Rheoencephalography (REG) is an effective and simple type of examination that can determine various abnormalities in the brain. With an insignificant cost of examination, it has high information content. Considering changes in the functioning of the vessels of the brain of the head, REG helps to clarify the diagnosis with a high degree of reliability in a short time and much faster than, for example, tomography, since the last stage can take up to a month.
REG of brain vessels
Features of REG of cerebral vessels
Using the REG procedure, doctors can assess blood circulation in the brain . The level of blood supply and vascular tone in a certain part of the brain helps to determine the developing disease and begin treatment immediately, without waiting for the development of severe stages of the disease.
Among the results of REG, one can determine the viscosity of the blood, the speed of propagation of the pulse wave, the severity of the reaction of the vessels of the head and neck, the speed of blood flow and the flow time.
But some doctors are convinced that the method of studying REG is now outdated, and in terms of completeness and accuracy of the data, it cannot be compared with the results of brain tomography. This is true to some extent, but it cannot be said that this examination is completely useless - it significantly clarifies the clinical picture and allows the doctor to begin treatment as quickly as possible, and this can sometimes prevent death. That’s why doctors still do REG of cerebral vessels, especially in controversial situations.
What is Rheoencephalography (REG)?
Rheoencephalography is a diagnostic method based on graphic recording of electrical resistance of tissues. Along with ultrasound, REG is a safe method that has long been used in medicine. To carry out the procedure, electrodes are used that send impulses to the body tissues, the reaction to which is assessed by the device. REG allows you to evaluate the tone and elasticity of blood vessels, as well as nearby tissues. In addition, this method provides information about the filling of brain vessels with blood.
When is REG prescribed?
Typically, REG is prescribed to study large and small vessels of the brain in addition to ultrasound. Rheoencephalography is also indicated for an already diagnosed vascular problem to monitor the treatment of the disease.
How is the REG procedure performed?
Before the procedure, you must refrain from smoking, drinks and drugs that affect vascular tone. The patient must be at rest: the study is carried out in a lying or sitting position. Electrodes are attached to previously degreased areas of the head. The patient’s task is to remain still and calm, if necessary following the doctor’s instructions to carry out functional tests that increase the effectiveness of the study. The duration of the REG procedure is 15-30 minutes.
#!UZIseredina!#
How is a REG study of the vessels of the head performed?
The study is carried out using a special rheograph - recording equipment . The process is done in this way: a person sits or lies down, closes his eyes, electrodes are applied to certain areas of the head and neck and secured with special tapes. Often, the receiving part of the electrodes for better sensitivity of the equipment is treated with a special gel, which plays the role of a conductor. Preparation for the procedure lasts about 5 minutes .
A person needs to be prepared for the fact that the doctor will degrease the areas of the skin where the electrodes with alcohol, and then apply contacts that are coated with a conductive compound - this can cause some discomfort. Afterwards, during the examination, a weak current passes through the electrodes, and information about the resistance of brain tissue is recorded, which is then deciphered. The procedure itself, when performed correctly, is completely painless. But contact paste in some cases causes discomfort due to its presence, but a person does not need to worry because it is easily washed off .
The main difficulty during the examination is that the patient, under the stress caused by the procedure itself, becomes very nervous, because of this the blood vessels narrow, and the results are sometimes distorted . To prevent this from happening, the doctor explains the entire process in advance and talks to the patient during the examination.
Advantages and disadvantages of diagnostics
Among the advantages of this technique are:
- ease of conducting research;
- non-invasive;
- the ability to conduct REG for any necessary time;
- obtaining separate results on the condition of arteries and veins;
- fairly low cost;
- the ability to study collateral circulation and blood flow speed;
- minimal influence of external factors on the research results.
The disadvantages include the following factors:
- study of the functional state of blood vessels, on the basis of which it is impossible to make a diagnosis;
- low information content of the results, requiring additional research.
Diagnostics is carried out using a special rheograph device. It has from two to six channels, which allow the study of several areas of the brain at once.
Most often, readings are taken using electrodes that are attached to the scalp using special rubber bands. They range in diameter from 5 to 30 mm, are round in shape and are made of metal.
