Hydrocephalus of the brain does not develop spontaneously in adults. It is the result of pathologies of the central nervous system or head injuries, which provoke the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the cerebrospinal fluid ducts and ventricles.
Symptoms of pathology in adults differ from signs of the disease in childhood. The first manifestation in the latter case will be an increase in head circumference. This is explained by the fact that in children the bones of the skull are mobile after birth, and the increased volume of cerebrospinal fluid simply pushes them apart.
In adults, everything is different: their brain is already formed, and excess fluid puts much more pressure on the organ. One way or another, a pathology such as hydrocephalus of the brain, regardless of the patient’s age, should be treated under the supervision of a specialized specialist - a neurologist.
Hydrocele of the brain in an adult
Types
Depending on the causes of the disorders and their forms, the following types of this disease are distinguished:
- Hydrocephalus is open. Cerebrospinal fluid is produced, but brain cells do not absorb it.
- Closed hydrocephalus. It is characterized by blockage or difficulty in the movement of fluid, as well as its accumulation in the brain tissue. Blood clots, tumors, formations that appear due to inflammatory processes suffered by the patient, and hematomas can act as obstacles that block the liquor channels.
- External hydrocephalus of the brain is non-occlusive (or replacement). The fluid fills the spaces in the brain structures that are vacant due to a decrease in the amount of gray matter, that is, brain atrophy. This pathological form is dangerous if there is no timely therapy, since it is characterized by the appearance of symptoms at a late stage of development.
- Hydrocephalus is moderate. Liqueur fluid, due to defects in its circulation, directly accumulates in the subarachnoid space.
- Hypotrophic hydrocephalus. It appears when there are defects in the nutrition of brain tissue and is accompanied by a number of acute symptoms, including vomiting, decreased vestibular functioning, nausea, and intense headaches.
- Hypersecretory hydrocephalus is a consequence of too high production of cerebrospinal fluid, brain tissue is not able to absorb large amounts of it, and the fluid in this case fills the cavities inside the skull.
External hydrocephalus in its origin can be acquired or congenital. An acquired disease appears after ailments of the spinal and vascular systems, intracranial injuries, enlarged tumors, inflammatory and infectious processes that affect the brain.
Causes of replacement hydrocephalus
In older people, NDH most often occurs due to atherosclerosis or high blood pressure.
The cause of the onset of the disease may be alcohol abuse.
Those who have suffered a concussion are at risk.
In newborns and young children, NDH can begin due to an infection of the nervous system before birth or in the first weeks of life. The cause may also be intrauterine hypoxia.
However, most brain clips today are made of non-magnetic material, so this shouldn't be a problem. If you know you have brain clips, but you don't know what material they are made of, ask your neurosurgeon. There is a small risk of exposure to radiation.
If cost is a limiting factor for you, talk to your doctor about it before he orders any diagnostic tests. Some insurance companies may only cover part of the cost, so it's important to find out how much, if any, you'll be required to pay.
In older children, adolescents and adults, the disease can develop as a result of metabolic or cervical vertebrae dysfunction, infection of the nervous system, brain injury, endogenous or exogenous intoxication.
Symptoms in an adult
In an adult patient, if there is no diagnosis, the pressure on the brain system increases, and external hydrocephalus of the brain of a pronounced type appears, characterized by a number of specific symptoms:
- migraine and headaches;
- drowsiness;
- nausea;
- impaired vision (double vision);
- excessive fatigue;
- weakness.
If signs of external hydrocephalus occur after an injury or illness, you should immediately consult a specialist.
Diagnostics
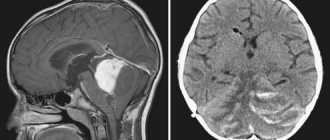
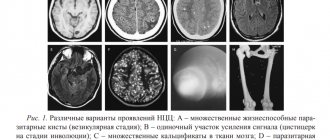
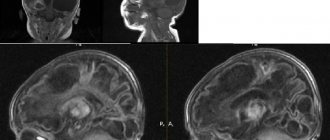
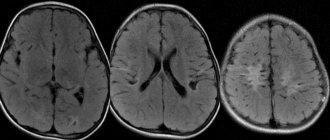
Although there are quite a few diagnostic methods for determining an excessive amount of fluid in the brain of the head, the main role in the examination is most often given to CT, that is, computed tomography, and MRI, that is, magnetic resonance imaging. Such procedures help to quickly make a correct diagnosis.
