Advantages and disadvantages of ultrasound
Ultrasound allows you to examine parenchymal and hollow organs, soft tissues, blood vessels, joints, muscles and glands.
The first experiments in the use of ultrasound in medicine were carried out back in 1955 by Ian Donald.
Since then, ultrasound has been improved, developed and become an important examination method in most areas of medicine.
Over the years, inventors have minimized the disadvantages of this method, making it informative, accessible and safe.
There are three types of ultrasound examination. Each type is based on the parameters of the image that is displayed on the screen and the organs being examined.
Ultrasound is rightfully considered one of the most accessible and fully informative diagnostic techniques, with the help of which a specialist can examine any organs and tissues.
The World Health Organization, based on many years of scientific data, confirms that all types of ultrasound techniques are safe for the health of patients of all ages.
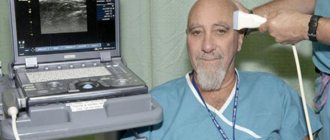
During an ultrasound examination, the patient does not feel any discomfort or pain. The specialist passes a special sensor over the surface of the patient’s body, and the picture is displayed on the monitor.
It is possible to copy the image onto a digital medium and print a paper version. One of the main advantages of ultrasound examination is that the specialist can see not only static, but also dynamic processes of the body .
Today, ultrasound examination is carried out in three types:
- Standard 2D examination. The mode is two-dimensional, the image has two projections. On the screen, the specialist can see the organ and measure its length and width. The procedure takes about 15 minutes. The device produces a flat black and white image.
- Three-dimensional 3D image. In three-dimensional imaging, a specialist can examine an organ or tissue in depth. The monitor displays a picture in color, which allows the specialist to diagnose other pathologies during the examination. The research procedure takes about an hour.
- The 4D generation ultrasound machine provides a combination of 3D images and a time component.
Ultrasound is difficult to replace with anything. Research devices are installed everywhere: in clinics, hospitals, in ambulances and in operating rooms.
Despite the fact that more advanced research methods have appeared in the form of MRI and CT, ultrasound remains still popular: a universal, informative, accessible and inexpensive method.
Video on the topic:
Advantages of ultrasound:
- low cost;
- safety (ultrasound is not dangerous to humans, unlike ionizing radiation used for x-ray examination);
- Ultrasound clearly shows soft tissues (radiography does not visualize them);
- Ultrasound can be performed with the required frequency, due to the absence of harmful effects on the body;
- Ultrasound is performed in real time, which gives a reliable picture of what is happening;
- Ultrasound is a non-invasive method and does not require incisions or punctures;
- painlessness of the procedure;
- the ability to explore an object in different projections.
Disadvantages of ultrasound:
- some objects are difficult to visualize due to projection layering;
- computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging have greater spatial resolution;
- if you are overweight, ultrasound is partially absorbed by adipose tissue, which makes diagnosis difficult;
Indications and contraindications
In order to understand what ultrasound of cerebral vascular structures is and what it can show, first you should familiarize yourself with the main methods of ultrasound examination of this organ:
- Echoencephalography allows you to evaluate the physical features of the structure of the brain matter, as well as identify developmental pathologies in parts of the brain.
- Neurosonography (NSG) - using this ultrasound research method, the characteristic features of the structure of the brain are studied in children of the first year of life, or until the large fontanel is open.
- Doppler ultrasound (USD) is a combined method that combines the capabilities of ultrasound and Dopplerography. There are two types:
1. Transcranial ultrasound Doppler allows you to assess the condition of the arterial and venous circulatory system located in the brain. To perform a study in this way, access to acoustic windows in the temple, occiput, eyes and the area of the articulation of the cervical spine and occipital bone is required.
2. Extracranial ultrasound. Makes it possible to examine large cervical blood vessels outside the skull.
Duplex and triplex ultrasound scanning are modern methods for studying the vascular system of the brain. They allow you to interpret the characteristic features of the structure of each artery separately and estimate the speed of blood flow in them. This test also evaluates the tissues and joints surrounding the blood vessels.
