What are the lateral ventricles of the brain and what are they responsible for?
In the fetal brain there are four communicating cavities - the ventricles, which contain cerebrospinal fluid.
A pair of them are symmetrical lateral, located in the thickness of the white matter. Each has an anterior, inferior and posterior horn, they are connected to the third and fourth ventricles, and through them to the spinal canal. The fluid in the ventricles protects the brain from mechanical influences and maintains stable intracranial pressure. Each of the organs is responsible for the formation and accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid and consists of a single system of movement of cerebrospinal fluid. Liquor is necessary for stabilizing brain tissue, maintaining the correct acid-base balance, ensuring the activity of neurons. Thus, the main functions of the ventricles of the fetal brain are the production of cerebrospinal fluid and maintaining its continuous movement for active brain activity.
| Gestation period, weeks | Large cylinder head tank, mm | Head circumference, mm | Fronto-occipital size, mm | Distance from the outer to the inner contour of the crown bones (BPR), mm |
| 17 | 2,1–4,3 | 121–149 | 46–54 | 34–42 |
| 18 | 2,8–4,3 | 131–161 | 49–59 | 37–47 |
| 19 | 2,8–6 | 142–174 | 53–63 | 41–49 |
| 20 | 3–6,2 | 154–186 | 56–68 | 43–53 |
| 21 | 3,2–6,4 | 166–200 | 60–72 | 46–56 |
| 22 | 3,4–6,8 | 177–212 | 64–76 | 48–60 |
| 23 | 3,6–7,2 | 190–224 | 67–81 | 52–64 |
| 24 | 3,9–7,5 | 201–237 | 71–85 | 55–67 |
| 25 | 4,1–7,9 | 214–250 | 73–89 | 58–70 |
| 26 | 4,2–8,2 | 224–262 | 77–93 | 61–73 |
| 27 | 4,4–8,4 | 236–283 | 80–96 | 64–76 |
| 28 | 4,6–8,6 | 245–285 | 83–99 | 70–79 |
| 29 | 4,8–8,8 | 255–295 | 86–102 | 67–82 |
| 30 | 5,0–9,0 | 265–305 | 89–105 | 71–86 |
| 31 | 5,5–9,2 | 273–315 | 93–109 | 73–87 |
| 32 | 5,8–9,4 | 283–325 | 95–113 | 75–89 |
| 33 | 6,0–9,6 | 289–333 | 98–116 | 77–91 |
| 34 | 7,0–9,9 | 293–339 | 101–119 | 79–93 |
| 35 | 7,5–9,9 | 299–345 | 103–121 | 81–95 |
| 36 | 7,5–9,9 | 303–349 | 104–124 | 83–97 |
| 37 | 7,5–9,9 | 307–353 | 106–126 | 85–98 |
| 38 | 7,5–9,9 | 309–357 | 106–128 | 86–100 |
| 39 | 7,5–9,9 | 311–359 | 109–129 | 88–102 |
| 40 | 7,5–9,9 | 312–362 | 110–130 | 89–103 |
Functions of the cerebellum
The main function of the cerebellum is to adapt any movements. The embryos of the “small brain” are determined by three levels of the organ:
- Vestibulocerebellum. The most ancient department from an evolutionary point of view. This area connects to the vestibular apparatus. It is responsible for the balance of the body and the joint coordination of the eyes, head and neck. The vestibulocerebellum ensures synchronous rotation of the head and eyes in response to a sudden stimulus.
- Spinocerebellum. Thanks to connections with the spinal cord, from which the small brain receives information, the cerebellum controls the position of the body in space. The spinocerebellum controls muscle tone.
- Neocerebellum. Connects with the cerebral cortex. The newest department is involved in the regulation and planning of movements of the arms and legs.
Other functions of the cerebellum:
- synchronization of the speed of movement of the left and right eyes;
- synchronous rotation of the body, limbs and head;
- calculation of movement speed;
- preparation and compilation of a motor program for performing higher manipulation skills;
- precision of movements;
Little-known functions:
- regulation of the muscles of the speech apparatus;
- mood regulation;
- speed of thinking.
Counting methods
There are a number of methods to determine the gestational age. Let's talk about them in more detail.
