Oxygen is something without which our body cannot live for even a few minutes. All human organs without exception are sensitive to its deficiency. But the most sensitive is the brain. Oxygen starvation, or hypoxia, leads to damage to its cells within a few seconds; after 20 seconds, a person falls into a coma, and after 4 minutes, brain death occurs. Therefore, it is so important to understand why oxygen starvation of the brain occurs and what hypoxia can lead to.
Types of oxygen starvation
Depending on how quickly oxygen starvation develops, hypoxia occurs:
- Spicy. The occurrence of obstacles to the blood supply to brain tissue. May appear as a result of large blood loss, poisoning or heart attack.
- Chronic. May occur in patients with cardiosclerosis, heart failure and other heart diseases.
- Lightning fast. It is developing rapidly. The duration of this hypoxia phase can last several seconds or minutes.
Depending on what caused the disorder, the following forms of hypoxia are distinguished:
- Exogenous. Occurs when a person inhales air with low amounts of oxygen.
- Respiratory. The cause is various disturbances in the functioning of the body, which prevent the supply of the amount of oxygen necessary for the brain.
- Circulatory. This form can be caused by disturbances in the functioning of the heart or blood vessels. Characterized by rapid development.
- Fabric. Appears due to a violation of the absorption of oxygen by the tissues of our body.
Cellular and tissue hypoxia is characterized by a certain cyclicity. You can understand this by reading this diagram.
- Hemic. It is a consequence of a decrease in the amount of oxygen dissolved in the blood.
- Reloading. It occurs in people when the amount of oxygen that enters the body does not fully satisfy its need. May occur during heavy physical exertion.
- Mixed. Most often it develops gradually and can have serious consequences. It arises as a result of a whole complex of negative factors.
Treatment options
After diagnosis, only the attending physician decides how to treat hypoxia. The choice of treatment depends on the type and cause of the disease. These can be preparations with iron, antidotes that eliminate pathological compounds, as well as drugs aimed at improving blood flow and diluting it.
When the lumen of blood vessels in the brain narrows, medications aimed at reducing their tone are indicated. Cocarboxylase during pregnancy can improve women's well-being. It will restore metabolic processes in tissues, improving the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
A prerequisite for stabilizing well-being in a serious condition is oxygen therapy, which improves the gas composition of the blood. To carry it out, special devices are needed - oxygen devices or oxygen concentrators.
Does the brain recover after pathology? Only early treatment and subsequent rehabilitation will achieve remission, which can compensate for the resulting disorders.
Brain hypoxia, the treatment of which requires intensive care, requires hospitalization. In case of severe disturbance of blood gas composition, oxygen therapy is prescribed. For this, an oxygen generator with a gas cylinder is used, which allows you to regulate the partial voltage.
An oxygen apparatus can be prescribed continuously or with intermittent use. If hypoxia develops in newborns, treatment is carried out in the first hours after birth. Therapy will help reduce the risk of complications.
Active drugs
In most cases, iron-based preparations are used, as well as vitamin complexes, which are aimed at improving metabolic processes and blood circulation.
Treatment of oxygen starvation of the brain with tablets and drugs in the form of injections must be carried out under the control of well-being. Among the most effective drugs are a group of cardio and neuroprotectors.
Respiratory exercises
Increasing ventilation is what the body does if there is not enough oxygen in the body.
Respiratory tract exercises refer to methods of physiotherapeutic effects on brain tissue. Most popular destinations:
- Yoga
- Strelkova's technique
- Bodyflex
- Breathing system with retention method
The selection of optimal methods is carried out based on the patient’s condition under the supervision of a specialist.
Reasons that provoke oxygen starvation of the brain
The most common causes of hypoxia in adults are:
- A stroke, which results in acute oxygen deficiency in one of the hemispheres of the brain.
- Stressful situations accompanied by a decrease in blood pressure.
- Anemia.
- Osteochondrosis.
- Staying for a long time in a closed, unventilated room or when rising to a high altitude (to the mountains).
- Gassing.
- Cardiac arrest, which leads to the cessation of oxygen supply to the brain tissue.
- Heart failure.
- Paralysis or respiratory diseases.
- Suffocation.
How to provide first aid to a person who is choking. In such cases, you cannot wait for the doctors to arrive; you need to act immediately
- Various circulatory disorders of the body.
- Reaction to alcohol.
- Complications after surgery.
- Diseases of the nervous system.
- An allergic reaction that contributed to the development of laryngeal edema.
What is the problem
Oxygen starvation is, as the name implies, a pathological condition of the body in which an insufficient amount of oxygen enters the cells of organs. Reduced air content in tissues is also called hypoxia.
There are several types of this disease:
- Exogenous hypoxia can develop when there is a lack of oxygen in the air.
- respiratory hypoxia may develop . Some of the causes of oxygen starvation and low oxygen content in the brain tissue in this case are mechanical injuries to the respiratory and chest organs, as well as drug overdose.
- If there are not enough red blood cells and hemoglobin in a person's blood, a disruption in the transport of oxygen by blood cells may occur, resulting in hemic hypoxia .
- Circulatory starvation of an organ can develop as a result of circulatory disorders of this organ due to heart failure, thromboembolism, and atherosclerosis.
- Overload hypoxia occurs due to high load on the brain.