In the first case, the specialist receives a two-dimensional display along and across the arteries, and in the second, more extensive information about the state of the vessels, containing, in addition to standard data, indicators of the direction and speed of blood flow, which are colored in different colors.
Let us consider in more detail the capabilities of the listed methods.
Ultrasound of the brain (echoencephalography) helps to diagnose and identify the following pathological processes in this organ in real time:
- destruction of brain tissue due to inflammatory infectious diseases (for example: meningitis or encephalitis);
- formation of tumors and cysts of various nature;
- ischemic disease;
- swelling of the brain;
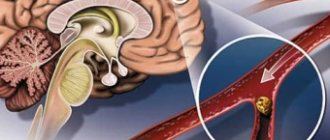
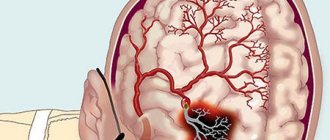
- hemorrhagic stroke;
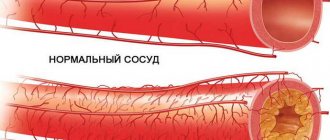
- atherosclerotic changes;
- stenosis of head vessels;
- violation of the patency of the liquor passages;
- the presence of structural changes in the brain matter due to traumatic brain injury.
Also, using this research method, a medical specialist can determine where the hemorrhage is located and assume the degree of destruction it caused.
Despite the obvious advantages, a final diagnosis cannot be made based on the results of a brain ultrasound, since this examination method is screening, that is, it makes it possible to predict the development of certain complications due to impaired blood supply. Therefore, to make an accurate diagnosis, more accurate methods of studying this organ using MRI or CT are required.
Often, to determine the functional abilities of blood vessels, a Doppler ultrasound of the brain is required. This research method is based on the fact that the sound wave sent by the sensor is reflected only from a moving object, that is, blood cells.
Carrying out this procedure is no different from a standard ultrasound examination: the difference lies in the principle of processing incoming information: the Doppler sensor sends ultrasound waves at a certain speed and receives them back at another. That is, the quality of the blood circulation of the vessel depends on how quickly the ultrasound wave returns.
The picture is clickable
- degree of passability;
- the presence of deposits in the form of atherosclerotic plaques;
- the presence of blood clots, their physical parameters;
- blood flow speed, valve condition;
- presence of aneurysms, anastomosis.
Since in children under one year of age there are several non-ossified areas (fontanelles) in the skull, they are prescribed an ultrasound of the brain (Neurosonography), which allows us to identify structural pathologies of this organ. Using this method, the following indicators are assessed:
- symmetry of the cerebral hemispheres;
- map of the location of the convolutions of the cerebral cortex;
- ventricle size;
- crescent shape;
- cerebellar contours;
- the presence or absence of the 5th fontanel between the hemispheres;
- the presence of cysts and other neoplasms in the medulla;
- indicators of homogeneity of the vascular plexus.
Since neurosonography is a diagnostic method for studying brain structures, it is done only when indicated, to refute or confirm a preliminary diagnosis. After decoding, the obtained data should be provided to a pediatric neurologist.
Ultrasound examination of brain structures, or echoencephalography as it is also called, is a non-invasive examination method based on measuring the displayed echo signal from the deep structures of the brain.
The information received by a special sensor is processed and displayed on the monitor in the form of a two-dimensional black and white image. Due to the fact that ultrasound is the most bladeless examination method and has virtually no contraindications, it is prescribed to patients of any age, including children.
Carrying out an ultrasound scan of the brain in adults is no different from the process of undergoing an ultrasound scan of any other organ: the patient lies down on a couch with his head on a special pillow. Next, the specialist examines the head using his fingers to identify areas of skull deformation, hematomas, and the presence of asymmetry.
The examined area is lubricated with a special gel to improve the conductivity of the ultrasound signal, special sensors are placed on the sides, and the received data is recorded on the monitor. If necessary, the specialist may also ask the patient to change his position, hold his breath or blink. After the study, the sensors are removed and the gel is wiped off with a paper towel.
