Brain edema is a consequence of interrelated physical and biochemical processes occurring in the body as a result of diseases or pathological conditions.
This complication, depending on the severity, may remain unnoticed and pass without a trace, for example, with a mild concussion (symptoms). Much more often, the consequences of cerebral edema are further severe complications in the form of:
- changes in mental and mental activity
- visual impairment
- auditory
- motor
- coordination functions of the body that are the cause of disability
- cerebral edema often ends in death
Cerebral edema during stroke: what causes it
One of the common causes of the mentioned edema in a patient is a hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke he has suffered. Unfortunately, these types of circulatory disorders are almost always accompanied by the described problem, expressed to one degree or another and which is a kind of indicator of the severity of the pathological process.
Ischemic stroke is caused by obstruction of blood flow to certain parts of the brain as a result of blockage of blood vessels for one reason or another, which provokes oxygen deprivation, cell death and, as a result, brain swelling.
And with a hemorrhagic stroke, hemorrhage occurs under the lining of the brain, which becomes the impetus for a rapid increase in intracranial pressure and, accordingly, causes cerebral edema. The causes of this type of stroke are usually the same - high blood pressure, stress, physical exertion, causing blood vessels in the brain to rupture or blood to leak through their walls.
Surgical intervention
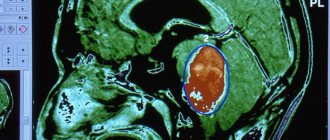
Surgical elimination of the pathology is resorted to in the absence of a positive effect after drug therapy. In a situation where the edema is caused by neoplasms of various types, local edema is corrected during neurosurgical treatment of the tumor.
In some cases, it becomes necessary to correct the pressure inside the skull. In such a situation, the meninges are dissected through the fontanelles and decompression is performed.
How does edema develop during a stroke?
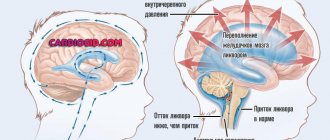
Initially, swelling is caused by metabolic disorders (metabolism) in the affected area. In medicine, this phenomenon is called cytotoxic cerebral edema, and it is localized mainly in the gray matter. Six hours later, vasogenic edema, localized in the white matter of the brain, joins the mentioned pathology. It is caused by the process of so-called sweating of fluid and proteins from small vessels into the extracellular space, caused by a slowdown in blood flow or its stasis (stop).
Simultaneously with the above-mentioned cerebral edema, necrosis also develops, which leads to the accumulation of osmotically active substances in the intercellular space, which cause an even greater release of fluid from the capillaries.
Cerebral edema during stroke develops very quickly and spontaneously, and it can be located in the lesion (local edema), in one hemisphere (diffuse edema) or in both hemispheres (generalized edema). It is very important to notice its signs and take action in time, although, of course, during a stroke it is quite difficult to determine the development of edema, since the patient, as a rule, is in a state of clouded consciousness or in a coma.
Treatment of the disease
Therapy is aimed mainly at eliminating the root cause and restoring oxygen metabolism in brain cells. In most cases, the newborn is on artificial ventilation. To maintain normal pressure and prevent infection, intravenous infusions of drugs are performed. The following main groups of drugs are used in treatment:
- osmodiuretics and saluretics – remove excess fluid
- corticosteroid drugs – inhibit the development of edema
- muscle relaxants – relieve seizures and focal symptoms
- drugs that normalize blood circulation in the cerebral vessels
- angioprotectors.
The method of hypothermia, an artificial decrease in body temperature, is very rarely used.
Signs of cerebral edema
Regardless of how the causes of cerebral edema are classified, its symptoms cannot be called specific and, therefore, it is quite difficult to determine the presence of a dangerous pathology in a patient, focusing only on them.
In medicine they are divided into three main groups:
- signs associated with increased intracranial pressure;
- signs of focal disorders;
- signs of stem pathology.
As a rule, cerebral edema (the causes, the consequences of which we are considering) is accompanied by severe headache, nausea and vomiting - these symptoms can be attributed to signs of intracranial hypertension.
Impaired speech, vision, hearing and touch, problems with orientation in space, as well as paresis and paralysis are signs of focal disorders.
With cerebral edema, patients often complain of shortness of breath, their breathing is impaired, a feeling of drowsiness and anxiety develops, blood pressure rises, clouding of consciousness develops, sometimes accompanied by convulsions - all these are signs of brainstem edema that require urgent resuscitation measures.
Oxygen therapy
Oxygen therapy is a procedure that uses oxygen for therapeutic and preventive purposes. Under the influence of oxygen, various substances are oxidized, and the body receives the energy that is necessary to maintain its normal functioning and other biochemical processes.
The most effective method of oxygen therapy is inhalation, when the patient inhales pure oxygen or a special gas mixture through a mask. Thanks to this procedure, it is possible to get rid of headaches, increase immunity, improve the functioning of the cardiovascular system and neutralize toxins.
