Encephalopathy of combined genesis is a collective concept that combines a number of pathological conditions that lead to suffering in the brain. The word encephalopathy in the diagnosis indicates suffering of the brain (encephalon - brain, pathos suffering, disease). The words of combined genesis in the formulation of the diagnosis indicate the presence of a combination of factors that can lead to brain suffering. Most often, such factors include a combination of a vascular component (dyscirculatory encephalopathy, a history of stroke), and a dysmetabolic process (diabetes mellitus, decompensated conditions of the thyroid gland), and such pathological conditions as traumatic brain injury, consequences may also be involved in the genesis toxic brain damage (including long-term chemotherapy for cancer), consequences of brain surgery, chronic and acute hyposkic conditions (bronchial asthma, carbon monoxide poisoning, COPD, etc.). Sometimes (although, in the author’s opinion, this is not the best approach) the terminology used is encephalopathy of mixed origin, or, which is clearly incorrect terminology, mixed encephalopathy or encephalopathy of complex origin.
Information for doctors. According to ICD 10, the diagnosis is encrypted with code G93.4 - encephalopathy, unspecified. Although the term encephalopathy of combined genesis and as such a diagnosis are not used in foreign practice. In our country, there are no clear standards for the management and approach to diagnosing patients with this condition. The diagnosis must indicate all the factors that led to the development of the pathological condition; after these factors are indicated, there is a list of syndromes, for example, vestibulo-coordinator syndrome, indicating the degree of its severity.
A little about encephalopathy of combined genesis
Encephalopathy of combined genesis, as mentioned above, develops due to various factors. One of the main ones is a chronic discirculatory process, leading to chronic cerebral circulatory failure. The cause of these conditions are conditions such as cerebral atherosclerosis, as well as hypertension, which leads to micro- and macroangiopathy of blood vessels.
Often, some other process is no less important and has a predominant nature, including repeated brain injuries, and sometimes there is a combination of 3 or more factors leading to brain suffering. That is why it is important to identify all risk factors and pathological conditions of a systemic nature (for example, diabetes mellitus).
Traditional treatment
Traditional recipes will also help eliminate the signs of cerebral encephalopathy. However, their use must be agreed with a doctor. Traditional treatment cannot be considered the only possible way to get rid of pathology. It only reinforces conservative therapy. Self-treatment is fraught with serious consequences: from disability to death. The following recipes will be useful:
- Rose hip decoction. Berries, fresh or dry, are poured into a thermos and poured with boiling water. You will need 2 tbsp. l. fruits and half a liter of water. The drink should be consumed daily. To improve the taste of the liquid, you can add a little honey to it.
- Hawthorn infusion. Dry raw materials are poured into an enamel pan and filled with hot water for 12 hours. Fresh berries, which can simply be eaten, also have a good effect.
- Propolis. It is necessary to pour 100 g of raw material with one liter of vodka and leave for 10 days. The liquid should be consumed 1 tsp. before eating. The product may first be diluted with the same amount of water.
- A mixture of motherwort, lingonberry leaves, valerian. Each component is taken in equal quantities. You will need 1 tbsp. l. mixture and 200 ml of boiling water. This medicine is suitable for the treatment of encephalopathy in young children. They need to be given one dessert spoon 3 times a day.
- Infusion of clover flowers. It is effective for the treatment of cerebral encephalopathy in older adult patients, as it helps to get rid of tinnitus. For cooking, take 2 tbsp. l. raw materials and pour 300 ml of boiled water. For infusion, you will like 2 hours. You need to drink half a glass of medicine before each meal.
Traditional therapy can enhance the results of medications. However, before using it, one must take into account possible contraindications, the effects of herbs, as well as side effects that may aggravate the patient’s condition.
Symptoms and diagnosis of encephalopathy of combined origin
The symptoms of encephalopathy are varied. The disease may cause such syndromes as vestibulo-coordinator (non-systemic dizziness), cephalgic (i.e., headache), asthenic (general weakness), cognitive impairment (memory loss), sleep disorders, symptomatic epilepsy, hemiparesis and many others. violations. Dizziness to one degree or another occurs in more than half of patients with this diagnosis, ranks first in importance among all manifestations and will be considered separately.
There are no clear diagnostic criteria for making a diagnosis. The diagnosis is initially made mainly on the basis of complaints, anamnesis (identifying risk factors, the presence of chronic diseases, traumatic brain injuries, etc.), data from a neurological examination. The neurological status may include reflexes of oral automatism, anisoreflexia, the presence of pathological reflexes, and coordination disorders.
