on whether an MRI shows a brain tumor in the early stages. Magnetic resonance imaging is the only generally accepted method for diagnosing brain pathologies. The rest are either dangerous or complicated and expensive.
When is research needed?
An MRI of the brain is indicated if the following symptoms are present:
- gradual increase in intracranial pressure;
- disorders in the central nervous system;
- dull, growing pain in the head;
- the presence of constant pain caused by displacement of healthy areas of the organ;
- dizziness and lightheadedness;
- frequent cases of nausea and vomiting after waking up;
- manifestations of seizures;
- decreased or complete loss of hearing;
- disorientation in space;
- decreased vision or a feeling of “clutter” in front of the eyes;
- speech disorders;
- constant drowsiness and weakness;
- bouts of causeless irritability;
- behavioral disorders;
- mental disorders;
- numbness of individual parts of the body;
- weakness felt in the facial muscles or limbs.
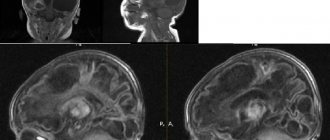
Clinical manifestations of pathologies vary depending on the size, location and type of tumor. They are differentiated using data collected through laboratory and instrumental examinations and histological analysis. In particular, brain tumors can be successfully detected on MRI.
Note!
Based on the appearance of the tumor on MRI, one can assume its nature, but verification of formations is carried out only through histological analysis.
Diagnostic costs and alternatives
If the procedure is not possible, the doctor should recommend alternative studies:
- Doppler ultrasound to study the condition of the blood vessels of the head;
- radiography with contrast to visualize tumors;
- PET and CT to detect the presence of tumors, nerve damage, and vascular dysfunction.
The cost of scanning depends on many factors. This is not only localization and difficulty of interpretation, but also the prestige of the clinic and the competence of the specialist performing the examination. On average, prices for tomography without contrast start from 2,500 rubles, with contrast - from 5,000 rubles.
Source: idiagnost.ru
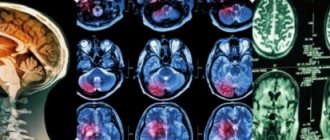
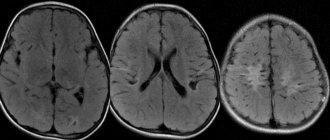
What can an MRI show?
MRI diagnostics of a brain tumor allows you to obtain visual images of the area being studied. The images are taken in color, and since different tissues of the body have different colors, the pathological area is painted in a different shade compared to healthy tissues. This allows diagnosticians to determine the location of the affected area in the early stages of its development. In this case, it is possible to determine not only the existence and location of lesions, but also the presence of metastases, as well as the degree of penetration of blood vessels into them.
Tomography makes it possible to detect the following pathologies:
- Neoplasms
that are primary in nature. This is the rarest type of gray matter abnormality in which aggressive cells spread exclusively to the body of the brain. - Oncological lesions
of a secondary nature. With this development, the disease, which appeared in other parts of the body, metastasizes to the head area. - Malignant formations
. In this case, MRI reveals oncology, in which there is rapid and uncontrolled growth of cancer cells, crowding healthy tissue and growing through them. At the same time, it is difficult to mark clear boundaries. - Benign lesions
. These areas are characterized by clear dimensions and boundaries. They are separated from the gray matter by their own membrane and have no penetrating processes.
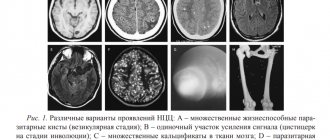
The distinctive signs of malignant tumors in the images include:
- fuzzy outlines;
- irregular shape;
- mass effect, that is, displacement of nearby structures;
- clear perifocal edema;
- heterogeneous distribution of contrast, which sometimes does not accumulate at all;
- hydrocephalus;
- “variegation” caused by necrosis, hemorrhages and/or cysts.
Note!
If cancer is suspected, an examination using a contrast agent administered intravenously is usually prescribed. It colors the damaged areas, making them visible even in the early stages.