Thanks to CT and MRI, the causes and symptoms of the pathology, its stage and, naturally, the level of its neglect are determined. Using procedures, specialists examine the cranial cavity, the contours of the brain of the head and possible tumors and cysts.
When examining the brain for the presence of external hydrocephalus, a contrast agent is not required, but many doctors still advise injecting it into the body in order to simultaneously check the condition of the blood vessels. Of course, the effect of the circulatory system on the excess amount of cerebrospinal fluid is not too great, however, CT or MRI with contrast in some cases makes it possible to diagnose other diseases, if any, in the patient’s body.
In addition, specialists can sign up a patient for a procedure such as cisternography. This is one of the newest diagnostic methods for studying the brain, which is aimed at analyzing the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
Classification of the disease
External replacement hydrocephalus of the brain is classified into types:
Until there is an accepted and established standard for the treatment and monitoring of hydrocephalus, neurosurgeons will continue to differ in their choice of imaging device. Ask your doctor to explain his thoughts on which test to order. If you have serious concerns, consider getting a second opinion before proceeding.
Benign extra-axial fluid of infancy
Although rarely misdiagnosed by modern imaging techniques, the condition of hydrocephalus is sometimes mistaken for benign extra-axial fluid of infancy and Alzheimer's disease in adults. At birth and for the first few months, the baby's head circumference will be normal, but will suddenly begin to grow rapidly over a short period of time. Because abnormal head growth is an indicator of the presence of hydrocephalus, the child should be referred to a pediatric neurosurgeon for further evaluation.
- In origin, the disease can be hereditary or acquired.
- According to the nature of the development of the disease, acute, subacute and chronic NMH are divided. In the acute form, it takes up to 3 days from the appearance of the first symptoms to the appearance of disorders in the brain. The subacute form of NDH lasts for approximately a month. The chronic form develops over 6 months or longer.
The passive form of the disease is called “moderate severe external hydrocephalus.” Doctors believe that this form is more dangerous than the progressive form. The point is the absence of symptoms. When the patient realizes that the problem still exists, externally, replacement hydrocephalus is quite advanced.
However, they will notice that this is an abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the subarachnoid space. This is known technically as benign extra-axial fluid of infancy and may also be called benign subdural hygroma or external hydrocephalus.
In cases of benign extra-axial fluid of infancy, subarachnoid accumulation usually recovers by the time the child reaches 18 to 24 months. When benign extra-axial fluid is detected, your child's neurosurgeon will require a follow-up scan to ensure fluid has accumulated in the brain.
The disease may have a permanent course
. In this case, the volume of the brain does not decrease, and the volume of cerebrospinal fluid does not increase.
If the patient feels satisfactory, the treatment is mild. The patient is prescribed regular observation by a specialist and examinations.
With the progressive nature of NDH, it is necessary to treat with drastic methods.
Alzheimer's disease is commonly confused with normal pressure hydrocephalus because some of the symptoms of both are the same. Once hydrocephalus is detected, and if shunt surgery is recommended, it is important to act on the neurosurgeon's recommendations as soon as possible. The longer the condition remains uncontrolled, the greater the risk of neurological damage.
This manifestation of the disease has its own types
It is your right to ask for a second opinion. Neurosurgery, whether performed on a child or an adult, has inherent risks and many possible complications. Ask your neurosurgeon if you have time for a second opinion. If so, your neurosurgeon should help you find another neurosurgeon in your area. If the neurosurgeon indicates some urgency in performing a bypass or revision, ask him if it is possible to meet you with a neurosurgeon as soon as possible.
Otherwise, the patient faces dementia or urinary incontinence, severe headaches and impaired motor functions. Sometimes an exacerbation or too late going to the hospital leads to the death of the patient.
