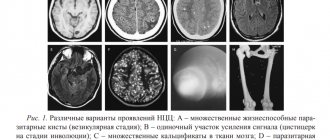
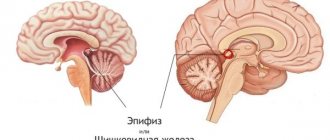
Multiple cystic cavities in different parts of the brain are common in newborns. Most species are not dangerous, as they go away on their own by the age of one year. Large multicysts cause encephalomalacia due to the capture of a large part of the brain parenchyma and hemispheres.
The nature of tissue damage is determined by the method of radiation neuroimaging - MRI. Other synonyms for pathology:
- Polycystic transformation;
- Multicystic encephalopathy;
- Cystic encephalomalacia;
- Multicystic brain disease.
The frequent occurrence of nosology in newborns is explained by perinatal pathology, hypoxic conditions during childbirth, and injuries during passage through the birth canal. The consequences of the pathology are dangerous: necrosis, multiple hemorrhages inside the brain parenchyma. The disease is accompanied by a concomitant proliferation of neuroglia and the formation of non-functional areas of the cerebral parenchyma.
Morphological structure of multicystic encephalomalacia in children
A section of the brain of a deceased child reveals a number of morphological features:
- Reduction in size;
- Multiple cysts separated by glial septa;
- Thin layers inside the cavity (trabeculae);
- Atrophy of cortical structures, white matter;
- Excessive fluid accumulation.
Microscopic examination of the brain reveals areas of calcium accumulation within the cystic cavities. Areas of neuronal calcification are observed around the defects. Histologists identify astrocytes, basophilic fibers, macrophages, and accumulation of basophilic clumps inside axons.
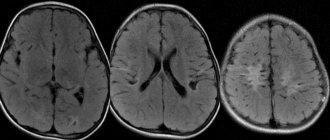
Encephalomalacia in a newborn MRI
Brain cyst in newborns and infants
When making any diagnosis related to formations in the brain, parents have many different questions. It is very important to know about the manifestations of such diseases in infants.
This will help prevent life-threatening conditions in the future. Many parents are interested in brain cysts in newborns and infants.
When making any diagnosis related to formations in the brain, parents have many different questions. It is very important to know about the manifestations of such diseases in infants. This will help prevent life-threatening conditions in the future. Many parents are interested in brain cysts in newborns and infants.
Causes of cerebral multicystic disease in newborns
The main etiological factor is perinatal damage to the central nervous system due to infection of the mother, the presence of concomitant diseases, a large fetus, or the birth of a child prematurely. Statistics show a high incidence of periventricular leukomalacia in babies weighing up to two kilograms.
The acquired form of multicystic leukomalacia is not observed. The main causes of nosology:
- Drug use while pregnant;
- Bacterial infection;
- Inflammatory process of the umbilical cord (funisitis);
- Microbial infection of the membranes (chorioamnionitis);
- Infection of amniotic fluid;
- Prenatal, vaginal hemorrhages of pregnant women;
- Formation of placental vascular anastomoses.
In newborns, symptoms of multicystic disease do not appear immediately, especially with small cavities.
The main stages of multicystic encephalopathy
Morphological changes suggest the extent of the disease:
- First, nerve cells die, scar tissue forms at the site of the defect;
- The second is that circulatory disorders in damaged areas provoke ischemic conditions. Foci of necrosis appear;
- Third, multiple cysts with perifocal inflammation cause destruction of the white matter of the hemispheres and cortical structures. Clinical symptoms appear.
The severe form of the disease leads to multiple consequences of hypoxic damage to the central nervous system.
Encephalopathy
Symptoms and signs of cerebral encephalopathy develop in children and adults for various reasons and are difficult to treat. Often the consequences of degenerative changes in white and gray matter are irreversible and potentially fatal.
Encephalopathy of the brain is a disease that is a variant of cerebrovascular disease (CVD). It occurs as a result of metabolic disorders in the neurons of the brain, against the background of chronic cerebrovascular insufficiency (CCF). Oxygen deficiency leads to the death of neurons. Swelling of the meninges occurs, local areas of hemorrhage form, and the functioning of the central nervous system is disrupted.
If you follow a special regime and regularly undergo courses of treatment procedures, a person with such a diagnosis will live a long and full life.