If it is necessary to perform an ultrasound examination of the arteries supplying the brain, then in this case the patient is prescribed transcranial Doppler ultrasound (TCDG).
The difference between this procedure and standard ultrasound lies in the way the data obtained is recorded - changes in the displayed sound waves from moving blood cells are recorded. This research method is based on the use of the Doppler effect, that is, changes in the frequency and wavelength of ultrasound perceived by the receiver due to the movement of the source of ultrasound radiation. To obtain more detailed information, the patient may also be asked to undergo a duplex scan.
To assess blood flow using the Doppler method, you will need access to the temples, back of the head, forehead and eye sockets. Then everything is carried out as usual: the gel is applied, the specialist presses and moves the sensor over the examined area. The result is presented on a computer monitor in the form of a scale colored in different colors.
Using transcranial Doppler sonography, specialists diagnose almost all diseases caused by impaired blood flow in the brain vessels, such as atherosclerosis and hypertension. Also, the use of this method significantly reduces the time for diagnosing acute conditions - hemorrhagic stroke or ischemic attack.
Unlike Doppler ultrasound (USDG), duplex scanning combines two research functions: with the help of Doppler ultrasound, the blood flow of vessels is characterized, and B-mode makes it possible to visualize the structural features of arteries and veins.
Echo EG in children differs from ultrasound of the brain in that in the first case, the sensors are attached directly to the head, then an ultrasound signal is applied and an image is displayed on the screen in the form of a graph, which determines the echogenicity of the area under study, and in the second case, the ultrasound is generated by the sensor, which is leaned directly against the fontanel, and the ultrasound image familiar to everyone appears on the monitor. Parents should not worry - an EG echo is as painless as a regular ultrasound, but may take a little longer.
After the study, the doctor compares the results with normal values, draws up a conclusion and, if necessary, takes pictures of possible pathology.
Since ultrasound radiation is safe, ultrasound of the brain can be performed on people of any age and condition.
If the patient knows in advance about his fear of ultrasound, then he should spend some time on psychological preparation, or choose a different examination method.
An ultrasound scan of the vessels of the brain, neck and limbs can be performed on adults, the elderly, and infants. To detect pathologies, medical centers use Doppler to check veins and arteries, noting the structure of their walls, diameter and the presence of plaques. The linear velocity of blood flow must be measured.
Using the ultrasound method, not only the general condition of the arterial walls is diagnosed, but also the degree of their damage. Doppler of the arteries and veins of the head and neck shows whether the diameter of the artery has narrowed or everything is normal. If there are circulatory problems, the clinic conducts other tests and prescribes treatment.
Centers perform ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck in different ways; the method is chosen based on the required diagnosis. Clinics use the following types of ultrasound scanning:
- Transcranial. The sensors are fixed on the head. The medical center uses Doppler ultrasound to diagnose diseases of the arteries of the head and vertebral artery;
- Transorbital. The place of fixation is the upper eyelid. In this way, clinics determine the speed of blood flow in the orbital artery;
- Carotid. Ultrasound examination of the neck arteries is usually done using this method. Dopplerography of the vessels of the neck is indicated for patients from the neurological department of the clinic, and Dopplerography of the carotid artery should be done for people with frequent dizziness, poor memory and insomnia. These symptoms are closely related to the functioning of the carotid artery and circulatory disorders. As a result, the brain does not receive enough nutrition.
What does ultrasound of the vessels of the brain and neck show?
The Doppler effect shows the movement of blood through the vessels of the brain and neck.
When prescribing ultrasound of cerebral vessels and ultrasound of the neck, they imply duplex scanning of the vessels of the brain and neck - it combines the use of the Doppler effect and visualization of blood vessels.
Ultrasound of the cerebral vessels and cervical spine allows the specialist to examine the vessels from the outside and inside . This subtype of ultrasound examination is called neurosonography.
