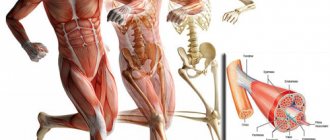
Fasciculations are contractions of several or one motor muscle, which can be noticed due to active muscle movement; these movements occur due to damage to the area of the anterior roots or anterior horns of the spinal cord.
In a relaxed state, the muscle should not involuntarily contract. The clinical significance of fasciculations is small, since they do not cause any serious harm.
Every person has experienced something similar at least once in their life. For example, after severe stress, people experience an involuntary twitching of the eyelid, which is commonly called a nervous tic. Such muscle contractions disappear as imperceptibly as they appear. Concerns arise only in those cases in which the patient experiences changes in reflexes and muscular dystrophy.
Fasciculations should be distinguished from fibrillations. The term fibrillation is used to refer to the spontaneous, discrete contraction of a muscle fiber. Contraction of the entire muscle or group of muscles does not occur. Unlike fasciculation, fibrillation cannot be seen under the skin. In exceptional cases, it can be seen when individual muscle fibers of the tongue contract.
The appearance of fibrillation can be observed with injuries to the axon of a motor neuron or with serious damage to the body. In addition, it can occur with primary muscle disorders. Fasciculations are not observed in the same cases.
Fasciculations occur due to damage to the anterior horns of the spinal cord
Crampy syndrome: causes, symptoms and treatment features
Crampy syndrome is involuntary muscle contractions or painful muscle spasms that may appear suddenly or are triggered by movement.
The duration of the seizures ranges from 10 seconds to 3 minutes. This phenomenon is well known to almost every person. However, some people experience seizures regularly.
Mostly painful spasms appear in the legs, usually in the calf muscles.
Crumpy: what is it and why does it occur?
Involuntary muscle contractions most often appear unexpectedly or after physical activity. They capture the entire muscle or part of it. The spasm manifests itself as a muscle roll, hard to the touch.
During the daytime, the syndrome worries people suffering from local neuroosteofibrosis in the area of the popliteal fossa with vegetative-irritative manifestations in cervical and lumbar osteochondrosis. At night, seizures occur in patients with clear cerebral disorders. Crampy syndrome appears day and night, usually in persons with cerebral, local and spinal disorders.
Causes of painful muscle contractions
Factors that provoke the development of spasms are the following:
- Iatrogenic. In other words, they appear as a result of therapy, after hemodialysis, treatment with diuretics and taking lithium drugs.
- Metabolic. Convulsions can occur due to liver cirrhosis, tetany, hypothyroidism, gastrectomy, and various electrolyte disturbances. Moreover, sudden muscle spasms often bother women carrying a child, especially at 6-7 months.
- Neurological. Such factors play a significant role in the appearance of involuntary muscle contractions. Neurological causes include amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and other pathologies of the anterior horn.
Sudden muscle contractions also occur as a result of myotonic type disorders, rigid person syndrome (rare), and hyperactivity of motor units. It can also be triggered by spasms, which are caused by systemic damage to the tissues of the lower extremities. For example, with diffuse myositis and Becker's dystrophy.
In addition to the reasons listed, the following ailments can lead to the appearance of painful muscle contractions: myalgia syndrome, lameness, exposure to toxic substances on the body (strychnine and insecticides). Experts sometimes talk about idiopathic seizures, which are associated with the individual structure of the body, hereditary factors and personal predisposition.
In completely healthy people, crampy syndrome can occur due to dehydration, heavy alcohol intoxication, or excessive physical activity. Pathologies of peripheral muscles, veins, arteries and nerves contribute to the development of painful spasms.
At rest, such attacks occur as an early manifestation of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Crumpy syndrome manifests itself in the muscles of the lower jaw, thighs, tongue, neck, back, abdomen and arms. Such painful spasms can still be observed in the presence of such factors:
- Damage to peripheral nerves in the form of sensory disturbances such as burning, tingling, painful sensitivity or numbness.
