Alcoholic encephalopathy requires special treatment. This is a complex chronic disease and a quick cure should not be expected; rather long-term specific therapy is required. In the Preobrazhenie Clinic, over more than 20 years of successful work, unique techniques have been developed that can not only reduce the treatment time for alcoholic encephalopathy, but also achieve significantly better final results. This is explained by the fact that under the influence of our specific procedures, brain tissue is restored more fully and much faster.
Alcohol or toxic encephalopathy is often otherwise referred to as Wernicke encephalopathy (WE). This is an acute condition that requires emergency medical care to prevent a sharp decline in intelligence and, often, death of the patient.
According to Wikipedia, “Wernicke encephalopathy and WKS are most often observed in people who abuse alcohol. Errors in diagnosing WE and therefore in treating the disease result in death in approximately 20% of cases, while 75% are left with permanent brain damage associated with WKS. Of those affected, 25% require long-term treatment to receive effective care.”
Treatment of alcoholic encephalopathy in the clinic is carried out using the latest technologies of restorative medicine using neurometabolic therapy.
In the vast majority of cases, unlike other methods, we achieve restoration of brain function, and our patients return to their normal lives.
What is alcoholic encephalopathy
Alcohol destroys not only a person’s social life, but also his psyche. People who abuse alcoholic beverages become inadequate over time, as they cannot resist severe psychosis. Alcoholic encephalopathy is a mental illness that occurs with systematic alcohol consumption, during which the nervous system is destroyed. Pathology develops, as a rule, at the third stage of chronic alcoholism.
As a result of the disease, disorders of the autonomic, somatic, nervous and other systems of the human body are observed. Encephalopathy has the most unfavorable effect on metabolic processes, which leads to deterioration in physical health. The disease worsens in spring and summer, accompanied by paranoia and obsessive delusions, since brain cells die due to alcohol abuse. This is a whole complex of diseases that occur simultaneously in chronic or acute form.
Development of the disease - stages, stages, sequence
According to the Ministry of Health, this disease is a problem associated with disturbances in metabolic processes. A lack of vitamin B leads to serious pathological changes in the cells of the nervous system. With the systematic intake of alcohol-containing drinks from the body, rapidly decreases and their deficiency occurs.
In this case, hypovitaminosis is provoked by :
- Decreased appetite and irregular food intake during a binge;
- Reducing the ability of the intestine to absorb nutrients , in particular vitamin B;
- Disorders of the liver, which is the main participant in the metabolic processes of breaking down alcohol and absorbing vitamins.
Lack of nutrients and vitamin B leads to metabolic disorders in the tissues of the nervous system, eating disorders, increased permeability of brain vessels with edema, hemorrhages and strokes. The consequences of alcoholic encephalopathy are disability and death .
Symptoms of alcoholic encephalopathy
In the picture of the disease, mental symptoms with a complex combination of somatic and neurological manifestations come first. Toxic encephalopathy develops in people suffering from alcoholism after 6–20 years of alcohol abuse. Often the onset of the disease is preceded by months of heavy drinking. The condition is aggravated by the fact that patients do not eat food. An aversion to food is accompanied by heartburn, belching, vomiting, and nausea. Constipation gives way to diarrhea, and catastrophically rapid weight loss occurs.
Symptoms of alcoholic encephalopathy appear one at a time or all at once. They look like this:
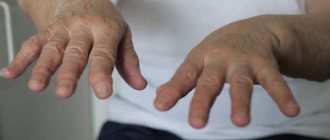
- trembling of limbs, loss of coordination and balance;
- feeling of dullness, fatigue, narrowing of interests;
- loss of appetite, refusal of protein and fat-containing foods;
- mood swings, aggressiveness, fear, anxiety;
- sleep disorder;
- amnesia;
- stiffness of movements;
- memory impairment;
- delusions, hallucinations;
- acute psychoses in which oral automatisms are present.