Other procedures
In addition to the listed outpatient research methods for determining hydrocephalus, in some cases procedures such as:
- angiography – used to diagnose the condition of blood vessels, the presence or absence of cysts, tumors, blood clots and aneurysms;
- Ultrasound of the head brain;
- radiography;
- examinations for infections and viruses.
It is also mandatory for the specialist to interview the patient regarding existing complaints. The patient must describe the symptoms that he is experiencing. Thanks to this, doctors will be able to make the correct diagnosis and choose the right therapeutic course, which will reduce the external manifestation of pathological signs.
Let's look at how external hydrocephalus is treated.
Legislation on military service for men diagnosed with hydrocephalus
Having received a summons from the military registration and enlistment office, the conscript must appear at the appointed time, having with him a passport, birth certificate and outpatient card.
Having checked the arrival mark, the young man receives a referral to undergo a military medical examination. If a young man has a medical history and is concerned about whether he will be accepted into the army with this pathology, he must present additional certificates and extracts from the medical history.
Medical experts then analyze the data to make a decision. In doing so, they are guided by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 565 of July 4, 2013, as amended on March 30, 2020, which includes the “Schedule of Diseases.” The question of whether someone with hydrocephalus will be accepted into the army is regulated by Art. 23.
This article deals with systemic atrophies affecting the central nervous system, extrapyramidal and other degenerative pathologies, diseases of the myoneural synaptic node and muscle structure, congenital malformations of the nervous system, brain tumors with significant, moderate, insignificant growths and in the presence of objective information without dysfunction. The progressive course also matters: fast or slow.
Thus, hydrocephalus is a slowly progressive disease with mild symptoms, that is, the conscript suffers from headaches and dizziness. Thus, the young man falls under category B, receives a military ID and is sent to the reserve for conscription in wartime.
If the cause of dropsy is a brain cyst, the young man receives a delay in order to undergo treatment. If the therapy has a positive effect and symptoms do not appear for a long time, theoretically the young man can be drafted into the army after examination, assigning him category B4, that is, limited suitability.
But in practice, military medical experts rarely do this, leaving category B. The only thing that may be needed is an additional examination to confirm the diagnosis of cerebral hydrocephalus with impaired function. For this, the conscript is sent to undergo a series of diagnostic tests: CT, MRI, X-ray, spinal puncture.
If you are sure that your illness falls under the category of unfitness, and the military medical commission decides that you will have to serve, you need to go to court. Ask questions to our lawyers directly on the website, they will tell you how to draw up a statement, whether the decision is illegal and whether you have the right to challenge it.
Chronic sinusitis must be purulent or polypous in addition to exacerbations at least 2 times a year in order to receive a ticket.
As for the meniscus, at a minimum you should be given a deferment, and if the joint is unstable, it should be released.
Alexey Voronin yesterday at 12:06 Good day, the military registration and enlistment office sent me to the FGS, in the conclusion they wrote: Focal ***ral gastroduodenitis (I couldn’t make out the first 3 letters of the second word). Do they take it with a tax diagnosis? And another question: the conscription lasts until July 15, and the deferment from the technical school until the 1st. How can I get a deferment for these 15 days in order to go in the fall?
Most likely they will take it. Category B is assigned to gastroduodenitis with impaired secretory and acid-forming functions, frequent exacerbations, requiring repeated and prolonged hospitalization (more than 2 months) with unsuccessful inpatient treatment.
The grounds for not appearing on a summons are:
1. Your appeal of this subpoena; 2.Your illness or injury associated with loss of ability to work; 3. The serious health condition of your father, mother, wife, husband, son, daughter, brother, sister, grandfather, grandmother or adoptive parent of a citizen or participation in the funeral of these persons; 4. An obstacle that arose as a result of force majeure, or another circumstance that does not depend on the will of the citizen; 5. Other reasons recognized as valid by the draft commission or court. After the expiration of a valid reason, citizens appear at the military commissariat immediately, without an additional call.