Calculation of PDR based on the time of the last menstruation. In the practice of obstetricians and gynecologists, the method of determining the date of upcoming birth based on the first day of the last menstrual period before pregnancy is widely used. It is from this moment that the uterus begins to prepare for fertilization; in place of the rejected mucous membrane (endometrium), a new endometrium is formed, ready to receive a fertilized egg. Around the same time, an egg begins to mature in a woman’s ovary, which will be fertilized by a spermatozoon, which will give rise to pregnancy.
Determining the true duration of pregnancy is usually difficult. This is due to the fact that it is difficult to establish the exact date of ovulation (unless special diagnostic methods were used - an ovulation test, ultrasound monitoring of follicle maturation), the time of sperm movement through the organs of the woman’s reproductive system, as well as the exact date of fertilization (unless this was the only sexual intercourse for a month or an in vitro fertilization procedure - in vitro fertilization).
In most cases, the duration of pregnancy, calculated from the first day of the last menstruation, is 280 calendar days, 10 obstetric months (40 weeks) or 9 calendar months. However, there is evidence of the birth of mature (capable of independent extrauterine life) children during pregnancy that lasted 230-240 days.
It must be said that a full-term pregnancy is considered already at 38 weeks, since in most cases by this time the baby is ready for independent extrauterine life and may well “ask” to leave. By this time, the child has lost all signs of prematurity and has all the indicators characteristic of a mature fetus.
In order to determine the expected due date based on the first day of the last menstruation, it is necessary to add 280 days to this day. To make the calculation easier, you can count back 3 months from the date of the first day of your last menstruation and add 7 days. For example, if the first day of the last menstruation was June 23, then by counting back 3 months (May 23, April 23, March 23) and adding 7 days, you will get the estimated due date of March 30.
| Gestational age (in weeks and days) | Coccyx-parietal size (cm) |
| 2 n. | 0,3 |
| 3 n., 2 d. | 0,4 |
| 4 n., 3 d. | 0,5 |
| 4 n., 4 d. | 0,6 |
| 4 n., 5 d. | 0,7 |
| 4 n., 6 d. | 0,8 |
| 5 n. | 0,9 |
| 5 n., 2 d. | 1 |
| 5 n., 3 d. | 1,1 |
| 5 n., 5 d. | 1,2 |
| 5 n., 6 d. | 1,3 |
| 6 n., 1 d. | 1,4 |
| 6 n., 2 d. | 1,5 |
| 6 n., 3 d. | 1,6 |
| 6 n., 4 d. | 1,7 |
| 6 n., 5 d. | 1,8 |
| 6 n., 6 d. | 1,9 |
| 7 n. | 2 |
| 7 n., 1 d. | 2,1 |
| 7 n., 2 d. | 2,2 |
| 7 n., 3 d. | 2,3 |
| 7 n., 4 d. | 2,4 |
| 7 n., 5 d. | 2,5 |
| 7 n., 6 d. | 2,6 |
| 8 n. | 2,7 |
| 8 n., 1 d. | 2,9 |
| 8 n., 2 d. | 3 |
| 8 n., 3 d. | 3,1 |
| 8 n., 4 d. | 3,3 |
| 8 n., 5 d. | 3,4 |
| 8 n., 6 d. | 3,5 |
| 9 n. | 3,6 |
| 9 n., 1 d. | 3,8 |
| 9 n., 2 d. | 3,9 |
| 9 n., 3 d. | 4,1 |
| 9 n., 4 d. | 4,2 |
| 9 n., 5 d. | 4,4 |
| 9 n., 6 d. | 4,5 |
| 10 n. | 4,7 |
| 10 n., 1 d. | 4,9 |
| 10 n., 2 d. | 5,1 |
| 10 n., 3 d. | 5,2 |
| 10 n., 4 d. | 5,3 |
| 10 n., 5 d. | 5,5 |
| 10 n., 6 d. | 5,8 |
| 11 n. | 6 |
| 11 n., 1 d. | 6,1 |
| 11n., 2d. | 6,3 |
| 11n., 3d. | 6,5 |
| 11n., 4d. | 6,7 |
| 11n., 5d. | 6,9 |
| 11n., 6d. | 7,1 |
| 12 n. | 7,3 |
| 12 n., 1 d. | 7,5 |
| 12 n., 2 d. | 7,7 |
| 12 n., 3 d. | 7,9 |
| 12 n., 4 d. | 8,1 |
| 12n., 5d. | 8,3 |
| 12 n., 6 d. | 8,5 |
| 13 n. | 8,6 |
Calculation of MDP by ovulation. Another method of determining the expected date of birth (ED) is to calculate it by ovulation (the time the egg is released from the ovary). The method is as follows: from the first day of expected but not occurring menstruation, you need to count back 14-16 days and add 273-274 days to the resulting date. However, the accuracy of this method depends on several factors.
