External replacement hydrocephalus (ERH) of the brain is the most common form of hydrocephalus, which is popularly called dropsy.
Due to disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system, cerebrospinal fluid is absorbed into the skull.
NDH is characterized by a decrease in brain volume; the space freed from brain cells begins to fill with cerebrospinal fluid.
Another difference between NDH and other forms of dropsy is that the disease can develop without obvious symptoms, even over several years.
Classification
Hydrocephalus can be either acquired or congenital. The latter begins to manifest itself in infancy, while the acquired form is typical for adults and even elderly patients. Depending on the prerequisites for the appearance of hydrocephalus, the following types are distinguished:
- Closed, occlusive hydrocephalus occurs due to disruption of the flow of cerebrospinal fluid due to blockage of the fluid-conducting pathways. Most often, blockage occurs due to a tumor, the presence of a blood clot or adhesions.
- Open, or dysresorptive, hydrocephalus. It develops against the background of a violation of the structures that are involved in the process of absorption of cerebrospinal fluid into the system of cerebral veins (arachnoid villi, venous sinuses, cells and pachyonic granulations).
- Hypersecretory hydrocephalus. Production of large amounts of cerebrospinal fluid into the plexus of ventricular vessels.
- Replacement mixed hydrocephalus of the brain. It develops as a result of an increase in the amount of cerebrospinal fluid both in the subarachnoid space and in the cerebral ventricles. In this case, atrophy of brain tissue occurs.
The last option is considered the most dangerous to the life and health of the patient.
What are the symptoms of the disease?
First of all, replacement hydrocephalus of any type affects the central nervous system. This may result in various symptoms of the disease:
- headache (especially in the morning);
- pressure surges;
- arrhythmia and rapid heartbeat;
- increased sweating;
- the appearance of nausea or vomiting;
- drowsiness during the day and difficulty falling asleep at night;
- decreased performance;
- state of nervousness and appearance of irritability;
- possible vision impairment;
- gait may change.
In older people, moderate external replacement hydrocephalus most often occurs against the background of hypertension or atherosclerotic vascular lesions. It can also appear as a result of a past concussion or alcoholism. Later forms of the disease are characterized by deterioration.
Causes
Severe replacement mixed hydrocephalus is most typical for newborns. In adults, this pathology is less common, but also occurs. Research in the field of medicine has shown that any disturbance in the functioning of the human nervous system can provoke the development of hydrocephalus. Acquired causes of hydrocephalus can be:
- Ruptures of hematomas or hemorrhages in the brain.
- Severe traumatic brain injuries.
- Birth injuries.
- Severe cerebrovascular accident.
- Previously suffered infectious-inflammatory diseases, including encephalitis, meningitis, arachnoiditis, etc.
- Infection of brain structures by various parasites.
- Germinomas, astrocytomas, tumors in blood vessels and other neoplasms.
- Metastasis of tumors of other organs to the brain.
- Formation of cetacean cavities in the third ventricle.
- The occurrence of vascular malformations.
- Atrophy of brain tissue as a result of organ damage by encephalopathy.
Dropsy of the brain can have a negative effect on all organ systems. Therefore, to eliminate hydrocephalus, it is necessary to accurately determine the cause of the pathology.
What are the signs of mixed replacement hydrocephalus?
Survey
The algorithm is based on a competent analysis of the patient’s complaints by a neurologist and MRI results. In laboratory studies, it is necessary to determine the level of cholesterol fractions in the blood, blood clotting and a number of other biochemical indicators, including the hormonal profile. You may need to consult an endocrinologist, ophthalmologist, as well as study the vessels of the neck and brain using ultrasound scanning and Doppler diagnostics. It is necessary to determine whether hydrocephalic syndrome is caused by excessive production of cerebrospinal fluid or whether the atrophy of the brain matter comes first. This is important because different causes require different treatment approaches.
NDH differs from other types in that it does not pose a clear threat to life. Infections, injuries, tumor processes, hormonal disorders, lack of B vitamins and psychogenic factors have only an indirect effect on its development. The determining factors in the occurrence of the disease are the individual characteristics of the body: heredity, lifestyle. It is they that lead to true hydrocephalus, causing the corresponding symptoms, and require a radically different approach to diagnosis and treatment. The opportunity to treat and correct NDH still exists, including at the stage of primary medical care.
