In this article we will look at the signs of cerebral gliosis.
During the functioning of neurons, various nerve impulses are transmitted throughout the human body. Some factors contribute to the instant destruction of nerve cells, against the background of which they are replaced by glial elements. In medicine, this condition is called cerebral gliosis. This physiological phenomenon serves as a natural process during the aging of the body. But it happens that metabolic microprocesses are significantly disrupted due to a decrease in brain performance. Such a failure can occur if the foci of gliosis in the white matter grow significantly, becoming large-scale. We will tell you what gliosis is, what its symptoms are and how treatment is carried out in our article.
Basic information about pathology
Experts in the field of neurology believe that such a deviation in brain cells cannot be classified as a separate disease, since this pathology is most likely a consequence of other disorders in the human body. Until changes in the cellular composition of the brain become abnormal, the performance of glial nerve cells is not affected in any way, but rather, even the opposite. They can have a protective effect, preventing various injuries and infections from entering the affected areas of the brain.
By replacing areas of dead neurons, glia perform the function of the previous structure and supply the metabolic processes of brain tissue. But the positive effect associated with the formation of glia occurs only before the onset of a certain condition. Immediately after its achievement, any changes become pathological, which over time can manifest itself in the form of certain clinical manifestations. Now let's figure out what causes cerebral gliosis.
What can the disease lead to?
Cystic gliosis changes in the brain, the consequences of which can lead to disorders of the brain and other body systems, are damage to the central nervous system, and their cause is pathological processes. The consequences may be changes in pressure, brain encephalitis, hypertension and hypertensive crises, multiple sclerosis, circulatory pathologies in organs and tissues. Any violation of the central nervous system does not go unnoticed and leads to tangible problems in all body systems and individual organs.
Studies are typically limited by small samples, flawed designs, and potentially biased cell counting methods. The interpretation of these studies is further complicated by the frequent presence of glial reactions in older adults without psychiatric illness. However, some of the positive results in the literature cannot be dismissed easily.
Neuroglia itself does not harm neurons and brain structures; on the contrary, it performs a protective function, protecting the brain from injury and infection. Therefore, in healthy people, glial cells are present normally, although they do not develop cerebral gliosis of vascular origin.
The main causes of gliosis development
A variety of factors can provoke the death of nerve tissue, and, consequently, gliosis of the brain. Here are the most common of them:
- The presence of a genetic or hereditary pathology.
- Development of tuberculous sclerosis.
- The appearance of chronic circulatory pathology in the brain.
- The appearance of skull and brain injuries.
- Inflammation that is triggered by neuronal infection.
- The presence of long-term progressive hypertension.
- The appearance of trauma at birth.
- Reducing sugar content.
- The effect of surgical interventions on the brain.
Against the background of birth trauma, which is accompanied by asphyxia, the death of cellular neurons can occur. This pathology in the first few months does not in any way affect child development. Regression, as a rule, occurs after the sixth month, which is expressed in the form of mental and physical developmental disorders. Factors that directly affect foci of gliosis in the brain are the following:
- Alcohol consumption. If you drink alcoholic beverages in moderation, it will help increase blood circulation. But increasing the dose of alcohol can cause disruption of neural connections.
- Taking drugs. Absolutely any type of narcotic drugs can lead to inflammation of blood vessels with focal death of brain tissue.
Causes of gliosis
Gliosis occurs due to damage to the central nervous system as a result of pathologies of fat metabolism. They are often caused by a hereditary factor. In 25% of all cases of the disease, they speak of an autosomal recessive mode of inheritance.
Alcohol and drug use damage neurons
The development of the disease is provoked by the use of narcotic substances - slow atrophy of the white matter occurs. With alcohol abuse, alcohol metabolites cause neuronal death.
The lesions develop against the background of diseases (secondary type of gliosis):
- encephalitis;
- epilepsy;
- stroke;
- multiple or tuberculous sclerosis;
- encephalopathy;
- chronic hypertension;
- hypoxia.
Less commonly, pathology is caused by traumatic brain injuries, infectious diseases with a large inflammatory focus.
In children, the death of neurons is often provoked by birth injuries, when prolonged asphyxia is observed during delivery. Symptoms develop no earlier than 4–6 months, manifesting themselves in the loss of sucking and swallowing reflexes, convulsive syndrome, paralysis, and muscle atrophy.
Forms of pathology and the degree of its development
The initial stage of the formation of gliosis in the brain is usually asymptomatic. Doctors, as a rule, detect the clinical manifestation of disorders against the background of the subsequent pathological spread of the gliosis focus. During necrotic processes, large areas of the brain are released in place of dead neuronal cells that form foci of gliosis. The forms of brain gliosis directly depend on various signs, nature and localization of its position:
- Single gliosis of the brain. This supratentorial type of disorder appears as a result of aging of the body or during birth trauma in a newborn. Such a deviation does not manifest itself in any way and is not dangerous to humans.
- Multiple gliosis of the brain can occur when cerebral circulation is impaired. This condition may be a manifestation of neurological pathology.