For differential diagnosis, it is important to conduct a neuroimaging study (MRI, MSCT of the brain), to exclude oncological lesions of the brain, determine the size of the defect after injury, etc., duplex scanning of the vessels of the neck and head, and electroencephalographic studies.
Diagnostic features
Before prescribing treatment for cerebral encephalopathy, the patient undergoes a set of diagnostic measures. It includes:
- Clinical general and biochemical blood and urine tests. Additionally, the level of glucose in the body is determined. The results of such a study will allow you to see metabolic disorders.
- Ultrasound of the arteries located in the neck. Thanks to the procedure, their patency is assessed.
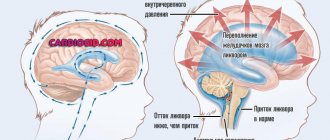
- Transcranial Dopplerography. It shows the blood circulation inside the skull. This method is safe and very informative. Using this technique, the carotid and vertebral arteries are studied.
- Magnetic resonance urography (MRI). Thanks to this study, a specialist has the opportunity to study the structure of brain tissue layer by layer, determine negative changes in them, and the presence of blood clots. This technique makes it possible to establish possible causes of the development of encephalopathy: tumor processes, cysts.
- Rheoencephalography. The study is carried out to determine the condition of the vascular walls.
- Electroencephalography. Thanks to the technique, the doctor receives data on the functionality of the brain.
- CT scan. This method of diagnosing cerebral encephalopathy in the elderly is used if the patient is suspected of having its external form. The study may require the introduction of a special marker.
- Angiography of blood vessels using a contrast agent.
In order to maintain the quality of health at a high level, you need to fight not only the symptoms and consequences of the pathology, but also try to eliminate the cause itself and its development. Additionally, a specialist can prescribe neurological tests for a person, checking reflexes and coordination of movements. The patient's mental state is also assessed.
Dizziness with encephalopathy of combined origin
Dizziness with encephalopathy can usually be non-systemic in nature and is expressed more in the form of feelings of instability and weakness. The time of occurrence and provoking factors can be very diverse. There are no clear criteria for diagnosing this syndrome; often dizziness with this disease is completely psychogenic in nature.
Objectification of the presence of dizziness due to pathological processes is a complex process. The most important symptoms tested for dizziness are fairly routine (but no less important) procedures: identifying nystagmus, conducting corrdinator tests, identifying instability in the Romberg position, and gait disturbances.
Complications
To understand the importance of proper therapy, it is necessary to find out why cerebral encephalopathy is dangerous. With prolonged progression of the disease, destroyed areas of tissue appear inside the organs, and they are constantly expanding. This situation negatively affects not only the patient’s well-being, but also his abilities. The following consequences of cerebral encephalopathy can be distinguished:
- Impaired motor function. If at first the patient has a tremor of the limbs, then over time it develops into convulsions. The patient simply cannot move independently on the street or even at home. The final stages of the pathology require outside assistance to the victim.
- Speech problems. Subsequently, mental dysfunction in a person significantly reduces vocabulary. His mental activity changes. It becomes difficult for the patient to do the most basic mathematical calculations; he is unable to build cause-and-effect relationships.
- Memory impairment. A person cannot navigate in time and space, often forgets what is happening to him, where he is.
Most of these consequences cannot be eliminated; the patient becomes disabled, so it is better to prevent their occurrence at all.
Treatment of encephalopathy of combined origin
Therapy for encephalopathy of combined origin should be directed, first of all. To eliminate factors leading to brain damage, if possible. It is necessary to correct blood sugar levels, normalize cholesterol metabolism, and correct changes in blood pressure. This part represents basic therapy; symptomatic therapy is also often equally important, which is selected taking into account the existing manifestations, as well as the individual characteristics of each person.
For cognitive deficits, nootropic drugs are used (Pronoran, Gingko preparations and others). In the presence of symptomatic epilepsy, adequate anticonvulsant therapy is used. For headaches, it makes sense to use courses of “vascular” or neuroprotective drugs. It is important to conduct rational psychotherapeutic conversations in which it is necessary to explain the causes of the disease, as well as available methods for correcting disorders with the elimination of modifiable risk factors.
It makes sense to carry out a course of treatment of encephalopathy of combined genesis in an outpatient setting, because There is usually no need for injection drugs and long-term correction of risk factors and teaching the patient the correct lifestyle are required.
Course of the disease
Encephalopathy of mixed origin can develop gradually or rapidly. Features of the clinical picture depend on the stage of the pathological process, the causes of its occurrence, and the quality of care provided.
The sooner the problem is identified and specialized therapy is started, the higher the chances of a favorable outcome. At the initial stage of the disease, it is possible to completely restore the functionality of the brain. If no action is taken, the patient will develop dementia and there is a high probability of the patient becoming disabled.