An ultrasound examination involves exposure of a sensor to a sound wave with a certain frequency. Signals from tissues are reflected (echo principle), processed by a computer program and displayed on the screen.
Problems that ultrasound of this department can solve:
- detect areas of narrowing (stenosis) or blockage of blood vessels, assess their degree of influence on the development of the disease;
- detect whether there are systemic vascular diseases;
- determine the sources (first and initial signs) of vascular diseases;
- check whether the therapy is effective;
- assess how strong the reserve capacity of blood vessels is;
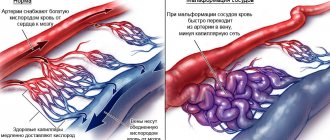
- detect defects and congenital vascular pathology, the presence of aneurysms, spasmodic areas.
The main task that a specialist faces during an ultrasound procedure of cerebral vessels is to detect changes that have caused disturbances and manifestations of clinical symptoms.
After an ultrasound examination of the cerebral vessels, the question of the advisability of surgical intervention is decided. An ultrasound examination of cerebral vessels lasts about half an hour, after which a diagnostic specialist issues a research protocol and a conclusion.
What is ultrasound
Ultrasound is an ultrasound examination that is performed using a special device. It functions by using sound waves of different frequencies. Using a certain frequency, a specialist is able to conduct research on internal organs, tissues and muscles. A special gel, which is widely used during diagnostics, enhances the throughput. With its help, it is possible to significantly improve image quality.
Once the waves used by the sensor reach the area being examined, they are reflected from it. The waves reflected by the organ are returned to the sensor, which converts them into digital format. The result of this transformation is displayed on the monitor. This study is carried out quite quickly. In total, the procedure takes from 10 to 30 minutes. And this is also one of the advantages of the method.
All devices operate on the basis of ultrasonic waves
Indications for use
The patient is referred for an ultrasound examination if the doctor suspects signs of cerebrovascular accident.
Indications for the ultrasound procedure are also:
- chronic cephalgia of various etiologies;
- vision disorders, speech, hearing disorders, problems with coordination of movements;
- conditions with impaired consciousness, chronic nausea with dizziness;
- persistent hypertension, arrhythmia;
- cerebrovascular pathology;
- increased blood cholesterol levels;
- condition after a stroke or heart attack;
- pain syndrome in the cervical spine due to osteochondrosis.
The doctor prescribes ultrasound of the vessels of the brain and neck if there is suspicion or presence of certain signs of cerebrovascular accident.
Typically, ultrasound examination of the cerebral vessels is performed after ultrasound examination of the cervical vessels. Often the cause of cerebral circulation disorders is found during research in this area.
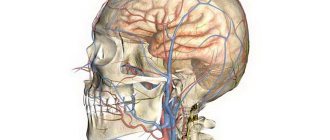
Anatomically, cerebral vessels originate from four main arteries: the right and left carotid, right and left vertebral.
Ultrasound examination has no contraindications, and it can be performed many times without any negative impact on the human body at any age and with any pathology.
Symptoms that are an indication for ultrasound examination:
- pain in the head and neck;
- dizziness;
- presence of tinnitus;
- frequent loss of consciousness (fainting);
- deterioration of memory, concentration;
- decreased visual acuity;
- coordination problems;
- insomnia.
In addition, there is a certain group of people who should undergo a routine ultrasound of the vessels of the brain and neck, without waiting for symptoms to occur:
- people over 45 years old;
- patients with osteochondrosis;
- smokers;
- have had a heart attack or stroke;
- people who have had concussions, skull or neck injuries;
- people with arterial hypertension;
- patients with diabetes mellitus.
There are no contraindications to ultrasound examination of the blood vessels of the brain and neck.
How to check blood vessels using ultrasound
There are several ways to check the condition of the brain vessels when performing ultrasound diagnostics. The first method is neurosonography. It is used exclusively in pediatrics. Consequently, this research method is relevant only for performing examinations on children under 12 months of age.