Causes of cerebral edema in newborns
Separately, it is worth considering this pathology in newly born children. The reasons that cause cerebral edema in them most often lie in the severe course of labor in the mother and the birth trauma of the baby. But it can also be caused by congenital malformations or acquired diseases. Abscesses, tumors, meningitis, encephalitis, intrauterine hypoxia - all this can cause cerebral edema in an infant.
By the way, the course of the described pathology in children looks somewhat different than in adults, since their body still has very limited capabilities for maintaining vascular tone, regulating intracranial pressure and cerebrospinal fluid dynamics. The child’s only salvation in such a situation lies in the peculiarities of the connection of the skull bones, between which he has either soft cartilaginous tissue or a gap (fontanelles). By the way, this anatomical feature protects the baby from compression and swelling of the brain, which could end with any cry of the baby.
Differential diagnosis
Differentiated diagnosis is indicated if the baby has:
- hypoxic-ischemic damage to the central nervous system
- congenital abnormalities of brain structures
- hydrocephalus
- infection during fetal development, which is accompanied by damage to nerve cells
The difficulty of differentiation lies in the fact that such diseases can be supplemented by the appearance of local edema or damage to the parenchyma already at the stage of decompensation. It is for this reason that differential diagnosis is carried out only after the acute stage of the condition has been relieved.
Features of symptoms of cerebral edema in infants
Cerebral edema in newborns has a lightning-fast course. At the beginning of the development of pathology, the baby, as a rule, becomes lethargic, sleepy, he may have convulsions, and lose consciousness. In some children, on the contrary, swelling causes an excited state, expressed by constant non-stop crying.
At the same time, the fontanel swells even in a calm state, the volume of the head increases, the baby begins to vomit, and the temperature rises.
In newborns with cerebral edema, a characteristic sign of this pathology is a very rapid deterioration in the general condition and, unfortunately, in many cases it ends in death.
Drug therapy
Treatment of cerebral edema involves taking various groups of medications, which are selected by a specialist. Their main goal is to eliminate the factor that provoked the accumulation of large amounts of fluid in the brain structures. Symptomatic therapy is auxiliary and allows you to cope with the signs that arise during the pathology.
To get rid of excess fluid in the brain, the child may be prescribed certain groups of medications (see Table 2).
| Group | Description |
| Diuretics | Drugs in this group form the basis for the treatment of any diseases that are caused by the formation of edema. When taking diuretics, it is possible to achieve a pronounced therapeutic effect and improve the child’s well-being. It is possible to cope with unpleasant symptoms with the help of medications such as Lasix, Fonurit and Novurit. |
| Decongestant treatment | The drug that helps to cope with swelling is glycine. It is usually prescribed to infants along with drinks, such as juice or compote. |
| Dehydration therapy | This treatment involves intravenous administration of various solutions. Thanks to this therapy, it is possible to improve metabolic processes within cells, which restores brain function and reduces fluid volume. When treating newborns, hypertonic solutions such as calcium chloride, glucose and sodium chloride are administered. |
| Protein solutions | With the help of drugs of this group, it is possible to restore metabolic processes in tissues and have a beneficial effect on the protein balance in the child. For therapy, medications such as albumin solution are mainly prescribed, or plasma is administered. |
| Glucocorticosteroid drugs | With their help, it is possible to cope with the manifestations of cerebral edema and improve the overall well-being of the child. Typically, hydrocortisone is used for this purpose, which is selected individually taking into account the weight of the baby. |
Treatment methods on video:
In case of depression syndrome, the baby can be prescribed vitamins, among which Encephabol is considered the most effective. It has a complex trophic effect at the neural level. With the help of the medication, it is possible to normalize glucose metabolism occurring in the brain tissue. The drug has an antioxidant effect, improves the plasticity of red blood cells and increases ATP levels.
Cough and runny nose without fever in an infant: preventive measures
Cerebral edema: consequences
The sooner a patient with this diagnosis is provided with qualified medical care in full, the higher his chances of recovery. But quite often the recovery is only partial - it all depends on the severity of the pathological process.
The consequence is sometimes, for example, the development of epilepsy caused by impaired blood supply to certain parts of the brain. The patient may experience increased intracranial pressure, which in turn leads to constant headaches, dizziness, disturbances of consciousness, and even decreased social communication skills.
In many patients diagnosed with cerebral edema, the consequences of the pathology are manifested in the adhesive process in the ventricles, between the membranes or in the cerebrospinal fluid space, which leads not only to periodic headaches, but also to a depressive state and a disorder of neuropsychic activity.
If the swelling was prolonged, then its consequences may be impaired brain function and a decrease in a person’s mental abilities.
Symptoms of pathology
General medical – involves examination and diagnosis by a pediatrician.
