Causes of cerebral vasoconstriction
Narrowing of brain vessels, or their stenosis, develops due to atherosclerosis. This is a vascular disease accompanied by the deposition of fat, calcium and cholesterol on their inner walls. All these substances form atheromatosis (plaques). Foreign formations negatively affect the condition of the arteries, the walls of which lose elasticity. In addition, thickened walls narrow the lumen, and this provokes stenosis of large vessels that supply blood to the brain and other organs. Atherosclerosis can be caused by the following reasons:
- hypertension;
- obesity;
- diabetes mellitus;
- poor nutrition combined with a sedentary lifestyle;
- hereditary factor.
The most severe consequence of atherosclerosis is a narrowing of the blood vessels in the brain, which completely closes their lumen and blocks the blood flow to the organ. The patient experiences cerebral ischemia (stroke), which is dangerous not only with a high risk of disability, but also with death.
Hypertension can be considered not only as a cause of the development of atherosclerosis, but also as an independent factor that provokes a narrowing of cerebral blood vessels. Constant fluctuations in blood pressure lead to depletion of the walls of blood vessels and loss of their elasticity, resulting in stenosis. Hypertension most often develops with obesity, constant stress and infectious diseases that affect blood vessels. The disease affects older people and those whose blood relatives also suffered from high blood pressure.
There are also less common causes of cerebral vasoconstriction:
- Congenital vascular pathologies.
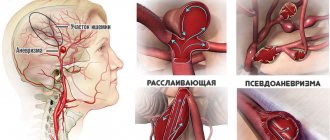
- Aneurysms.
- Vasculitis.
- Infectious damage to the walls of blood vessels with syphilis, tuberculosis, etc.
- Consequences of surgical interventions.
- Oncological diseases.
Causes
Vasoconstriction is a polyetiological disease; a person can have it either from birth or acquired.
In newborns, stenosis occurs due to a violation of the anatomy of internal organs, if any organs compress each other in utero for a long period during a woman’s pregnancy. Adults acquire narrowed blood vessels due to bad habits, abuse of junk food and a sedentary lifestyle.
At the moment, factors for the development of the disease can be divided into three different groups:
- Damage to the vascular wall.
- External influence on blood vessels.
- Circulatory disorders.
The first group of diseases includes:
- Atherosclerosis.
- Diabetes.
- Collagenosis and vasculitis.
Atherosclerosis is the process of deposition of fatty plaques in arteries and veins. In 60% of cases, the vessels are narrowed and clogged precisely because of the presence of this pathology. The disease is often accompanied by hypertension and obesity, which also negatively affects the state of blood circulation in the brain, causing hypoxia. Intracranial atherosclerosis developing in the circle of Willis is more dangerous than extracranial atherosclerosis in the carotid and vertebral arteries.
The process begins with a violation of lipid metabolism - the conversion of high-density lipids into low- and very low-density lipids. When there is an excess of them, the body begins to produce phagocytes, which transfer lipids to the cell wall. Everything is complicated by the appearance of concomitant damage to the wall.
Diabetes mellitus complicates the course of atherosclerosis by disrupting the process of neutralizing fats in the blood and increasing their amount. Diabetes mellitus also slows down microcirculation, often causing thrombosis of arterioles and venules in the brain.
Collagenosis is a pathological autoimmune process characterized by disruption of the organization of connective tissue, including blood vessels, which leads to their narrowing and obstruction. A similar disease is vasculitis, an inflammation of the intima in which the artery wall can swell and narrow the passage.
External factors include:
- Cervical osteochondrosis.
- Dysplasia of the cervical vertebrae.
- Traumatic brain injuries.
The peculiarity of the anatomy of the cervical spine lies in the passing vertebral (main) artery, which, rising through a series of holes in the vertebrae, enters the skull and forms the anterior and posterior cerebral arteries at the base of the brain. For this reason, most pathologies at the level of the cervical spine cause problems in cerebral circulation.