The technique for performing the procedure is quite simple. The examination is carried out through the fontanel, the anterior and lateral surface of the neck.
The second method is indicated for adults. This is duplex scanning. This method is especially popular due to the fact that it allows you to correctly assess not only the structure of blood vessels, but also the nature of blood flow. The doctor uses this information to make an accurate diagnosis. The technique of the procedure is also not complicated. The specialist moves the sensor over several areas of the skull, as well as along the side and front surface of the neck.
The doctor must conduct a vascular examination
Preparing for the study
This research method does not require lengthy and complex preparation.
The patient is not required to take any special preparatory measures before performing an ultrasound examination, which is a clear advantage.
To see the real picture of the tone of the vascular wall, doctors stopping the consumption of caffeine, strong tea, energy drinks that contain guarana and alcoholic beverages 24 hours before the examination
It is recommended to refrain from spicy foods and dose salt in moderation . If the patient is taking vascular medications , he should consult with a specialist in advance whether or not to temporarily suspend the intake.
It is undesirable if the patient takes painkillers or antispasmodics the day before. Five hours before the test, the patient is prohibited from smoking , as nicotine increases blood pressure and the test result will not be reliable.
How the research is carried out
The procedure is completely painless for the patient. He sits or lies, turning his head in the desired direction at the doctor’s request. Ultrasound examination of the vessels of the brain and the cervical spine is carried out in two directions :
- In two-dimensional mode. The doctor sees a clear picture of the structure of the vascular wall, adjacent tissues, and studies the substance of the brain. The two-dimensional mode does not make it possible to examine cerebral vessels.
- In duplex (transcranial) scanning mode, the diagnostician receives detailed information about blood circulation. Intracranial vessels are examined.
Before the ultrasound, you must remove all jewelry from your neck and ears. The patient lies on his back on the couch, throws his head back, and turns away from the sensor. The doctor applies a special gel to the patient’s neck and head, designed to ensure that there are no air bubbles (transducer) between the sensor and the skin of the head and neck.
The study is carried out through three approaches: orbital, transtemporal (in the area of the temporal bones), and occipital. Transtemporal access makes it possible to examine the vessels of the base of the brain .
Using the occipital approach, the intracranial sections of the vertebral and basilar arteries are examined. The orbital approach to ultrasound makes it possible to study the dynamic characteristics of the venous outflow.
The results of an ultrasound examination provide a picture of the presence of aneurysms, narrowings and vascular abnormalities. Based on the dynamic characteristics of the ultrasound examination, a conclusion is made about the cause of the circulatory disorder: swelling, spasm, hyperfusion (weak circulation) .
Video:
To assess the ability of the vascular wall to expand or contract, additionally, during an ultrasound examination, tests are performed on holding the breath, on intense breathing, on opening and closing the eyes, while taking nitroglycerin.
Difference between ultrasound and UDSG
Both types of examination are carried out using the same equipment and feel no different for the patient. However, in fact, there are differences between conventional ultrasound and Doppler ultrasound (UDSG) and they are as follows:
- Ultrasound allows you to determine the thickness of the wall of the blood vessels of the head and neck, identify the presence or absence of pathological processes occurring in them, and also assess the condition of the soft tissue adjacent to them.
- UDSG (ultrasound with Doppler, Dopplerography) provides more detailed information about the condition of the vessels, namely the speed of blood flow, its nature and symmetrical passage through the vessels of the same name, as well as the presence or absence of tumor-like formations.
The choice of a specific diagnostic test should be made by the attending physician based on the patient’s complaints, manifested symptoms and a preliminary diagnosis.
Data decryption
The doctor will decipher and explain all indications after the ultrasound examination for each patient individually.
The examination results are assessed by a doctor. The patency and structure of the vessels of the brain and neck, systolic and diastolic blood flow, the nature of the blood flow, the direction of the blood flow, the systole-diastolic ratio are determined.
The result of an ultrasound examination is a graph with three wave complexes : initial, middle, final.