- Due to poisoning of the body with chemicals and medications, as well as poisons, the process of oxygen utilization by cells is disrupted, which often results in tissue oxygen starvation .
- Finding a person in an environment with an increased concentration of toxic substances is fraught with the development of man-made hypoxia .
Diet for psoriasis to improve the condition: table of allowed and prohibited foods
The development of the disease occurs according to the following scheme:
- After just 5 seconds, the transmission of nerve impulses in the organ is disrupted;
- After another 10 seconds, the person loses consciousness and faints;
- After half a minute, brain activity drops so much that the person falls into a coma.
If blood circulation is not started within the first 5 minutes, the cells of the nervous tissue begin to die.
Thus, the most common causes of the disease:
- Anemia or anemia;
- Atherosclerotic plaques in blood vessels (the greatest danger is represented by cholesterol deposits in the great vessels of the neck and brain);
- Problems with the respiratory organs and especially the larynx (swelling, injuries, spasms);
- Working and generally staying for long periods of time in an unventilated area;
- Complications after surgical intervention in the body;
- Sudden jumps in blood pressure due to stress and other diseases;
- Stroke;
- Airway paralysis;
- Gas and chemical poisoning.
Who needs a lactose-free diet and how to follow it?
Symptoms of the disease
Oxygen starvation of the brain in adults has standard symptoms that often help with diagnosis. These include:
- Increased excitability, which has not been observed before. A slight oxygen deprivation of the brain provokes a state of euphoria; a person may not control his behavior. Excitability gives way to lethargy and a feeling of depression.
- Sharp headache. Most often it has a pressing character.
- Arrhythmia and tachycardia.
Find out more about the causes and symptoms of the disease from Vladimir Matveevich Podkhomutnikov, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Head of the Department of Cardiology of the Novokuznetsk State Institute:
- Change in skin color. It becomes pale and may have an overly red or bluish tint. In such a situation, the brain tries to restore normal blood supply, which can manifest itself as increased sweating.
- Slowness of the nervous system, which is a manifestation of post-hypoxic brain damage. In this case, the patient notes dizziness, nausea or uncontrollable vomiting. At the same time, vision may be impaired and darkening of the eyes may occur. Hypoxia provokes loss of consciousness.
- Perinatal brain damage as a consequence of oxygen starvation. This condition provokes cerebral edema, and the patient’s conditioned and unconditioned reflexes disappear. If the blood supply to the brain is not restored, the functioning of all internal organs is disrupted, and the skin stops responding to external stimuli.
We must remember that oxygen deprivation manifests itself differently in everyone, so if you notice some of the signs, you need to consult a doctor who can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Symptoms of hypoxia
Signs of oxygen starvation vary depending on the form of the pathology.
During acute hypoxia, patients experience motor and psychoemotional agitation, heartbeat and breathing become more frequent, the skin turns pale, sweating increases, and midges “flash” before the eyes. Gradually the condition changes, the patient calms down, becomes lethargic, sleepy, his eyes darken, and tinnitus appears. At the next stage, the person loses consciousness, clonic convulsions and chaotic muscle contractions may occur. Movement disorders are accompanied by spastic paralysis, an increase and then a decrease in muscle reflexes. The attack develops very quickly, coma may occur within 1–2 minutes, so the patient needs urgent medical attention.
Chronic brain hypoxia occurs slowly. Characterized by constant fatigue, dizziness, apathy, and depression. Hearing and vision often deteriorate and performance decreases.
Depression is characteristic of brain hypoxia
Neurological signs of hypoxia in adults:
- With diffuse organic damage to the brain, posthypoxic encephalopathy develops, accompanied by visual and speech disorders, impaired coordination of movements, tremors of the limbs, twitching of the eyeballs, and muscle hypotonia.
- With partial impairment of consciousness, the symptoms of hypoxia manifest themselves as lethargy, numbness, and stupor. A person is in a depressed state, from which he can be brought out with persistent treatment. Patients retain protective reflexes.
- Asthenic state: increased fatigue, exhaustion, deterioration of intellectual abilities, motor restlessness, low performance.
Acute hypoxia is accompanied by cerebral edema and dystrophic changes in neurons. Even after normalization of oxygen delivery to brain cells, degenerative processes persist and progress, leading to the formation of softened lesions. Chronic hypoxia of brain tissue does not cause pronounced changes in nerve cells, therefore, when the causes of the pathology are eliminated, patients recover completely.
Diagnosis of hypoxia
To make a diagnosis, laboratory and instrumental studies are carried out:
- Pulse oximetry. This diagnostic method is rightly called the most accessible way to determine cerebral hypoxia. To do this, a special device, a pulse oximeter, is placed on the patient’s finger.
- Study of acid-base balance. The method is based on an analysis of blood composition, which allows one to evaluate the quantitative indicators of many body functions.
- General blood analysis.
To understand the results of your tests, you need to know the norms. Basic norms for general blood test indicators for men and women are given in this table
- Electroencephalogram.
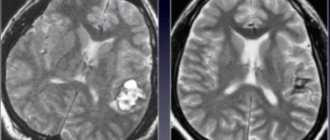
- Computer and magnetic resonance imaging of the brain.
- Electrocardiogram.
- Rheovasography.
You can see the procedure for obtaining electrocardiogram data in this figure.
