Is there a diagnosis of brain immaturity?
There is a lot in ICD-10. You will come across systemic atrophies, congenital mental retardation, or oligophrenia, from debility to idiocy, perinatal lesions of the central nervous system, or even the mysterious lissencephaly, which is a flattening of the sulci of the brain. But you won’t find such a thing as brain immaturity in children, much less such a diagnosis, there.
But there is an official international classification of diseases of the 10th revision, according to which every doctor’s appointment, both outpatient and inpatient care, from the maternity hospital to the last breath is coded with a special alphanumeric designation, or code.
Having looked through all the sections, from oncology to parasitic infestations, and from nervous diseases to injuries, you will also not find such a diagnosis as “immaturity of the cerebral cortex”
What's the matter?
Parents' Concerns
If we haven’t found anything official about this diagnosis, let’s turn to RuNet - the Russian-language segment of the Internet, in which this mysterious “immaturity of the child’s cerebral cortex” is “exaggerated.” Do you think this diagnosis appears in medical online publications, is discussed at consultations of specialists, and famous neurologists seriously discuss its features?
Not at all like that. Everything that can be read about him does not go beyond the forums of worried mothers, and the situation is quite ordinary: “I came from the clinic (ultrasound room) today in shock (hysterical, on weak legs). I (we) were told that my daughter (son, granddaughter) has signs of brain immaturity. Girls (girlfriends, people), tell me what this is and HOW WE NEED TO LIVE WITH THIS.
In these chats, an incomprehensible wave of a completely unclear diagnosis splashes, and at the same time it does not occur to anyone that the child is an immature creature. His task is to grow and develop.
For some reason, none of the mothers on the site will write, for example, about the well-known congenital mental retardation, that is, oligophrenia, for example, the following: “Girls, my 11-year-old son has poor academic performance, delayed development, we were transferred to a special school, we have been receiving treatment for a long time A psychiatrist and a speech therapist finally conducted tests, checked memory, attention, mental abilities and said: your son is retarded...”
Introduced? That’s just it, no one will write like that, and if they do, they will receive the answer: “We sympathize. Well, now not everyone can be an academician; watchmen are also needed...” It is clear why such a diagnosis does not shock anyone: because everything for mental retardation has long been provided for: diagnostic criteria, symptoms, causes, and means of rehabilitation and social adaptation of the mentally retarded. In a word, this is a well-known and sad topic.
Another thing is the incomprehensible and terrible “immaturity of the child’s cerebral cortex.”
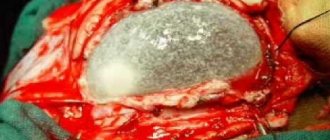
Anencephaly is a fetal developmental defect
Anencephaly is a congenital abnormality of fetal development that develops at an early stage of intrauterine life.
The pathology is characterized by the complete or partial absence of individual fragments of the skull and brain - the cerebral hemispheres and other parts, bones of the cranial vault, and soft tissues. The defect leads to the death of the patient in 100% of cases. The timing of death varies slightly. In 7% of cases, the fetus dies during pregnancy. The remaining children are born alive and can live up to several weeks.
Cases have been described in which the life expectancy of patients was more than 3 years.
Characteristics of the pathology
Anencephaly is a pathology that in the medical classification refers to dysraphism (non-fusion) of the cranial region, which is caused by a violation of the formation of the mesodermal and ectodermal germ layers. Such fetal malformations are accompanied by abnormal formation of the meninges, cranial bone structures and soft tissues of the head.
The prevalence of the pathology is 1 case per 10 thousand newborns (US statistics), 1 case per 1 thousand newborns (statistics from European countries). It is more often detected among female infants (the ratio of sick male to female newborns is 2:3). Full-term babies survive after birth in 75% of cases.
In 9% of cases, concomitant anomalies and diseases are detected simultaneously with the tube defect - absence of the pituitary gland, heart defects, underdevelopment of the adrenal glands, cleft palate, spina bifida (the vertebrae do not close together, which leads to prolapse of the spinal cord).
One of the most famous patients with anencephaly is an American, a native of Virginia, Stephanie Keene, who received the nickname Baby Kay.
The name of this patient is associated with many public controversies regarding issues of bioethics.
The parents consciously supported the life of a doomed child whose future was predetermined. Medical experts insisted that the girl be taken off the ventilator.
The mother defended her daughter’s right to exist in court, supporting her position with religious beliefs. Organizing Stephanie's care cost the clinic more than $500,000.
The child died of cardiac arrest 2 years 5 months after birth.
Baby Kay’s compatriot named Jackson Emmett Buell, also known as Jackson Strong (translated from English as “strong”), was born in 2014 with a diagnosis of anencephaly. In 2020, he turned 4 years old and was recognized as the record holder for life expectancy among patients with a similar pathology.
How long people live with anencephaly is determined individually, taking into account such factors as the general health of the newborn, the presence of concomitant diseases, the nature and degree of influence of the defect on life activities, the type and amount of available medical care. Life expectancy in most cases does not exceed several weeks.