- Periventricular manifestations affect areas of the ventricles of the brain. As a result, cystic and gliotic changes may form.
- Anisomophoric manifestations can be detected in any part of the brain. They are a consequence of the chaotic proliferation of glial fiber.
- Perivascular disorders manifest themselves by entangling damaged vessels through glial cells, which is a sign of multiple sclerosis.
- Subcortical foci of gliosis in the white matter of the brain are diagnosed under the cortex.
- Diffuse lesions form multiple foci of cerebral gliosis, which can subsequently spread to the spinal cord.
- The marginal appearance may involve the surface of the brain.
Next, we will find out how this pathology can manifest itself.
What happens in the neuron graveyard?
They say that nerve cells are not restored or are restored, but very slowly, so they need to be protected. Such statements are still devoid of deep meaning, since people, dropping them in the right place and out of place, mean something completely different - you need to be less nervous. However, if neurons die, then other cellular elements take their place, because the central nervous system consists of different types of cells:
- Neurons, which we know as the basic structural units of nervous tissue - they generate and transmit signals;
- Ependymas - cellular elements that make up the lining of the ventricles of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord;
- Neuroglia are helper and protector cells that provide metabolic processes and form scar tissue after the death of neurons.
What actually happens in the event of massive neuronal death? Here's what: the place of dead nerve cells is trying to be (and is) taken by glial elements - neuroglial cells, which are the supporting tissue of the central nervous system. Neuroglia (or simply glia) is represented by a community of individual cells - derivatives of glioblasts: ependymocytes (researchers have different opinions regarding these cells - not everyone associates them with glial elements), Schwann cells, astrocytes. Glia are located between neurons and actively cooperate with them, helping to fulfill their main purpose - the generation and transmission of information from the site of excitation to the tissues of the body. Thus, glial elements cannot be called superfluous in the central nervous system. On the contrary, they, taking up to 40% of the entire substance occupying the skull, create optimal conditions for the proper functioning of the central nervous system; they are always “on the wing” and do not allow the biochemical reactions that ensure metabolic processes to stop. In addition, glia take over the tasks of nerve cells in case of extreme situations.
an example of the development of gliosis due to ischemia
In general, gliosis is compared to the healing of wounds on the skin, however, regarding the brain, events can be presented somewhat differently. Like this, for example: neurons die irreversibly, and their “cemetery” (the place where the necrotic process develops) comes, albeit alive, but still somewhat different cells, which, no matter how hard they try, cannot fully provide all the functions of neurons.
Meanwhile, something similar to a “scar” (scar), saturated with “successors”, at first tries in every possible way to perform the important tasks of the nervous tissue:
- They support metabolic reactions in the brain;
- Glia cells, instead of neurons, receive and transmit signals as best they can;
- Glial elements participate in the formation of new nerve fibers and protect tissues that remain healthy.
But no matter how hard neuroglial cells try to become full-fledged neurons, they will not succeed, because they are still different structures. Moreover, by multiplying and growing, new “hosts” trigger the development of a process such as gliosis.
Thus, gliosis of the brain is the result of the death of neurons and recovery processes that occur after the damaging effects of various factors. The essence of gliosis is the replacement of dead neurons with other cells, which form a kind of scar (irreversible process), saturated with glial elements. The new cells that replace the neurons isolate the foci of gliosis and thus protect the tissues that remain healthy.
Symptoms of pathology and its consequences
Single occurrences of cerebral gliosis usually do not reveal themselves. Such lesions are discovered randomly during a magnetic resonance examination. However, if the pathology is not detected in time, gliosis will multiply, forming new islands of atrophic change. The following symptoms of a disorder in the body should certainly alert a person:
- Observation of sudden and frequent changes in blood pressure.
- The presence of constant intense headaches that are not relieved by antispasmodics.
- Observation of decreased performance with the appearance of periodic dizziness.
- Loss of concentration and attention along with memory lapses.
- A significant decrease in auditory and, in addition, visual function.
- Disturbance in the functioning of the motor system.
It should be noted that the manifestation of the disease with the intensity of its symptoms directly depends on the specific area where foci of gliosis have formed in the brain:
- The supratentorial form can most often be expressed by visual disturbances.
- Gliosis in the white matter of the brain is often a consequence of traumatic injury and surgical intervention in this organ. This disorder can manifest itself in the form of dizziness, and, in addition, in the form of a convulsive state of the brain.
- Frequent and at the same time severe pain in the head can be a consequence of injury to the temporal lobe. In addition, such headaches can lead to gliosis of vascular origin, which will provoke constant pressure surges.
- In the absence of any other diseases that stimulate glial proliferation, the appearance of gliosis can be considered as a primary pathology. Such changes are considered age-related and appear against the background of natural aging.
Diagnostics
The proliferation of glial tissue does not have any special symptoms. Therefore, if the patient experiences any manifestations of dysfunction of the nervous system, the doctor prescribes a detailed examination, which can reveal the formation of gliosis. These diagnostic methods include:
- Computer (CT) or magnetic resonance (MRI) imaging. These methods allow not only to identify changes in the brain, but also to determine the cause of their occurrence. Tomography using a contrast agent can detect abnormalities associated with vascular dysfunction, the presence of brain tumors and other abnormalities. MRI makes it possible to detect changes in the white matter of the frontal lobes that cannot be seen using any other diagnostic methods.