Depending on the patient’s health status, the degree of hypoxia and the suspected cause of oxygen deficiency in the brain, the doctor will prescribe an individual diagnostic program.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made based on the clinical manifestations of the pathology, as well as the results of laboratory and instrumental studies. The patient needs to do:
- Blood test (general to determine the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin level, gas to determine the level of oxygen in the blood);
- Encephalogram to assess the condition of individual areas of the brain and its cells;
- Rheovasography to assess the condition of the blood vessels supplying the brain;
- Angiography to determine the quality of blood flow in general;
- MRI for suspected coronary artery disease;
- Capnography to determine the volume of carbon dioxide released.
Treatment of oxygen starvation of the brain
Before starting treatment for oxygen starvation in adults, it is necessary to establish the exact cause that provoked this condition. Therefore, it is important for the patient to clearly formulate the factors that could lead to this. Most often in an adult it is smoking, alcohol abuse, and prolonged stay in a poorly ventilated area.
Having assessed the severity of oxygen starvation, the doctor will recommend treatment in a hospital or at home. The patient is prescribed medications that stabilize the normal functioning of the body. It is also necessary to take medications whose action is aimed at restoring normal blood supply to brain tissue.
Sometimes, to relieve symptoms of mild oxygen starvation, it is enough for an adult to ventilate the room in which he is located or go outside. The situation is different if the cause is some kind of disease or disruption of the body.
If oxygen starvation provokes a disease of the blood, cardiovascular or respiratory system, the patient will require more serious measures to eliminate it.
- For exogenous hypoxia, oxygen equipment (masks, pillows, etc.) is used.
- To treat respiratory hypoxia, analgesics, antihypoxanes and drugs that dilate the bronchi are used. Sometimes artificial ventilation is performed.
Remember that some analgesics have a negative effect on the body and are addictive. It is important to be able to distinguish which of them are narcotic and which are non-narcotic
- Hemic hypoxia requires blood transfusion, which helps normalize blood circulation.
- With a circular form of oxygen starvation, surgical intervention on the heart or blood vessels is necessary.
- To treat the histoxic form, antidote drugs are used.
If the patient sees a doctor in time and is prescribed effective treatment, the prognosis for recovery will be favorable. However, if oxygen deprivation continues for a long period of time, irreversible consequences may develop that cannot be eliminated.
You can learn interesting facts about the disease from pediatrician, family doctor Konstantin Borisovich Zabolotny:
Brain hypoxia: symptoms, causes, consequences
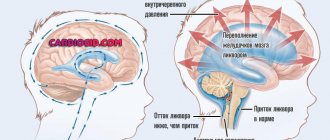
It’s not for nothing that the nervous system has so many blood vessels: it vitally needs uninterrupted gas exchange and the supply of nutrients.
As soon as there is a deficiency of oxygen, which neurons need, their vital activity is inhibited. The cessation of oxygen supply entails the death of the nervous tissue, and then the entire body. Brain hypoxia often occurs in modern humans, but in some cases he may not notice it: if the deficiency of neuronal respiration is not critical, the body will live, but because of this, dangerous complications subsequently arise.
The essence of the problem
What is hypoxia? This is an insufficient supply of oxygen to living tissues, which is why they cannot fully perform their functions and even die.
In the human body, one of the most actively working systems is the nervous system, so its need for oxygen is enormous. Oxygen starvation of the brain causes inhibition or complete cessation of innervation of all organs.
Brain hypoxia varies depending on the mechanism of its development:
- Lightning fast. Its duration is calculated in minutes and seconds. Occurs when respiratory processes are completely blocked.
- Spicy. Associated with poisoning, severe heart disease, and bleeding.
- Chronic. It is also associated with heart disease (failure, defects), but develops more slowly.
The future of a person experiencing oxygen starvation depends on the duration and intensity of this process. If the patient does not fall into a coma, his rehabilitation is faster. After emerging from a comatose state, neurons return to their usual rhythm of operation much more slowly.
If the coma continues for more than a year, the patient may die. Long-term exposure of the brain to a state of hypoxia in adults entails the loss of certain functions (speech, motor abilities).
In the case when a person survives, his neurological processes can be restored completely or partially.
Neurons that are especially sensitive to oxygen deficiency are lost forever. But their role can be taken over by neighboring nerve cells.
Moreover, after restoration, some functions may be disabled again after a few months.
Chronic disruption of cell gas exchange leads to the development of the following diseases:
- sleep apnea syndrome;
- vertebral artery syndrome;
- cerebral atherosclerosis;
- encephalopathy (dyscirculatory and hypertensive).
The following types of hypoxic processes in the brain can be distinguished:
- Ischemic stroke with multiple lesions of the nervous system.
- Cerebral central ischemia is a defect in the blood supply in a separate area (for example, in the presence of a blood clot).
- Cerebral global ischemia is a complete blockage of gas exchange in the nervous system.
- Disseminated ischemia – with low oxygen content in the bloodstream.
Causes of cerebral hypoxia
Brain hypoxia can be associated with the influence of numerous factors, depending on which the following forms are distinguished:
- Exogenous - occurs when there is a lack of oxygen in the environment (at altitude, at low atmospheric pressure, in a closed space).
- Respiratory – associated with the inability of the respiratory system to perform its functions due to injuries, poisoning, tumors, bronchial asthma and other disorders.