Chronic encephalopathy
The chronic course of the disease is more common. In the early stages, encephalopathy of toxic origin is manifested by difficulties when trying to remember recently received information or reconstruct events, decreased mental performance, attentiveness, and sleep disturbances. Patients report daytime sleepiness, increased irritability, and pain that does not have a specific localization.
Chronic encephalopathy in patients is expressed in different ways. With a neurological status, muscle hypotonia, decreased vision, moderate hyperreflexia, and signs of autonomic dysfunction are possible. If the chronic form of the disease progresses, it is accompanied by a worsening of symptoms, in which neurological syndromes are formed: pseudobulbar, hyperkinetic, parkinsonian, vestibulo-atactic.
- Car loan for a new car without a down payment
- How to withdraw money from a mobile phone - cash out
- How to cook squid tasty and quickly
Acute toxic encephalopathy
The main feature of the clinical picture in acute encephalopathy is sudden psychomotor agitation. It manifests itself as intense headaches, vomiting, numbness of the tongue, and visual disturbances. After excitement, acute toxic encephalopathy is manifested by a sharp change in mood - the patient is apathetic, disoriented, he experiences disturbances of consciousness of varying depths, up to coma.
Without medical assistance, such conditions can lead to disruption of cerebral centers and circulatory disorders. The degree of destruction depends on the duration of alcohol intoxication and associated health problems. Acute toxic encephalopathy of the brain, if left untreated, does not go away without leaving a trace and often leads to death.
Clinical picture of the pathology
Complicated damage affecting brain neurons due to the toxic effects of ethanol in the vast majority of cases is accompanied by oxidative stress.
Oxidative stress (or oxidative damage) is the process of active accumulation of free radicals in the body, which causes metabolic problems and damage to body cells.
In the pathogenesis of this disease, doctors often diagnose the following situations:
- Severe exhaustion of the whole body. This happens due to existing chronic diseases.
- The development of hepatitis, cirrhosis and various gastrointestinal pathologies. These disorders manifest themselves due to prolonged intoxication of internal systems with acetaldehyde.
- The formation of various pathological processes related to the functioning of the brain.
- A clear lack of vitamins and nutrients (micro-, macroelements).
Prodromal syndrome
Before the pathology manifests itself in full bloom, the victim initially faces some prodrome, accompanied by pronounced symptoms. Before true alcoholic encephalopathy comes, the following symptoms of the pathology are noted:
- pronounced general malaise;
- tachycardia, increased sweating, heat and fever;
- there is an aversion to foods that contain large amounts of proteins and fats;
- sleep problems, frequent awakenings at night, nightmares, daytime lethargy is noted;
- persistent memory impairment, manifestation of aggressiveness, hallucinations and delusional states;
- severe disorders in the gastrointestinal tract (diarrhea, constipation, bloating, flatulence, nausea, vomiting);
- development of numerous neurological disorders: difficulties in movement, tremor, convulsive syndrome;
- due to persistent lack of nutrients, the patient experiences symptoms of severe malnutrition.
The duration of this (preliminary period) varies and can range from 2-3 months to a year or more. Doctors also note some nuances of the prodromal period, namely:
- If the pathology occurs in an acute form, this period is characterized by an increased rate of progression compared to the chronic form.
- The fastest period was recorded in the acute type of pathology. It was only 14 days.
Period of manifest psychosis
Causes of alcoholic encephalopathy
The occurrence of this disease is provoked by the consumption of high doses of alcohol over a long period of time. The main cause of alcoholic encephalopathy is intoxication of the body. Binges continue for several weeks or months before the first signs of the disease appear. When consuming surrogates or technical fluids, the risk of pathology increases.
The disease can develop without alcoholism. Sometimes, due to individual characteristics, against the background of rare alcoholic excesses or taking small doses of alcoholic beverages, a person can also receive a diagnosis of alcoholic encephalopolyneuropathy. In this case, the cause of the disease lies in metabolic disorders, a lack of vitamin B1 in the body, which is caused by a monotonous diet.
