with a high degree of probability, parenchymal hemorrhage can occur. The brain tissue is saturated with blood. In addition to these manifestations, damage to the walls of blood vessels and arteries can lead to high permeability, as a result of which blood fluid will leak through the walls and be absorbed into the nerve tissue of the brain, creating a diffusion phenomenon of fibers and cells.
Treatment
Therapy is etiotropic and symptomatic. That is, it is necessary to fight both the manifestations and the causes of the pathological process.
If we talk about correcting the main factor:
- Hypertension. Drugs are prescribed to lower blood pressure. Calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, sartans, centrally acting agents, diuretics. In strictly controlled dosages.
- Diabetes. Diet low in carbohydrates and without sugar. Insulin as needed during an acute attack.
- Bad habits. Refusal of cigarettes, alcohol, drugs. If necessary, get help from a narcologist.
- Arrhythmias. Specialized means for recovery: Amiodarone, Quinidine, beta blockers.
- Atherosclerosis. Fibrates, statins, nicotinic acid. Diet correction.
- Heart and vascular defects. Operation. Plastic or prosthetics.
- Anemia. Depends on the type. The use of iron supplements, vitamins, etc.
- Hormonal imbalances. Correction with synthetic substituents or other methods. Depends on a situation.
- Wrong lifestyle. Sufficient level of physical activity, drinking regime, etc.
- Use of certain medications. Refusal or replacement of medications.
Treatment of cerebral hemorrhage concerns eliminating the very cause of the pathological process and correcting the symptoms of the disorder.
Symptoms of hemorrhage
This condition can have many manifestations, depending on the cause of the hemorrhage, its location, volume and other factors.
As a rule, it develops spontaneously, against the background of complete or relative well-being, most often during the day, during wakefulness. The provoking factor is often a head injury, emotional or physical stress, or severe stress.
Testing simple nerve reflexes allows a doctor to identify a cerebral hemorrhage
Manifestations can be extremely varied and include the following symptoms:
- Severe, sharp headache.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Visual impairment.
- Uneven pupil size.
- Loss of coordination and balance.
- Impaired sensitivity and mobility of the limbs.
- Confusion or loss of consciousness, coma.
If such symptoms appear, you should contact an ambulance as soon as possible. A variety of disorders can manifest themselves in this way, but they all require timely initiation of treatment.