Pathogenesis of encephalomalacia of the brain
Cysts take a week to form. Under the influence of provoking factors, white matter necrosis develops and neurons are destroyed. Defects are dissolved by macrophages and phagocytes. Cysts form in places of destruction. Neuroglial growths appear along the periphery. The final stage is the development of scar tissue. If the process continues, atrophic changes in cerebral tissue develop after three to four months.
Periventricular leukomalacia can form in utero, but more often develops in the first hours after birth. There is a high probability of multicystic rearrangement of the hemispheres in newborns whose mothers had severe toxicosis, suffered from hepatitis, and pyelonephritis.
Doctors at the maternity ward diagnose the baby’s atypical condition:
- Convulsive syndrome occurs;
- Atypical reflexes;
- Increased muscle tone.
Hyperexcitability syndrome is observed in 50% of children.
Subsequent progression of the nosology causes persistent divergent strabismus in sixty percent of children, cerebral palsy in 90%.
Multicystic encephalomalacia: causes, symptoms, diagnosis
Multiple cystic cavities in different parts of the brain are common in newborns.
Most species are not dangerous, as they go away on their own by the age of one year. Large multicysts cause encephalomalacia due to the capture of a large part of the brain parenchyma and hemispheres. The nature of tissue damage is determined by the method of radiation neuroimaging - MRI. Other synonyms for pathology:
- Polycystic transformation;
- Multicystic encephalopathy;
- Cystic encephalomalacia;
- Multicystic brain disease.
The frequent occurrence of nosology in newborns is explained by perinatal pathology, hypoxic conditions during childbirth, and injuries during passage through the birth canal.
The consequences of the pathology are dangerous: necrosis, multiple hemorrhages inside the brain parenchyma.
The disease is accompanied by a concomitant proliferation of neuroglia and the formation of non-functional areas of the cerebral parenchyma.
Morphological structure of multicystic encephalomalacia in children
A section of the brain of a deceased child reveals a number of morphological features:
- Reduction in size;
- Multiple cysts separated by glial septa;
- Thin layers inside the cavity (trabeculae);
- Atrophy of cortical structures, white matter;
- Excessive fluid accumulation.
Microscopic examination of the brain reveals areas of calcium accumulation within the cystic cavities. Areas of neuronal calcification are observed around the defects. Histologists identify astrocytes, basophilic fibers, macrophages, and accumulation of basophilic clumps inside axons.
Encephalomalacia in a newborn MRI
Causes of cerebral multicystic disease in newborns
The main etiological factor is perinatal damage to the central nervous system due to infection of the mother, the presence of concomitant diseases, a large fetus, or the birth of a child prematurely. Statistics show a high incidence of periventricular leukomalacia in babies weighing up to two kilograms.
The acquired form of multicystic leukomalacia is not observed. The main causes of nosology:
- Drug use while pregnant;
- Bacterial infection;
- Inflammatory process of the umbilical cord ( funisitis );
- Microbial infection of the membranes ( chorioamnionitis );
- Infection of amniotic fluid;
- Prenatal, vaginal hemorrhages of pregnant women;
- Formation of placental vascular anastomoses.
In newborns, symptoms of multicystic disease do not appear immediately, especially with small cavities.
The main stages of multicystic encephalopathy
Morphological changes suggest the extent of the disease:
- First, nerve cells die, scar tissue forms at the site of the defect;
- The second is that circulatory disorders in damaged areas provoke ischemic conditions. Foci of necrosis appear;
- Third, multiple cysts with perifocal inflammation cause destruction of the white matter of the hemispheres and cortical structures. Clinical symptoms appear.
The severe form of the disease leads to multiple consequences of hypoxic damage to the central nervous system.
Pathogenesis of encephalomalacia of the brain
Cysts take a week to form. Under the influence of provoking factors, white matter necrosis develops and neurons are destroyed. Defects are dissolved by macrophages and phagocytes.
Cysts form in places of destruction. Neuroglial growths appear along the periphery. The final stage is the development of scar tissue.
If the process continues, atrophic changes in cerebral tissue develop after three to four months.
Periventricular leukomalacia can form in utero, but more often develops in the first hours after birth. There is a high probability of multicystic rearrangement of the hemispheres in newborns whose mothers had severe toxicosis, suffered from hepatitis, and pyelonephritis.
Doctors at the maternity ward diagnose the baby’s atypical condition:
- Convulsive syndrome occurs;
- Atypical reflexes;
- Increased muscle tone.