Osteochondrosis means degeneration of connective tissue, which is accompanied by ossification of adjacent areas and the formation of a bone ring. The formations can put pressure on the vertebral artery, which compresses and causes circulatory problems.
Cervical vertebral dysplasia also affects the patency of the vertebral artery. Often this pathology is accompanied by neurogenic problems due to compression of the spinal cord.
Traumatic brain injuries rarely affect the state of blood circulation, especially in terms of narrowing of the arteries, but they can cause the development of hematomas, which will already lead to the disease. Mechanical narrowing is also possible when the bones of the base of the skull are displaced - sphenoid, temporal, occipital.
Circulatory disorders include:
- Hypertension.
- Hypotension.
- Arrhythmias.
Hypertension, namely, constant tension in the arteries, leads to hypertrophy of the muscle layer, which is forced to respond to increased pressure. With a decrease in blood volume, the arteries become severely stenotic, which leads to cerebral circulatory failure. Additionally, the process is worsened by smoking, which causes a reflex contraction.
With low blood pressure, hypotension, arteries and veins can collapse due to lack of blood in them. This is expressed by severe hypoxia of the brain, dizziness in an upright position. The main development factor is shocks of various origins, alcoholism.
The body responds negatively to any arrhythmia. In terms of cerebral circulation, this can manifest itself as stenosis, which is very dangerous. With arrhythmia, the chance of blocking the lumen of the vessel with a thrombus is increased, and the muscular wall of the vessel is in good shape to compensate for the consequences of temporary hypoxia.
The narrowing can also be congenital, due to abnormalities in the cerebral circulation. In this case, angiocerebral dystonia is often diagnosed, but the name of the disease usually only hides the true pathology. It is impossible to completely cure the disease, but in most cases there is no need to do anything about it - other body systems compensate for the phenomenon.
Most often, angiocerebral dystonia is found in adolescents. Often, over time, a child can completely restore vascular health, since the vegetative balance catches up with the real needs of the body. In the future, dysfunction with this outcome is not detected.
All of these causes can be further complicated by obesity and smoking. The first accelerates the development of atherosclerosis and hypertension, and the second leads to permanent vascular stenosis and complications of the disease.
Today, the following causes of cerebral vasoconstriction are distinguished: atherosclerosis, hypertension, aneurysm, genetic diseases, osteochondrosis, and third-party negative factors.
Atherosclerosis
One of the main reasons for the narrowing of blood vessels in the head (about 60% of cases) is atherosclerosis. This disease is characterized by the appearance of cholesterol plaque on the artery wall. Gradually growing, it can completely block the vessel.
Hypertension
An equally common cause of cerebral vasoconstriction is hypertension. With this disease, a person has high blood pressure, which is why the vascular muscles are constantly toned, which over time leads to their thickening. Due to the increase in the volume of wall tissue, the lumen becomes narrow, which leads to insufficient blood flow to the brain.
Aneurysm
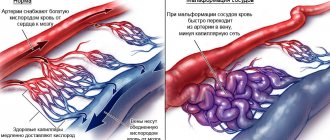
Stenosis of cerebral vessels can also develop with the formation of an aneurysm. An aneurysm is a bulge in the wall of a vessel that is filled with blood. If it is large enough, it can put pressure on the vessel, thereby making the lumen narrow.
Deviations in their genetic structure can lead to narrowing of the blood vessels in the head. The most common pathologies are Williams and Ehlers-Danlos syndromes. In these diseases, the thickness of the walls of the vessels is initially greater than in an ordinary person, and, as a result, the lumen has a smaller cross-section.
Osteochondrosis
Another reason why cerebral vessels may narrow is osteochondrosis. With this disease, the artery is blocked by the vertebrae in the neck, due to their deformation or protrusion. If stenosis occurs due to osteochondrosis, the entire brain is exposed to oxygen starvation, and not its individual areas.
External negative factors that lead to narrowing of the blood vessels in the head include smoking, alcohol and exposure to toxins. When harmful substances enter the body, they cause spasms, disrupt the elasticity of the walls, and also contribute to the formation of cholesterol plaques.