To improve signal conductivity, it is necessary to use a special gel that is applied to the electrodes. The patient is asked to take a comfortable position (sitting or lying on the couch), relax as much as possible and close his eyes.
During the diagnostic process, the obtained data is displayed either on a computer screen or printed directly on paper.
The electrodes are placed depending on which part of the brain needs to be studied:
- When assessing the external carotid artery, electrodes are placed above the brow ridge and in front of the ears;
- to study the internal carotid artery - on the bridge of the nose and under the earlobes;
- To examine the vertebral artery basin, the area of the mastoid process and occipital protuberances is selected.
Rheoencephalography for children
Separately, it is necessary to say about rheoencephalography for children. The entire process takes at least 15 minutes, in some cases it extends to 40 minutes.
All the time during this procedure, the child needs to lie or sit motionless, often with his eyes closed, so as not to be distracted by external stimuli.
Not everyone can sit through this amount of time, so doctors advise either to act educationally on the child, or not to undergo the examination at all when the child is restless.
Unfortunately, in this case the limitations are the same as during tomography. However, the main task of adults in this case is to tell the child why this is required, and to convince the baby of the need to lie down or sit quietly for a short time. The most important thing is that the persuasion does not take place in a stressful environment, since these consequences will blur the entire picture of the examination.
Interpretation of results
Moderate reactions to external stimuli and hyperventilation are normal. A significant increase in the signal during the test occurs in foci of epileptic activity in the cerebral cortex or around any pathological process. A decrease or absence of response to tests indicates a functional deficiency, a decrease or destruction of connections between this area of \u200b\u200bthe cortex and the underlying sections. The brain's reaction to hyperventilation is associated with changes in metabolism, temporary oxygen starvation of brain tissue, and may differ from reactions to light and sound stimulation.
The standard duration of electroencephalography is about 15 minutes. Moreover, the longer the examination is carried out, the more informative it is. A detailed assessment of the bioelectrical activity of the brain may require 2 hours or daily monitoring. The patient can sleep, read or communicate with relatives whose presence is permitted. If necessary, the manipulation is temporarily interrupted, the wires are disconnected, and the patient wearing a cap can go for tea or visit the restroom.
Interpretation of REG of cerebral vessels
There are a number of characteristics of the results obtained: the presence of a location relative to the downward main wave of the additional tooth, the magnitude of the amplitude, and the shape of the waves. Combinations of these results make it possible to distinguish ongoing organic changes in the brain from negative ones and, without penetrating the skull, to find out for certain where the lesion is located.
The wave has catacrotic and anacrotic phases, that is, a gentle downward and upward steep wave; in addition, the catacrot has a dicrotic special tooth, which is usually located in the center of the catacrot.
The magnitude of systolic inflow is shown by the rheographic index, the time of complete opening of the vessel is shown by the duration of anacrosis in seconds, the tone of the arterioles is shown by the dicrotic index, and the tone of the veins and blood outflow is shown by the diastolic index. Different REG patterns are characteristic of different pathologies, for example:
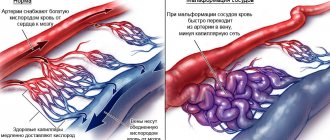
- Atherosclerosis of the brain vessels of the head - waves look like a dome or arches.
- Cerebral atherosclerosis – on the descending section of the wave there are no additional waves, the apex is flattened, the wave is smoothed.
- Increased tone of the arteries - on the anacrotic there are additional waves, the size of the anacrotic is lengthened and the steepness is reduced, the amplitude is small, and the tooth is reduced in size and shifted towards the apex.
- Reduced arterial tone - shortening of anacrotic and greater steepness, increased amplitude, displaced and large dicrotic tooth, sharp apex.
- Venous outflow is obstructed - convex and long catacrota, before the next cycle there are many additional waves.
- Vascular dystonia – additional waves on the catacrota, floating prong.
- Hypertension – there is no single picture, different shapes and amplitudes of the curves.
- Vasospasm - rounded peaks.
