Types of diplopia
Modern medicine classifies this pathology into binocular and monocular forms. Each of them has several separate subspecies depending on the causes of their occurrence. According to the main 4 signs, double vision is divided as follows:
| Classification feature | Type of diplopia | a brief description of | |
| Cause of occurrence | neuroparalytic | develops when the nerves that innervate the extraocular muscles are damaged | |
| strabogenic | characteristic of persons with strabismus - during development, after treatment (surgery) | ||
| restrictive | occurs with tumors and after injuries associated with displacement of the eyeball, pinching of the extraocular muscles | ||
| oculogenic | develops after surgery in the treatment of retinal detachment, strabismus, cataracts | ||
| Development mechanism | motor | due to peripheral or central paresis (partial paralysis) of extraocular muscles | |
| sensory | occurs when the healthy position of the visual axes is restored after strabismus | ||
| mixed | against the background of injuries to the orbit with dislocation of the eyeball, pinched muscles, ligaments; endocrine ophthalmopathies | ||
| Development time | constant | doesn't go away with time | |
| fickle | passes over time, develops under the influence of:
| ||
| Clinical picture | Character of double vision | vertical | vertical ghosting |
| horizontal | bifurcation of an object along a horizontal axis | ||
| cross | the image of the right eye is displayed on the left and vice versa | ||
| Localization of the visual field | full | double vision throughout the entire field of vision | |
| partial | double vision with or without preservation of the central field of single vision | ||
Symptom Definition
When a pathological condition occurs, the image that a person sees doubles. In this case, blurred and unclear outlines are observed. With minor deviations, this condition can manifest itself only as vagueness of the contours, but severe double vision syndrome causes a feeling of incorrectness of the perceived image, which is why the patient begins to experience very strong uncertainty.
Diplopia is most often the result of misalignment of the visual axes, as a result of which the brain receives not one focused image from both eyes, but from each separately. This disorder may result from a genetic predisposition or be an acquired condition. An example of a hereditary disorder of this type is strabismus.
Why do you see double?
The physiological cause of the pathology is a displacement of the central fovea of the eye or the visual axis. The image of the object falls on the peripheral region of the retina, so it is perceived not in front of itself, but shifted. Each eye transmits a signal to the brain, but due to the different locations of the 2 visual axes, images of the same object overlap each other with double vision. Less commonly, diplopia is associated with impaired light transmission to the retina, which is facilitated by:
- keratoconus of the corneal surface;
- subluxation of the lens;
- structural defect of the eye;
- damage to the anterior visual cortex;
- astigmatism.
Pathological causes of double vision
A child under 5 years of age may experience double vision due to polio. With congenital strabismus in children, such a symptom is often absent. The following diseases and pathologies can provoke diplopia:
- cervical osteochondrosis – due to pinched nerve roots;
- multiple sclerosis;
- cerebrovascular accidents;
- tuberculous meningitis;
- carotid artery aneurysm;
- thyroid diseases;
- infectious processes in the brain stem - rubella, diphtheria, mumps;
- acute botulism;
- intracranial neoplasms;
- stroke;
- encephalitis;
- epilepsy;
- diabetes;
- myasthenia gravis (muscle weakness), ocular myositis.
Gymnastics to restore vision
Bates gymnastics includes a set of exercises for the eyes and muscles of the cervico-brachial region.
Exercise therapy should be performed an hour before or after meals 2 to 4 times a day. This complex is recommended not only for sick patients, but also for ordinary people who spend most of their time at the computer, TV, and reading books. Which eye ointment is effective for eye inflammation, read here.
Before you begin the exercises, you should sit comfortably, relax and blink your eyes for a few seconds. When performing gymnastics, you should remember that only the eyes will move, and the body should be motionless. Between exercises you should take a short break for 10-15 seconds, and then blink.
Gymnastics for the eyes:
- Roll the eyeballs up as much as possible, and then lower them down, fixing them in the extreme position for several seconds.
- Move your eyes to the right and left, holding them in the extreme position for several moments.
- Move the eyes diagonally: first one way, then the other.
- Perform rotational movements of the eyeballs in a clockwise direction. Do the same thing counterclockwise.
- “Outline” an imaginary square with your eyeballs clockwise. Then do the same in the other direction.
- Close your eyes tightly for 3-5 seconds, and then slowly open them.
Since the cervicobrachial region contains many nerve endings associated with the optic nerve. This is especially true for those who spend a significant portion of their time sitting.
Exercise therapy for the collar area of the back:
- Sit up straight and alternately turn your head to the right and then to the left.
- Tilt your head, trying to place it on your right shoulder. Do the same in the other direction.
- Tilt your head forward, then back.
- Rotate your head clockwise and then do the exercise in the other direction.
- Straighten your back, feet shoulder-width apart, arms extended along the body. Make circular movements of your shoulders back and then forward.
- Place your hands on your shoulders and make rotational movements in this position.