Third-party causes also include frequent emotional outbursts, as well as prolonged stress, which cause an increase in pressure, as a result of which the walls of blood vessels thicken.
Forms and symptoms of cerebral vasoconstriction
Acute form
Constriction of cerebral vessels in adults and children occurs differently: it can occur suddenly, or it can be chronic. The acute form is extremely dangerous for human life, as it causes a stroke or cerebral hemorrhage, which often leads to premature death.
The first symptoms of a stroke, which in no case should be ignored and urgently call an ambulance, are headache, numbness of the tongue, limbs, impaired thinking and a general serious condition. If these signs occur, the first thing to do is call an ambulance: if the patient is not provided with immediate medical care, the acute form of the disease can be fatal.
A cerebral hemorrhage is characterized by a blood clot blocking a blood vessel. This leads to the fact that, under the influence of strong blood flow, the walls of the arteries break through, blood enters the brain and damages its structures. This usually happens suddenly, due to physical or emotional stress. Cerebral hemorrhage is characterized by the following symptoms:
- flushed face;
- severe headache;
- vomiting, rapid breathing;
- slowing or speeding up heart rate;
- disturbance of consciousness.
How dangerous this condition is depends not so much on the size of the hemorrhage, but on the location where it occurred. In any case, if such symptoms appear, if timely assistance is not provided to the patient, the patient may fall into a coma and die.
Chronic form
The chronic form has mild symptoms for a long time. At the initial stage, a person periodically feels a mild headache, fatigue, nervousness, and drowsiness. After some time, he becomes distracted and his memory begins to deteriorate.
At the second stage of development of the disease, the symptoms become more obvious. Symptoms of an approaching exacerbation are a significant deterioration in well-being, migraines intensify and become more frequent, the gait becomes shuffling and unsteady, and problems arise with the urinary system. The disease also affects the functioning of the nervous system: performance decreases, and frequent mood swings often lead to conflict with others.
Many people do not pay attention to the symptoms of the first two stages, relieving headaches with painkillers. Therefore, the disease continues to progress and enters the third stage. At this time, severe problems are observed in the functioning of the musculoskeletal system: the patient often stumbles, loses balance, and may completely lose the ability to move. Sometimes speech is impaired and vision loss occurs.
Involuntary urination often occurs, and dysfunction of the pelvic organs is observed. Memory continues to deteriorate, the first signs of dementia appear when a person loses the ability to speak, walk, control his actions, and orient himself in space. After some time, a stroke or cerebral hemorrhage may occur.
Stages of development of pathology and corresponding symptoms
The disease has two forms - acute and chronic. Acute is characterized by rapid narrowing of blood vessels with partial or complete closure of the lumen. The disease leads to the development of ischemia of brain tissue followed by ischemic stroke.
Symptoms of an acute form of narrowing are:
- I often have a headache.
- Feeling of numbness in the arms and legs.
- Loss of consciousness, dizziness.
- Deterioration of vision in one eye.
- Weakness of one of the arms.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Lethargy.
- Changes in blood pressure and pulse, very rapid or slow breathing.
The presence of these signs indicates a possible stroke, so you should immediately call an ambulance. The possibility and speed of recovery depends entirely on the time elapsed since the cessation of oxygen supply to the brain cells.
The manifestation of symptoms increases with a decrease in the lumen of blood vessels.
In medicine, there are three stages of cerebral vasoconstriction:
- The first, when they narrowed by 15-20 percent.
- The second, when they narrowed by 50-70 percent.
- The third, when they narrowed by 70 percent.
First stage
The initial stage is characterized by primary changes. In atherosclerotic disease - the formation of a spot followed by an increase in plaque; in a tumor process - slight compression of the vessel, and so on.
Characteristic symptoms:
- Intermittent migraine, periodic headache.
- Fatigue during mental work.
- Dizziness.
- Drowsiness.
- Mild memory impairment.
- Sleep disorders - difficulty falling asleep and waking up.
- Depressed mood, irritability.