#433 Lawyer - Human Rights Defender today at 12:51 Roman Tourist Bazhenov yesterday at 21:41 hello. What can you say about this diagnosis (antespondylolisthesis of the L5 VERTEBRE. PROTRUSION OF INTERVERTEBRAL DISCS L4/L5. L5/S1 with this
The diagnosis of anthespondylolisthesis falls under paragraph “b” of Art. 66 Disease schedules - spondylolisthesis 1 and 2 degrees. It is important how many mm/cm the vertebra is displaced. To release, a displacement of 1/4 and 1/2 of the transverse diameter of the vertebral body is necessary, respectively. Documented pain syndrome is also required. With protrusions it is also possible to obtain release if there is a documented pain syndrome.
When considering the question of whether people with hydrocephalus are recruited into the army, it is worth noting that this disease is not a contraindication for military service. However, brain pathologies have serious complications and require careful monitoring and proper treatment.
Therapy with medications
Despite the fact that drug therapy is not the most effective, it is at the same time more gentle. Conservative treatment can be prescribed based on the patient's age, general condition and type of hydrocephalus. The main attention is paid to diuretics, vasodilators and strong saluretics, which increase the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. At the same time, pharmacological drugs are prescribed that slow down its production. The patient is also prescribed concomitant medications to treat external hydrocephalus.
The standard recipe includes the following:
- "Acetazolamide" is a drug that lowers pressure inside the eye;
- “Glimarit”, “Diakarb”, “Manit” are diuretics;
- barbiturates and painkillers;
- ethacrynic acid and Furosemide - agents that remove salts and excess water from the body;
- albumin solution at a concentration of 20% to adjust the composition of plasma and blood;
- magnesium sulfate solution 25%, “Troxevasin” and “Glivenol” - drugs that improve blood circulation;
- Prednisolone, Methylprednisolone, Dexamethasone, Betamethasone are hormonal steroids that have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Conservative treatment only in some cases leads to recovery; its primary goal is to alleviate the patient’s condition and develop external hydrocephalus. If it is impossible to achieve a stable condition within two to three months, surgical intervention is necessary. Drug therapy is also not allowed for diseases in acute clinical form.
Treatment
The most common treatments since the 50s are bypass surgery and endoscopy. At the same time, for the last three decades, endoscopy, which appeared in the 80s, has occupied a leading position. Both of these operations are aimed at restoring normal circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
On this topic
- Hydrocephalus
What is the danger of open hydrocephalus?
- Ekaterina Nikolaevna Kislitsyna
- March 26, 2020
Bypass surgery, in particular, has a large number of disadvantages. The number of revisions after bypass surgery is at least two, and a person’s life depends entirely on the proper operation of the shunt. In addition, in almost half of the cases bypass surgery is fraught with complications. Therefore, endoscopy is currently the priority and most progressive direction of treatment.
Neuroendoscopic operations are also very effective, in particular, ventriculocisternostomy of the bottom of the third ventricle, during which pathways for the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid into the cisterns of the brain are artificially created. During this process, the secretion is reabsorbed, and the absence of foreign bodies (as with bypass surgery) minimizes the risk of complications and infections.
The least popular method is external drainage. It represents the removal of liquor from the outside. This method is extremely risky, associated with a high probability of infection and a huge number of complications.
With successful surgical intervention, a person has the opportunity to recover and return to a normal, fulfilling life. However, often even surgical intervention can only slow down the progression of the disease.
Bypass surgery
In adult patients, one of the most effective methods of treating external hydrocephalus of the brain is brain shunting. In 85% of cases of operations performed, a satisfactory result is achieved. Thanks to a system of valves and tubes, excess amounts of cerebrospinal fluid are removed by forced and natural means into those cavities of the body in which the accumulation of fluid is not so critical.
Complete recovery is the main advantage of this technique, however, along with this, there is a possibility of inconvenience and complications for the patient, among which the most common are:
- from time to time the need for complete or partial replacement of the shunt;
- the risk of hematomas due to intense fluid outflow;
- dependence on the functioning of the system;
- churn is too low;
- the possibility of epilepsy, bedsores, inflammation.
There are also contraindications for bypass surgery:
- neurological diseases;
- hydrocephalus in chronic form;
- blindness;
- epilepsy;
- mental disorders.