Hyperexcitability syndrome is observed in 50% of children.
Forms with the presence of a stage of “imaginary well-being” are characterized by the appearance of clinical symptoms in the fourth to eighth month. Manifestations are caused by cerebral insufficiency, impaired swallowing, increased pressure, and decreased respiratory movements.
Subsequent progression of the nosology causes persistent divergent strabismus in sixty percent of children, cerebral palsy in 90%.
Main clinical symptoms of multicystic leukomalacia
Signs of the disease are determined by the size of the formation. A small lesion provokes mild symptoms. Localization of a large multicyst in the frontal lobe leads to the most pronounced manifestations:
- Severe headaches;
- Decreased hearing, vision, tactile sensitivity;
- Hypertonic contractions of many muscles of the limbs;
- The appearance of extraneous sounds (auditory hallucinations);
- Paralysis, paresis of limbs;
- Vomiting reflex;
- Increased psycho-emotional state;
- Convulsive seizures;
- Pulsation of cerebral vessels.
The main symptoms depend on the location of the damaged area of the brain. Each segment of the brain performs specific functions.
Consequences of multicystic disease in newborns and infants
The most dangerous complication is periventricular leukomalacia. In practice, doctors have determined the relationship between the baby’s low weight and the increased incidence of the condition. The nosology is especially common in newborns weighing up to two kilograms.
Hypoxic-ischemic damage to the central nervous system in infants causes life-threatening consequences:
- Extensive hemorrhages;
- Damage to the respiratory and cardiovascular centers;
- Cerebral infarction from dystrophy, softening of the white matter.
An aggravation of the condition can be observed in spring and winter. The etiological factor of the pathology is the meteorological dependence of the woman’s blood vessels.
The cause of death may be pneumonia and distress syndromes. Without artificial ventilation, such children die.
There is also a risk if the newborn is of normal weight. Encephalomalacia is caused by hypoxic conditions during fetal development. Lack of oxygen leads to the death of cerebral structures, which are quickly destroyed.
Oxygen starvation becomes an etiological factor in the subsequent launch of a whole cascade of biochemical and metabolic disorders. The gradual progression of the disease contributes to the formation of blood clots and hemorrhages.
The prognosis for life and health depends on the degree of multicystic disease, size, and localization of formations. Localization of cysts in the area of vital structures shortens the baby’s life expectancy. Mortality is caused by progressive multiple cysts of the hemispheres, stem structures, and cortical structures.
Diagnosis of leukomalacia
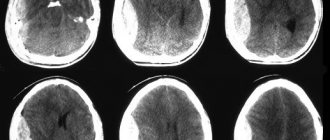
The clinical picture helps determine the nosology immediately after birth. Identification of any sign requires confirmation by neuroimaging methods. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging (CT and MRI) help to detect all changes in the cerebral parenchyma. Impaired blood supply is verified by contrast examinations - angiography.
Encephalomalacia on CT is visualized in the presence of medium and large cysts with a scar wall. Differential diagnosis using MR angiography makes it possible to verify primary multicystic encephalomalacia of the brain from echinococcal and alveococcal cavities.
In newborns, the fontanelles are represented by cartilaginous tissue. Before complete healing, ultrasound allows one to study the child’s cerebral structures.
Source: //mrt-kt-golovnogo-mozga.ru/article/mul-tikistoznaya-encefalomalyaciya
Main clinical symptoms of multicystic leukomalacia
Signs of the disease are determined by the size of the formation. A small lesion provokes mild symptoms. Localization of a large multicyst in the frontal lobe leads to the most pronounced manifestations:
- Severe headaches;
- Decreased hearing, vision, tactile sensitivity;
- Hypertonic contractions of many muscles of the limbs;
- The appearance of extraneous sounds (auditory hallucinations);
- Paralysis, paresis of limbs;
- Vomiting reflex;
- Increased psycho-emotional state;
- Convulsive seizures;
- Pulsation of cerebral vessels.
The main symptoms depend on the location of the damaged area of the brain. Each segment of the brain performs specific functions.
Diagnosis of leukomalacia
The clinical picture helps determine the nosology immediately after birth. Identification of any sign requires confirmation by neuroimaging methods. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging (CT and MRI) help to detect all changes in the cerebral parenchyma. Impaired blood supply is verified by contrast examinations - angiography.