- An electroencephalogram can detect disturbances in brain activity. Lesions formed in the white matter often contribute to the appearance of epilepsy attacks. Therefore, the EEG of the brain detects an increase in seizure activity, which makes it possible to prevent the occurrence of seizures.
Find out how an EEG works from functional diagnostics doctor Yulia Alekseevna Krupnova:
Gliotic transformations of the frontal lobes often provoke natural aging of the body, so it is usually diagnosed in elderly patients. This condition is normal.
Danger of developing gliosis
The location of the catalyst that causes pathological disorders primarily affects the consequences of gliosis of the brain substance. Pressure surges along with hypertension, encephalitis, multiple sclerosis and skull injuries can lead to subsequent formation of glia.
The life expectancy of people suffering from such changes primarily depends on the degree of damage to the systems and organs that are most important for life. The favorable prognosis of this disease depends on the timely diagnosis of disorders, and, in addition, on the adequacy of treatment. Next, we will look at what measures are being taken these days to treat brain gliosis.
Your IP address is blocked.
There is not a single organ or tissue in our body that can do without the oxygen and nutrients carried by the blood. This is especially true for vital organs - the heart and brain, because it is in them that metabolic processes proceed the fastest. But what happens if the delivery of nutrients from the blood is disrupted? What if small vessels and capillaries poorly supply blood to the body's tissues? Microangiopathy of the brain is a pathological process in the wall of the capillaries, as a result of which their patency is disrupted, which leads to a decrease or cessation of blood supply to the neurons of the brain. This in turn leads to the replacement of healthy neurons with foci of gliosis. The disease affects small vessels, causing consequences including death. Microangiopathy of the brain does not appear out of nowhere. Disturbances in the vascular wall can occur for 4 reasons:. Depending on the form of microangiopathy, the pathology can have the most negative consequences, so it is very important to monitor your condition and seek help at the first symptoms.
This brain disease can be present in different diseases at different stages. Most often, microangiopathy is equated to a complication of diabetes mellitus, impaired blood circulation in the lower extremities, or pathology in the brain.
Diagnosis and consequences of gliosis
Urine and blood tests do not provide accurate information for diagnosis, so examination is carried out using magnetic resonance and computed tomography (MRI and CT), and angiography is also effective. Children are examined using neurosonography.
MRI will help identify the following abnormalities:
- foci of gliosis, their number, size and location;
- at what level the brain structures are affected;
- what condition are the surrounding structures in?
Also, based on this procedure, there is a high probability of determining the cause of the pathology, which will make it possible to successfully overcome the disease in the future.
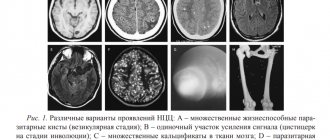
The lesion on MRI is determined from the ratio of extracellular and intracellular fluid in the existing formation.
There are several criteria that characterize the resulting image and provide information about the nature of the lesion:
- The intensity of the image matters - hyperintense and isointense signals are most often observed.
- The nature of the image is also assessed - there is a heterogeneous or homogeneous structure.
Before proceeding to treatment
Before treating gliosis, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination of the patient, and first of all, his brain. For this purpose, diagnostics are carried out using high-precision equipment, which include: MRI, CT, angiography. Magnetic resonance imaging is the most optimal option; it does not require additional diagnostic methods, since it is independently capable of providing information about the number of foci of gliosis, size, location, degree of damage, and the condition of nearby structures.
In addition, the study may reveal one important detail - the cause of pathological changes, which gives great hope for stopping the progression. Despite the fact that the irreversible changes that occur after the death of neurons and their replacement by glial cells no longer leave a chance to completely cure this pathology, it is unacceptable to refuse any measures of influence and give up. If the treatment started to eliminate the root cause (the underlying disease) is sufficiently effective, then the further development of glial replacement will most likely stop.
Gliosis of the brain and its treatment
In the event of suspicious symptoms, it is foolish to hope that the started process will not progress without the necessary treatment, remaining at its previous level. Even the most harmless disorder in the condition, which is characteristic of gliosis of vascular origin, can cause various complications, ranging from complete loss of speech function to paralysis of the limbs, intellectual and mechanical disorders, along with dementia.
It is possible to live with such symptoms, but all these manifestations will create discomfort for the patient, being at the same time very dangerous for his life. In the most severe cases, for example, with improper treatment or even a complete lack of therapy, death is possible. In this regard, treatment for such a disease should begin immediately after it is detected. On MRI, foci of gliosis in the brain are very clearly visible.
Effective therapeutic methods to combat this pathology have not yet been developed. First of all, it is necessary to treat the underlying disease that provoked this pathological algorithm. Such measures will help prevent the subsequent formation of a secondary lesion and stop the development and further aggravation of the disease.