- Pulsation in temples.
The manifestation of symptoms is often ignored by the patient. At this level, the process can be easily stopped through drug therapy and dietary nutrition.
Second stage
The second stage of progression is characterized by active narrowing of the vessel due to the development of pathology. They can be the appearance of an atherosclerotic plaque, changes in the structure of the vessel along its entire length, hypertension.
The following symptoms are typical for this stage:
- Severe fatigue during mental work, fatigue.
- Periodic memory loss, loss of skills, fixation.
- Constant headaches.
- Loss of consciousness, fainting.
- Temporary or permanent visual impairment.
- Orthostatic collapse – severe dizziness when changing position.
- Gait disturbances, sluggish movements.
- Lack of interest in anything.
- Sudden urge to urinate, defecate.
- Convulsiveness.
- Severe drowsiness, difficulty waking up.
Symptoms increase as the lumen decreases. In some cases, it may be absent until the vessel is more than 50% closed, with an abrupt onset. This option is easier for diagnosis - a person immediately goes to medical institutions.
Already at this stage, complete closure of the narrow lumen of the vessel is possible, followed by ischemia and stroke.
Blockage usually occurs due to blood clots, in rare cases - when other foreign bodies enter the bloodstream.
Third stage
The last, decompensated stage is characterized by the final development of pathology with a lack of compensatory reactions of the body. The lumen of the vessel is only 10-30 percent open and can easily be blocked by a thrombus, which seriously increases the possibility of an ischemic stroke.
Symptoms:
- Confusion.
- Tired state.
- Ataxia, hypokinesia.
- Loss of performance, inability to self-care.
- Constant severe headache. In this case, the head may hurt without a clear localization.
- Disorders of other organ systems.
Progression of the pathology to this stage is quite rare, since patients with chronic vasoconstriction undergo earlier surgical treatment to eliminate the cause, if possible.
Doctors distinguish three stages of narrowing of the blood vessels in the head.
At the first stage, the reduction in lumen is no more than 20%. At this stage of pathology, brain cells do not die, but only experience oxygen starvation, which leads to disruption of their functions. This can manifest itself in a person in the form of periodic causeless headaches, dizziness, and fatigue during mental stress.
The second stage is diagnosed if the lumen has decreased from 20% to 50%. In this case, there is a significant decrease in blood flow, which causes the death of brain cells in small areas.
In this case, a person may experience symptoms such as tremors of the arms and legs, convulsions and spasms of the facial muscles, problems with walking (shuffling feet and sudden falls), fainting, inability to think and reason logically, minor memory lapses, hypertrophy when expressing any emotions and frequent urge to urinate.
When the lumen of blood vessels is reduced by more than 50%, doctors speak of the third stage of the disease. It is characterized by the death of all brain cells in the area supplied by the damaged artery. In this case, irreversible degenerative changes in the brain occur. This stage corresponds to symptoms such as a delusional state of consciousness, dementia, involuntary urination, memory loss, and complete disability.
It is worth noting that cerebral vasoconstriction does not occur quickly. Usually, it takes months and even years for the pathology to move to the next stage, while symptoms, especially in the initial stages, may appear and disappear. As a result, a person is in no hurry to seek help from doctors.
However, this is fundamentally wrong, since in the first and second stages, in almost 100% of cases, the pathology can be cured with medications rather than surgery. Therefore, if any of the above symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor for a comprehensive examination of the blood vessels.
Diagnosis of the disease
There are several complementary types of diagnostics:
- During diagnosis, a large amount of information is obtained by conducting a physical examination of the patient. The presence of neurological changes is determined, the parameters of breathing and the functioning of the cardiovascular system are recorded;
- The next diagnostic method: Doppler sonography. This study is aimed directly at studying the patency of blood vessels and their anatomy, and the speed of blood flow. This study identifies changes in the great vessels caused by the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in them or other physiological reasons;
- The most modern and effective methods for diagnosing blood circulation disorders in the vessels supplying the brain are MR angiography and CT angiography. Angiography provides an accurate picture of vascular conditions, including narrowing, aneurysms, and thrombosis.