Encephalomalacia on CT is visualized in the presence of medium and large cysts with a scar wall. Differential diagnosis using MR angiography makes it possible to verify primary multicystic encephalomalacia of the brain from echinococcal and alveococcal cavities.
In newborns, the fontanelles are represented by cartilaginous tissue. Before complete healing, ultrasound allows one to study the child’s cerebral structures.
Encephalopathy is not a disease, but a syndrome that is caused by certain factors. Represents disturbances in the functioning and structure of the brain. Due to the slow development, it is quite easy to stop progress. Treatment comes down to eliminating the causes. If proper attention is not given, coma and subsequent death are possible.
Possible consequences
The flexibility of brain structures significantly increases the compensation that is required in the presence of such a dangerous disease.
Lack of treatment leads to persistent disorders:
- vascular encephalomalacia of the brain - to dementia;
- after injury – to epilepsy;
- bilirubin - to loss of hearing and vision in children, developmental delays.
The most dangerous stages of development:
One of the severe types of encephalopathy is encephalomalacia - softening of brain tissue with the formation of multiple cysts, accompanied by the development of serious neuropsychiatric disorders that affect lifestyle and the functioning of the central nervous system. Over time, the symptoms, like the pathology, progress. Therefore, at the first suspicion of this syndrome, it is necessary to urgently seek help from doctors and carefully comply with all treatment conditions.
Causes
Encephalopathy is divided into 2 main categories:
In children it occurs against the background of:
- various genetic malfunctions in brain formation;
- birth injuries affecting the baby's head;
- lesions during pregnancy by toxins and infectious agents.
If encephalopathy begins in the perinatal period, then doctors take the problem as seriously as possible, because it is at this moment that the disease is most dangerous for the future health of the little person.
Depending on the type of encephalopathy, specific causes of the disease can be identified:
- presence of severe infections;
- pathologies in the vessels of the central nervous system;
- the presence of neoplasms (multycystic encephalomalacia);
- traumatic brain injury (TBI).
- Post-traumatic.
As the name suggests, the main cause is injury.
Appears as a result of poisoning. Expressed by severe nerve and mental disorders.
Occurs after ion radiation.
Features of the disease
The diagnosis of cerebral encephalopathy in adults or children means that for some reason the metabolism of the main organ of the human body has been disrupted.
Regular oxygen deficiency sooner or later leads to critical cell damage, which the body no longer has enough resources to restore.
This is a disease that always occurs against the background of some pathology.
The prognosis of vascular encephalopathy of the brain (encephaloneuropathy) in adults and children is questionable; with regular treatment and following the doctor’s recommendations, the increase in negative phenomena can be slowed down. But it is impossible to avoid deviations and recover.
The person will experience deterioration and then loss of cognitive function. In this case, acute attacks may be replaced by a temporary improvement in the patient’s condition.
Symptoms and signs
They are determined by the type of encephalopathy and the degree of development of the syndrome.
- sleep disorders;
- failures in coordination;
- fatigue, fatigue;
- signs of apathy;
- memory loss that progresses over time;
- noise in the ears and head;
- dizziness, loss of orientation;
- depression, inability to cope with bad mood;
- severe headaches;
- disruptions in thinking;
- the appearance of speech defects;
- limb spasms;
- lack of interest in familiar things;
- inability to control one's own behavioral reactions.
Basic diagnostic methods
When collecting anamnesis, specialists pay special attention to:
- patient complaints;
- the presence of diseases in the perinatal period and accompanying symptoms;
- are pathologies observed in the vascular system of the brain (atherosclerosis);
- whether there has been a history of poisoning with neurotoxic substances;
- TBI;
- whether chronic organ diseases are indicated in the medical record.
To clarify the diagnosis, additional instrumental diagnostics are performed:
- Electroencephalography. Detects signs of epilepsy, disturbances in wave activity and rhythms.
- CT. Allows you to assess the consequences of injuries, identify hemorrhages, and tumor processes.
- MRI. Finds diffuse or focal lesions of the central nervous system.
- MRI with contrast. Allows you to identify pathologies of cerebral vessels.
Treatment
Self-medication is unacceptable! Any error in the selection of medications and treatment regimens will seriously worsen the patient’s condition and lead to the development of new pathological changes in the brain.
After analyzing the type of encephalopathy, the following is prescribed:
- therapy;
- cleansing the body of toxins.
Medicines are intended to eliminate the causes of the syndrome, as well as correct possible underlying problems.