- Lack of iron and magnesium.
- Becker's muscular dystrophy. This genetic disease is characterized by damage to the proximal muscles of the lower extremities.
- Use of certain medications.
- Pain in the lumbar region, spreading to the legs.
- Hemodialysis and plasmapheresis are procedures aimed at extrarenal blood purification.
- Intervertebral hernia.
Cramps quite often occur during pregnancy, as well as during obliterating atherosclerosis of the legs, during which blood circulation is completely or partially disrupted due to blockage of blood vessels with cholesterol plaques.
Main signs of the disease
Crampy syndrome is not a disease; most likely, it is a phenomenon that manifests itself even in a healthy person. In most cases, it affects the lower extremities, especially the quadriceps femoris.
Symptoms and treatment of Crampy syndrome are aimed at alleviating the patient’s condition. During an involuntary spasm, the muscle becomes hard, very painful and tense. Women carrying a baby regularly experience such unpleasant sensations at night. To alleviate the condition, you should massage the sore spot and engage in passive stretching of pinched tissues.
Attacks most often occur in a horizontal position at night, as well as after physical exertion. Under such conditions, the tissue is capable of intense and rapid contraction. The occurrence of cramps is caused by the fact that the antagonist muscles do not provide resistance.
To activate their work, you just need to change your body position. For example, getting out of bed, leaning on a sore limb. Sometimes such attacks occur in the diaphragm or chest.
In this case, lung and heart diseases may develop.
How to identify Crampy syndrome
ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases) includes painful spasm, the diagnosis of which is aimed at detecting the underlying pathology. The ICD-10 code is M79.1.
An attack can be provoked directly during a medical examination by squeezing the calf. After the initial examination, the patient may be referred for a blood test to determine hormone levels and biochemical profile.
They also check the electrolyte content.
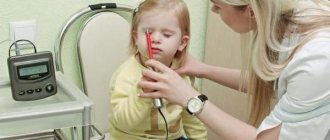
By the way, some diagnostic techniques, for example, electromyography without seizures will not provide a specialist with useful information. When an EMG detects a seizure, the neurologist can see important abnormalities and changes.
How to get rid of painful cramps
Crampy syndrome, the treatment of which is aimed at restoring the functioning of muscles that act as antagonists of spasm, is not considered a pathology. This phenomenon is most likely a feature of the tissues of the human body.
When a painful cramp appears, you should pull your foot upward with all your might, while keeping your knee straight. In this way, it will be possible to stretch a muscle that is seized by a sudden spasm.
With this technique you can get rid of severe pain. Some people with crampy syndrome are helped by pressing their feet firmly on the floor surface. But the first method is considered more effective.
You can eliminate involuntary muscle contractions using other methods:
- walking on your heels for 2-3 minutes;
- a hot foot bath or shower, the duration of warming the affected muscle should be at least 5 minutes;
- walking with high legs;
- massage using ice cubes.
Treatment of neurological causes
Crampy fasciculations syndrome is a symptom of a large number of neurological diseases, including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
With such an illness, it is unlikely that it will be possible to stop an attack using the methods listed above. For treatment in this case, powerful medications are used - Diazepam, Baclofen and other similar drugs.
Of course, they can only be used as prescribed by a neurologist.
Quite often, complications of lumbar osteochondrosis result in painful muscle contractions. In this case, all medications and methods that are usually used to treat the underlying disease become effective.
When crampy syndrome bothers you regularly, it is recommended to use mineral and vitamin complexes to saturate the body with useful substances.
But first you should consult your doctor, informing him about all the medications you are currently taking.
The most popular medications for painful cramps containing magnesium and calcium are Asparkam and Panangin.
Crampy syndrome causes, symptoms and treatment of which are aimed at eliminating spasm, in some situations requires more serious measures. If a person suffers from a chronic disease, for example, diabetic polyneuropathy, then he needs complex treatment. In this case, alpha-lipoic acid drugs are prescribed to restore the affected nerves.