Treatment methods for cerebral vasoconstriction
Treatment for cerebral vasoconstriction depends on the form of the disease. In case of acute circulatory disorders, assistance should be provided immediately with medications aimed at eliminating all changes that have occurred.
The most dangerous thing is a sharp narrowing of the blood vessels in the brain, which leads to irreversible consequences.
When a disease is detected in the chronic stage, therapy and selection of medications for the patient should ideally be carried out by specialists in several fields - cardiologists, angioneurologists, and therapists.
Treatment of the disease depends on the patient’s condition and on the data obtained during diagnosis, and mainly consists of several stages.
Drug treatment
Conservative treatment – taking pharmaceutical drugs of different groups. Some of the medications are prescribed for lifelong use.
Drugs to treat vasoconstriction
Depending on the condition of the blood vessels, the doctor prescribes medications from the following groups:
- Statins. These include Mevakos and Mefakor.
- Fibrates – Atromidine, Clobifrate, Zocor.
- Lecithin.
- Iodine therapy.
- Vitamin and mineral complexes.
- To increase the lumen of blood vessels, papaverine and aminophylline.
All medications for the treatment of cerebral vasoconstriction are selected in individual dosages; if other pathologies are detected, the doctor prescribes appropriate therapy.
Surgical intervention
The purpose of the operations is to restore normal blood flow, bypass surgery or endarterectomy is performed. During bypass surgery, a special stent is inserted into the vessel, providing a normal frame to the altered vessel walls.
Endarterectomy – removal of atherosclerotic plaques under local anesthesia. The decision to undergo surgical intervention is made in the absence of effect from medications and in the probable development of an acute disorder as a result of blockage of the lumen of the arteries by a thrombus or a large atherosclerotic plaque.
What is the treatment for cerebral vasoconstriction?
Treatment of cerebral vasoconstriction is a complex and lengthy process. Prescribing adequate treatment requires a lot of knowledge from the doctor and a lot of patience from the patient. Therapy for narrowing of cerebral vessels largely depends on the degree of reduction in their lumen, the duration of the disease and the severity of clinical manifestations. After making a diagnosis, the doctor determines the treatment tactics for the patient.
Conservative treatment of cerebral vascular constriction includes:
- Non-drug treatment methods:
maintaining a daily routine and a healthy lifestyle. A proper balance between work and rest time and stopping the use of drugs, alcohol and smoking in the early stages of the disease can normalize cerebral circulation;
- moderate physical activity. Morning exercises, gymnastics, jogging, cycling, rollerblading, skiing, skating, even walking to work on foot train blood vessels and normalize blood pressure;
- diet therapy. Limiting the consumption of salt and foods that increase cholesterol levels in the blood reduces the manifestations of atherosclerotic damage to cerebral vessels;
- herbal medicine;
water procedures. Visiting the pool and taking contrast showers have a beneficial effect on the tone of the cerebral vessels, training and hardening them;
lipid-lowering drugs;
antihypertensive drugs;
Phytotherapy
Products made from plant materials are useful for cerebral vessels:
decoction of hawthorn fruits and flowers (2 tablespoons of fruits and flowers, pour 1 tablespoon of water, boil for 30 minutes, take 1 tablespoon 3 times a day);
- infusion of St. John's wort herb (pour 1 tbsp herb over 1 tbsp boiling water, leave for 12 hours, take 1/3 tbsp three times a day);
- tincture of Japanese Sophora pods (1 tbsp of crushed pods, pour 0.5 liters of vodka, leave in the refrigerator for 3 weeks, take 1 tbsp three times a day before meals);
- infusion of flax seeds (1 tbsp. seeds per 1 tbsp. water, leave for 12 hours, drink 1 tbsp. morning and evening).
Herbal remedies are gentle, but to obtain the expected effect they must be taken for at least 1 month.