One of the most important criteria in preventing further development of the disease is diet. First of all, it is necessary to exclude fatty foods, since it is precisely this that can have a positive effect on the progression, and, in addition, on the worsening of gliosis of the brain substance. This factor will have the greatest impact if the patient has a congenital disorder in fat metabolism. Immediately after the recommendations of a specialist, it is permissible to use nootropic drugs along with vasoactive and metabolic agents. But it must be said that the presented therapy is nonspecific. If the factors that provoked the development of the pathological disorder are not eliminated, therapy will be useless.
How else can foci of gliosis in the white matter of the brain be treated?
Traditional Treatments
If suspicious symptoms occur, you should not hope that the process that has begun will not progress without treatment and will remain at the same level. Even the most harmless at first glance disorder of the condition, which is characteristic of gliosis of vascular origin, can cause complications: complete impairment of speech functions, paralysis of the limbs, intellectual-mechanical disorders and dementia.
It is possible to live with such symptoms, but these manifestations create discomfort for a person and are dangerous to his life. In the most severe cases, with improper treatment or complete absence of therapy, death is likely. Therefore, treatment of cerebral gliosis must begin immediately after its detection.
No matter how many medications are prescribed to the patient, additional support for the body with the help of folk remedies will help improve the condition.
- Thus, at the initial stage, with a few lesions, herbs support the body well, helping to stabilize the blood supply and increase metabolism.
- For obesity, a raw food diet, fasting days, and fasting are recommended. It also helps cleanse the body of harmful substances that interfere with its normal functioning.
- The use of tinctures and decoctions, the action of which is aimed at combating the symptoms of the disease. You can buy ready-made balanced preparations for treatment at the pharmacy.
I would like to note that treatment with traditional methods can be effective only as a supplement to the main therapy prescribed by specialists. There will be no lasting effect from the use of medications and treatment with folk remedies if the cause of glial formation is not eliminated.
A special feature of the NS is that its main components, namely nerve cells, cannot be restored. Therefore, treatment of cerebral gliosis consists of treating the underlying disease, relieving symptoms of pathological changes, and also preventing pathological growth of the lesion.
In this case, the basic selection of medications must be agreed upon with a number of medical specialists and appropriate to the specific situation:
- The patient is prescribed drugs that affect brain activity. These include the following nootropics: “Glycised” or “Piracetam”;
- to improve cerebral circulation, the use of Actovegin or Cinnarizine is allowed;
- if the patient has thrombophilia or increased blood thickening - Ascorutin, Warfarin or Acetylsalicylic acid, which have a thinning effect;
- When a headache occurs, the use of antispasmodics, for example, the drug "Ketanov", is allowed.
Also, in some cases, multivitamin complexes are prescribed to quickly restore the body.
The use of surgical methods for excision of foci of gliosis is limited and is used only in extreme cases, for example, if the patient has persistent neurological problems in the form of epileptic seizures, convulsions, or disturbances in the functioning of internal organs and coordination of movements.
The sick person himself needs to more carefully monitor his lifestyle, follow all the doctor’s prescriptions, give up bad habits and adhere to a special diet.
The main prevention of any gliosis changes in the structures of the brain is maintaining a healthy lifestyle, while people at risk are recommended to do all possible physical exercises and ensure proper rest at night. It is also necessary to provide access to fresh air in stuffy rooms and, if possible, engage in mental work, with the help of which the process of restoring the cognitive functions of the brain will begin.
There are no medications that could eliminate the replacement process. Therapy is aimed at treating the underlying disease, which is associated with neuronal death, and improving the patient’s quality of life.
Medicines
Medicines:
- Vasoactive agents – Cinnarizine, Cavinton, Vinpocetine.
- Antiplatelet agents – Wessel Due F, derivatives of acetylsalicylic acid.
- Nootropics – Glycine, Actovegin, Cortexin.
- Vitamins E, B – Multi-Tabs, Complivit.
Glycine is a nootropic that is prescribed for gliosis.
These drugs improve fiber conductivity and brain activity. If gliosis of vascular origin is diagnosed, means are recommended to improve the elasticity of the vascular walls.
Surgical removal of gliosis lesions is rarely performed; neurosurgical intervention does not stop the emergence of new areas of gliosis without treating the underlying disease. The operation makes sense only when the lesions are single.
Indications for surgical treatment:
- glial lesions in the white matter cause seizures;
- the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is impaired;
- there is a malfunction in the functioning of internal organs;
- a tumor was discovered.
Surgical intervention is possible for tumors and other serious pathologies of the brain
With multiple multifocal lesions, only lifelong conservative treatment provides an effect.
Folk remedies
Conservative treatment is supported by folk remedies that improve the functioning of the cardiovascular system and metabolism:
- Grind the lemon and ginger root in a meat grinder or blender in a ratio of 1:2. Brew as tea in a thermos - 1 tbsp. l. gruel per 200 ml of boiling water. Dosage – 1 glass per day after meals.