Firstly, the method is suitable only for those women whose cycle was regular and lasted 28-30 days. Only in this case can we assume that ovulation took place on the 14-16th day of the menstrual cycle.
Secondly, fertilization does not always occur on the day of ovulation. In other words, it happens that ovulation has occurred, but sexual intercourse took place only after some time. The fact is that the ability of an egg to fertilize on average is 24 hours, but the important question is the survival of sperm in the woman’s genital tract. There is evidence in the literature that sperm viability lasts 2-3 days, and according to some data - up to 7 days.
The baby's first movement. This is an important event for any expectant mother and, as a rule, every woman remembers the day when her baby first “made itself known.” And for the doctor leading the pregnancy, this day is another landmark in determining PDR. To the date of the first movement, 5 obstetric months (20 weeks lasting 7 days) are added if the pregnancy is the first, and 5.5 months (22 weeks) for multipregnant women and the estimated due date is obtained.
- the emotional state of the woman (if the expectant mother is positive about her pregnancy, there is a high probability that she will feel movement before the expected period);
- physical activity (if the expectant mother leads an active lifestyle - plays sports or is passionate about work, then, most likely, the first movement will be “postponed” to a later date);
- the physique of the expectant mother: if a pregnant woman has excess fat deposits on the anterior abdominal wall, then she may miss the first movement and feel fetal movements several weeks later than expected; conversely, thin mothers have a thin anterior abdominal wall, and through it it is much easier to feel the baby’s movements in the stomach.
Level of beta subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin (B-hCG). When conception occurs, the fertilized egg divides, and during this division, the embryo and membranes develop, one of which is called the chorion. It is the chorion that produces hCG, which is detected in a blood test.
Where does this accuracy come from? Let's count: 2 days - for fertilization. 4 days for the fertilized egg to move through the fallopian tube and 2 days for implantation (attachment to the wall of the uterus). Maximum concentrations of this hormone in the blood are observed at 8-10 weeks of pregnancy. Thus, different stages of pregnancy have their own levels of hCG in the blood.
Ultrasonography. The most reliable information when diagnosing pregnancy and determining its timing is obtained from early ultrasound examination (ultrasound). With transabdominal scanning (when the sensor is placed on the anterior abdominal wall), the presence of pregnancy can be established from the 5-6th week, with transvaginal echography (examination through the vagina) - 1-1.5 weeks earlier.
There are a number of methods for determining the duration of pregnancy.
When the delay in menstruation is still very small (up to 7-10 days), ultrasound diagnosis of pregnancy depends on the qualifications of the doctor and the quality of the equipment. In the early stages, the diagnosis of pregnancy is established on the basis of identifying the fertilized egg, yolk sac, embryo and its heartbeat in the uterine cavity, and in later stages - on the basis of identifying the fetus (or fetuses in case of multiple pregnancy) in the uterine cavity.
Depending on the information obtained during an ultrasound in the first week, one or another stage of pregnancy can be assumed. So, from the 3rd week from the moment of conception, a fertilized egg of a round or ovoid shape with a diameter of 5-6 mm begins to be detected in the uterine cavity. At 4-5 weeks it is already possible to detect an embryo - on the monitor it is determined as a strip measuring 6-7 mm. The head of the embryo is determined from the 8-9th week of pregnancy.
It is important to remember that only in the early stages the embryo grows in proportion to the expected gestational age, so for all women with the same period, its size will be identical. The size of the fetus is informative for determining its gestational age up to a maximum of the 15th week; later, this indicator can already be influenced by hereditary characteristics.
The most accurate indicator of gestational age in the first trimester is the coccygeal parietal size (CTR). The error in establishing the gestational age when determining the coccygeal-parietal size in 80% of cases does not exceed 1 day, and in 20% - 3 days. In this case, the accuracy of the determination increases when calculating the arithmetic mean of three consecutive CTE measurements.
