Ivan Drozdov 07/19/2019 0 Comments
The brain is the main organ responsible for the functioning of all vital systems of the body. A person’s general well-being, his ability to adequately perceive the situation, evaluate and respond to internal and external unfavorable factors depend on its proper functioning. There are many threats in the form of diseases and pathological processes that can provoke a malfunction of the structures of the brain and nervous system. One of these threats is a brain cyst, which quite often is asymptomatic, but at the same time can provoke the development of life-threatening consequences.
Symptoms
Arachnoid cysts are either asymptomatic or appear before the age of 20, while the nature and severity of symptoms depend on the location and size of the cysts, which makes diagnosis difficult.
Arachnoid cysts can be accompanied by headaches, nausea and vomiting, ataxia and hemiparesis, hallucinations, convulsive syndrome, mental disorders, etc. (more often, general cerebral symptoms associated with secondary hydrocephalus predominate, less often - focal symptoms, including with traumatic rupture of the cyst with the formation of hygroma). A spinal arachnoid cyst can simulate a herniated disc [2].
Additional facts
A brain cyst is a local accumulation of fluid in the membranes or substance of the brain. A small cyst, as a rule, has a subclinical course and is detected accidentally during a neuroimaging examination of the brain. A large volume cyst due to the limited intracranial (intracranial) space leads to intracranial hypertension and compression of the surrounding brain structures. The clinically significant size of cysts varies significantly depending on their location and compensatory capabilities. Thus, in young children, due to the flexibility of the skull bones, a long latent course of cysts is often observed without signs of severe liquor hypertension. A brain cyst can be detected at different age periods: from newborns to old age. It should be noted that congenital cysts more often appear in middle age (usually 30-50 years) than in childhood. According to generally accepted practice in clinical neurology, watchful and expectant management tactics are used for frozen or slowly progressing small-volume cysts.
Diagnostics
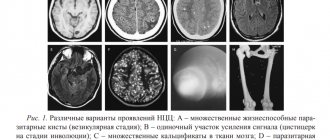
Arachnoid cysts are usually identified and differentiated from other types of cysts during MRI examination, often as a “finding” during examination for another reason.
Treatment of arachnoid cysts is indicated when symptoms manifest. There are a variety of methods for decompressing arachnoid cysts.
- Bypass: drainage into the subdural space or abdominal cavity
- Fenestration: craniotomy with cyst excision, various endoscopic techniques, including laser
- Drainage using needle aspiration
Notes
- ↑ 12
[https://www.medico.ru/articles/ino/arachnoid_cyst.pdf Manifestations of intracranial arachnoid cysts in children: correlation between localization and clinical symptoms - ↑ 12
NINDS Arachnoid Cysts Information Page - ↑
Flaherty AW.
The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Neurology
2000 Jan 1;105. (ISBN 0-683-30576-X) (English)
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
See what “arachnoid cyst” is in other dictionaries:
Arachnoid cyst - ICD 10 Q04.604.6 ICD 9 348.0348.0 OMIM ... Wikipedia
ICD-10: Class VI - List of classes of the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision Class I. Some infectious and parasitic diseases Class II. Neoplasms Class III. Diseases of the blood, hematopoietic organs and certain disorders involving the immune... ... Wikipedia
ICD-10: Class G - List of classes of the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision Class I. Some infectious and parasitic diseases Class II. Neoplasms Class III. Diseases of the blood, hematopoietic organs and certain disorders involving the immune... ... Wikipedia
ICD-10: Code G - List of classes of the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision Class I. Some infectious and parasitic diseases Class II. Neoplasms Class III. Diseases of the blood, hematopoietic organs and certain disorders involving the immune... ... Wikipedia
Help Me (Dr. House) - “Dr. House” Help Me (Russian Help me) Episode number 132 Release date May 17, 2010 Writer(s) Peter Blake, Russell Friend, Garrett Lerner Director(s) Guest actors Final diagnosis Crane operator arachnoid cyst . Hannah ... ... Wikipedia
Arachnoid mater - A section of the skull showing the membranes of the brain. The arachnoid mater is one of three membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. Located between the other two shells of the most superficial hard... ... Wikipedia