Lipid-lowering therapy
Statins are effective medications that lower the concentration of cholesterol in the blood. The mechanism of their anticholesterol action lies in blocking the enzyme that affects cholesterol synthesis.
The most effective statins currently are:
- Simvastatin;
- Cardiostatin;
- Fluvastatin;
- Liprimar;
- Livazo;
- Rozulip.
For high cholesterol levels, doctors supplement statin therapy with fibrates - drugs that activate an enzyme that accelerates lipid metabolism.
Among the fibrates that are prescribed by doctors in conjunction with statins, the following are effective:
- Gemfibrozil;
- Fenofibrate (Lipantil);
- Bezafibrate;
- Ciprofibrate (Lipanor).
Antihypertensive drugs
If blood pressure is elevated, the use of antihypertensive drugs is indicated:
- beta blockers (Atenolol, Metoprolol, Bisoprolol);
- ACE inhibitors (Enalapril, Captopril, Lisinopril, Perindopril);
- antispasmodics (Eufillina, Papaverine).
Antihypertensive drugs are part of the classical standards of treatment for diseases associated with cerebral vasoconstriction.
Traditional methods of treating cerebral vasoconstriction
Meanwhile, everyone can protect themselves from the consequences of vasoconstriction without resorting to drug treatment.
Pine infusion
The best folk remedy is young pine shoots emerging from the buds in late spring or early summer. Or rather, honey from them.
For preparation you will need 70 ten centimeter young branches. They need to be boiled in a liter of water until softened. The water will boil away, so after finishing cooking and straining, you need to add it to get a liter of broth. But you can add little by little during the cooking process.
Then, add a kilogram of granulated sugar and lemon chopped in a blender (along with zest) to the still hot broth. Boil the prepared mixture for another 5 minutes and pour the fragrant honey into the jars.
Use it once a day, no more than a tablespoon.
Hawthorn
Constriction of blood vessels in the head, at its first manifestations, is effectively treated with blood-red hawthorn flowers and berries. This plant is widespread throughout our country. Dried flowers and berries can be brewed at the same time as tea in a teapot.
Or prepare an infusion of two tablespoons of a mixture of flowers and berries (you can brew berries and flowers separately) in a glass of water. Drink a tablespoon of infusion every time before meals. Hawthorn perfectly strengthens blood vessels.
For the same purpose, you can use a pharmacy alcohol tincture of hawthorn, or prepare it at home by infusing freshly picked flowers or picked berries in vodka. Use by adding 10 drops to tea or a glass of water.
Clover
Alcohol tincture from meadow clover copes well with the first signs of atherosclerosis.
To prepare it, any container is filled to the top with flowering clover heads and filled with vodka. Infuses for two weeks. Take in the same way as hawthorn alcohol tincture.
You can make clover flower tea daily and drink it instead of water. Clover improves memory and reduces tinnitus.
Dandelion
Dandelion is familiar not only to rural residents. A delicious and very healthy jam is prepared from its yellow heads. But few people know that dried and fresh dandelion roots are an effective remedy for treating narrowing of the spaces between the walls of the arteries.
- Grind dry dandelion roots to a powder. For medicinal purposes, eat a spoonful of powder before each meal. Can be mixed with honey to reduce the bitterness inherent in the roots.
- The juice of fresh roots is mixed with rice broth in a 1:1 ratio. A quarter glass is taken for administration. This remedy improves memory.
Treatment options
The treatment chosen depends on the findings obtained during the examination. A set of necessary measures is prescribed by different doctors - a therapist, a neurologist, a cardiologist. Since the disease affects different organs, the consultation should be multifaceted. The dosage and course of treatment are selected individually, based on the patient’s personal characteristics, the severity of the disease, and the presence of secondary diseases.