Good to know
During normal functioning of the body, cerebrospinal fluid is absorbed by the tissues. The slightest failure in this process can lead to excessive release of cerebrospinal fluid, as a result of which it will not have time to be absorbed by the tissues and will begin to put pressure on the brain, which will lead to increased intracranial pressure and the development of the disease.
Bypass surgery is impossible if the dropsy resulted from hemorrhage in the lateral ventricles (so-called post-hemorrhagic hydrocephalus), since the cerebrospinal fluid contains blood, the entry of which into the abdominal cavity is fraught with serious complications.
The use of endoscopy in such a clinical picture also does not always end positively, since the hole formed during the operation quickly closes due to inflammation of the ventricles.
This disease is one of the most difficult that a child can face. The most favorable prognosis awaits patients with a mild form of hydrocephalus. When a disease is detected at an early stage of development, it is much easier to combat it.
Endoscopy
The most common indication for endoscopy in adult patients is a tumor or traumatic formation. Thanks to this technology, it is possible to remove an obstacle that impedes liquor circulation without opening or trepanning the skull. Using an endoscope, instruments are inserted into the places where cerebrospinal fluid accumulates, through which excess fluid is sucked out to normal limits. Compared to this method, the advantages of endoscopy are obvious: its initial goal is to normalize the natural flow of cerebrospinal fluid, minimize trauma during surgery, and increase the likelihood of recovery. In addition, there is no foreign body in the body. Thanks to the endoscope, it becomes possible to completely eliminate tumors that have caused blockage of the cerebrospinal fluid circulation, as a result of which the patient’s condition improves almost immediately after the end of the operation. Often, this is the only method of eliminating a malignant or benign tumor. The attending physician decides on the use of endoscopic intervention for external hydrocephalus of the brain in an adult.
Causes of the disease
Hydrocephalus can be congenital or acquired and can be caused by a variety of internal and external factors.
On this topic
- Hydrocephalus
How is shunting performed for cerebral hydrocephalus?
- Natalia Sergeevna Pershina
- March 26, 2020
The most common causes of congenital hydrocephalus are considered to be:
- inflammation of the meninges suffered in the womb
- deviations in brain development as a result of pathology of fetal formation;
- cerebral hemorrhage suffered in the womb
- taking potent medications .
In such a situation, the occurrence of this disease cannot be ruled out. The development of the disease is characterized by brain deformation. As the disease progresses, the patient's brain changes significantly in size and becomes smaller than the volume of the cranium.
The space freed up as a result of the reduction in brain size is filled with the produced cerebrospinal fluid. At the same time, the size of the skull increases due to an increase in intracranial pressure, and its walls and bone tissue become narrower. At the same time, the patient’s blood circulation is also impaired.
The causes of acquired hydrocephalus may be as follows:
- malfunction of the body due to exposure to toxins;
- infectious disease (measles, meningitis, etc.) that occurs with complications;
- due to diseases spread by parasites ;
- benign and malignant tumors;
- stroke;
- thrombus formations in the blood vessels of the brain.
One of the factors described above is enough to disrupt the production of this secretion, which will inevitably lead to the occurrence of this disease.
Diet
Dietary prescriptions for adults with external hydrocephalus of the brain are aimed at stabilizing the water balance in the body. The diet includes foods that do not contain salts and sugar:
- steamed lean meat;
- boiled eggs or steamed omelet;
- vegetables and herbs;
- stale bread;
- porridge.
Dishes that promote fluid accumulation should be excluded from the patient’s menu:
- confectionery and freshly baked flour products;
- fried, smoked, fatty meat, sausages;
- mushroom and fish soups;
- carbonated drinks;
- onion, garlic, radish.
A little about liquor and its functionality
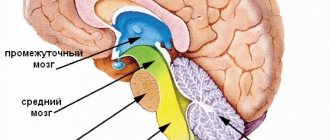
In the human skull there are soft tissues, which are nothing more than his brain. A fluid (CSF) circulates between the bone and the meninges, which fills not only the internal ventricles, but also all existing depressions (grooves) on the surface of the main organ of the central nervous system.