- Tissue hypoxia of the brain is associated with problems with the absorption of oxygen molecules in living tissues. Such disturbances can be caused by poisons and certain medications.
- Circulatory form – appears in diseases of the body’s vascular system (blood clots or atherosclerotic plaques in the brain).
- Overload - occurs under very heavy loads, when the lungs and heart are unable to ensure complete gas exchange of tissues.
- Hemic - occurs in people suffering from anemia, since their oxygen transport is impaired due to a lack of hemoglobin.
- Brain hypoxia in children at birth develops due to a delay in the birth canal, birth injuries, or if the child suffered from oxygen starvation during intrauterine development. Oxygen does not reach the fetus well if the mother smokes, experiences stress, or does not spend much time outdoors.
In addition, blockage of cerebral breathing can be caused by:
- unsuccessful and complex operations;
- foreign bodies entering the mouth or nose;
- carbon monoxide poisoning;
- alcohol intoxication;
- paralysis of the muscles responsible for breathing;
- some congenital pathologies, for example, this can be observed with an empty sella turcica in the brain.
As you can see, the human brain is very vulnerable to the influence of various negative factors.
Symptoms and diagnostic methods
Oxygen starvation of the brain is accompanied by various symptoms, they depend on provoking factors:
- Overexcitement of a person. With oxygen starvation, the ability to control movements and actions is sharply reduced.
- Changes in the properties of the skin: paleness, blueness or redness, as well as intensification of sweat production.
- Inhibition of nervous processes and the associated consequences of brain hypoxia (vomiting, decreased visual acuity, fainting).
- Acute lack of air can lead to coma.
- Symptoms of brain hypoxia in newborn babies include reflex disorders. Children with hypoxic-ischemic syndrome are more tearful and irritable. In severe cases, sensitivity is turned off and the operation of internal systems is inhibited.
Such manifestations are characteristic of a short-term disruption of gas exchange. Signs of brain hypoxia in chronic form are more varied:
- headache;
- tinnitus;
- dizziness;
- morning sickness;
- daytime drowsiness and nighttime insomnia;
- unstable mood;
- worsening of attention and memory processes;
- decreased intellectual qualities;
- speech problems;
- poor coordination of movements;
- inability to perceive information;
- depression and irritability.
If the lack of breathing of brain cells is chronic, then the body tries to adapt to such new, unfavorable conditions. It compensates for the deficit by incorporating the following mechanisms:
- Increased frequency and intensification of breathing, including using the reserve alveoli of the lungs.
- Increased heart rate.
- Changes in the blood supply to organs (more vital ones receive more blood).
- The blood picture changes: the level of red blood cells increases, and with it the risk of blood clots.
- Those areas in the brain that are most affected by hypoxic processes may acquire new blood supply pathways - additional vessels may appear in them.
All of these changes are aimed at compensating for the lack of respiration of nerve cells, but they themselves are unfavorable for the body.
In particular, constant shortness of breath, increased blood density, and palpitations lead to additional health problems and cause pathologies in other organs.
To verify the presence of hypoxic phenomena in the brain, doctors conduct the following examinations:
- MRI.
- Ultrasonography.
- EEG.
- Angiography.
- Rheovasography.
If the examination results contain data on pathological changes caused by respiratory failure, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
Emergency care and treatment of cerebral hypoxia
Clogged arteries are one of the reasons for the development of hypoxia of brain tissue
Everyone needs to know what it is - brain hypoxia, the symptoms of this most dangerous condition, because blockage of breathing can occur for one reason or another in any person. Knowledge of the basic methods of treating this pathology is no less important.
Treatment of cerebral hypoxia includes restoration of normal gas exchange in nerve cells and the entire body, as well as methods for stabilizing the patient’s condition, after which rehabilitation begins. But first of all, it is necessary to establish and eliminate the root cause of the violation of vital functions.
In many cases, the provoking factors depend on the person himself, especially if he is a heavy smoker, constantly stays indoors or abuses alcohol. In these situations, the fight against pathology should begin with lifestyle changes.
If the respiratory function is difficult in a newborn, he may need to clear the respiratory tract of mucus and amniotic fluid, administer surfactants, and use decongestant therapy. In many cases artificial respiration has to be performed.
Drug therapy for brain hypoxia involves prescribing medications for:
- normalization of vascular function;
- improving blood supply;
- blood thinning;
- elimination of atherosclerotic vascular disorders;
- eliminating pain and nausea;
- general strengthening of the body.
It is advisable to use nootropic drugs, sometimes antidepressants. Not only medications, but also vitamins will help support the vital activity of neurons.
If a person’s condition is not critical, the attending physician can prescribe treatment at home, without resorting to hospitalization. But if there are obvious signs of neuronal death or malfunction of internal organs, it is imperative to send the patient to a hospital, because only there it will be possible to save his life and do everything possible to preserve and restore vital functions.
In situations where a person’s condition has worsened due to being in a stuffy room or in a rarefied atmosphere, it is necessary to use oxygen pillows. For more effective assistance, artificial lung ventilation devices are used. To ensure active access of fresh air to the alveoli, medications that dilate the bronchi are used.
To quickly replenish oxygen deficiency, the method of hyperbaric oxygenation is used, which involves placing the patient in a special chamber with increased oxygen content and pressure.