Arachnoid mater - A section of the skull showing the membranes of the brain. The arachnoid mater is one of three membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. Located between the other two membranes of the most superficial dura mater... ... Wikipedia
Arachnoid mater - A section of the skull showing the membranes of the brain. The arachnoid mater is one of three membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. Located between the other two membranes of the most superficial dura mater... ... Wikipedia
Arachnoid mater - Section of the skull showing the membranes of the brain. The arachnoid mater is one of three membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. Located between the other two membranes of the most superficial dura mater... ... Wikipedia
List of episodes of the television series "M.D. House" - Main article: M.D. House ... Wikipedia
International Classification of Diseases
More details about the ICD-10 classifier
Date of placement in the database 03/22/2010
Relevance of the classifier: 10th revision of the International Classification of Diseases
Showing 10 entries
Home → DISEASES OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM → OTHER DISORDERS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM → Other brain lesions Code Name Additional data —> G93.0 Cerebral cyst G93.1 Anoxic brain lesion, not elsewhere classified G93.2 Benign intracranial hypertension G93.3 Fatigue syndrome after a viral illness G93.4 Encephalopathy, unspecified G93.5 Compression of the brain G93.6 Brain edema G93.7 Reye's syndrome G93.8 Other specified brain lesions G93.9 Brain lesion, unspecified
- ICD-10 codes
- G00-G99
- G90-G99
- G93
Diagnosis with code G93 includes 10 clarifying diagnoses (ICD-10 subheadings):
G93.0 - Cerebral cyst G93.1 - Anoxic brain damage, not classified elsewhere Excluded: complicating: . abortion, ectopic or molar pregnancy (O00-O07, O08.8). pregnancy, labor or delivery (O29.2, O74.3, O89.2) . surgical and medical care (T80-T88) neonatal anoxia (P21.9).G93.2 - Benign intracranial hypertension Excluded: hypertensive encephalopathy (I67.4).G93.3 - Fatigue syndrome after a viral illness G93.4 - Encephalopathy, unspecified Excluded : encephalopathy: . alcoholic (G31.2) . toxic (G92).G93.5 - Cerebral compression G93.6 - Cerebral edema Excluded: cerebral edema: . due to birth trauma (P11.0) . traumatic (S06.1).G93.7 - Reye's syndrome G93.8 - Other specified brain lesions G93.9 - Unspecified brain lesion
Chain in classification:
1 Classes of ICD-10 2 G00-G99 Diseases of the nervous system 3 G90-G99 Other disorders of the nervous system 4 G93 Other brain lesions
There is no additional information about the diagnosis G93 in the ICD-10 classifier.
Dangerous pathology #8212; brain cyst
ICD10 code
Most often, the development of the disease is influenced by the following reasons:
- inherited anomalies;
- head injuries;
- infectious processes;
- post-stroke complications;
- processes during which cystic tissue is formed;
- disruption of intracerebral lymph circulation.
If it was not possible to determine the main reasons for the development of the cyst, then its size will increase.
Symptoms
- tapping, bursting pain in the head;
- headaches, constant dizziness;
- hearing loss;
- ringing in the ears while maintaining auditory function;
- blurred vision, resulting in double vision, blurred images and spots;
- hallucinations;
- paralysis of limbs;
- epilepsy attacks;
- involuntary twitching of arms and legs;
- temporary loss of consciousness;
- poor sleep;
- feeling of nausea, vomiting;
With a brain cyst, the symptoms are not pronounced, but the neoplasm itself can be diagnosed only with a thorough examination.
Depending on the location of the tumor, certain types are distinguished. Each of them has its own characteristics and developmental features.
Arachnoid
- rehabilitation period after brain surgery;
- inflammation of the intracerebral membranes;
- Marfan's disease.
Tumor of the septum pellucida
Lacunarnaya
Lacunar acid of the brain is the next fuel of the arachnoid growth. It can be concentrated in the voids that form between the membranes of the brain.
Cerebral
Retrocerebellar
Colloidal
The areas where this growth is concentrated remain the third ventricle of the brain. A colloidal cyst of the brain is presented in the form of a cavity, which is filled with a thick liquid of a jelly-like consistency. This type of cyst is inherited.
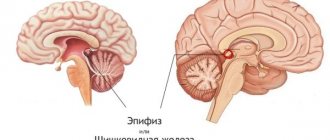
Pineal
This cyst forms on the pineal gland. That, in turn, performs a number of important functions, including:
- melatonin production;
- determination of human biorhythms;
- leveling of growth hormones in adolescence;
- regulation of puberty.