Forms of the disease
Pathology refers to the group of organic lesions of brain tissue. Anomalies in the development of parts of the telencephalon that occur in the embryonic period as a result of non-fusion (lack of closure) of the neural tube are divided into types:
- Anencephaly is the absence of the cerebral hemispheres in the brain, bone structures of the cranial vault and surrounding soft tissues.
- Hemiencephaly is underdevelopment (partial absence) of one hemisphere of the brain.
- Agenesis (complete absence, aplasia) of the corpus callosum is the absence of a plexus of nerve fibers connecting the hemispheres and called the “corpus callosum.”
- Hypoplasia (absence of part) of the corpus callosum.
- Exencephaly is the absence (partial or complete) of the bone structures of the cranial vault.
There are abnormalities in the development of parts of the telencephalon, which are associated with impaired differentiation (formation of a certain phenotype) of cells of the nervous tissue. These are agyria, microgyria, microcephaly, macrocephaly, which, along with anencephaly, are manifested by severe disorders of mental and physical activity. Brief description of pathologies:
- Agiriya. Absence of grooves and convolutions on the surface of the cerebral hemispheres.
- Microgyria. A large number of small convolutions, chaotically, abnormally located on the surface of the hemispheres.
- Microcephaly. Reduced diameter and weight of the brain.
- Macrocephaly. Abnormal, non-standard increase in the diameter and weight of the brain. It is accompanied by an incorrect location of the gyri, the appearance of foci of heterotopia (the appearance of tissue areas in uncharacteristic places) in the white medulla. Usually the skull is enlarged in size and pathological changes occur in the cytoarchitectonics (cellular structure) of the cortex.
In 40% of cases, when anencephaly is diagnosed during the perinatal period, a woman experiences premature birth - before the 37th week of gestation.
According to statistics, the birth of a child by planned cesarean section is associated with a reduced risk of infant death immediately after birth (only 4% of newborns died after birth by cesarean section). With vaginal birth, the risk of infant death is 2 times higher.
Causes
The mechanism and causes of fetal anencephaly are not fully understood. In some cases, the pathogenesis is based on chromosomal mutations in combination with negative external influences.
10% of children have a gene mutation, chromosomal abnormalities, or a history of teratogenic exposure.
The development of the anomaly is influenced by many factors, which are mainly associated with environmental conditions.
As a result, the process of formation of the primordium of the central nervous system - the neural tube, which occurs on days 20-28 of gestation, is disrupted. Normally, the cells that make up the neural plate subsequently form the central nervous system. During normal formation, the edges of the plate close to form a tube, which is the basis for the further development of the brain and spinal cord.
With fetal anencephaly, the front of the tube remains uncovered. As a result, the child often lacks important parts of the brain - the cerebral hemispheres, the cerebellum, and the meninges. Sometimes patients have a brain stem. The remaining parts of the brain are protected by a thin membrane. Main teratogenic factors:
- Adverse environmental influences (poor environmental conditions, ionizing radiation).
- Intoxication (chronic, acute) suffered by the mother.
- Infectious diseases that the mother suffered from during pregnancy.
Among the influencing factors are alcohol abuse, smoking, sudden changes in body temperature and blood pressure of the pregnant woman, and severe stress. The disease is not associated with hereditary predisposition. In 95% of cases, the parents of a sick child do not have neural tube defects.
Symptoms
Externally, a child suffering from the disease often does not show pronounced abnormalities and lesions. He lacks a cranial vault above the eyebrows. The back half of a child's head is usually protected by skin and hair. At the back of the head there is a hole through which dark red nerve tissue is visible.
The hole sizes are individual. The eyeballs sometimes protrude forward due to defects in the formation of the orbits. Different children's brains are affected to varying degrees. Some of them can swallow and eat, cry, feel vibrations, and hear. Some children respond to light stimuli and touch.
Diagnostics
Anencephaly is detected by ultrasound examination of the fetus, which is carried out starting from 11-12 weeks of gestation. A blood test of a pregnant woman, starting from 13-14 weeks of gestation, shows an increase in the concentration of alpha-fetoprotein - a glycoprotein that is formed during the development of the embryo.
If the level of alpha-fetoprotein increases, an additional examination in the format of ultrasound or amniocentesis (study of a sample of amniotic fluid) is prescribed. The diagnosis of anencephaly is usually an indication for termination of pregnancy. Some parents choose to keep the child and care for him.
Treatment methods
Specific treatment protocols have not been developed. Therapy is palliative (supportive) in nature. Typically, patients are in perinatal hospices, where they receive the necessary medical care.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis is unfavorable. Death occurs as a result of a gross disruption of the activity of internal organs and systems, most often the heart and respiratory system.
Statistics show that 20% of newborns die immediately after birth, in 50% of cases life expectancy varies from several hours to several days. In 23% of cases, newborns live longer than 1 day.
It is believed that developmental anomalies can be prevented by taking folic acid before conception and during pregnancy.