MRI: how the research procedure is carried out
Magnetic resonance imaging is a highly informative research technique that helps obtain a layer-by-layer image of the affected area of the brain.
Detects structural changes, structural anomalies, traumatic lesions, pathological neoplasms. Progress of the procedure:
- the patient removes metal jewelry (including piercings), takes a horizontal position, puts on protective headphones,
- communication with the doctor remains throughout the procedure,
- if necessary, a contrast agent is administered intravenously,
- duration of the study without contrast agents is up to 20 minutes, with contrast up to 40 minutes,
- the procedure does not cause pain or discomfort.
The radiologist deciphers the image. The doctor determines the presence and structure of the formation, its boundaries, and the pathological effect on neighboring tissues.
MRI for tumors in the pelvis
Currently, it is difficult to imagine modern oncology without MRI for tumors in the pelvis. In a fairly short period of time, gynecologists and urologists have managed to appreciate the significant contribution of MRI to the diagnosis and monitoring of the effectiveness of treatment of oncological diseases.
Prostate adenoma, or in the modern world, benign prostatic hyperplasia, is a manifestation of an increase in the volume of glands near the urethra.
Compression of the urethra causes such a common symptom of adenoma as difficulty urinating. These changes can occur as early as 40 years of age in ten percent of the male population, and after 80 years of age in almost 100% of the male population.
How to determine oncology?
To determine brain cancer, a patient must undergo a series of diagnostic measures to make an accurate diagnosis and determine the stage of cancer.
Radiation diagnostics
If there is a suspicion of brain cancer, diagnosis can be carried out using X-rays, ultrasound, or radiomagnetic resonance. This must be done to identify the localization of the formation: benign and malignant, contours, size and inclusion of the formation.
Laboratory diagnostics
Such an examination makes it possible to determine the general health of the patient. However, it is unrealistic to determine the presence of an oncological process in the brain using laboratory diagnostics; one can only identify the presence of inflammatory processes, as well as their stages, by which diseases, including cancer, can be suspected.
Often, a study of cerebrospinal fluid is carried out in a laboratory setting. A certain factor allows one to recognize oncology in the brain, for example, the amount of protein, which is three times higher than normal, as well as moderate cytorz formed by lymphocytes.
Radioisotope diagnostics. It is required if it is necessary to identify disorders that may be characteristic of a particular type of cancer.
Endoscopic diagnostics. To determine the condition of the mucous membranes of the internal organs, studies such as gastroscopy, colonoscopy, laparoscopy and cytoscopy are performed. Also, this diagnostic method involves taking material for subsequent biopsy.
Biopsy
To diagnose the presence of an oncological manifestation, it is also recommended to undergo a biopsy, which is an extremely important analysis. The cancer process can be determined by the presence of cancer cells in the waste material.
A biopsy is a surgical procedure during which tissue is taken from a suspicious area to be examined for signs of malignancy under a microscope. Based on the results, the tumor cell type can be determined. A biopsy is performed as a separate diagnostic procedure.
If a patient has a glioma, performing a standard biopsy can be extremely dangerous to health. Damage to healthy tissue can cause disruption to the functioning of the body as a whole.
Stereotactic biopsy is performed under computer control. At the same time, those obtained from a computed tomography or magnetic resonance scanner make it possible to assess the exact location of the formation.
A spinal tap is a procedure in which a puncture is taken to obtain a sample from the spinal cord. The resulting material is carefully examined to determine the presence of cancer cells. The puncture needle is inserted between the third and fourth vertebrae.
Advantages of MRI in diagnosing brain tumors
There are other ways to examine the brain and detect cancer. They differ from each other because they are based on different principles. To make a diagnosis, they often complement MRI diagnostics. What are these alternative examination methods:
- Pneumography examines the nature of respiratory movements. The results obtained are recorded by the device.
- Positron emission tomography is the newest and most sensitive diagnostic method that provides the most complete picture of the disease. The tomograph records not only the size and location of the tumor, but also changes in cell activity.
- Computed tomography or MSCT shows organs in cross-section. This diagnostic is suitable for examining solid structures.