- Grind the dried ginseng root into powder in a coffee grinder, pour in 1 tbsp. l. 200 ml of water, leave for 10 minutes. After straining, drink 1 glass for 30 days.
- Mix 1 tbsp. l. chamomile, elderberry, linden, ground fennel, pour 300 ml of boiling water, leave for 1 hour. Take 1 glass per day on an empty stomach.
- Dandelion tea to strengthen blood vessels is prepared from 200 g of ground roots and 1 liter of boiling water. Directions for use: 50 ml before meals three times a day, course duration 1 month.
- To strengthen the walls of blood vessels, take 50 g of rowan fruit, 1 tbsp. l. linden blossom, 1 tsp. dill seeds, 1 tsp. dried wormwood. Pour 1 liter of boiling water, leave for 15 minutes. Drink 100 ml 2 times a day before meals for 20–30 days.
- Mix nettle leaves and rowan in a ratio of 3:7, pour 0.5 liters of boiling water, boil for 10 minutes, and leave for 3 hours. Drink the decoction daily, 200 ml per day for 30–60 days.
- A drink to improve cerebral circulation. Take 1 tsp. alfalfa seeds, pour half a glass of boiling water, take this portion once a day before meals for 9 months.
- Orchis tincture. Cut 10 plant roots into 2 parts and place in a dark glass bottle. Pour 1 glass of 96% alcohol, transfer to a dark room for 2 weeks. Take 1 tsp on an empty stomach. infusion, course 1 month.
- Grind 10 mulberry leaves, pour 500 ml of boiling water, boil for 3 minutes, strain. Use for 3 months once a day after meals.
- To clean the walls of blood vessels from cholesterol plaques - garlic tincture. Grind 5 cloves in a meat grinder, mix with 1 tbsp. l. grated horseradish, pour 50 ml of unrefined olive or sunflower oil. Transfer to a jar, close the lid tightly, and put in the refrigerator. Before use, mix 1 tbsp. l. prepared mixture with 0.5 tbsp. l. fresh lemon juice. Take three times a day for a minimum of 3 months for 30–35 minutes. before meals.
Garlic tincture cleanses the walls of blood vessels from cholesterol plaques
Some components of products prepared according to folk recipes can cause allergies. Be careful with citrus fruits and honey. Alcohol-based tinctures should not be taken during pregnancy or by children under 18 years of age.
Treatment of cerebral gliosis can be divided into 3 important stages:
- Preventative. If a few (single) accumulations of glia were found, no matter in what part of the brain, the human body is capable of independently eliminating such problems. There will be no consequences from small formations. However, the doctor may recommend that the patient take the necessary measures - lead a healthy lifestyle, regularly engage in light physical activity (exercise, walking), give up alcohol and smoking, as well as taking drugs, and eat healthy foods.
- Drug therapy. The doctor prescribes medications to the patient whose action is aimed at restoring brain activity and regulating nerve impulses (nootropics). In addition, if necessary, medications are used that normalize the functioning of blood vessels, strengthening them (vitamins C, P, E). For elevated cholesterol levels, antiatherosclerotic drugs (statins, fibrates) are prescribed.
- Brain surgeries. This type of treatment is used only in extreme and advanced cases. So, for example, they come to the surgical method if the patient suffers from regular attacks of epilepsy and seizures. Removal is possible only if there are single foci of gliosis. Numerous accumulations cannot be removed by surgery.
In addition, doctors advise obese and overweight patients to lose weight and adjust their diet.
We have roughly explained the concept of “brain gliosis” - what it is and how it can be identified. With this information, you will know when and where to go to improve your health problems. Don't forget to visit your doctor and stay healthy!
There is currently no effective treatment for such scars. After a general diagnosis of all remaining body functions has been carried out, the neurologist will prescribe symptomatic treatment. It will be aimed at the catalyst that provoked the appearance of scars. The purpose of the drugs is to reduce its influence. Medicines are also prescribed to help avoid the appearance of new lesions.
An important role is played by the patient’s willingness to comply with all the neurologist’s instructions. He must not only take medications, but also adhere to a diet, give up bad habits, and lead an active life. We must fight with all available means.
Turning to Traditional Medicine
Many people can live for years without knowing about this disease. But it is not recommended to trigger glial brain disorders. The longer patients delay treatment, the more difficult it will be to cope with the consequences of the disease in the future. There are no drugs that would eliminate glial formations, since glial disorders are not classified as an independent disease. In order to improve the patient's well-being, traditional medicine turns to the following three areas of treatment:
- Carrying out prevention. At an early stage of the disease, the body of an adult can cope with negative changes on its own. Experts recommend that patients completely quit bad habits by changing their diet. It is also very important to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
- Use of medications. Doctors prescribe the necessary treatment for the disease that provoked gliosis of vascular origin in the brain. If lesions appear, medications are prescribed that restore and strengthen the walls of the arteries. Drugs are also used that increase brain activity by improving nerve fiber conduction.
- Carrying out surgical treatment. If a patient has abnormalities in the functioning of internal organs along with convulsive and epileptic seizures, then neurosurgical intervention is considered appropriate.
