14.09.2017
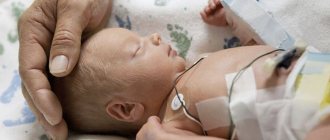
Newborns are diagnosed with unpleasant and even dangerous pathologies within an hour after birth. One of these common pathologies is hypoxia in newborns. Many people are aware that hypoxia is an oxygen deficiency. And the consequences of the phenomenon can be insignificant and dangerous, affecting the baby’s central nervous system.
Hypoxia in newborns is not an independent disease, but a pathological phenomenon indicating the presence of a problem of a congenital or acquired nature.
It can arise from an unfavorable course of pregnancy or the birth process. Hypoxia can be chronic (develops in the prenatal period) or acute (during childbirth or immediately after it) form. This provokes disorders in the nervous system, as well as in the entire body of the newborn.
The consequences of the pathology can be dangerous, including disability and death. It is necessary to know what hypoxia is, its prerequisites and symptoms in order to prevent or detect the disease.
Causes of hypoxia in newborns
This is a pathological condition in which the baby receives an insufficient amount of oxygen, which can lead to various disorders in the development of the baby. There are various forms of this pathology, which can develop during gestation (primary form) or at the moment the baby is born (secondary).
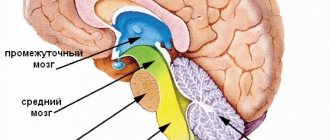
Quite often, newborns experience cerebral hypoxia, in which an insufficient amount of oxygen reaches the newborn’s brain, which can lead to serious and even irreversible consequences.
The primary form can be caused by:
The main causes of the secondary form can be considered:
Principles of therapy
In the first few minutes after birth, doctors restore the lumen of the breathing tube (suction of mucus and amniotic fluid). An oxygen mixture is supplied through a mask, and if necessary, tracheal intubation is performed. To restore the temperature, the baby is heated on a changing table or in a special incubator. Drug therapy is carried out with the administration of drugs that stimulate respiratory tract), solutions of glucose, sodium bicarbonate, calcium gluconate. Antibiotics are prescribed to prevent bacterial complications.
What happens in the body of newborns during hypoxia?
In a newborn, the blood thickens and its viscosity increases. In this case, red blood cells begin to actively attach to each other, which leads to increased aggregation of these blood particles. This leads to disruption of blood microcirculation and can cause hemorrhage, ischemia, swelling of the tissues of the brain, heart, kidneys, adrenal glands or liver.
Rehabilitation activities
After discharge from the maternity hospital, the child will require high-quality rehabilitation. It includes the following activities:
- clinical observation by a pediatrician and pediatric neurologist;
- special care;
- good nutrition;
- frequent walks outside;
- massotherapy;
- physiotherapy.
On the recommendation of a neonatologist or neurologist, drug therapy is carried out during the recovery period, which may include various groups of drugs. An overview of the funds is presented in the table.
Table - Drug therapy of hypoxic conditions in newborns
| Group of drugs | Examples of drugs |
| Improves cerebral circulation | "Cavinton" |
| Decongestants | — “Diacarb”; — “Glycerol” |
| Improving metabolic processes | — “Magne B6”; - "Panangin"; — “Actovegin” |
| Nootropics | - “Pantogam”; - "Cogitum" |
| Anticonvulsants (if necessary) | — “Finlepsin”; — “Sodium valproate” |
At home, it is extremely important to provide a calm environment for your child. It is necessary to limit it from loud sounds and the noise of a working TV. During the first months, it is better not to gather noisy companies in the house and avoid visiting crowded places with your child.
Signs of hypoxia in newborns
As soon as the newborn is born and another 5 minutes after birth, the condition of the newborn is assessed using the Apgar scale, thanks to which the degree of hypoxia can be determined. A child does not have this pathology if it scores 8-10 points, a mild degree is determined if there are 6-7 points, a medium degree is observed with 4-6 points, and a severe degree is observed when the newborn’s condition is assessed at only 0-3 points.
In mild cases, the following symptoms are observed:
With moderate hypoxia, the following symptoms are observed:
In severe pathology, the following is observed:
Signs and symptoms
This condition has a characteristic picture, so it can be recognized in the early stages, which significantly improves the prognosis.
Among the main symptoms are: tachycardia (an increase in heart rate), which soon gives way to bradycardia (a decrease in heart rate), arrhythmia (violation of the correct rhythm of heart contraction), pathological heart murmurs , meconium in amniotic fluid (baby’s original feces) .
As a result of pathological changes, hypovolemia (decreased blood volume) increases in the baby, blood clots form in large vessels (they become clogged), and small tissue hemorrhages occur.
To determine the degree of hypoxia, a special Apgar scale , which helps assess the degree of functioning of the newborn’s systems.
The lower the score, the more severe the condition and the more difficult it is to get the baby out of it. An indicator of 9-10 points indicates the normal functioning of the newborn’s body.
Treatment
This condition should be treated immediately after diagnosis, and the sooner this is done, the more effective the treatment will be. First you need to make sure that the baby's airways are clean, so immediately after birth the doctor clears them using special equipment. If the newborn still does not breathe, an oxygen mask is put on him.
In case of a mild form, no special treatment is carried out; it is enough to undergo massage courses, therapeutic exercises and various physical procedures on time.
In cases of moderate severity, medications are prescribed that improve blood circulation in the brain and normalize metabolic processes in the body. If the newborn has a severe form, he is sent to intensive care. If there is swelling of the brain tissue, diuretics may be prescribed; if severe muscle tension and convulsions occur, anticonvulsants may be prescribed.