Some studies suggest that taking folic acid in pregnant women reduces the risk of neural tube defects.
There are medications that lower folic acid levels and may increase the risk of neural tube defects. Among them:
- Oral contraceptives.
- Valproic acid. Typically used in the treatment of epilepsy, bipolar disorders, and migraines.
- Antimetabolic drugs. Used to prevent excess scarring after fistulizing surgery for glaucoma.
When planning your next pregnancy, you should take into account that the risk of having a child with anencephaly increases by 2-5% after a similar episode in the past.
Anencephaly is a congenital malformation characterized by the absence of parts of the cerebrum. Leads to the death of the child. The anomaly is detected during an ultrasound examination of the fetus during gestation. Detection of signs of illness is usually a reason to terminate the pregnancy.
Source: https://golovmozg.ru/zabolevaniya/anentsefaliya
Could the cerebral cortex be immature?
Everyone knows that the cerebral cortex is what distinguishes humans from monkeys. The cortex is emotions, abstract thinking, level of communication, vocabulary, tendency to analyze, fine motor skills, behavior, temperament, character. The cortex is what makes us an individual. And naturally, it is necessary to talk about signs of immaturity of the cerebral cortex not in a baby, or, especially, a newborn, but in an adult and mature person .
We know that sometimes adults do stupid things, and in other situations they show what can definitely be called “functional immaturity of the brain.” For example, they leave their family and chase the next “skirt”. But for some reason no one gives such a “diagnosis” to adults.
Amazing, isn't it? It would seem that after the stage of puberty, when the formation of a person is completed, it is possible to completely distinguish between normality and pathology, but such a diagnosis is not given to adults either. There are schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, post-traumatic encephalopathy, epileptoid and hysteroid psychopathy and a host of other, but very specific diagnoses that distinguish between normal and disease in neurology and psychiatry. But for some reason, such a strange diagnosis of “immaturity” is given exclusively to children, and exclusively in Russian clinics.
Of course, children also have many things, for example, hyperexcitability syndrome, attention deficit disorder, or even autism. But all these are conditions that have a scientific basis, decades of observation by specialists, recommendations for treatment and, especially, for making a diagnosis. What is the reason? And why are our mothers afraid of the “consequences of brain immaturity”?
Why is this diagnosis made?
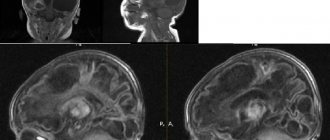
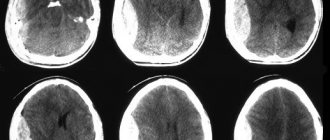
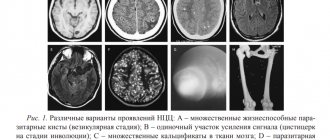
The thing is that this ridiculous diagnosis is not made by those specialists who seriously study the brain and see it. For example, in the conclusion of an MRI of the brain one can find hydrocephalus, the presence of cysts, cortical atrophy, smoothness of the grooves and a host of other morphological and specific abnormalities.
And “signs of immaturity of brain structures” are seen either when examining the brain through the fontanel, that is, when performing neurosonography, or by pediatric neurologists based on two or three deviations in the reflexes found.
But deep knowledge of child neurology remains only with elderly professors who devoted their whole lives to it, and, by the way, they will never give you such nonsense as a diagnosis. So consider this a complex and important formulation of a simpler answer: “I don’t know what’s wrong with your child, it seems like there are some deviations from the norm, but maybe not, I just don’t know how to figure it out, and I don’t have time.” .
And now everything falls into place. Instead of coming to a child psychologist or a specialist in the development of preschool children, crowds of mothers flock to a child neurologist who works three shifts at a district clinic. It’s not good to just admit your powerlessness and lack of time, but you need to say something...
And, instead of a conclusion, simple advice . The next time you hear a similar diagnosis, do not forget to politely but persistently ask the doctor what code this diagnosis has in ICD-10 (since any diagnosis must be coded), and, secondly, on the basis of what symptoms and syndromes, such a comprehensive diagnosis was made without the participation of a psychologist or psychiatrist. After that, smile and don’t believe fairy tales. In fact, the “cortical immaturity” is not in the child at all, but in the one who told you this.
Convulsive readiness: symptoms
The symptoms of the condition are very clear. Often, convulsive readiness symptoms are convulsive. However, they can manifest themselves differently at different stages.
Tonic seizures are characterized by loss of contact with the outside world. The person does not respond or react to any external manifestations. Characteristic muscle contractions can be observed both in one muscle group and throughout the body. The duration of the attack is up to 2 minutes. The head is thrown back, the upper limbs are bent, and the lower limbs are fully straightened.
After the attack of tonic convulsive readiness is over, clonic convulsions occur. The frequency of movements increases greatly. Starting from the face, the spasms spread to the whole body. The speed of inhalation and exhalation increases significantly. The skin becomes very white. Foam often appears from the lips. Based on the duration of a clonic attack, a diagnosis of convulsive readiness is made and the severity of the disease is determined.