Treatment of cerebral gliosis is not limited to this.
Causes
Only a doctor can tell you which lesions in the brain were detected on MRI for which diseases.
And therefore, it is necessary to carry out diagnostics and obtain data after the study. Foci of damage to nervous tissue in the brain are present on MRI images in the following diseases:
- Atherosclerosis;
- Angiopathy;
- Hypertension;
- Multiple sclerosis;
- Vasculitis;
- Beignet's disease;
- Neurosyphilis, tick-borne borreliosis;
- Progressive multifocal leukoncephalopathy;
- Disseminated encephalomyelitis.
Their presence may be a consequence of carbon monoxide poisoning, head injury, its complications, or concussion.
In young children, chromosomal abnormalities, hypoxia, and improper lifestyle of a pregnant woman can also provoke the appearance of multiple foci of brain damage.
Brain diseases are always quite serious. Of course, any problems in the body require attention, but in the case of the brain, even the smallest problem must be carefully considered.
One of the brain diseases is gliosis. This term refers to the process of replacing dead nerve cells with special glial cells. They protect the nervous system, help neurons transmit impulses and form new connections.
Their number is 10 times higher than that of other cells of the nervous system, but it is the accumulation of glia in a certain area of the organ that is called cerebral gliosis.
Gliosis of the white matter of the brain interferes with the full functioning of the nervous system, but it is necessary to fight this disease not directly, but by investigating its cause.
Basically, the catalysts for the appearance of glial accumulations are infectious or other causes of diseases of the nervous system, such as:
- hereditary diseases associated with the death of neurons;
- multiple sclerosis - destruction of nerve tissue fibers in the brain and spinal cord;
- tuberous sclerosis is a genetic disease in which benign tumors develop;
- epilepsy;
- trauma at birth (in infants);
- head and back injuries;
- high blood pressure and encephalopathy;
- cerebral edema;
- chronic or acute cerebrovascular accident (CVA/CVA);
- hypoxia – acute lack of oxygen in tissues;
- neuroinfections such as leukoencephalitis, encephalomyelitis, etc., caused by viruses or bacteria;
- low blood sugar;
- high consumption of animal fats;
- previous operations;
Glial accumulations are often observed in athletes who have suffered head concussions, as well as in those who are exposed to bad habits such as alcohol and drugs that contribute to the destruction of neurons. These changes may also occur in patients taking narcotic-based medications.
Symptoms
Gliosis is a disease that can masquerade as a number of problems associated with the cardiovascular and nervous systems. Its most common symptoms are:
- constant headaches, migraines, dizziness;
- sudden changes in blood pressure;
- the appearance of problems with vision or hearing;
- memory and attention disorder;
- the appearance of convulsions, paralysis.
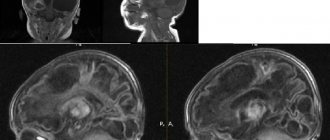
These problems can also appear in a number of other diseases that are completely different from gliosis, so for an accurate diagnosis you need to contact a specialist. Sometimes cerebral gliosis is detected already with an MRI of the brain, although the patient does not feel any negative changes.
The distribution of glial cells occurs in different ways. Depending on their location in the body, their foci are divided into:
- anisomorphic – irregular order of glia distribution;
- isomorphic – correct formation of glial cells;
- marginal – growth of glial cells in the intrathecal spaces of the brain;
- diffuse – accelerated spread of gliosis both in the brain and spinal cord;
- perivascular or vascular - gliosis located along the vessels. Most often it appears after atherosclerosis.
- fibrous – processes of glial cells exceed the size of their bodies;
- marginal - glial elements are located on the surface of the brain;
Foci of gliosis according to their size can be divided into single, few (up to 3 foci) and multiple. Accordingly, isolated areas of development of glial cells can occur in old age, when the body can no longer carry out proper tissue regeneration, for example, the spread of gliosis in the frontal lobes.
Diagnostics
Detection of this disease is impossible without the use of special electronic equipment. Diagnosis can be carried out using one or more methods:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) – obtaining images of internal organs and tissues by exposing the object of study to electromagnetic waves. This method is used to find abnormalities in the functioning of organs, tumors and improper tissue regeneration;
- computed tomography (CT) – obtaining images of internal organs using x-rays and subsequent data processing on a computer. It helps to identify changes associated with blood vessels, for example, obstructed blood circulation, thrombosis, etc.;
- electroencephalography (EEG) - measurement of brain activity using electrodes and computer data processing. It is applicable when it is necessary to record problems of the nervous system, such as seizures or epilepsy.
All these methods are applicable in specialized clinics equipped with modern medical devices.
Treatment
Cerebral gliosis itself is not a disease, but a complication that was caused by chronic or acquired diseases of the nervous system. Therefore, there is no specific medicine or procedure to eliminate such tumors.
Treatment is aimed at the specific disease that caused the development of gliosis. It should be noted that medications are prescribed directly by a doctor.
During drug treatment, it is necessary to take special agents that can maintain and improve the condition of blood vessels. Also, with this disease, the brain may experience a lack of oxygen, so patients are often prescribed antioxidants that neutralize oxidative processes, and nootropics that help improve brain activity.