Oscillography
Oscillography (in biology and medicine) is the recording of electrical potential fluctuations in animal tissues using an oscilloscope.
Oscillography is used to study the activity of the heart (see Electrocardiography), brain (see Electroencephalography), muscles (electromyography), recording vibrations of arterial walls (arterial oscillography), etc.
Rice. 1. Arterial oscilloscope: 1 - scribe; 2 - paper cassette; 3 — rubber bulb; 4 — rubber cuff in a case. Rice. 2. Oscillogram of a healthy person. Rice. 3. Membrane oscillometer: 1 - tonometer showing the height of blood pressure; 2 - oscillometer; 3 — cuffs (upper and lower); 4 - pump.
For arterial oscillography, an oscilloscope of the “Red Guards” type has found wide use (Fig. 1). The principle of its operation is as follows: using a rubber bulb, air is pumped into the system, the pulsation of the arteries of the limb is perceived by the cuff and sets the membrane into oscillatory motion, which in turn sets the writing lever in motion; the latter's pen records vibrations on paper mounted in a cassette. The curve obtained from oscillography is called an oscillogram. It reflects the condition of the main (main) arteries of the limb, located directly under the cuff, and indirectly allows one to judge the condition of the overlying arteries (subclavian, axillary, iliac, aortic bifurcation).
Oscillography is performed by a paramedic, and a doctor gives a conclusion based on the oscillogram. The study is carried out in a warm room, with the patient lying down. Recording is made alternately from symmetrical areas of the limbs. When oscillography of the lower third of the thighs, the cuff is placed above the knee joints, of the forearms - under the elbow joints, of the lower third of the shoulder - above the elbow joints, of the shins - in the lower and upper thirds. The cuff should not be applied tightly; when applied correctly, the index finger should fit comfortably under it. Air is injected into the cuff until the pulsation of the artery under it stops, after which the oscillogram recording begins. Then open the valve in the bulb and gradually reduce the pressure. The first pulse wave on the oscillogram is revealed by a distinct tooth directed upward - maximum blood pressure -Mx (Fig. 2). As the air pressure in the cuff decreases, the range of oscillogram wave oscillations increases: the highest wave, called the oscillographic index (OI), corresponds to the mean arterial pressure (My), which is constant for each person. A further decrease in pressure in the cuff leads to a decrease in the values of the oscillogram waves, and its last wave shows the minimum blood pressure (MP).
The state of pulse oscillations of the arteries and arterial tone can also be judged from oscillometry data (registration of pulse oscillations of the artery on the oscillometric scale, Fig. 3).
Oscillography and oscillometry are performed for congenital and acquired malformations of large arteries to identify hidden hypertension.
Indications for REG
This encephalogram is carried out both for preventive and diagnostic , as it is completely safe. This is especially true for elderly and mature people, since vascular indicators only worsen over time and any disease is best identified in advance.
For what complaints do doctors prescribe examinations using REG:
- Various types of dizziness;
- Headache;
- Poor heredity – among relatives there are patients with vascular lesions;
- Injuries of the cervical spine;
- Elderly age;
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- Meteor dependence;
- Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels;
- Crises;
- Unexplained deterioration of memory, vision, hearing.
This examination eliminates doubts during diagnosis, and also has a formal character in the case where the clinical picture is relatively clear, but there remains the possibility of medical error.
In addition, together with Doppler ultrasound, this examination can completely compete with tomography in terms of the volume of data obtained, while remaining more efficient and accessible.
Research results
A rheoencephalogram has the form of a graph with plotted curves, which is deciphered using reference samples and a conclusion is drawn about the state of the circulatory system. Each curve has its own parameters (degree of slope, maximum value, periodicity). Different pathologies have their own reference curves. When examining both hemispheres of the brain, rheoencephalograms are compared, which may differ in the manifestation of vegetative-vascular disorders.