If brain hypoxia is caused by problems with blood composition, blood transfusion may be necessary to urgently restore normal tissue supply.
If there is a lack of red blood cells, the production of blood cells can be stimulated to compensate for the dysfunction.
In case of poisoning with substances that block respiratory function at the tissue level, antidotes can save a person’s life, which must be administered in a timely manner to neutralize the poisons.
Conclusion
Sport is the best prevention of hypoxic brain damage
It should be understood that treating brain hypoxia is much more difficult than preventing its development. To prevent this pathology in babies, their future mothers should not abuse alcohol and smoke; they need to be outside more often.
Proper management of childbirth is also very important. As for older children, their parents should ensure that foreign objects do not enter the baby’s respiratory organs. To avoid the death of neurons, you need to walk more often and be physically active to ensure sufficient ventilation of the lungs. Diseases leading to hypoxic changes must be treated promptly.
Source: https://golovnie-boli.com/bolezni-golovnogo-mozga/gipoksiya-mozga.html
Folk remedies for the disease
Along with traditional methods of treatment, folk remedies are often prescribed that help restore blood supply to brain tissue. Decoctions of rowan fruits, horsetail herbs, motherwort, wood lice and periwinkle have proven themselves to be effective.
As an example, we can give a recipe for a folk remedy made from crushed woodlice leaves. To prepare such a tincture, take 1 tablespoon of the herb, pour 1 glass of boiling water, stir, cover the container with a lid and leave to infuse for 7-8 hours. Take this medicine 50 ml 30 minutes before meals.
But it is worth noting that before taking any folk remedy, you should consult a doctor, as some of them can cause allergic reactions.
Consequences of hypoxia
When making a prognosis for a patient, doctors focus on the degree of damage to brain tissue, which depends on how long the brain experienced oxygen starvation.
If the lack of oxygen does not last long, the prognosis is usually favorable and the patient manages to eliminate its consequences. But if hypoxia is left untreated for a long time, it can lead to the development of a vegetative state. In this state, the patient retains the basic functions of the body (breathing, blood pressure, etc.), but the person will not respond to what surrounds him. As a rule, such patients live within 1 year.
Oxygen starvation in some patients leads to loss of appetite, blood clots and the development of pulmonary infections.
Characteristics of the disease
The brain is equipped with a large number of blood vessels through which various nutrients and oxygen flow to its parts. Insufficient content of this element in the body leads to oxygen starvation, that is, brain hypoxia .
The organ reacts very sensitively to a decrease in oxygen levels, and this is manifested by the occurrence of certain dangerous symptoms. Brain cells begin to die, as a result of which the organ can no longer perform its functions. This negatively affects a person’s intellectual activity, behavior, mental development, as well as his general well-being. The severity of the clinical picture and the nature of negative changes depend on the duration of the pathology.
Hypoxia in newborns
Oxygen deficiency in brain tissue can occur in a newborn at any stage of its development: during childbirth or even during intrauterine development. Hypoxia is one of the most commonly diagnosed disorders in newborns.
In some cases, this condition is life-threatening for the child. If a severe form of the disease occurs, the baby dies or becomes seriously disabled.
The following factors can influence the occurrence of oxygen starvation:
- Maternal illness, severe pregnancy and childbirth. The fetus may lack oxygen due to anemia or heart defects of the pregnant woman, premature abruption of the placenta, or bleeding from the placenta.
- Pathologies of blood flow through the umbilical cord and impaired placental-uterine circulation. This also includes entanglement with the umbilical cord, damage to its vessels, trophic disorders of the placenta, prolonged or rapid labor, and the use of special medical instruments (forceps, etc.).
Gynecologist Raisa Zanitullina talks about fetal hypoxia in this video:
- Genetic abnormalities in the fetus, anomalies of its development, Rh conflict, infectious diseases, congenital heart disease, skull injuries.
- Asphyxia, as a result of which the fetal airway is partially or completely blocked.
After birth, the baby must be examined by a neonatologist, who can pay attention to the symptoms of oxygen starvation in the newborn. In this case, the baby experiences tachycardia. Subsequently, it turns into arrhythmia and heart murmurs. A child who has suffered hypoxia may develop blood clots and numerous hemorrhages in tissues and organs.
Consequences
The most dangerous is the acute manifestation of hypoxia. It can be fatal if the necessary medical care is not provided in time. The severity of heart failure directly depends on the location of the damage in the brain tissue.
The body suffers from overload and the presence of a large number of brain disorders. The state of health worsens due to neurological deficit, severe dizziness, and chronic cephalgia. The patient has speech problems, blurred vision, and memory disorders.
Rehabilitation helps to fully restore brain activity. Most often, only periodic manifestations of mild hypoxia remain.
In case of acute oxygen starvation, death cannot be avoided if medical assistance is not provided on time.
Having become chronic, the pathology will negatively affect a person’s quality of life. However, over time, the body will be able to adapt even in the event of periodic oxygen starvation:
- The intensity and frequency of breathing changes. A person may notice shortness of breath due to the functioning of the reserve alveoli.
- The heart begins to beat much faster. Against this background, an increase in blood pressure is recorded. Hypoxia is accompanied by a redistribution of blood flow, which leads to serious trophic changes. The situation is dangerous and can lead to loss of functionality of vital organs.
- The bone marrow begins to produce large numbers of red blood cells. In this case, the risk of blood clots increases. The situation is especially dangerous for children.