Diagnostics
Given the variability of the processes that occur during the development of alcoholic pathology, doctors need to make a differential diagnosis as early as possible and begin therapeutic intervention. To correctly diagnose alcoholic encephalopathy, you need:
- find out what kind of alcoholic drinks the patient drinks;
- determine the time of onset of symptoms;
- conduct a visual inspection;
- collect information on the amount of alcohol taken now and in the early stages.
The final diagnosis is made by a doctor if the main factor is confirmed - alcoholism. During the examination, the patient is prescribed electroencephalography, which detects the presence of epileptic activity. To confirm diagnoses such as toxic-dysmetabolic encephalopathy or alcoholic pseudoparalysis, CT and MRI are performed. Nuclear magnetic resonance is often used to detect all pathological abnormalities. Additionally, the results of urine, blood, and cerebrospinal fluid tests are taken into account.
- Treatment of prostatitis with physiotherapy
- How to properly freeze strawberries for the winter
- Vitamin B6 - instructions for use, which products contain it
Treatment of alcoholic encephalopathy
Once diagnosed, the patient is referred for treatment, which depends on the severity of the symptoms. Therapy is usually carried out over a long period of time using large doses of B vitamins, nootropics, drugs that stabilize intracranial pressure and blood sugar. At the initial stage, treatment of alcoholic encephalopathy is aimed at removing metabolic products from the brain, which includes the following measures:
- reduction of intoxication in a hospital setting with the help of vitamins B, C, nicotinic acid, which are administered using intramuscular injections (injections into the muscle);
- to improve cerebral circulation and the supply of nutrients to the brain, vasodilator drugs Hydralazine, Apressin are prescribed;
- for seizures, anticonvulsant drugs Amizepine, Tegretol are prescribed;
- The doctor must get the patient to completely abstain from alcohol, otherwise drug treatment will be ineffective.
We will help you get rid of alcoholism!
To successfully get rid of “drunk” addiction, you will need to choose the right medication . Unfortunately, it is not always possible to visit a qualified specialist due to various factors. Therefore, we suggest that you independently select the drug using the “Select a medicine” section on our website. In the meantime, you can determine the stage of alcoholism based on the basic parameters of an addicted person:
Addiction calculator
Your addiction
Dependency type:
light
There is no danger to the body, the habit of drinking is typical for many people, but in the specified quantities and with the specified parameters of the patient, it does not cause any harm to the body. Many people relieve stress with alcohol on holidays and after work, but are not addicted to it.
The patient sees alcohol as a way out of difficult situations and resorts to hard drinks more and more often. This stage is dangerous because in any difficult situation in life, this stage can smoothly transition into the next one, which is much more dangerous to health.
At this stage, an addicted person can no longer do without alcohol, but is firmly convinced that he is capable of quitting at any time, but not today. Already here complications with the liver and other difficulties with organs and well-being may begin.
Special treatment and a short course of rehabilitation, plus the support of relatives, can bring you out of this stage. This stage can provoke very serious problems with the liver and other organs, which will lead to illness for the rest of life.
This stage is not hopeless, but it requires an extremely serious approach to treatment and a long period of rehabilitation, with regular medical procedures, many medications and, often, expensive treatment.
Treatment period for addiction:
Do you want to speed up your treatment?
Speed up treatment?
Teturam - an effective fight against alcoholism May 24, 2018
Alcoholism has long been recognized as one of the most severe addictions, addiction to which occurs very quickly. But getting rid of it requires time and serious treatment. Most people who regularly...
Product review
You can go to the section by clicking on the Select a medicine icon at the top of the site. After which you will need to enter some information about the alcoholic , namely:
- Gender of the dependent person;
- His age ;
- Duration of dependence on alcohol;
- Type of alcohol consumed;
- Frequency of drinking alcohol;
- And also rate the addict’s willpower on a triple scale.
After all the data has been entered, submit the form by clicking the “Select medications for alcoholism” icon. Based on the results of processing the information received, you will be offered the optimal means for treating the disease.