In the second and third trimesters, the gestational age is determined based on the determination of various fetometric parameters: biparietal size, or transverse size of the fetal head (BPR), head circumference (HC), average dimensions of the chest and abdomen, abdominal circumference (AC), length of the femur.
Of the listed measurements in the second trimester, the most informative for determining the duration of pregnancy is BDP and head circumference. Moreover, the longer the gestational age, the less accurate its determination. An ultrasound examination performed before the 24th week is considered optimal for determining the duration of pregnancy.
Separately, it is necessary to say about the size of the fetal cerebellum. The most reliable method for determining the gestational age is considered to be based on the interhemispheric size of the cerebellum, the accuracy of which reaches 1-2 days. The size of the cerebellum not only makes it possible to most reliably determine the duration of pregnancy and PDR, but also plays a large role in the diagnosis of such a formidable complication of pregnancy as fetal growth restriction syndrome.
The size of the fetal cerebellum is not affected by pathological processes affecting the development of all organs and systems of the fetus. The cerebellum is well protected and is the last to respond to changes in blood flow. Thus, when fetometric indicators are less than normal and the size of the cerebellum is normal (corresponding to the gestational age of the fetus), a diagnosis of “fetal growth retardation syndrome” is made.
Decoding ultrasound results
The woman is informed about the priority parameters of the fetus, and in case of pathological abnormalities, directly during the procedure. A detailed interpretation of the ultrasound is performed by a gynecologist who is managing the pregnancy. A specially developed table of normative indicators for the mother and fetus at the twentieth week helps to analyze the results.
Parameters of development and growth of the child in the uterine cavity at twenty weeks of pregnancy:
- fetometry (total size of the fetus): weight – about 300 g, height – from 160 to 230 mm;
- abdominal circumference and head circumference: 124–164 and 154–186 mm, respectively;
- chest diameter – 48 mm;
- LZR (fronto-occipital distance between the outer contours of the occipital and frontal parts of the skull) – 56–68 mm;
- BPD (biparietal distance from the upper contour of the outer surface of the crown bone to its lower contour) – from 55 mm to 77;
- the length of the thigh bones is 29–37 mm, and the length of the lower leg bones is 26–34 mm;
- length of humerus and forearm: 26–34 mm and 22–29 mm;
- foot – about 3 cm;
- Heart rate or heart rate – up to 150–160 beats/min.
The anatomical structure and structure of the internal organs of the child's respiratory system are assessed for the presence of cystic neoplasms in the lungs and fluid in the pleural cavity. In the heart, the location of the atria, chambers, interventricular septa and valves is taken into account. The abdominal organs are studied according to their location and size.
From the subcortical structures of the brain, the following are analyzed: the cerebellum, cavities with cerebrospinal fluid (ventricles), symmetrical halves of the brain (large hemispheres), interstructural space (cisterns), thalamus (optic thalamus).
In addition to the child’s parameters, the doctor determines the normative development of the provisional (temporarily present in the woman’s body) organ - the placenta and possible deviations. Ultrasound standards for the placenta are as follows. Amniotic fluid is in the range of 86–230 (with multiple embryonic pregnancies, the volume increases). These numbers indicate the average volume of amniotic fluid or AFI (amniotic fluid index).
If there is insufficient water (oligohydramnios), fusion (combination) of the membranes of the placenta and fetus is possible. This leads to fetal tissue atrophy, bone transformation, and oxygen deficiency of the embryo. Excessive fluid volume (polyhydramnios) threatens premature delivery, placental abruption, and impaired contractility of the uterine muscles after childbirth.
A prematurely ripened placenta indicates a developmental delay in size of the fetus (developmental delay syndrome or FGR). The structure of the temporary organ must be homogeneous (homogeneous). Possible compactions are a sign of premature aging of the placenta. In this case, we may be talking about a deviation in the baby’s development. Until week 30, there should be no calcifications (calcium deposits) in the placenta. Their presence can threaten the fading of pregnancy, spontaneous termination (miscarriage), and physical abnormalities in the development of the baby.
Chorionic tissue is one of the structures that forms the placenta; in the second trimester, it is a membrane with villi that faces directly towards the baby. At this stage of pregnancy there should be no serious depressions or bulges on it (only slight waviness).