- The number of collateral vessels increases in the human body. Thanks to them, the affected area is enriched with blood and oxygen.
The body cannot make the most of all means of adaptation. They provide high-quality life activity, but lead to secondary changes.
If you cannot get rid of the disease in time, you will experience a deterioration in your health. Hypoxia leads to new compensatory changes that aggravate the overall clinical picture of manifestations.
Treatment of the disease in newborns
Treatment of children differs significantly from treatment of adult patients. If there is a suspicion of a lack of oxygen in the fetus, doctors try to speed up labor without harming the mother and baby. This can be done by caesarean section or by using obstetric forceps. After the child is removed, everything possible is done to provide him with the necessary amount of oxygen.
During childbirth, doctors can use special medications, the effect of which is aimed at increasing blood circulation in the placenta and the human body. A set of resuscitation measures is also often used to clear the newborn’s airways of mucus and perform artificial respiration.
Until the child’s condition stabilizes, he is advised to administer the following drugs: sodium gluconate, glucose solution, etimizol. In the future, a child who has suffered hypoxia should be under the supervision of a pediatrician and a neurologist, who will monitor his development and, if necessary, correct possible changes in the body’s functioning.
However, doctors are not always able to provide effective therapy that would help the baby completely get rid of the consequences of oxygen starvation. In this case, the child remains disabled. This leads to a delay in physical or mental development. Therefore, doctors always recommend that pregnant women carry out prevention, which consists of a balanced diet, taking vitamins, frequent exposure to fresh air, and light exercise that will correspond to the specific stage of pregnancy.
Hypoxia is not a disease, but a condition that can be effectively treated. Only for this, it is necessary to identify the pathology in time and begin the correct treatment.
Hypoxia, or in simple terms - oxygen starvation of the brain, is a serious disease that requires diagnosis and treatment. Hypoxia blocks the flow of oxygen to nerve connections. In the case where there are no symptoms of dysfunction, the brain can withstand 4 seconds of acute hypoxia; just a few seconds after the cessation of blood supply, the person loses consciousness; after 30 seconds, the person falls into a coma.
The most serious outcome of this violation is the death of a person. Therefore, it is important to know the main causes of oxygen starvation of the brain and the symptoms that will help to identify the first signs of the disorder and avoid serious consequences and long-term treatment.
There are 3 types of hypoxia:
- Fulminant hypoxia – development occurs quickly, within a few seconds and minutes;
- Acute hypoxia - lasts for several hours, the cause may be a heart attack, poisoning;
- Chronic insufficiency - develops over a long time, the causes are heart failure, cerebral atherosclerosis, heart disease.
Therapy
To prescribe effective treatment, it is important to correctly determine the root cause of the disorder. Therefore, it is necessary to explain to the patient what preceded the appearance of hypoxia. Do not forget that prolonged consumption of alcoholic beverages and a long stay in a stuffy room can be factors.
Depending on the severity of oxygen starvation of the brain, treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis or in a hospital. Medicines are prescribed to normalize the functioning of the body, as well as vitamins that restore brain tissue.
For a mild form of pathology, it is enough to take a walk in the fresh air or ventilate the room well. If the disorder is caused by an organic factor, such as a disease of the cardiovascular system, lungs, or blood, it is necessary to treat the primary disease.
- For respiratory hypoxia, antihypoxants, bronchodilators, and respiratory analeptics are prescribed. Oxygen concentrators are used. In difficult cases, artificial ventilation is performed.
- For exogenous, oxygen pillows, masks, and cans are used.
- The histotoxic form of the disease requires antidotes, drugs that improve oxygen utilization by tissues, and mechanical ventilation.
- Treatment of hemic hypoxia is accompanied by blood transfusion and stimulation of hematopoiesis. In case of circulatory disorders, corrective surgery on the blood vessels and heart is required.
Causes of oxygen starvation
Oxygen deficiency in the brain can be caused by several reasons:
- Respiratory – the brain is not able to receive the proper amount of oxygen due to impaired respiratory processes. Examples include diseases such as pneumonia, bronchial asthma, and chest trauma.
- Cardiovascular - a violation of blood circulation in the brain. Causes may include: shock, thrombosis. Normalizing the functioning of the heart and blood vessels helps prevent the development of cerebral stroke.
- Hypoxic – oxygen starvation, which occurs when oxygen in the air decreases. The most striking example is climbers who, when climbing a mountain, most clearly feel the lack of oxygen.
- Blood – with this factor, oxygen transport is disrupted. The main reason is anemia.
- Tissue – development occurs due to disruption of oxygen transport. The cause may be poisons or medications that could destroy or block enzyme systems.
Diagnostic tests
Diagnosing an acute form of oxygen deficiency in the brain is not particularly difficult, since the disease has pronounced, clear symptoms. Things are more complicated with chronic hypoxia. Diagnosis of hypoxia includes a number of medical tests and examinations.
The patient needs to donate blood for a detailed and biochemical blood test. An encephalogram is performed to analyze the functioning of nerve cells in the brain. If it is necessary to clarify the diagnosis, the patient must undergo an MRI and rheovasography - a method by which the condition of the vessels of the circulatory system is studied.
Main symptoms
Symptoms of lack of oxygen in the brain may manifest differently in each person. In one patient, sensitivity may decrease, lethargy may appear, and in another, headaches may begin.