Consequences of toxic encephalopathy of the brain
At an advanced stage of the disease, character changes caused by alcohol addiction are irreversible. Only the early stages of mental deviation can be corrected. For this reason, an important point in the issue of severe or milder consequences of toxic encephalopathy of the brain is the degree of alcohol poisoning at the time of contacting a doctor. The patient develops epileptic seizures, damage to the nervous system, and trophic disorders. Other effects of alcohol on the brain that are irreversible:
- stroke;
- weakening of mental abilities;
- schizophrenia;
- severe stun;
- a brain tumor;
- coma;
- death.
Prognosis of alcoholic encephalopathy of the brain
Since alcohol has a destructive effect on the brain, manifest schizophrenic attacks progress, and other severe complications begin that permanently reduce the patient’s standard of living. Even the use of the latest medical advances will not help achieve favorable results if a person does not want to give up alcohol in the future. In this case, the 100% prognosis for alcoholic encephalopathy of the brain is death. Due to the impossibility of refusing to drink alcohol, mortality in this pathology is high and ranges from 30 to 70% of all patients.
Prevention
Toxic encephalopathy in alcoholism cannot be completely cured, so a person who has undergone treatment should stop drinking alcohol forever. The effect of alcohol on the brain is long-lasting, for this reason your body needs to be helped after undergoing therapy for several years: eat well, exercise, and rest properly.
Prevention of alcoholic encephalopathy should include avoidance or minimal doses of alcohol-containing drinks, especially for young girls. The female body is more susceptible to the influence of alcohol due to genetic inability. The fight against alcoholism among adolescents, women and men should be carried out at the state level, through a set of social, legal, economic, medical and administrative measures.
Forms of the disease
Alcoholic encephalopathy has two main forms, which are characterized by specific symptoms and the course of the disease. These varieties, in turn, may have subspecies.
Acute
At the moment, experts identify only one subtype of acute alcoholic encephalopathy of the brain, which is called Gaye-Wernicke syndrome. Initially, it manifests itself as a significant deterioration in physical health. The timing of manifestations in a particular patient may vary. For some, this period lasts a couple of weeks, while others live with it for months.
The patient experiences many other disorders, which can be either somatic, mental or nervous. In addition, there is an exacerbation of existing diseases that are typical for patients with alcoholism. These include pancreatitis with gastritis and hepatitis, and others.
This form of the syndrome is characterized by the following manifestations:
- weakness;
- breathing problems;
- disturbances of heart contraction (arrhythmia) under minor loads;
- frequent pain in the heart, head, arms and legs;
- increased hand tremors;
- impaired coordination of movements, motor stiffness;
- sensations of burning and squeezing in the chest;
- attacks of anxiety and panic, fear;
- interrupted sleep;
- frequent nightmares;
- weakened muscle tone;
- increased body temperature;
- increased sweating;
- dry skin and peeling;
- speech disorder;
- confusion, which can be complicated by stupor and then coma.
A characteristic feature of Gaye-Wernicke syndrome of alcoholic encephalopathy is the absence of a feeling of relief or satisfaction after drinking alcoholic beverages.
Chronic
There are two subtypes of chronic types of alcoholic encephalopathy - alcoholic pseudoparalysis and Korsakoff psychosis.
Alcoholic pseudoparalysis most often occurs in men aged 40-50 years. They experience mental disorders, which manifest themselves in memory loss, delusional and manic states. This condition is characterized by neurological disorders in the form of tremors of the limbs and changes in the facial muscles.
The stages of this syndrome are manifested by the same symptoms as Korsakoff psychosis, but they are not as pronounced and can go unnoticed.
Korsakoff psychosis is more often observed in women, and this syndrome is characterized by the following manifestations:
- the presence of false memories that the patient perceives as real (confabulation);
- disorientation;
- an amnestic disorder that manifests itself during questioning. There are fixation and retrograde varieties. The first is characterized by loss of memory for current events, and the second - for past events (from a week to several years);
- polyneuritis of the hands and feet.