- Place your hands on your belt, feet shoulder-width apart. Turn your body to the left, holding your torso as much as possible, then to the right.
- Bend your whole body forward, stretching your arms out in front of you. Arch your back as much as possible.
- “Boat” Lie on your stomach, stretch your arms forward in front of you and bend over as much as possible. Raise your legs as well.
- "Basket". Take a position with your stomach on the floor. Raise your legs up, bending them at the knees and clasp your hands behind you. Bend over as much as possible, trying to reach the top of your head with your toes and, if possible, rock back and forth. This exercise brings great benefits not only to the eyes, but also to the back.
Instructions for using cyclopentolate eye drops can be found here.
How does diplopia manifest?
The main symptom of the pathology is double image. It can occur both when looking into the distance and when studying nearby objects. You can independently separate this problem from other ophthalmological disorders by:
- image restoration - if you move your head, close one eye, look up or down;
- the nature of the displacement - occurs horizontally, vertically, diagonally.
The severity of the manifestations of diplopia is influenced by the reasons for its development. If there are concomitant diseases, additional specific symptoms will appear. The localization of the pathological process also plays a role. The progression of the disease reduces the patient’s performance and quality of life. In addition to double vision, a person may experience:
- migraine;
- dizziness (does not depend on body position in space and physical activity);
- sharp pain in the eyes;
- habit of tilting your head to stabilize the image;
- difficulty in assessing the location of objects;
- rapid eye fatigue when performing visual work.
Articles on the topic
- 6 types of congenital cataracts - causes and treatment
- Symptoms of pituitary adenoma in men - how to recognize in the early stages
- Endocrine ophthalmopathy - symptoms of the disease
Monocular
Double vision with this form of pathology is constant. If you lower 1 eyelid, the situation does not change. The main object is perceived as clearer and brighter, while the “double” is perceived as pale. Monocular diplopia is associated with abnormalities and diseases of the cornea, retina, and lens. Clinical picture:
- a spot or thorn on the cornea;
- decreased photosensitivity;
- grayish or yellow pupil;
- departure of the pupil from the iris;
- the appearance of a “dark cloud” before the eyes;
- general decrease in visual acuity.
Binocular
The ghosting of the image does not affect the quality of the picture. The brightness of both elements, contrast and clarity are the same. Visual disturbances disappear if you cover one eye. The main common symptom is strabismus - multidirectional position of the eyes. The clinical picture is determined by the primary disease, predominantly non-ophthalmological:
- stroke;
- encephalitis;
- tuberculosis;
- botulism;
- infectious processes.
What diseases are accompanied by this symptom?
Monocular or binocular diplopia can be caused by many ophthalmological diseases.
When looking into the distance
Some anomalies do not pose a threat to human health, others pose a serious danger. Binocular double vision can be caused by the following diseases:
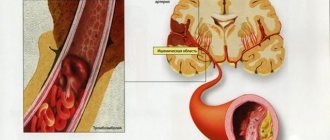
- Aneurysm. Develops due to stratification of blood vessels. If the damaged artery is located in the brain, then the symptom of the disease is diplopia;
- Multiple sclerosis. The disease is accompanied by damage to the central nervous system. A distinctive feature of the pathology is that the patient’s immunity “attacks” healthy cells of the spinal cord or brain;
- Myasthenia. An autoimmune disease, the protracted nature of the disease leads to a decrease in muscle tone;
- Diabetes. It develops due to a lack of a hormone called insulin in the body. The anomaly often damages the nerve endings responsible for eye movement;
- Strabismus. Accompanied by a violation of the position of the eyes, they look in opposite directions. Due to the lack of focusing of the gaze on the object, there is a “reproduction” of the picture.
Binocular diplopia can be caused by circulatory disorders, however, it is much less often accompanied by double vision than the above diseases.
Patients often turn to ophthalmologists with complaints about image clarity in the left or right eye. This is called monocular diplopia, and the following pathologies can cause it:
- Lens luxation. One of the most important elements of the visual apparatus moves out of its usual position, and a person experiences a distortion of the resulting picture;
- Insufficient moisture of the cornea. Occurs if there is dry air in the room or during prolonged work at the computer;
- Astigmatism. One of the most common eye diseases. It is characterized by a violation of the shape of the organ of vision, lens or cornea. The split is most pronounced when reading, when it is necessary to strain the eyes;
- Cataract. The second name for the anomaly is lens opacity, which usually affects people after forty years of age, but young people are not protected from it either;
- Infectious diseases of the cornea.
| While some ailments, such as dry eyes, can be easily treated with special drops, infections require protracted and complex treatment. |
The cause of the anomaly is hidden in damage to the central part of the brain responsible for the functioning of the visual apparatus.
Dizziness is often one of the signs of increased intraocular pressure. Moisture accumulates in the skull due to a violation of its outflow. The liquid puts pressure on the nerve endings, paralyzing their work.