The main symptoms of oxygen starvation of the brain:
- Dizziness, the possibility of loss of consciousness due to inhibition of the activity of the nervous system. The patient experiences severe attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- Visual impairment, darkness in the eyes.
- Change in skin color. The skin turns pale or red. The brain reacts and tries to restore blood flow, resulting in cold sweat.
- Adrenaline increases, after which muscle weakness and lethargy occurs in the patient. A person ceases to control his movements and actions.
- Irritability, resentment appear, depression and other mental disorders develop.
- Inattention, the patient has difficulty absorbing information, mental performance decreases.
The final stage of the disease with oxygen starvation is the development of coma, and then soon respiratory and cardiac arrest.
If the patient receives timely medical care, all body functions can be restored.
Diagnosis and treatment
To determine the patient's current condition and whether he is truly sick, a number of medical tests are required.
These include:
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain. This method shows the consequences of oxygen deficiency. With this method, you can see areas of the brain where sufficiently saturated oxygen enters.
- Ultrasound is a method that allows you to determine deviations from the norm during the development of a child in the womb. Allows you to determine oxygen starvation at the initial stage.
- Complete blood count and clinical tests for acid-base balance.
- General and selective angiography.
Treatment of oxygen deficiency primarily involves restoring the required supply of oxygen to the brain.
If there is a lack of oxygen in the brain, the following measures are prescribed:
- Maintaining normal functioning of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems;
- Drugs to improve blood circulation in the brain;
- Antihypoxanes;
- Decongestants;
- Bronchodilators.
Radical treatment of the disease is also carried out when the patient is already in serious condition. This treatment includes: blood transfusion, installation of an oxygen mask, procedures for resuscitation of the patient.
Healing procedures
Treatment of cerebral hypoxia is based on correct identification of the causes and their effective elimination. To do this, the doctor examines the patient’s medical history and appearance.
In some cases, ECG diagnostics and chest x-ray are used. To determine the degree of oxygen saturation in the blood, a pulse oximeter is often used, and the CO2 meter method is based on the analysis of exhaled air.
Let us analyze the treatment methods used in relation to the causes of hypoxia:
- For exogenous reasons, the use of oxygen equipment is effective.
- In respiratory cases, various drugs are used that cause dilatation of the bronchi, antihypoxants (drugs that improve the absorption of oxygen), organization of direct oxygen supply to the lungs, the extreme case is forced ventilation of the lungs. Many patients with chronic hypoxia constantly use an oxygen cylinder.
- In hemic cases, they are also treated with oxygen, additionally blood transfusions are used, and techniques that improve hematopoiesis are used.
- Circulatory hypoxia is most often treated with surgery and the use of anticoagulants.
- For tissue, antidotes are used (for poisoning), hyperbaric oxygenation (the patient is in an oxygen chamber at high pressure) and antihypoxants.
In all cases the use of oxygen therapy ; this is worth remembering, especially in acute forms of hypoxia.
For example, in case of carbon monoxide poisoning, it is important to take the victim to fresh air so that there is no further entry of carbon monoxide into the body.
Preventive measures to prevent fetal hypoxia begin in the first trimester to prevent intoxication of the mother’s body, timely treatment of diseases, correction of pathologies and possible complications during pregnancy and childbirth, and avoid post-maturity.
For this reason, the entire period of pregnancy and childbirth should be under the supervision of a doctor, since prolonged hypoxia can make your child disabled with a delay in physical and mental development.
Prevention of hypoxia
Preventing a disease is always easier than treating it. For normal oxygen intake into the body, you just need to follow the recommendations of specialists. These tips can be used both for the prevention and treatment of oxygen deficiency.
Key tips include:
- Fresh air Walks should take at least 2 hours, preferably before bedtime. It is better to take walks in environmentally friendly places (parks, forests).
- Sport. Light exercise in the morning promotes better blood circulation, and if you do it outside, the effect will be doubled.
- Correct daily routine. You need to normalize your routine, allocate the required time for rest and sleep. To normalize processes in the body, you need to devote at least 7-8 hours to sleep. Don't forget to warm up if you work at a desk.
- Proper nutrition. For the normal supply of oxygen to the brain, nutrition plays an important role. The diet should consist of a large number of vegetables and fruits. You should eat foods rich in iron (buckwheat, meat, dried fruits), while dairy products and coffee consumption should be kept to a minimum.
- No stress. Try to avoid stressful situations and not get nervous in vain.
Respiratory prevention of oxygen deficiency
One of the most convenient and simplest ways to prevent disease is breathing exercises. This method is very easy to use and does not require any additional effort.
A few useful exercises to take note:
- Relax completely, take a 4-second deep breath, then hold your breath for the same time and exhale slowly. Repeat about 12-15 times. After 1 month, increase the time of inhalation and exhalation.
- Take a deep breath and take at least 6-7 short exhalations through your nose. The mouth remains closed. Repeat 3-4 times.
It is advisable to repeat these exercises 2 to 4 times a day.
Human defense mechanisms during hypoxia
The human body has in its arsenal a number of adaptive mechanisms to combat hypoxia:
- The simplest way is to increase the frequency of inhalations - breathing is frequent and deep, then due to depression of the respiratory center, breathing becomes intermittent, rare and superficial. It is most clearly observed among climbers who rise to great heights.