- Angiography is a method of contrast X-ray examination of blood vessels, used in radiography, fluoroscopy, computed tomography (MSCT) and hybrid operating room. He studies the functional state of blood vessels, blood flow and the extent of the pathological process.
- MRI angiography is a method of studying blood vessels using contrast. The results are monitored using MRI.
- An electroencephalogram studies brain activity. This method makes it possible to observe how brain structures, including the cerebral cortex, function.
- A lumbar puncture collects cerebrospinal fluid. The samples are then examined for their chemical composition.
- Magnetoencephalography measures and visualizes magnetic fields resulting from electrical activity in the brain. Helps in the treatment of epilepsy, as well as for diagnosing multiple sclerosis, schizophrenia, etc.
- Biopsy is a mandatory method of examination for oncology. First, cells and tissues are collected, which are then examined under a microscope.
A blood test is also done during the examination. It allows you to determine its chemical composition and identifies pathologies.
MRI diagnostics is prescribed for the following symptoms:
- Frequent dizziness.
- Severe headache, and the head hurts for no obvious reason.
- Cramps.
- Intoxication phenomena (for example, vomiting).
- Hallucinations.
- Fainting.
- Mental difficulties (memory impairment, inability to concentrate, unmotivated actions).
The technique also has certain contraindications. This is, first of all, the presence in the patient’s body of metal and/or electronic devices that cannot be removed during the study period. If there are contraindications, other diagnostic methods (CT) are selected.
Very often, the injection of a contrast agent is required to accurately determine the diagnosis.
Very often, the injection of a contrast agent is required to accurately determine the diagnosis. With its help, the pathological area takes on a clearer outline.
Some patients may have an allergic reaction to gadolinium-based agents used as contrast agents. This situation, which is rare, is a contraindication for contrast.
Whether a doctor can prescribe an MRI diagnosis if a tumor is suspected depends on his professionalism. After all, before prescribing an MRI for a tumor, it is imperative to make sure that the patient has no contraindications.
- The MRI procedure is strictly contraindicated for patients who have electronic devices in their bodies. These are devices such as pacemakers or hearing aids.
- The procedure is not performed on patients who have signs of mental disorders, the presence of claustrophobia, or in an unconscious state. If there is a need to undergo an MRI for a patient who has signs of claustrophobia, it is recommended that the diagnosis be carried out using an open tomograph or under anesthesia.
- The presence of metal implants in the body. If the patient has metal dentures, dental inserts, pins, braces and other products, then it is not rational to conduct an MRI, since the images will be distorted.
- Pregnancy period in the first trimester. Experts do not recommend undergoing the study, as this may negatively affect the development of the baby’s main organs and systems.
- Having tattoos. Most inks used for tattooing contain metallic impurities. These metal impurities negatively affect the test results.
Preparation for an MRI is usually not required, with the exception of relaxing your diet. Before lying on the tomograph bed, the specialist makes sure that there are no contraindications.
If necessary, a contrast agent is injected into a vein. The patient is given a special panic button, which must be pressed if their health worsens.
The duration of the diagnosis is about 1 hour. Upon completion, the patient receives images in the form of sections, a diagnostician’s conclusion, and a disk with a recording of the procedure.
MRI for tumors in the abdominal cavity
MRI has become the leading method in diagnosing liver tumors worldwide. The liver is most often affected by metastases from colorectal, pancreatic, stomach and breast cancer.
MRI for tumors in the abdominal cavity allows you to visualize even small metastases measuring less than one centimeter. In some cases, this can significantly affect further treatment in terms of the choice of tactics.
This will allow the patient to avoid useless manipulations at this stage and best prepare him for radical tumor removal.
There are two types of pancreatic cystadenoma: serous pancreatic cystadenoma and mucinous pancreatic cystadenoma. Each of them has its own characteristic features on MRI for tumors in the abdominal cavity.
This allows for accurate diagnosis, indicating the entire range of information that interests the surgeon to make a decision and perform surgery or leave the patient under dynamic observation.
Prostate cancer
Pancreatic cancer is a very insidious cancer. It develops almost asymptomatically until it becomes either an incidental finding or reaches a significant size.