Determination of pathology after discharge from the hospital
Most often, hypoxia is diagnosed immediately after the birth of a child. However, in some cases, signs of pathology can only be detected within several months after birth. Parents should consult a doctor if the following symptoms occur:
- strong screaming and crying while bathing;
- sharp twitching when touched;
- trembling of the chin, arms, legs while crying;
- causeless anxiety;
- muscle hypertonicity;
- feeding difficulties;
- frequent regurgitation.
The presence of even a few of the above signs should definitely be a reason to contact a pediatric neurologist.
Clarifying the diagnosis
Diagnostics includes the following methods:
- electroencephalography;
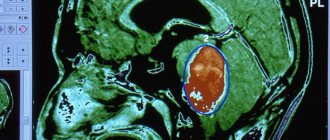
- neurosonography (ultrasound of the brain through the fontanelle);
- Dopplerography of the great vessels of the head (ultrasound of the great vessels);
- MRI of the brain.
Caring for a child after hypoxia
If the child’s condition is satisfactory, the child is discharged home and in the future he should be observed by a local pediatrician and a neurologist. As a rule, such children continue to take medications that improve blood circulation and nourish the brain. If he has had seizures, he continues to take anti-seizure medications. They may also recommend medications that normalize the baby’s intracranial pressure.
In the future, the baby’s metabolism is monitored and, if necessary, vitamins and supplements can be prescribed that help normalize and better absorb the body of vitamins and microelements. It is also important to monitor the baby’s nutrition so that he does not overeat, since this is an additional burden on the entire body, and it is extremely undesirable.
If there was hemorrhage, neonatologists may recommend not breastfeeding for a while so that he does not strain his facial muscles and head in general.
Additionally, massage, herbal baths and therapeutic exercises may be prescribed. It is also very important that there is a calm environment in the house so that the baby can feel comfortable and at ease. Many parents try to teach their baby to sleep separately in a crib, and often this is not so easy to do; the baby can cry and scream for a long time, straining the nervous system and brain. And if the newborn had hypoxia, this can harm his health, so in such a situation it is worth considering co-sleeping with the child. Firstly, he will fall asleep faster, and his sleep will become much calmer and longer.
Fetal hypoxia and its consequences
Hypoxia is oxygen starvation of the fetus. The reasons for its appearance may be different, depending on its type: intrauterine or intrapartum. The first occurs during pregnancy and depends on the behavior and condition of the mother, and the second occurs during childbirth and, for the most part, depends on the actions of doctors. There are two forms of hypoxia: acute and chronic. The first of these is less common, but has more serious consequences. CIGP is an intrauterine condition of constant lack of oxygen. At the same time, the baby’s development suffers greatly. There is a risk of premature birth and a premature baby.
In acute hypoxia, the supply of oxygen to the fetus’s body completely stops. This can happen both in the womb and during childbirth. Most often, this situation occurs as a result of the umbilical cord being entangled around the baby's neck. After just 15 seconds of lack of oxygen, brain cells begin to die. Doctors must correct the situation as soon as possible. In this case, serious consequences cannot be completely avoided, but they can be reduced to an acceptable minimum. The consequences of fetal hypoxia in a child after birth in most cases can be diagnosed immediately. This is especially true for severe cases.
Oxygen starvation of the fetus during pregnancy can lead to the following consequences for the child:
- retardation in physical development;
- mental retardation;
- diseases of organs due to their underdevelopment;
- diseases of the nervous system, in particular brain diseases.
The lack of oxygen has a detrimental effect on the entire body of the fetus, but this condition causes greater damage to its brain. During fasting, hemorrhage may occur, swelling may form, and other serious processes may occur. As a consequence of this, a child may develop various neurological ailments in infancy or at an older age. A serious consequence of hypoxia is cerebral palsy. In extreme cases, cardiac arrest and brain death can occur.
Video
The mildest complication is considered to be weak immunity. Such children are more susceptible to colds than others. Regardless of the severity of the hypoxia, appropriate treatment will be required in the future. One way or another, the child will have to be observed by a neurologist, who will prescribe therapy if necessary.
Note! Elimination of the consequences of hypoxia should begin immediately after childbirth. At the maternity hospital, specialists will prescribe medications and necessary procedures.
If hypoxia cannot be prevented, all measures must be taken to minimize its consequences. If, in addition to dysfunctions of the nervous system, no pathologies of other organs were detected, only a neurologist will treat the child for the first time. During the development process, the help of a speech therapist and psychologist may be required.
Measures to prevent hypoxia in newborns
Every woman should plan a pregnancy and prepare her body for pregnancy. Prevention begins with proper preparation:
During pregnancy you must:
Successful preparation helps to avoid many problems not only during pregnancy, but also during childbirth.
Non-traditional methods of rehabilitation
In addition to the basic treatment of hypoxic lesions, non-traditional techniques are often recommended. They practice in rehabilitation centers specializing in the treatment of young children. The most commonly used:
- psychotherapy (mother-child, tactile stimulation);
- music and aromatherapy;
- swimming.
These techniques speed up recovery after hypoxic brain damage and contribute to better social adaptation of the child.
Folk remedies include bathing in decoctions of sedative herbs. To prepare them, take thyme, string or chamomile. A tablespoon of dry herb is poured into a liter of boiling water and brought to a boil. Let it sit for about two hours and then add it to the baby’s bathing water.
Prevention
Prevention of this pathology should begin long before the child is born. Activities include:
- treatment of chronic diseases in women before pregnancy;
- timely detection and treatment of diseases during pregnancy;
- identification and correction of intrauterine fetal hypoxia;
- adequate obstetric care.
If hypoxia is diagnosed in a newborn, timely therapeutic and resuscitation measures are necessary. This significantly improves the prognosis for maintaining the health and further development of the child.