Using them, a specialist deciphers them and diagnoses possible pathology. The main parameter is the symmetry of the graph.
If there is no pathology, all distance measurements (initial-middle, middle-final) will be approximately the same in length, a shift of up to 2 mm is allowed.
The norm for ultrasound examination is:
- The wall of the artery of the neck and brain is 0.9-1.1 mm thick;
- Free patency of the vessel;
- The absence of turbulent directions of blood in places where there is no branching of blood vessels;
- The diameter of the vertebral arteries is the same, not less than 2 mm;
- The speed of blood movement through the vertebral veins is no faster than 0.3 m/s;
- Absence of pathological vascular network;
- No external compression of cerebral vessels.
After decoding, the result is assessed by a neurologist to make a diagnosis, prescribe treatment or determine the effectiveness of the treatment.
The meaning of ultrasound results
The diagnostician deciphers the data obtained as a result of ultrasound of the structures and vessels of the head, so you should not try to independently interpret the information presented in the conclusion. After conducting the study, the following data is usually assessed and deciphered:
- size and structure of the ventricles;
- physical characteristics of the cerebral hemispheres;
- the presence of tumors, cysts, their structural features, size, location;
- patency of the blood vessels of the head and neck, their diameter, lumen, presence of inclusions on the walls, aneurysms, anastomosis, blood flow speed;
- The amount of space between the soft and arachnoid membranes of the brain and spinal cord, within which cerebrospinal fluid circulates, is also calculated.
The following indicators are considered the norm:
- cerebral hemispheres - symmetrical, without changes;
- the ventricles are of a homogeneous structure, with clear contours, anechoic;
- the basal ganglia should have moderate echogenicity;
- There should be no shift in the M-echo signal, since volumetric processes (tumors) cause its change;
- the volume of cerebrospinal fluid in the subarachnoid space should not exceed the permissible value at this age;
- absence of foreign inclusions, cysts.
Blood vessels should have clear contours, and their walls should be free of aneurysms and other structural pathologies. The lumen should be free of blood clots and there should be no anastomosis. The thickness of the vertebral arteries should normally be more than 2 mm in diameter.
Ultrasound of the structures and vessels of the brain is widely used in diagnosing cerebral hemorrhages as a result of traumatic brain injury, as well as after a stroke. Also, if necessary, using this research method, specialists ascertain physiological brain death.
Based on the results obtained during neurosonography (NSG), a pediatric neurologist makes a final diagnosis and prescribes the necessary treatment. Since such an examination is safe and takes a minimum of time, it is often prescribed when monitoring brain defects in children in the first year of life, as well as to confirm and remove the diagnosis.
It is important to understand that the ultrasound examination method is not a final diagnosis. For this reason, after undergoing the study, the patient must contact his attending physician for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment of vascular pathologies.
Interpretation of examination results for the patient can only be of an informative nature. Do not try to diagnose yourself only on the basis of the ultrasound doctor’s conclusion.
In the absence of pathological processes, the following indicators are considered normal:
- Absence of pathologies and anomalies, external compression of blood vessels and turbulence of blood flow in places with missing capillaries;
- The thickness of the vessel wall is no more than one centimeter;
- Complete vascular patency;
- The speed of blood flow is not lower than 0.5 m/s;
- Vertebral arteries of equal diameter, not less than 0.3 mm;
- The carotid artery is localized on the left side of the aortic arch, and on the right its length is always slightly shorter (6-11 and 11-16 centimeters).
Do not worry if some indicators differ from normal - this may be an individual feature of the structure.
Only a doctor can make diagnoses and only after collecting anamnesis and conducting all the necessary examinations. Ultrasound of neck vessels helps to identify a number of pathological conditions at an early stage and begin treatment in a timely manner.
Usually, an ultrasound scan of the vessels of the brain and neck is done to check their narrowing, whether the diameter of the vein is normal, and what the linear speed of blood flow is. The evaluation criteria are standard and unchanged for several years.