Surgery
Surgical intervention is used when large single foci of gliosis appear and in case of their negative impact on an organ or system that cannot be ignored, for example, during seizures. But most often, surgery is resorted to if it is impossible to control the patient’s well-being with the help of medications.
In addition to traditional methods of treatment, a patient suffering from this disease must eat in accordance with a special diet and take preventive measures to maintain normal functioning of the body and prevent the development of pathologies against the background of gliosis.
Nutrition and supplements
With gliosis of the brain, it is necessary to normalize your daily nutrition. The most important condition here is the exclusion of fatty foods and dishes from the diet, because fatty compounds disrupt the functioning of neurons and lead to their death.
Alcohol and herbal infusions
As mentioned earlier, a patient with this disease may have problems with cerebral circulation.
Osteochondrosis of the spine: symptoms and treatment
In addition to medications that normalize this process, you can also take tinctures from various herbs, which will be a source of useful substances for the functioning of blood vessels. For example, you can buy ready-made herbal tinctures at the pharmacy, mix them and take them as an additional remedy, if this is possible for medical reasons.
For this alcohol infusion you need:
- tinctures of valerian roots, motherwort, evasive peony, hawthorn - in 100 ml containers;
- eucalyptus – 50 ml;
- mint – 25 ml;
- Corvalol – 30 ml;
- whole cloves – 10 pieces.
Before use, this mixture should sit for about two weeks in a cool place, avoiding exposure to sunlight. Take 3 times a day, 30 drops diluted in a glass of water, half an hour before meals. The total duration of the course is from 1 to 3 months.
To prevent the development of atherosclerosis against the background of weakened blood vessels and gliosis, patients need to take a herbal infusion. It may include components such as:
- immortelle, oregano, mint, flax seed - one part each;
- hawthorn and birch leaves - two parts each;
To prepare the tincture, you need to mix the mixture and add one tablespoon per 200 ml of water. Afterwards, you need to boil the broth and leave it for about 2 hours. Before taking, you need to strain and distribute the herb into 3 doses per day. The course of treatment lasts 1 month.
Herbs and herbs (treatment with folk remedies)
Also, to improve blood circulation, you can take herbs such as:
- Dandelion root helps lower cholesterol and strengthens blood vessels. Its decoction should be taken 50 g before meals.
- Dill seeds restore blood circulation and help with abnormal blood pressure.
- St. John's wort has the ability to relieve vascular spasms and restore tissue.
- lemon balm nourishes the cerebral cortex and the walls of blood vessels, helps calm the nerves and restore nerve cells;
- Celandine helps to recover from a post-stroke condition. Its decoction should be drunk 2 times a day.
- Sweet clover is saturated with many vitamins that nourish the heart muscle and its main vessels, and cleanse the lymph. It should be taken with caution and in small doses; the herb must be infused in the proportion of a teaspoon per glass of boiling water for two hours. After drinking 3 times a day before meals, one third of a glass, for about 30 days.
- Anise lofant helps with various diseases, cleanses blood vessels and ducts, it is especially useful for those who have had a heart attack or have problems with changes in blood pressure. Its collection, from 50 to 200 g, must be poured with 0.5 liters of cognac or vodka and left in a dark place for 20 days, not forgetting to shake every day. The infusion should be taken for about 30 days, 2 times a day, 30 minutes before meals, a teaspoon in 30 ml of water.
- Sophora japonica not only restores the balance of blood vessels, but also removes free radicals from the body. Its infusion can also be made with vodka or cognac. You need to take 100 g of fruit, pour in 0.5 liters of alcohol and leave for 3 weeks, after straining, take 3 times a day, about 35 drops, an hour after eating.
- mistletoe helps with convulsions, paralysis and sclerosis. One tablespoon of herb should be poured into a glass of chilled boiled water and left overnight. Drink 1/3 glass 3 times a day before meals, for about a month.
- Dioscorea Caucasica helps with problems with blood vessels and heart rhythm, vision and headaches. The root of this herb must be crushed and poured boiling water at the rate of a teaspoon to a glass of boiling water, and then kept in a steam bath for about 20 minutes. Take a tablespoon 3 times a day, after meals, for about 4 months with breaks of a week.
Turning to traditional methods of therapy
No matter how many medications are prescribed to the patient, additional maintenance of the body through the use of folk remedies will help improve the general condition.
- At the initial stage, in the presence of a few lesions, herbs perfectly support the human body, which help stabilize the blood supply system and increase metabolism.
- If a patient develops obesity, a diet based on a raw food diet is recommended; fasting days with periodic fasting are also required. This will contribute to the overall cleansing of the body from various substances that interfere with its healthy functioning.
- Taking tinctures and various decoctions, the action of which is aimed at combating the symptoms of the disease. At the pharmacy you can buy ready-made preparations that are balanced for treatment.