With large sizes in the area of the head of the pancreas, vascular invasion in the area of the porta hepatis and extrahepatic bile ducts and the development of obstructive jaundice are determined.
Jaundice begins from the sclera and with its sudden appearance, especially in people over 50 years of age, it is urgent to conduct a full examination with the obligatory use of radiation diagnostics in order to first rule out a tumor on MRI.
MRI for tumors in the pelvis allows you to confidently diagnose prostate cancer, even with small tumor sizes. It is important for both patients and urologists to understand that the right place to start is to perform an MRI of the prostate before performing a biopsy in patients with high PSA levels.
Most false-negative results in prostate biopsy are due to poor diagnosis. These recommendations are endorsed by the European Society of Urogenital Radiology.
Head pain as the main symptom
One of the first symptoms that help identify a tumor that has formed in the brain is headache, both morning and night. Rarely does the pathology occur without pain in the head area. More often, the intensity of attacks of cephalalgia increases after physical or mental stress. Painful sensations intensify in the following cases:
- immediately after waking up.
- bending and sudden head movements.
- abdominal muscle tension.
Instrumental diagnostics
Instrumental methods for studying the structures of the head, such as magnetic resonance and computed tomography, which highly accurately confirm the absence or presence of a tumor, will help check suspicions. A hardware test for the presence of a tumor in the structures of the brain will show the smallest neoplasms, the diameter of which does not exceed 1-2 mm. Ancillary instrumental diagnostic methods include magnetoencephalography, MRI angiography, positron emission tomography, and lumbar puncture.
Causes of oncology
Before asking the question of how to determine brain cancer, you should find out the reasons that contribute to the development of this oncological process. In fact, even doctors often wonder why some patients develop an oncological process?
Now it has not been possible to give a definite answer. There are a number of certain factors that increase the likelihood of developing oncological processes in this place.
There are factors that can influence the development of the oncological process in the body:
- alcoholism and smoking;
- living in radiation-contaminated areas and harmful working conditions;
- previous head injuries;
- secondary tumor, which can develop in almost all cases;
- exposure to electromagnetic pulses;
- stem infections, the presence of viruses in the blood;
- conducting diagnostic radiation (during the examination of one disease, the development of another can be provoked);
- genetic factors: some diseases can become a catalyst for cancer throughout life. For example, Li-Fraumeni syndrome and Turcotte syndrome, as well as von Hippel-Landau disease and Gorlin syndrome.
Studying analyzes
There are several methods to detect cancer. One of the common ones is analysis of brain tumor markers.
Thanks to a general blood test, it is possible to determine only the presence of abnormalities that are unclear in their occurrence. These can be both harmless colds and serious oncological processes.
Based on the rate of subsidence of red blood cells and the amount of hemoglobin, the presence of kidney, liver, gallbladder, and blood diseases is revealed. The composition of the blood informs about a number of different diseases, including oncology. In case of deviations from the average values during a general blood test, the specialist will send the patient for additional examinations.
If there is a suspicion of cancer, blood tests for tumor markers will most often be prescribed.
Tumor markers are characteristic substances that indicate poor-quality cell division. These include:
- metabolic products;
- particles that remain after the decomposition of the formation;
- enzymes.
These components are produced in excessive quantities by cells that have not been affected by the disease.
There is a list of non-invasive methods for detecting this substance in various organic liquids into which it has been released.
Due to their peculiarity, markers make it possible to detect exactly where the tumor has formed and at what stage it is developing. There are also markers without reference to a separate organ. Their presence determines only the formation of an oncological disease.
For brain cancer, obtaining a biopsy sample is difficult and sometimes impossible. The puncture is most often performed only before surgery in order to definitively make a diagnosis. Therefore, a blood test for cancer is considered a more preferable option.
Today, when donating blood to determine tumor markers for brain cancer, they cannot be detected. Since markers that are similar to this type of formation have not yet been identified. At the same time, you should not refuse to take tests. After all, there are various markers, the appearance of which will indicate an emerging pathological process. Their concentration increases if metastases appear in the brain.