It happens that no obvious cause can be found. Then the therapy algorithm is aimed at correcting risk factors: work and rest schedule, diet, eliminating habitual intoxications (alcoholism, smoking, occupational hazards), eliminating stress factors, and, if possible, normalizing relationships in the family and society.
Clinical picture
The characteristic clinical picture of mixed replacement hydrocephalus is the following:
- Constant pain in the head and a feeling of heaviness, intensifying during sleep and immediately after waking up. Inability to determine the source of pain. When a person is in a lying position, the symptom becomes more pronounced as the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid increases.
- Nausea and vomiting in the morning, regardless of food and time of consumption.
- Feeling of pressure on the eyes.
- Persistent hiccups.
- Constant weakness, increased fatigue, drowsiness.
- Difficulties with concentration and attentiveness; it is difficult for a person to perform basic actions.
- Apathy, nervousness, decreased intellectual abilities.
- A sharp drop in blood pressure, slowing or increasing heart rate.
- Permanent dark circles under the eyes. When the skin of the lower eyelids is stretched, blood-filled capillaries are clearly visible.
- Significant increase in sweat, tendency to faint.
These symptoms indicate intracranial increased pressure.
Symptoms of the disease
External replacement hydrocephalus most often has the following symptoms:
- headache;
- increased blood pressure;
- different parts of the body go numb, most often the limbs;
- a person may feel short of breath;
- darkens in the eyes;
- there are coordination problems;
- nausea;
- drowsiness.
There is no age limit for the appearance of NDH. Both older people and young children can get sick.
Is treatment of VSD effective with folk remedies? Reviews from patients who have used traditional medicine recipes.
Manifestation of neurological disorders
Neurological disorders with mixed replacement hydrocephalus of the brain in adults will manifest themselves as follows:
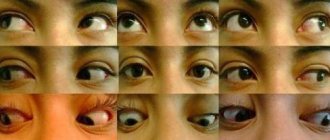
- Decreased quality of vision – bifurcation and difficulty focusing the gaze on one object.
- Loss of visual fields.
- Against the background of constant compression, atrophy of the optic nerve occurs, which in the future can cause complete loss of vision.
- Strabismus.
- Lack of pupillary response to bright light.
- Dysfunction of the vestibular system. Dizziness, unsteadiness in gait, tinnitus, and involuntary vibrations of the eyeballs appear.
- Paralysis of limbs.
- Increased reflexes and muscle tone.
- Decreased or complete loss of sensitivity.
- Involuntary fixation of the arms and legs, when due to increased tone it is impossible to straighten the limbs.
- Symptoms of cerebellar ataxia, accompanied by impaired motor function and splayed handwriting.
- Unstable emotional state, sudden mood swings.
- With a sharp increase in cerebrospinal fluid pressure, aggression occurs.
The combination of symptoms and diagnostic measures taken indicate mixed hydrocephalus.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of hydrocephalus, you must:
- avoid infections that lead to brain damage;
- after injuries and concussions, you must consult a doctor and follow his instructions;
- take care of the condition of blood vessels, avoiding stroke.
Hydrocephalus in the early stages has no specific symptoms. Therefore, at the first suspicion of it, you should consult a doctor and undergo an examination.
Replacement external hydrocephalus is an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid that can appear due to neoplasms, injuries, or infections. In newborns it manifests itself in the form of deformation of the skull bones, but in adults there may be no specific symptoms. With timely treatment, the prognosis is favorable.
Diagnostics
Confirmation of the diagnosis of mixed replacement hydrocephalus of the brain in adults occurs on the basis of a study using both laboratory and instrumental techniques. The latter are the most informative in the case of brain disorders. Laboratory tests show the patient's general condition and how the disease has affected his or her health.
To identify severe and moderate mixed replacement hydrocephalus of the brain, the following studies are prescribed:
- Measuring head circumference with a tape. If hydrocephalus is in question in a child, then an upward change in head circumference of more than 1.5 cm per month indicates the presence of the disease. In adulthood, any enlargement of the head is considered pathological, regardless of the period during which it occurred.
- Fundus examination. If swelling of the optic disc is detected, we can talk about increased intracranial pressure, which means hydrocephalus cannot be ruled out.