- There is an increase in the frequency and strength of heart contractions, and blood pressure rises. This increases the supply of oxygen to the tissues.
- Next comes the removal of all blood reserves (from the spleen and liver), due to which the total number of oxygen carriers in the body increases.
- The functioning of individual organs, tissues and systems of the body slows down in order to optimize oxygen consumption in the body.
The last resort in the fight against hypoxia is the transition to alternative sources of energy - the breakdown of carbohydrates is observed according to the type of anaerobic glycolysis.
During this process, there is an active accumulation of lactic acid in the body, which leads to acidosis, which is associated with disturbances of microcirculation in the tissues; it also impairs breathing and blood circulation in general.
Article on the topic: Neurosonography of the brain of newborn children
It is worth understanding that all these mechanisms in acute hypoxia give a short-term effect and if the cause is not eliminated, then death occurs after the body’s resources are depleted.
In chronic hypoxia , these mechanisms provide all possible assistance, but the patient will constantly experience serious discomfort from the side effects of these mechanisms.
Oxygen starvation in newborns
Symptoms of lack of oxygen in the brain can appear in a newborn during the period when the baby is still in the womb, or immediately during childbirth. Hypoxia in a severe stage, not rarely, can lead to serious consequences for both mother and baby.
Of these we can note:
- Premature birth;
- Intrauterine death of a child;
- Stillbirth;
- Severe disability of the child.
Reasons why these severe consequences may occur in children:
- Problems of the cardiovascular system;
- Intrauterine infections;
- Improper lifestyle (alcohol, cigarettes, drugs);
- Fetal pathology;
- Birth injuries.
Oxygen deficiency, as a diagnosis, is made in approximately 15% of pregnancies.
Most often, brain hypoxia in a child develops due to the mother’s poor lifestyle, drinking alcohol, and smoking.
Therefore, in order for your child to grow up as a healthy and strong child, you should give up bad habits.
Signs
Hypoxia in the fetus during pregnancy is diagnosed with great difficulty, since the only way to identify alarming symptoms is by counting fetal movements. If the baby suddenly becomes more active, his tremors become very frequent, sometimes painful for the woman, and with a high degree of probability he experiences a state of oxygen starvation. With his movements, he tries to tug at the placenta in order to get a little more of the substance he needs. In a state of prolonged hypoxia, fetal movements, on the contrary, slow down, become rare and sluggish.
Such complaints from a pregnant woman are the basis for an unscheduled ultrasound, with Doppler, to assess the speed and volume of blood flow in the mother-placenta-fetus system. From 29 weeks of pregnancy, a CTG (cardiotocogram) can be performed. But all these methods can only indicate some kind of trouble in the fetus in the womb, but, alas, they cannot answer the question of whether there is hypoxia for sure.
The state of acute hypoxia is determined during labor if the birth process occurs under the control of CTG. Neonatologists, examining the baby, note the effect of hypoxia on his condition, and this is reflected in the Apgar score. A baby who has experienced prolonged hypoxia in the womb or who has experienced it during birth usually does not immediately cry, and his skin is bluish. Often the child requires the help of resuscitators.
In early neonatal age, signs of hypoxia manifest themselves in the baby’s restless behavior and numerous neurological symptoms, which are noticeable not only to the neurologist, but also to the mother, who is completely far from medicine. Such children often cry and scream for no apparent reason, arch their backs and throw their heads back, they experience profuse and frequent regurgitation, sleep and appetite disturbances, may be pronounced in the limbs and chin, and nystagmus of the pupils of the eyes.
The exact list of disorders depends on which part of the brain was most affected by oxygen starvation. A mild form may not cause external symptoms; only an experienced doctor can discern small “problems” and “inconsistencies” in development. Hypoxia of the 2nd degree most often causes coronary artery disease, but this does not always pose a danger in the future.
Moderate and severe hypoxia are dangerous. Violations can be noticeable almost immediately. These are various forms of paralysis and paresis, cerebral palsy, encephalopathy, severe damage to the organs of vision, hearing, speech centers and the musculoskeletal system.
Very often, increased muscle tone in a newborn is “recorded” as symptoms of hypoxia. It is easier for the doctor to explain to the mother that tone is a consequence of lack of oxygen and to prescribe a massage than to tell her that tone is a normal phenomenon for all newborns without exception. However, generalized hypertonicity, covering all muscle groups of the baby, cannot be considered physiological. It may be a consequence of hypoxia.
When asked whether hypoxia affects a baby’s development, the answer is always affirmative. The only question is how great are the post-hypoxic changes in brain structures. Slight hypoxia, provided the doctor’s recommendations are followed, may not have a significant effect on the baby. It is difficult to talk about severe hypoxia, which was complicated by oxygen starvation and subsequent death of brain cells. The consequences will be as great as the cell loss.
Danger of brain hypoxia
A state of oxygen starvation can lead to pathological changes. Brain activity and basic brain functions are impaired.
Whether the prognosis is favorable depends on the degree of brain damage and at what stage the disease was discovered.
A person's chances of recovery also depend on his current condition. With a prolonged coma, the basic functions of the body are impaired and the chance of recovery becomes very low.
With a short-term coma, the chances of rehabilitation are very high. However, treatment may take quite some time.