For a specific type of pathology, the REG picture is different:
- Atherosclerotic changes - the amplitude of the wave is reduced and has several thickenings, as a rule, there are no additional waves;
- Hypotonic conditions of the vessels - high pointed waves are noted, additional waves (or dicrotic waves) are displaced;
- Hypertensive states of blood vessels - low-amplitude waves with a displacement of the dicrotic tooth to the apex;
- Dystonic conditions - on the rheoencephalogram there are many additional waves with a floating tooth;
- Obstruction of the outflow of venous blood - a convex but long decrease in waves with the presence of additional waves before the next cycle;
- Vasospasm - round peaks are observed.
Based on the above, several types of deviations are determined by rheoencephalogram:
- Dystonic type. The rheoencephalogram shows a constant change in vascular tone, the appearance of areas with a decrease in pulse pressure in the vessels and difficulty in venous outflow;
- Angiodystonic type. Disturbances manifest themselves due to damage to the walls of blood vessels, changes in their elasticity and the appearance of areas with obstructed blood flow;
- Hypertensive type. Manifestations in the form of vascular hypertonicity and difficulty in the outflow of venous blood.
It should be noted that determining the type of rheoencephalogram does not indicate a diagnosis. The graphical curve shows changes in the vessels of the circulatory system. Based on the data obtained in combination with other studies, the attending physician can make a diagnosis.
Advantages of REG
REG is absolutely safe for human health, this makes it possible to send a patient for research even if, according to a preliminary diagnosis, he is completely healthy, that is, for the purpose of prevention.
To perform the examination, additional laboratory space, expensive equipment and a lot of time are not required, as is the case with tomography. Moreover, the device separately takes readings about the work of veins and arteries, this facilitates diagnosis at any stage of the disease. The painlessness of the procedure for the patient and the simple conditions for its implementation are the main advantages in the question of what examination methods can be prescribed to minor children.
For observed elderly patients, this procedure is required more often than for other categories, but its implementation does not require significant material costs and it is available even when visiting a private clinic.
Other research methods
Other methods are also used to study cerebral vessels, which are excellent additions to reflect the full clinical picture of the disease:
- Ultrasound of the brain allows you to assess the condition of soft tissues and suspect the focus of damage to its structures. Sometimes, ultrasound and REG are complementary research methods. It should be noted that diagnostics using REG allows one to assess the condition of both large vessels and small ones.
- An electroencephalogram measures the electrical activity of the brain. In this case, the main factor being studied is the activity of neurons and their connections. This technique is indispensable in making some diagnoses based on identifying pathologically active areas of the brain (for example, epilepsy and similar conditions). The result of the study is an oscillogram of the brain, which reflects the activity of its main structures. As a rule, REG can be an additional research method that allows us to collectively determine brain structures with impaired blood supply;
- Computed tomography of the brain is an x-ray research method that visually displays all types of tissues, including bone structures. The results of the study are informative and allow us to evaluate the blood supply system to the tissues. It should be noted that this procedure has contraindications, since it is based on X-ray radiation, which is an exclusionary factor for some groups of patients;
- Magnetic resonance imaging allows you to assess the condition of soft tissues and blood vessels, which makes it possible to use it both together with REG and separately.
The attending physician determines the diagnostic method depending on the clinical picture and suspicion of any pathology. At the same time, it is necessary to be guided by the information content of the method, the patient’s condition and the presence of contraindications to certain types of research. As a rule, several types of research are prescribed.
Rheoencephalography is most often a complementary method, indispensable for the final assessment of the circulatory system. The availability of the procedure and the ubiquity of devices in medical institutions determine its widespread use. The complete absence of contraindications and side effects does not cause concern for patients during the research procedure.
Author of the article: Neurologist of the highest category Tatyana Mikhailovna Shenyuk.
Research principle
The principle of examining the device is to display a diagram on the monitor, which subsequently makes it possible to draw a conclusion about the physical condition.
The main element of the device is a cathode ray tube. A vacuum is created in it by pumping out air and a positive cathode is placed.
The cathode reacts to the action of electric current and begins to emit particles of a negative sign, which are subsequently focused using a special system and sent to the monitor screen.
Externally, on the screen it looks like the movement of a luminous point, which is further observed.
Thanks to the movement of the point, it is possible to trace possible changes in pulsation and identify violations, if any.