Criteria for evaluating results:
- Norm. Healthy veins and arteries normally do not have plaques or blood clots, their diameter is not less than permitted, and there is no thickening of the vessel walls. With ultrasound of the carotid artery, the linear velocity of blood flow corresponds to a maximum of 125 cm/s;
- Stenosis. The degree of deviation from the norm depends on the percentage of stenosis. If the gaps are too narrowed, the speed of blood flow will decrease, and this threatens the patient with complications. A small diameter of arteries and veins indicates severe stenosis. Normally, such indicators cannot be detected during diagnosis;
- Occlusion. The linear speed of blood flow is slow or absent altogether. The diameter of the walls does not correspond to the norm.
Medical centers conduct additional tests when a patient suspects heart disease or other serious circulatory problems.
Ultrasound of the vessels of the neck and brain can determine not only the presence of narrowing; diagnosis allows, based on a comparison of the blood flow velocity of the carotid artery, to draw conclusions about the presence of heart disease. Normally, there is no increase in speed when the internal artery narrows.
Price
Ultrasound room
Ultrasound as a diagnostic method is popular and accessible. To conduct an ultrasound examination of the vessels of the brain and cervical spine, you should take a referral to a neurologist at your local clinic.
The study will be carried out free of charge , but the possibility of a long queue cannot be ruled out. Multidisciplinary centers and specialized clinics offer ultrasound examinations at a fairly high level for a fee.
Prices for examination of the vessels of the neck and brain vary depending on the region and the status of the medical center. When choosing a place for an ultrasound scan, you cannot be guided only by the financial side of the issue, since the correctness of the future diagnosis depends on the experience and competence of the doctor.
By saving on the examination, there is a high probability of getting to a specialist who will do an ultrasound incorrectly and then interpret it incorrectly. Due to the low cost of research devices and its great popularity, some clinics purchase the necessary equipment without taking care of additional training for their employees.
Therefore, when choosing a clinic for an ultrasound examination, you need to consult with your doctor, look for reviews about uzists and choose the right price-quality ratio.
Cost of ultrasound services by region:
| City | Price |
| Vladimir | 800-1400 rub. |
| Penza | 1200-2200 rub. |
| Moscow | 2100-3500 rub. |
| Samara | 1300-2000 rub. |
| Tyumen | 2100-3000 rub. |
| Voronezh | 1300-2100 rub. |
| Chelyabinsk | 700-1100 rub. |
| Belgorod | 900-1700 rub. |
| Kazan | 1700-2700 rub. |
| Volgograd | 1700-2500 rub. |
Reviews
Natalya, 42 years old: We did it 3 years ago in Belgorod for 970 rubles. Fast, polite, I liked the doctor. The procedure took no more than 20 minutes.
Igor, 35 years old: A very revealing method. He came, he did it, he took the result to the doctor, he received a diagnosis and treatment. Now I go for a check-up ultrasound every 9 months.
Inna, 29 years old: I advise everyone to choose a clinic and specialist based on recommendations and reviews before going for an ultrasound. It is important to have new equipment and a qualified, experienced diagnostician. I learned from my own bitter experience. I was referred to the district clinic for an ultrasound, the doctor did not find anything, although there were complaints. They recommended another doctor at a paid clinic. He immediately identified the pathology of the blood vessels in the head.
Dmitry, 33 years old: There are good diagnostic doctors. Thanks to a professional doctor, an ultrasound examination revealed narrowing of blood vessels and the beginning of a blood clot. If you hadn’t gotten to such a doctor on time, there’s no telling how it would have ended. The main thing is to do everything on time, with a good ultrasound machine and a good doctor.
Marina, 46 years old: After the neurologist prescribed an ultrasound of the neck and brain, I began to look for where to go. In Moscow the choice is huge, prices range from minimal to heavenly. I didn’t want to end up with some student. Friends recommended a good specialist, I made an appointment with him within a week, he is a very polite young man. He did everything in the best possible way, my neurologist and I were satisfied.