With additional examination of blood vessels (Dopplerography):
- uterine artery resistance index – 0.52;
- pulsar index of the uterine arteries – 1.54;
- SDO (systole-diastolic ratio) in the uterine arteries – no more than 2.5;
- umbilical artery resistance index – 0.74;
- SDO in the umbilical cord arteries – no more than 4.4.
If a significant discrepancy with normal values is detected, the woman must undergo additional examination and treatment in an inpatient setting. A properly selected therapeutic course will avoid difficulties during delivery.
Plans and reality
But the “cherished” day has arrived, and the baby doesn’t even think about asking to come out. Should I wait, go to the doctor or still go to the maternity hospital? You can wait no more than a week on your own, i.e. until 41 weeks of pregnancy, then you should visit a doctor. The doctor will determine the readiness of the woman’s body for childbirth (immature or insufficiently mature cervix, decreased tone and excitability of the uterus in response to examination), and will also take into account the condition of the fetus; if there are no signs of labor, he will refer you for hospitalization in a hospital, where the expectant mother will be under constant care. observation. After a series of diagnostic procedures, the issue of timing and method of delivery will be decided.
There is no need to rush time - everything will happen when it is supposed to happen. Only in some cases, when the need arises, the due date is determined by the attending physician on an individual basis.
Eleonora Shagerbieva, obstetrician-gynecologist, Ph.D. honey. Sciences, Moscow
Main factors in the development of the disease
Most often, ventricular enlargement develops as an independent disease. But sometimes Turner, Down, Edwards syndrome, etc. are jointly diagnosed. Symptoms appear if a woman has various anomalies during pregnancy, and these do not necessarily have to be chromosomal diseases.
Dilatation of the ventricles is provoked by infectious diseases that a woman suffered while pregnant. The following provoking factors of ventriculomegaly are also identified:
- intrauterine infections;
- heredity.
What exactly provoked the expansion of the ventricles can only be determined by a neurologist after a thorough examination.
Ventriculomegaly is more often detected in newborns if the mother’s age exceeds 35 years. After reaching this age mark, a woman may develop deviations that must be taken into account when conceiving a child:
- the risk of genetic disorders increases;
- the maternal chromosome may be mutated;
- oxygen starvation in the fetus doubles;
- the risk of infectious diseases increases.
Based on this, we can say that in women under 35 years of age, the risk of developing the disease in their unborn child is unlikely, and after that it increases sharply, two to three times.
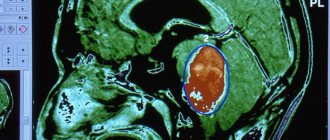
What is ventriculomegaly and what types of it occurs?
If, according to the results of an ultrasound at 16–35 weeks of pregnancy, an increase in the lateral ventricles to 10–15 mm is recorded, and the size of the child’s head is within normal limits, the sonologist questions ventriculomegaly. One study is not enough to make an accurate diagnosis. Changes are assessed over time, for which at least two more ultrasounds are performed with an interval of 2–3 weeks. This pathology is caused by chromosomal abnormalities, intrauterine hypoxia, and infectious diseases that the mother suffered during pregnancy.
Ventriculomegaly can be isolated asymmetric (expansion of one ventricle or its horns without changes in the brain parenchyma), symmetric (observed in both hemispheres) or diagnosed in combination with other pathologies of fetal development. Ventricular pathology is divided into three types:
- mild - organ dilatation is 10.1–12 mm, usually detected at 20 weeks and needs to be monitored before birth;
- moderate – the size of the ventricles reaches 12–15 mm, which impairs the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid;
- pronounced - ultrasound readings exceed 15 mm, which disrupts brain function and negatively affects the vital functions of the fetus.
If the lateral ventricles are enlarged to 10.1–15 mm (deviation from the table standards by 1–5 mm), borderline ventriculomegaly is diagnosed. It may be asymptomatic up to a certain point, but in fact it indicates the emergence of a complex pathological process that gradually changes the functioning of many important organs.
Survey time range
The specific timing of the second examination is based on the criteria for fetal growth and development. At 19-20 weeks, the baby’s production of somatotropin growth hormone increases. The baby increases significantly in size, which allows the doctor to examine its body parts and internal organs in detail. By this period, the baby’s skeletal system is clearly visualized. The doctor can evaluate the probable malformations of its development (curvature of the main skeletal rod, the length of the bones in relation to the norm, the size of the head frame, facial bones).