It includes a general examination of the child, a neurological examination, an assessment of the reaction to various kinds of stimuli, and an assessment of the psychomotor functions of the body. Instrumental – involves the use of various kinds of devices and tools to diagnose the condition of the baby. This includes electroencephalography, echoencephalography, neuroophthalmoscopy, and brain tomography.
Most often, not one method is used to make a diagnosis, but both in combination. This way you can get the most accurate assessment of the child’s condition and the severity of the disease.
Brain edema in children is a very serious and severe illness, the consequences of which directly depend on how quickly the disease was detected and treatment started.
In order to relieve cerebral edema, it is necessary to identify the cause of the pathological condition and eliminate it. In addition, a set of medications is most often prescribed that will help not only relieve the symptoms of the disease, but also eliminate it completely.
Most often this is:
- Osmotic diuretics, which include Furosemide, Mannitol, Lasix
- Hormone-based drugs
Treatment is selected only by a doctor, individually for each individual case.
In addition, regular monitoring of the child’s condition, assessment of his condition and the effectiveness of treatment is mandatory.
In some cases, effective drugs do not help cope with the disease and require replacement with analogue ones.
Brain edema in children develops gradually. Therefore, unfavorable signs can be detected in advance:
- the child becomes lethargic, moves little, does not take the breast or bottle well;
- gradually he develops a headache - the newborn reacts to this with sharp cries;
- upon examination, you can detect bulging fontanelles on the skull;
- limbs are in a state of hypertonicity - fists are clenched, hands are pressed to the chest,
- the toes are tucked, and the legs themselves are bent at the knee and hip joints;
- you can notice the dilation of the pupils;
- the child goes from lethargic to hyperactive and screams shrilly;
- there is an increase in body temperature.
As cerebral edema progresses, the child develops convulsions, instability of breathing and blood circulation is noted, and increasing compression of the brain substance leads to impaired consciousness up to coma.
Cerebral edema in an infant can be diagnosed based on:
- medical history data that will suggest the cause of this condition; inspection data;
- ultrasound examination of the brain through the fontanelles;
- radiography of the skull;
- computed tomography.
Diagnosis must be carried out in a short time in order to begin treatment as early as possible. Relief of this condition involves placing the child in an intensive care unit. Initial measures should be aimed at eliminating the cause, if possible.
MORE ABOUT: How to treat knee joints at home
In parallel with etiotropic treatment, intensive pathogenetic and symptomatic therapy is carried out. It includes the use of the following groups of drugs:
- Diuretics - Diacarb (eliminates overproduction of fluid by brain cells), furosemide (removes excess fluid from the body).
- Glucocorticoids to eliminate edema (Dexamethasone).
- Anticonvulsants (Seduxen).
- Sedatives are aimed at correcting psychomotor agitation. Relanium can be used in pediatric practice.
- Correction of circulatory and respiratory disorders - ceraxon, digoxin, dopamine.
- To improve metabolism - ATP, ascorbic acid, B vitamins.
All these means are aimed at eliminating life-threatening conditions. After stabilizing the child’s condition, medications are prescribed aimed at restoring brain cells, impaired body functions, and preventing complications:
- neuroprotectors - restore the integrity of brain cells (Cerebrolysin, Actovegin);
- nootropics - improve cerebral circulation (Cavinton, Vinpocetine);
- means for improving microcirculation - restore tissue damaged during hypoxia (Pentoxifylline, Trental).
Forecast and consequences
With early diagnosis and complete treatment of cerebral edema in infants, the prognosis for life is favorable. However, such severe damage as cerebral edema, in most cases, leaves consequences:
- formation of epileptic activity;
- cerebral palsy;
- decreased mental abilities;
- posthypoxic encephalopathy;
- mental disorder;
- motor dysfunction;
- disappearance of previously acquired speech skills;
- extinction of grasping and sucking reflexes;
- muscle hypertonicity;
- strabismus;
- death.
That is why timely and correct diagnosis of this condition in children is so important.
Content
What are the consequences of cerebral edema in children?
The consequences of the disease in question in children can also be serious and depend on the severity of the disease.
These include the development of cerebral palsy and hydrocephalus, epilepsy, as well as disorders of the formation of internal organs.
Swelling of the brain in some children can cause problems with speech and coordination of movement. The pathology suffered, unfortunately, causes neuropsychic instability and mental retardation in some patients.
From the above, it is clear that cerebral edema in children is a very serious pathology that requires constant monitoring of the child by a neurologist and pediatrician, and its duration depends on the severity of the consequences of the disease.
Prevention
Today there are no special measures that could prevent the development of pathology. Nonspecific prevention is practiced, which involves following all recommendations for a healthy pregnancy and labor.
It is important to exclude exposure to factors that could cause injury to the baby or infectious pathologies immediately after birth. An important place in disease prevention is given to proper care and prevention of various injuries.