Frontal sinus tumor
A sinus cyst is a pathological formation that is concentrated in the frontal sinus. The tumor is characterized by the presence of a wall, and it is filled with secretory contents.
Epidermoid or dermoid
Choroid plexus tumor
Porencephalic
Diagnostics
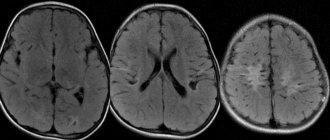
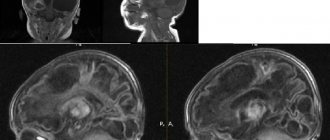
The presence of such growths should not always be associated with oncology. As a rule, tumors at the initial stage of development respond well to therapy. MRI of the brain must be performed regularly to monitor the dynamics of the disease.
Treatment with medications
It is possible to treat a brain cyst with the following medications:
- Medicines for resolving adhesions: Karipain, Longidaz.
- Medicines to normalize blood circulation and lower cholesterol levels.
- Medicines to normalize blood pressure and blood clotting.
- Medicines to enhance immunity.
- Antioxidants.
Operational path
How to treat a cyst to get rid of it forever? Most often, this involves surgical treatment.
Radical operations
Bypass surgery
Endoscopy
How to deal with the army
Consequences
If the patient is not diagnosed in time and not prescribed therapy, this will lead to the growth of a brain cyst, the consequences of which can threaten not only health, but also life.
So, why is a brain cyst dangerous?
- impairment of motor activity;
- impairment of hearing and vision;
- abundant concentration of pathogenic fluid in the ventricles of the brain;
- encephalitis;
- death.
Help
If you notice any symptoms of cerebral swelling in one of your loved ones, then you need to urgently call an ambulance, because if you do not take the patient to the hospital as soon as possible, he may face dire consequences. Such as, for example, subarachnoid hemorrhage, or death. If for some reason this cannot be done immediately, then first aid can be provided.
Proper help is to provide the patient with a sufficient amount of fresh air and immediately clear his airways of vomit and any other objects (which he could choke on at the onset of the attack). Then you need to apply ice or something cold to the sick person’s head. This will help improve the condition a little. If there is an oxygen mask nearby, put it on the patient.
Then, immediately take the injured person to the hospital. It must be transported strictly in a horizontal position, and under no circumstances should a pillow be placed under its head. Place a cushion under his feet and turn his head to the side. If the patient does have swelling, this position will help minimize damage to the brain.
Dangerous pathology #8212; brain cyst
ICD10 code
Most often, the development of the disease is influenced by the following reasons:
- inherited anomalies;
- head injuries;
- infectious processes;
- post-stroke complications;
- processes during which cystic tissue is formed;
- disruption of intracerebral lymph circulation.
If it was not possible to determine the main reasons for the development of the cyst, then its size will increase.
Symptoms
- tapping, bursting pain in the head;
- headaches, constant dizziness;
- hearing loss;
- ringing in the ears while maintaining auditory function;
- blurred vision, resulting in double vision, blurred images and spots;
- hallucinations;
- paralysis of limbs;
- epilepsy attacks;
- involuntary twitching of arms and legs;
- temporary loss of consciousness;
- poor sleep;
- feeling of nausea, vomiting;
With a brain cyst, the symptoms are not pronounced, but the neoplasm itself can be diagnosed only with a thorough examination.
Depending on the location of the tumor, certain types are distinguished. Each of them has its own characteristics and developmental features.
Arachnoid
- rehabilitation period after brain surgery;
- inflammation of the intracerebral membranes;
- Marfan's disease.
Tumor of the septum pellucida
Lacunarnaya
Lacunar acid of the brain is the next fuel of the arachnoid growth. It can be concentrated in the voids that form between the membranes of the brain.
Cerebral
Retrocerebellar
Colloidal
The areas where this growth is concentrated remain the third ventricle of the brain. A colloidal cyst of the brain is presented in the form of a cavity, which is filled with a thick liquid of a jelly-like consistency. This type of cyst is inherited.
Pineal
This cyst forms on the pineal gland. That, in turn, performs a number of important functions, including:
- melatonin production;
- determination of human biorhythms;
- leveling of growth hormones in adolescence;
- regulation of puberty.
Frontal sinus tumor
A sinus cyst is a pathological formation that is concentrated in the frontal sinus. The tumor is characterized by the presence of a wall, and it is filled with secretory contents.