In some cases, diplopia is diagnosed in patients who have recently undergone surgery to install an implant to replace a damaged lens.
The reason for double vision most often lies in the different refractive power of optical rays between the healthy eye and the operated one. The anomaly will not go away on its own; it may even get worse. In this case, a second intervention is most often performed and the lens is replaced in the second eye.
Diagnostic methods
Based on the results of the initial examination and examination of the patient’s complaints, the doctor can only make a preliminary diagnosis. Next, it needs to be clarified, to exclude the influence of other diseases and to identify the reasons for the double image before the eyes. For this purpose it is prescribed:
- endophony test;
- four-point color test;
- slit lamp eye examination;
- ophthalmoscopy - direct and indirect;
- determination of visual fields, its acuity;
- electromyography – assessment of bioelectrical activity of muscles;
- coordimetry – study of eye mobility.
Such diagnostic methods show which muscles and nerves are damaged. Only on the basis of the results obtained can a competent treatment regimen be drawn up. If secondary diplopia is established, examinations are prescribed to identify the primary disease and its stage. Additionally, we may recommend:
- CT scan;
- magnetic resonance imaging of the brain;
- Lumbar puncture.
Causes
The eye is a complex system that consists of the perception of colors, objects, optics, and sending information to the brain through the nervous system. Complications are possible in each of these components. When a patient experiences double vision, it is possible to assume the following causes of diplopia:
- Inflammation of the cornea of the eye. If the disease is not cured in time, it can lead to complications such as damage to the optic nerves and muscles. The main reason for monocular diplopia is various eye injuries.
- Aneurysm of the internal carotid artery, which compresses the optic nerve.
- Diabetic neuropathy is a complication of diabetes mellitus that occurs in patients who have been sick for a long time. This reason most often provokes the appearance of diplopia in older people (over 50 years old) with type 2 diabetes.
- Benign and malignant tumors, hematomas in the cerebral hemispheres and eye sockets affect the connections of nerve tissue and individual areas in the subcortex.
- Unilateral or bilateral diplopia often accompanies surgery for retinal detachments, cataracts, and strabismus.
- Traumatic brain injuries.
- Malfunctions in the functioning of the endocrine system and thyroid gland sometimes also act as a cause of double vision.
- Diseases of the nervous system - cerebral infarction, meningitis, stroke.
- Infectious diseases, especially mumps, tetanus, diphtheria and rubella.
- Increasing a single dose of Botox, which is administered during cosmetic procedures, can also cause double vision due to changes in neuromuscular conduction.
Botox injection
- Vegetovascular dystonia. In the case of VSD, we are talking about idiopathic diplopia. The reasons that the patient has double vision in this case are not physiological, but psychological. Doctors cannot come to a common opinion which area this is: neurology, or a state of neurosis, or a psychosomatic disease.
Sometimes completely healthy people experience double vision when looking at objects due to insufficient sleep, after heavy mental or physical work, or intoxication of the body, including alcohol and medication.
What to do if you have double vision
If symptoms of diplopia appear, you should visit an ophthalmologist, if necessary, a neurologist, an infectious disease specialist, and even an oncologist. Treatment includes:
- exercises for the eye muscles - in the initial stages of pathology and to prevent progression;
- use of corrective prisms - attached to glasses, worn for several months;
- therapeutic exercises for the spine - for cervical osteochondrosis;
- optical vision correction – for strabismus;
- occlusion of the eye - covering with a special tape to prevent participation in the visual process;
- laser surgery – for cataracts, astigmatism;
- intraocular lenses (replacement of the lens with an implant) – for binocular form that does not respond to conservative treatment methods;
- botulinum toxin injections into the muscle – for eye movement disorders.
It is imperative to eliminate the disease that caused the double image or the provoking factor. For this purpose, drug therapy and surgical intervention may be prescribed:
- for traumatic brain injuries and spinal injuries, the treatment tactics are chosen by a neurosurgeon;
- in case of acute inflammatory processes, the patient must be hospitalized in the infectious diseases department.
The prognosis of treatment depends on the cause of double vision. When the pathology is temporary, it is easy to eliminate. For diplopia due to ophthalmological diseases, which does not respond to conservative therapy, surgery is required. Intractable pathology is corrected by darkening part of the patient’s visual field.
Diagnostic measures
The disease be detected on the basis of subjective complaints from the patient , who clearly speaks about the splitting of visible objects.
Keep in mind! But to accurately determine the causes of the disease, the following diagnostic procedures may be additionally prescribed:
- ophthalmoscopy;
- visometry;
- Ultrasound of the eyeballs;
- in rare serious cases - head tomography .
Quite often, the disease is not a disorder of an ophthalmological nature, but can occur against the background of pathological processes in other organs and systems.
Therefore, diagnosis may require examination by other specialists: rheumatologist, neurologist, infectious disease specialist, oncologist, endocrinologist and traumatologist.