How is cerebrospinal fluid formed? This occurs as a result of a process such as the filtration of plasma (that is, the liquid part of the blood) through the walls of capillaries with the subsequent release of organic and inorganic substances into it. The composition of the cerebrospinal fluid circulating in the subarachnoid space and ventricles of the brain includes minerals, proteins and a very small number of cells such as lymphocytes and leukocytes. That is, in terms of the chemical composition, cerebrospinal fluid is very similar to the composition of blood.
What is the main function of cerebrospinal fluid? First of all, it is to protect the brain and the vessels located at its base from all kinds of mechanical influences (for example, shocks or jolts). Also, cerebrospinal fluid helps create a beneficial environment, which is so necessary for the normal functioning of the human central nervous system; maintains ICP at a certain level; participates in metabolic processes and nutrition of brain cells; and also acts as a protective barrier against bacteria, that is, it helps improve immunity.
Forecast
The prognosis of external hydrocephalus of the brain in adults is not always predictable. This is a fairly serious disease, the advanced form of which can be fatal. Even a successful and timely operation does not guarantee the absence of complications and some limitations in the future. Experts note not only physiological, but also psychoneurological disorders. Moderate physical activity and regular walks will help the patient relieve stress. Practice shows that in most cases, complete recovery after surgical treatment and a return to a full life are possible.
Category of suitability for brain cysts
Sometimes fluid accumulation occurs due to the appearance of tumors. If the cause of hydrocephalus is brain cysts, then the conscript will not be accepted into the army. First, the young man will receive a deferment and a referral for treatment. Theoretically, if medical intervention proves effective, the cyst will no longer interfere with the movement of cerebrospinal fluid, and the conscript’s health condition stabilizes - the man can be drafted into the army. But, as the practice of the Conscript Assistance Service shows, military registration and enlistment offices usually do not call for service with such a diagnosis.
With respect to you, Maria Krylova, lawyer of the Assistance Service for Conscripts.
We help conscripts obtain a military ID legally.
Reading time: min.
Hydrocele and the army - will a young man go to serve if he is diagnosed with such a disease? Whether they take into the army with dropsy of the testicles - this question is usually relevant for mothers, many of whom seek to protect their son from the army, especially if he needs to serve at a young age and those who have been diagnosed with this.
In order for a young man to be exempted from conscription into the army, it is necessary to provide relevant medical documents that will confirm that the patient had a relapse after secondary, in other words, repeated treatment. Moreover, this treatment had to be carried out through surgery. The volume of liquid must exceed 100 ml.
Hydrocele and the army: military service
Hydrocele and the army are something that can become a big obstacle for a person who is going to connect his life with a military career. Why? The fact is that, as a rule, it is necessary to enter higher military educational institutions in good health. To be more precise, this is an essential requirement for admission. Otherwise, mastering the military profession will be simply impossible.
In addition, as noted above, if there is a relapse after surgery and the volume of fluid exceeds 100 ml, it will be impossible to enroll at all.
What should a person who is faced with such a disease, but has a desire to join the army, do? First, you need to try to calm down and think that treatment is a completely possible and probable option. You can resort to traditional medicine recipes, you can resort to surgical intervention. However, it is important to understand that treatment through traditional medicine is unlikely to be effective, and it must be used for at least a month, or even more.
That is why the most optimal option in this case can be considered an operation. Some are afraid of such a measure, but this must be done in order to improve their own health and pass a medical examination upon entry into military service. The occurrence of cases of relapse after surgery is the exception rather than the rule. This is why the village should decide on the procedure. But since the period of time allotted to improve your health may be limited, it is worth considering having the operation paid for. Mainly, this can guarantee excellent quality, but then you will first need to choose a reliable clinic with good reviews.
Head of the legal department of the Assistance Service for Conscripts.
Tel. 8 800-333-53-63
People with hydrocephalus are accepted into the army. And the point is not that the military registration and enlistment office fulfills the norm for the number of conscripted citizens. The explanation lies in the document regulating the rules of conscription - the Schedule of Illnesses. Let's figure out together why the military registration and enlistment office is adamant in its decision and who can receive a military ID due to illness.