Epidermoid or dermoid
Choroid plexus tumor
Porencephalic
Diagnostics
The presence of such growths should not always be associated with oncology. As a rule, tumors at the initial stage of development respond well to therapy. MRI of the brain must be performed regularly to monitor the dynamics of the disease.
Treatment with medications
It is possible to treat a brain cyst with the following medications:
- Medicines for resolving adhesions: Karipain, Longidaz.
- Medicines to normalize blood circulation and lower cholesterol levels.
- Medicines to normalize blood pressure and blood clotting.
- Medicines to enhance immunity.
- Antioxidants.
Operational path
How to treat a cyst to get rid of it forever? Most often, this involves surgical treatment.
Radical operations
Bypass surgery
Endoscopy
How to deal with the army
Consequences
If the patient is not diagnosed in time and not prescribed therapy, this will lead to the growth of a brain cyst, the consequences of which can threaten not only health, but also life.
So, why is a brain cyst dangerous?
- impairment of motor activity;
- impairment of hearing and vision;
- abundant concentration of pathogenic fluid in the ventricles of the brain;
- encephalitis;
- death.
Prevention
In order to never encounter this violation, you must follow a number of recommendations. Preventing cerebral edema is not difficult, but it can help ensure a healthy future for you.
First of all, you need to give up such bad habits as alcohol, smoking and drug addiction. Next, you should try to avoid any head injuries (be sure to wear seat belts when driving in a car, use a helmet when engaging in extreme sports, and so on).
Monitor your blood pressure, and also treat any infectious diseases in a timely manner (swelling can occur even after the flu). Another preventive measure is proper nutrition and normalization of weight.
Symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of arachnoid cyst of the brain
Reasons for the development of cysts
- Previous birth injuries, malpresentation of the fetus and the use of forceps;
- Intracranial hematoma;
- Cerebrovascular accident;
- Inflammation of the meninges;
- Suffered mechanical damage (traumatic brain injury);
- Carrying out surgical intervention on the cerebral hemispheres.
The formation of arachnoid cysts is usually classified into congenital , acquired and false . The latter is distinguished by the fact that from the inside it is lined with epithelium, and not with the tissue of the organ from which it is formed, like the others.
Symptom complex of arachnoid cyst
- Dizziness not caused by concomitant factors (pregnancy, lack of adequate oxygen flow, fatigue, overwork, stress, etc.);
- Disenfranchised nausea and vomiting;
- Hallucinations and nervous disorders;
- Paresthesia and hemiparesis;
- Convulsions;
- Headache;
- Impairment in performing coordinated movements;
- Constant noises;
- Sensation of pulsation in the head.
With the secondary development of an arachnoid cyst (after an illness or injury), the symptoms may be supplemented by manifestations of the underlying disease, which served as a provoking factor in the formation of the cavity structure.
Diagnosis of cystic formation
An arachnoid cyst, as a rule, appears as a result of previous diseases or injuries, so the lion's share of attention should be devoted to collecting anamnesis and conducting a thorough examination of the patient. To establish the etiological cause, the following diagnostic methods are used:
Thanks to the correct identification of the cause of cyst formation, it is possible to select an accurate etiotropic treatment aimed at eliminating the existing symptoms and preventing further growth of the cavity formation.
Features of treatment
When diagnosing a progressive cyst, therapeutic measures are aimed at identifying the cause of its formation and removal. Drug therapy is used to reduce the intensity of inflammatory processes, restore adequate blood circulation in the nervous tissue and normalize the functioning of affected brain cells.
If conservative treatment methods are ineffective, surgical intervention is indicated for the patient. The main reasons for carrying out such radical techniques are:
- Risk of rupture of the fluid-filled tissue;
- Mental health problems leading to frequent development of convulsions and epileptic seizures;
- Increased intracranial pressure;
- Increased intensity of focal symptoms.
The main surgical treatment methods include:
- Drainage - performing needle aspiration and removing fluid;
- Shunting - drainage of the cyst cavity for the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid;
- Fenestration is excision of a cystic formation.
Types of cysts
A primary or congenital cyst develops during the formation of an embryo in the womb. The main reasons for its occurrence are genetic abnormalities or the negative impact of aggressive factors on the fetus (taking medications, alcohol, drugs or various poisonings). Such a cyst is diagnosed in newborns.