Each type has its own type of therapy, taking into account:
- degree of defective functioning of the central nervous system;
- the presence of other chronic diseases.
Common practice is to prescribe physiotherapy:
- acupuncture;
- infrared laser;
- bioresonance stimulation.
Additionally, massage is indicated. In particularly severe cases, doctors may consider surgery.
The result of treatment of encephalopathy should be:
- reduction of symptoms and, if possible, complete elimination of them;
- improvement of cerebral circulation;
- establishing local metabolism;
- reduction of signs of various nervous syndromes;
- correction of cognitive impairment.
Treatment and prognosis
Typically, when cystic cavities occur, the main treatment method is surgery. Such operations can be palliative or radical.
Palliative interventions are those in which the cyst is not completely removed, but only its cavity is cleared of its contents, as a result of which it becomes smaller.
Treatment of the tumor involves the use of surgical methods
These methods include:
- Endoscopic method. During this operation, the contents of the cavity are removed using an endoscope. Before this, small punctures are made into which the endoscope is inserted. This method is considered effective and safe. In addition, trauma during intervention is minimized.
- Shunting. The cavity is cleared of contents using shunts. This method is less traumatic than other interventions. However, with such an operation there is a risk of infection, since the shunt system remains in the organ for a long time.
- In radical operations, the neoplasm is completely eliminated along with its walls and contents. To do this, trepanation is performed, so this intervention is an open operation. The disadvantage of this method is that it is highly traumatic.
In some cases, conservative treatment may be used. It consists in the use of medications that eliminate the main causes of formation.
A favorable prognosis for cystic formations in the brain is possible provided that the diagnosis is made in a timely manner, the size of the cyst is small, immediate treatment is provided, and also in cases where the cavity does not grow. A favorable outcome is most often observed if the cyst is detected during pregnancy, in which case it usually resolves.
When the cyst rapidly increases in size, the brain tissue is compressed and the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is disrupted. This leads to dangerous complications. In such a situation, the prognosis is usually unfavorable, so there is a danger to the health and life of the patient.
The cyst is dangerous due to its complications!
As the cyst progresses, a hemorrhagic stroke may occur in the child. The following pathological conditions are also considered dangerous complications:
- Rapid increase in cyst size.
- Deformation of brain tissue.
- Convulsive seizures.
- Hallucinations.
- Mental disorders.
- Brain hernia.
- Increased intracranial pressure.
- Hydrocephalus.
- Hemorrhages.
With the rapid growth of education, developmental delay in the child is considered an undesirable consequence. In severe cases, the cyst is dangerous and can be fatal.
To prevent the development of complications, it is important to listen to the advice of a neurosurgeon and begin timely treatment. This will help reduce the risk of developing severe consequences several times.
Noticed a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl Enter to let us know.
If a brain cyst is discovered in a newborn, the consequences can be different. It all depends on the size and how it progresses. If the child has no symptoms, but it is growing, removal is necessary.
- Complete loss of vision and hearing;
- Impaired motor abilities;
- Hemorrhagic stroke;
- Hydrocephalus (filling of the brain cavity with fluid);
- Brain hemorrhage;
- To the sudden death of a child.
Multicystic brain disease in a newborn poses a great danger; the prognosis will depend on the timeliness of diagnosis. If the disease is in the middle stage of development, the prognosis is unfavorable. If the child survives, there is a high risk of mental and motor development disorders.
The prognosis of education largely depends on how and when the brain is diagnosed. If detected early, the prognosis will be favorable.
It is important to remove the pathology before complications appear, then the consequences can be avoided.
Small cysts (a few millimeters) have a favorable prognosis and do not lead to serious disorders.
Thus, a brain cyst in a newborn can have different consequences depending on the size and location. Therefore, parents must always pay attention to the symptoms of damage to the nervous system in their children and, if they exist, be sure to undergo a high-quality examination. This will avoid a number of complications that can cause disability.
from birth to school
If the pathology is detected early, the prognosis is favorable. If it is detected at later stages of development or tends to rapidly increase, then the prognosis worsens significantly. In such cases, the formation is dangerous because it can provoke the development of a number of consequences and complications that arise both in the absence of timely treatment and in the postoperative period:
- hydrocephalus or encephalitis;
- speech, hearing and vision impairments;
- motor dysfunction;
- chronic headaches;
- convulsive syndrome (epilepsy attacks);
- behavioral disorders, increased or decreased activity.