- Ultrasound examination of the skull, or neurosonography. This study is not prescribed for adult patients, as it is not very informative. In childhood, an ultrasound is performed through the child's fontanel.
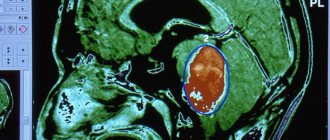
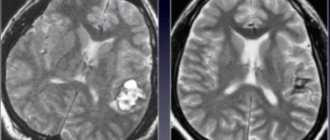
- Magnetic resonance imaging. This is the most accurate method for detecting hydrocephalus. Tomography will not only confirm the suspicion of the presence of pathology, but also determine the causes of its development, and assess the damage to brain structures and blood vessels. If MRI shows the presence of periventricular edema, the diagnosis of hydrocephalus is confirmed.
- CT scan. This is similar to an x-ray; the information content of the method is somewhat lower than in the previous version.
- Rheoencephalography and echoencephalography.
- Lumbar puncture. It is a collection of material for a histological examination of the composition and condition of the cerebrospinal fluid.
- Radiography. Makes it possible to identify thinning of bone structures.
The main criteria that a specialist relies on to clarify the diagnosis are the results of fundus examination and magnetic resonance imaging. After confirmation of the diagnosis, treatment for mixed replacement hydrocephalus of the brain is prescribed.
Signs of hydrocephalus in adults according to MRI
Manifestations of pathology in photographs can be direct or indirect. The first are associated with the expansion of the cerebral ventricles (III, IV and lateral (in the initial period - in the area of the anterior horns and body)), aqueduct and/or subarachnoid space (convexital, in the area of the basal cisterns, Sylvian fissures, etc.). Indirect signs on MRI scans:
- interventricular index over 0.5;
- periventricular edema with intense dropsy;
- downward displacement of the hypothalamus;
- local protrusion of the roof of the lateral ventricles, etc.
Additionally, tomograms determine the cause of cerebral hydrocele—the underlying disease.
Drug treatment
Mixed hydrocephalus is a dangerous and severe pathology. Treatment of hydrocephalus should include not only a set of measures related to taking medications, but also surgical intervention. Depending on the identified form of pathology, the selection of a separate therapeutic regimen is required.
Some patients try to use traditional medicine methods, but most specialists reject such methods of treating hydrocephalus of any type or allow their use only as auxiliaries.
Drugs
Drug therapy is carried out using the following drugs:
- Diuretics. The diuretic effect of these drugs allows you to stop the production of cerebrospinal fluid. Most often the choice falls on Piracetam, Diacarb and Glyserol. All these drugs are administered by injection. Along with diuretics, the patient is prescribed vitamin complexes, since diuretics wash out magnesium, potassium and sodium from the body.
- Antibacterial drugs. Prescribed to eliminate infectious pathogens.
- Medicines that promote blood circulation in the brain.
- Vitamin and mineral complexes. The most commonly prescribed vitamins are C, B and E. They improve cellular metabolism throughout the body.
- Enzymes of animal origin. Pyrogenal and lidase help break down and remove excess cerebrospinal fluid.
- Glucocorticoids.
If drug therapy for mixed replacement hydrocephalus in adults does not show positive dynamics in the patient’s condition, surgical intervention is prescribed.
Surgery
If hydrocephalus occurs in acute or chronic form, the patient is prescribed surgery. A contraindication for such treatment of mixed replacement hydrocephalus may be an infectious-inflammatory process that has spread throughout the body. Therefore, the infectious focus is first eliminated, and then surgery is prescribed.
Surgical treatment involves the formation of pathways for the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. This process is called bypass surgery and requires preliminary removal of adhesions and tumors.
Methods
In addition, hydrocephalus is eliminated by the following methods:
- Palliative intervention. It is carried out through puncture if hydrocephalus is characterized as open.
- Radical surgery. To eliminate excess fluid, special shunts are installed in the spinal canals. Internal drainage allows you to remove cerebrospinal fluid into an adjacent organ or system.
Most often, operations to eliminate hydrocephalus go well and allow you to get rid of the problem. If dropsy is caused by a tumor in the brain, surgical removal can prolong the patient's life by several years.