It must be emphasized that treatment using traditional methods can only be effective as a complement to traditional therapy, which should be prescribed by specialists. A long-term effect from the use of medications and treatment using traditional methods will not be achieved until the cause of glial formation is eliminated. Next, we will find out what preventive measures will help people avoid developing this disease.
How long do adults with cerebral gliosis live? This is a common question. More on this later.
Signs of gliosis
The human brain consists of an ependymal membrane, glial cells and neurons. The latter transmit nerve impulses throughout the body. Pathological processes affecting the central nervous system (CNS) in some cases lead to the death of neurons.
Glial cells in a normal state perform protective, trophic and secretory functions and are responsible for cellular metabolism. They make up 40% of the total mass of the brain matter. The destruction of neurons stimulates the process of filling the resulting voids with glia, which provide nutrition to the cells of the nervous tissue. In this case, the quantitative ratio of cerebral elements changes.
The process of replacing neurons with neuroglial cells is called gliosis and is considered a secondary disease of the central nervous system. The causes of the pathological phenomenon can be age-related changes, trauma, demyelination and ischemia of cerebral structures.
Microangiopathy of the brain, focal changes on MRI (axial projection)
In the early stages, gliosis has no clinical manifestations; the deviation can be diagnosed with a magnetic resonance scan of the brain. As the process progresses, characteristic symptoms arise:
- headache;
- paresis, paralysis;
- speech disorder;
- hearing loss;
- loss of visual acuity;
- lack of coordination in space;
- memory loss;
- decreased concentration;
- development of hypertension.
In newborns, loss of the swallowing reflex, hearing and vision impairment, and symptoms of hydrocephalus are noted.
The clinical picture depends on the type of gliosis, the localization of the process and the nature of the disease that caused the death of nerve cells. Supratentorial focal changes (located above the cerebellum) lead to impaired motor activity and fine motor skills.
Carrying out prevention
In order to be able to prevent the progression of glial formation and eliminate the occurrence of this disease, it is necessary to follow some rules of prevention, here are the main ones:
- Every person needs quality rest along with fresh air and good sleep. If you adhere to the correct daily routine, a person will be able to maintain a healthy nervous system.
- Engaging in feasible physical activity will also contribute to the overall strengthening of the nervous system. In order for the body to be resilient, and at the same time strong, it is not at all necessary to devote a lot of time to sports activities. It will be enough just to devote a little time to a certain set of exercises every day.
- Nutrition of the body. It is worth completely abandoning harmful animal fats. Products that are vitally important to include in your diet as part of the prevention of various disorders are, first of all, cereals along with vegetables, fruits and lean meats. When cooking, it is best to use the technique of stewing or steaming food.
- It is very important to completely give up bad habits.
The preventive measures presented above are useful for all people; they will significantly limit the possibility of developing such an unwanted disease as cerebral gliosis. In addition, they can help slow the progression of an existing disease.
Symptoms of the disease
A decrease in brain activity and the formation of atrophic tissue in it occurs due to the occurrence of foci of gliosis there.
Often this disease has no symptoms at all, but you should pay attention to the following changes in the body:
- high frequency and intensity of headaches (with any mental activity or attempts to concentrate);
- frequent changes in pressure (with vascular gliosis, the lumen in the arteries narrows, which leads to a deterioration in well-being);
- deterioration of coordination;
- presence of seizures;
- decreased hearing and vision;
- dizziness and seizures.
Symptoms in infants and newborns include:
- decreased degree of activity;
- changing the reaction to irritation;
- presence of signs of hydrocephalus;
- hypertonicity and hypotonicity of the limbs.
Single foci of gliosis can occur in many people (more often in those suffering from hypertension); identifying such foci is a rather complex process. They are usually found by chance during various examinations. In the process of neuroglial reproduction, new processes are formed, and changes occur in the structure of brain tissue, which leads to pathology.
Due to hypertension, hypertensive encephalopathy develops over time. The area of brain damage can be significant if the process of neuronal cell death is not stopped in time, so at the slightest suspicion it is worth undergoing an examination.
Often, gliosis provokes the occurrence of diseases of the nervous system that cannot be completely cured, but medicine can prevent their development.
In the diffuse form of the disease, multiple foci are found in the brain. The functioning of the nervous system is greatly hampered, and the symptoms are pronounced.
Most often, gliosis is a consequence of various diseases of the central nervous system, the symptoms of which may also be signs of gliosis. The symptoms of the disease are determined by the location of the lesion. To identify this pathology, it is necessary to conduct a complex of studies.
Glionic changes - what are they?
Until pathological processes of change occur in the structure of cells, the number of glia in the brain does not affect the performance of all brain functions.
Neuroglia in the brain perform certain functions that protect brain cells from the influence of infections, and also serve as protective ballast in case of brain injury.
The greater the number of glia in a healthy brain, the better the brain organs perform their functional duties.
Gliosis of brain cells is the body’s defense against damage to the fibers of the nervous system. When destruction and death of neurons occurs, glial cells take their place and completely try to replace neurons in all their functions.
Glia do not fully carry out metabolic processes in brain tissue, so the pathology of gliosis develops with its clinical manifestations.