Drug treatment is usually represented by the following drugs:
- fibrates are drugs that lower blood cholesterol levels. Contraindicated when used simultaneously with statins. Depending on the type of atherosclerosis, the optimal ones are selected. From this group, Atromid, Clofibrate and others are most often prescribed;
- statins are drugs that, like fibrates, reduce cholesterol levels, help destroy plaques and increase the lumen of blood vessels. They are divided into simvastatins (Actalipid, Vasilip) and lovostatins (Mevacos, Mefacor);
- agents that dilate blood vessels - Actovegin, Papaverine hydrochloride, etc. Not only increase the lumen, but also normalize blood circulation;
- painkillers - used mainly to eliminate migraines;
- antidepressants and tranquilizers - eliminate irritability, nervousness, prolonged depression, and a depressed state. Phenozepam is most often prescribed;
- comprehensive intake of vitamins of different groups and minerals;
- iodine-containing products.
If the narrowing of cerebral vessels was caused by hypertension, a course of treatment is prescribed aimed at reducing and stabilizing high blood pressure. The same applies to cervical osteochondrosis, then antispasmodics are used. Along with drug treatment, diet must be followed. This is an important step that will help prevent the formation of new plaques and accelerate the destruction of existing ones.
Basic dietary principles include: reduce fatty, smoked, salty foods to a minimum or abandon them altogether. It is preferable to replace coffee with green tea, hibiscus, rose hips, and hawthorn. The most useful foods for vascular disease are fruits, vegetables, herbs, and seafood. In this case, you should stop smoking and drinking alcohol. Regular walks in the fresh air and non-aggressive sports are recommended.
Surgery
At the last stage of a chronic form of cerebral vasoconstriction, drug treatment may no longer be effective. Then urgent surgical intervention is necessary. Carotid endarterectomy is one of the most common surgical options. It is considered quite simple and quick to implement. Typically performed under local anesthesia. During the operation, the vessel is dissected and the atherosclerotic plaque is removed from its inner wall. Postoperative complications are rare; blood circulation returns to normal within the first days.
Angioplasty is often used for hypertension and cervical osteochondrosis. During this operation, a catheter is inserted into the cavity of the narrowed vessel to increase blood flow. To fix the lumen, a special metal frame is used - a stent consisting of thin metal threads. It is also performed under local anesthesia. Once finished, a tight bandage is applied to prevent bleeding. The postoperative period rarely takes more than three days. The recovery guarantee is close to 100%. In some, complex cases, re-narrowing of blood vessels occurs within six months. The pathology is eliminated in the same way as initially.
Traditional medicine
Traditional medicine can be an excellent preventative measure or an adjuvant in the fight against vascular diseases in the initial stages. Never and under no circumstances should you self-medicate and rely only on the effect of decoctions and tinctures. Any of the prescriptions should be previously agreed with your doctor. And also make sure that none of the components can cause an individual allergic reaction.
Garlic is considered the most famous and effective product. Peel a few heads, chop well and put in a jar. Pour alcohol over the garlic mixture and leave in a dark place for 10 days. The tincture can be consumed three times a day for a month along with milk. You should start with one drop, gradually increasing the dose to 15 drops. For best results, take the medicine before meals.
Along with garlic, the following are excellent for the prevention and treatment of vascular pathologies: a decoction of pine shoots, rowan, hawthorn, dandelion root, and an alcoholic tincture of clover. A tincture made from a mixture of hawthorn, motherwort and peony will give a good result. Ground dried fruits with walnuts, as well as dandelion jam, are not only tasty, but also very healthy for blood vessels.
Prognosis and consequences of the disease
If the disease is detected at an early stage and appropriate treatment is prescribed, its prognosis is quite favorable. Full recovery and the beginning of a normal lifestyle depends not only on the medications taken, but also on changes in general lifestyle. A person needs to constantly monitor his own nutrition, use regular gymnastic exercises, lead a physically active life, and eliminate stress.
All these recommendations will help you avoid loss of ability to work and help you lead a normal, unrestricted life. If appropriate therapy is not carried out, then the prognosis can be very unfavorable: senile dementia, loss of ability to work, strokes, complete immobility - this is not a complete list of complications that can arise from narrowing of the blood vessels in the brain, without proper treatment.