Internal organs and systems are also formed by 20-21 weeks of intrauterine development. The state of health of the heart, nervous, genitourinary, and digestive systems can be fully analyzed. It is during this period that possible pathologies of a hereditary nature, or deviations that arose during the growth of the baby, are identified:
- severe defect of the nervous system (anencephaly);
- a serious form of genomic pathology (Down syndrome);
- chromosomal pathology – Edwards syndrome, otherwise trisomy 18 syndrome;
- rare genetic diseases (Turner syndrome and Patau syndrome).
If the doctor doubts the reliability of the diagnosis, the woman is asked to undergo amniocentesis in a hospital setting to confirm or refute the alleged abnormalities. This is a rather risky and complex manipulation of collecting amniotic fluid for detailed analysis, but the reliability of the results reaches 96%. Some pathologies detected in time, for example, heart defects, can be eliminated through intrauterine surgery. Then, by the time of birth, the baby will be healthy.
Based on ultrasound data in the second trimester, the doctor can diagnose diseases in the baby that make viability impossible. As well as severe deviations, when the child’s life activity will be impossible without the support of medical equipment. In this case, the question of termination of pregnancy arises. The possibility of abortion lasts only up to twenty-two weeks.
At the twentieth week, the child begins to differentiate night and day, actively work with his legs (pushing) and arms (clinging to the umbilical cord, sucking fingers). In addition, the baby may change facial expressions (smile or frown). Hair and nail plates are formed. An ultrasound examination at 20–24 weeks allows you to identify, and, if possible, correct deviations in the intrauterine development of the baby. It is absolutely impossible to ignore screening at this time.
Treatment of pathology
When treating a pathology, the doctor sets two goals: finding and eliminating the cause of abnormal organ enlargement and neutralizing its consequences for the newborn. In case of a mild isolated form, which is not caused by chromosomal abnormalities, the expectant mother is prescribed drug therapy: taking diuretics, vitamins, injections of drugs that prevent hypoxia and placental insufficiency.
In the postpartum period, infants are given several courses of massage aimed at relieving muscle tone, strengthening, and eliminating neurological symptoms. Monitoring by a neurologist is required in the first weeks, months and years of life. Severe forms of pathology require surgical treatment after the birth of the baby.
The prognosis for a child with a severe form and chromosomal abnormalities is unfavorable.
Diagnostics
Usually the disease is detected during pregnancy through ultrasound diagnostics. Subsequent monitoring of the child is carried out by a neurologist. He may prescribe treatment or rehabilitation procedures.
Unfortunately, cerebellar hypoplasia is considered an incurable disease, and children who are born with it rarely survive beyond the age of one year. All procedures that are carried out with such a child are aimed at restoring lost functions and curbing the development of the disease. Treatment methods include:
- exercises aimed at developing coordination;
- massage;
- to maintain speech, classes are held with a speech therapist;
- It is also recommended to communicate with such children as often as possible and instill in them various hobbies, such as drawing or origami, which develop fine motor skills of the fingers.
Possible consequences of ventriculomegaly
Abnormal development of the ventricles can lead to serious defects of the fetus, newborn, and death of the child. Such tragedies are a consequence of impaired outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, which interferes with the development and functioning of the nervous system. Pathology often provokes early labor, impaired brain activity, heart defects, and infections. In severe stages, the disease ends in hydrocephalus of the brain in children. The earlier such a change occurs, the worse the doctors' prognosis.
If the cause of the deviations is chromosomal abnormalities or complicated heredity, ventriculomegaly occurs together with the following pathologies:
- abnormal connection of blood vessels and lymphatic systems;
- Patau, Down syndrome;
- delay in mental and physical abilities;
- pathologies of the musculoskeletal system.
The prognosis for mild and moderate ventriculomegaly is favorable if the pathology is not accompanied by other disorders of the nervous system. This is confirmed by clinical assessments of the neurological status of babies who were given a similar diagnosis in fetal development. 82% of children do not have serious abnormalities, 8% have certain problems, and 10% have severe impairments with disability. The pathology requires constant monitoring by a neurologist and timely correction.
- Cerebellar tonsils at the level of the foramen magnum