Compensated stage
At this stage, the patient experiences mild cognitive and neurological impairment. Manifestations are minimal and are not constantly present. They can be triggered by a change in weather, physical fatigue or mental stress, or a stressful situation.
The clinical picture is characterized by the following signs:
- headaches of unknown origin, varying degrees of severity and localization;
- sleep problems;
- impaired attention and forgetfulness;
- sudden changes in mood for no reason;
- irritability.
If the causes of brain damage are identified and eliminated, the development of the disease can be stopped. At the same time, there is a high probability of complete restoration of tissue structure and return of their functions without negative consequences for the body.
Subcompensated stage
At the next stage, mixed encephalopathy occurs more aggressively. Symptoms intensify and become permanent. Problems with attention and intellectual functioning are obvious. Cephalgia practically does not stop, and is supplemented by tinnitus. A person has virtually no control over his behavior. He is characterized by tearfulness, capriciousness, touchiness and even aggressiveness. There are frequent manifestations of depression, which can drag on for several weeks. Blood pressure surges may occur.
As the pathology progresses, memory problems worsen and mental abilities decrease. The patient is absent-minded and may suffer from attacks of amnesia and paranoia. He already needs the help of strangers and is not able to live alone. Starting treatment at this stage can significantly reduce the severity of the clinical picture and improve a person’s quality of life. It will no longer be possible to completely restore lost brain functions.
Decompensated stage
The diagnosis indicates the fact of atrophy of large areas of the brain. Dead tissues cannot be restored; their functions are lost forever. In this case, even those areas that are responsible for the life support of the body suffer. This leads to the development of an extremely aggressive clinical picture.
Symptoms of stage 3 mixed encephalopathy:
- signs of dementia are obvious;
- weight loss occurs;
- symptoms of Parkinson's disease appear;
- uncontrollable behavior - calm periods interspersed with attacks of aggression, moodiness, tearfulness, hysterics and other mental problems;
- headaches are similar to migraine attacks, accompanied by tinnitus and dizziness;
- memory problems up to amnesia;
- the patient cannot control his body, spontaneous bowel movements and bladder emptying occur;
- malfunctions of the musculoskeletal system.
At this stage, encephalopathy of combined origin is subject to symptomatic treatment. It is aimed at facilitating the patient’s condition and the process of caring for him. The processes in the brain are already irreversible; it will not be possible to restore lost or lost functions.
Therapy of dizziness in encephalopathy of combined origin
Treatment of dizziness in encephalopathies of combined origin is sometimes a difficult task. The preparations classically used are betahistine (Betaserc, Vestibo), vinpocetine (Cavinton), and gingko biloba (Bilobil, Tanakan). The effectiveness of each of them is a matter of long-term analysis, because there is no drug that is ideal in any case of dizziness. Non-drug methods, in particular vestibular gymnastics, are also very important.
Dizziness due to encephalopathy is usually quite well corrected, although regular repeated courses of treatment are often required.
Surgical treatment of diencephalic encephalopathies
Indications for surgical treatment of diencephalic encephalopathies are the following disorders:
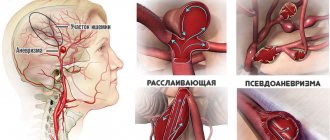
- severe stenosis (narrowing) of the internal carotid artery (over 70%);
- previous stroke (hemorrhage or ischemic cerebral infarction);
- significant impairment of cognitive abilities;
- episodes of transient ischemic attacks.
Surgical correction of diagnosed disorders is achieved through endovascular operations, during which the integrity of the vessels is not compromised.
During surgery, an incision is made in the intimate choroid to expand it; in other cases, an anastomosis (communication) with collateral vessels is formed.
The result of vascular stenting is an increase in blood flow to brain cells and, as a result, the normalization of impaired functions and the suspension of further progression of DE.
Surgical treatment of DE in elderly patients with combined stenosis of the carotid and vertebral arteries is especially important.
Scheme of artery stenting
Thanks to the reperfusion effect of stenting and endarterectomy, it is possible to achieve a positive therapeutic result in DE associated with atherosclerosis and prevent the manifestations of vascular dementia in old age.
After a concussion or other injuries, a consequence such as post-traumatic encephalopathy may occur. How it is expressed and how dangerous this disease is, read on our website.
What Wernicke encephalopathy is and who is at risk for this disease, we will tell you here.
Alcohol dependence can provoke such a dangerous condition as alcoholic toxic encephalopathy. The link provides a classification of diseases, as well as information about the dangerous consequences of the disease.