Narrowing of cerebral blood vessels, detected in the early stages, does not represent a serious disease. Constant and timely therapy, as well as following the doctor’s recommendations, will avoid complications. The only thing that is required from patients is constant adherence to the treatment regimen.
How does the disease manifest itself?
Since the causes of brain disorders are different, the symptoms and treatment can also be completely different. The first signs may manifest themselves as:
- minor headaches at the end of the day;
- low concentration;
- poor memory;
- irritability;
- fatigue;
- constant fatigue;
- convey the mood.
When the disease takes a new form, new symptoms appear:
- noise in ears;
- urge to urinate;
- fainting;
- midges before eyes;
- deterioration of speech;
- blurred vision;
- state of being lost.
Some of the most dangerous symptoms that appear at the last stage are:
- inability to move independently;
- uncontrolled urination and defecation;
- loss of strength and ability to work.
If you notice such symptoms, you should go to the hospital for tests and a diagnosis. Since the causes of the disease can be different, and the consequences of the symptoms that arise can be unpredictable.
At the hospital, doctors will order a general blood test and order a blood test for cholesterol. Hardware and computer tests will also be prescribed. Most likely, a patient with such symptoms will have to communicate with specialists. The latest generation computer research will allow us to obtain more accurate results, as well as answer questions about why blood vessels narrow. Also, according to the instructions of the attending physician, you may have to undergo Doppler ultrasound or MRI.
Prevention of cerebral vasoconstriction
To protect yourself from brain spasms, you must:
- Play sports: swimming, fitness, cycling.
- Temper the body with a contrast shower.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Maintain proper drinking regime.
- Eat right: eat more raw and minimally processed foods, avoid foods with flavor enhancers, preservatives, etc.
If you have a hereditary predisposition to atherosclerosis, hypertension and other diseases of the cardiovascular system, you should be regularly monitored by a doctor.
Vessels of the neck and head: treatment, folk remedies
- massotherapy;
- treatment with leeches;
- acupuncture;
- gymnastics.
For long-term effects, you must undergo a course of treatment in consultation with your doctor.
If you have a vasospasm, it is harmful to endure it. It is necessary to quickly relieve the spasm. To do this, soak your feet in cool water for a few minutes. Wash your face and take a comfortable position, lying or sitting. To soften the attack, you can drink a glass of warm water with dissolved honey.
To reduce headaches, give yourself a forehead massage: rub with gentle movements from the bridge of the nose to the temples, from the forehead along the cheeks and to the chin. Rub your temples with your fingertips in a rotating motion.
If possible, apply a drop of aromatic oil up your nose. You can use valerian, mint, jasmine or lavender oil.
To restore the flexibility and strength of capillaries and blood vessels, people, together with nature, have invented folk remedies for treatment and prevention.
One of the simplest available means of preventing the disease is pine honey.
At the moment of general flowering, young shoots grow from the pine buds. Take 7 meters of young pine branches, add 1 liter of water, boil until softened. During the cooking process, add water to compensate for what has boiled away. When the shoots soften, add a kilogram of sugar and a lemon minced with zest. Cook for another 5 minutes. The fragrant honey is ready, store it like any other jam.
For prevention, use 1 tbsp. in a day.
If the disease has already given its first manifestations in the form of headaches, strong tea with red hawthorn will help. Or you can drink the infusion as a stand-alone drink; to prepare it, brew 2 tbsp. dry berries or flowers per glass of water.
Clover has a similar effect. Add dried flowers to tea.
Dried fruits and nuts, especially walnuts, reduce the risk of cholesterol plaques. Make the mixture and eat 2 tbsp. in a day. The effect will be enhanced if you write such a salad with a fermented milk product.
Lemon and garlic, crushed 1:1 in a blender, help to successfully fight high cholesterol in the blood.
If you are at risk, follow these simple rules:
- do not abuse cigarettes, alcohol, coffee, sweets;
- avoid smoked and pickled foods;
- reduce the amount of salt, monitor this indicator in purchased products;
- eat more seaweed, grapefruit, gooseberries, apples, feijoa.