Prevention of the development of the syndrome
To avoid painful spasms, doctors advise performing special muscle stretching exercises. In addition, exercise on an exercise bike is an effective measure in the fight against the disease.
As a preventative measure, experts recommend drinking enough water and wrapping your feet in a blanket while sleeping.
You should also give up alcoholic beverages and minimize the consumption of tea and coffee.
Health effects
Involuntary muscle contractions do not pose a threat to human life, but may be the first symptom of the development of serious diseases associated with the nervous system. If such attacks occur daily for a long time, it is better to consult a neurologist.
Source: https://fb.ru/article/343839/sindrom-krampi-prichinyi-simptomyi-i-osobennosti-lecheniya
Crampy syndrome - what causes muscle cramps?
Involuntary muscle contraction is a phenomenon that many people experience. In medicine, it has a name - Crampy syndrome. It can manifest itself in different ways: as an independent random condition or as a symptom of another disease. If the syndrome occurs systematically, you need to undergo an examination and identify the true cause of involuntary muscle contractions.
- Description
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
Description
Crampy syndrome is a sudden painful contraction of muscle fibers.
It can affect either part of a muscle or an entire group of nearby fibers. The pathology manifests itself in people of different ages and genders; it is believed that every second person has encountered it at least once in their life. The syndrome code according to ICD 10 is R25.225.2.
The appearance of convulsive contractions is completely unpredictable. The syndrome appears abruptly, but passes just as quickly. In most cases, it occurs after high muscular activity; people who run, swim, or jump are more predisposed to it.
The presented syndrome is not dangerous to human life and health. If it appears regularly (at least once a week), the patient should contact a doctor. Such a manifestation of Crumpy may indicate damage to the nervous system that requires urgent medical intervention.
Causes
The reasons why muscle cramps appear can be:
- Features of rest: night time, horizontal body position, warmth, muscle strain during the working day. For these reasons, spasms occur in people who do not have any provoking pathologies.
- Muscle fatigue caused by heavy physical labor or intense training, especially weight training.
- Impaired blood circulation in tissues.
- Spinal diseases, as well as recent injuries to the back or legs.
- Pregnancy. More often, the syndrome appears in women in the later stages of pregnancy.
- Dehydration that occurs after poisoning, diarrhea and other pathological conditions.
- Hereditary predisposition to the syndrome.
- Becker muscular dystrophy.
- Myositis of diffuse type.
- Amyotrophic sclerosis, as well as progressive amyotrophies of various types.
- Malignant neoplasms affecting the nervous system.
- Polyneuropathy, as well as multifocal motor neuropathy.
- Late complications of polio.
- Compression lesions of muscles.
- Toxic damage to muscle tissue, which can be caused by the bites of poisonous insects, or by exposure to the body of certain types of poisons used in industry.
Often the syndrome appears while taking medications: diuretics, penicillin-based medications, lithium preparations. After the end of their use, repeated manifestations of muscle cramps are not observed.
Symptoms
The symptom of Crampy usually manifests itself in the form of fasciculations (convulsions) of the lower extremities, namely in the calf muscles. Less commonly, it affects the muscle tissue of the thighs or arms, as well as the intercostal muscles. When it appears, the muscle itself becomes dense, tense, and painful.
Often there is excessive competition of tissues, as well as their deformation and pain. Cramps may be accompanied by the appearance of a ridge on the affected area. The tension of the muscle tissue is tonic; it does not twitch during an attack.
Crumpy is accompanied by intense painful sensations.
Fasciculations are localized only on one side of the muscle. They appear suddenly, without any preliminary symptoms. In rare cases, they are accompanied by minor twitching of nearby muscle tissue, which usually appears at the end of an attack of Crump. Such phenomena indicate the presence of ALS and hereditary muscle pathologies in a person.
Expert opinion Pain and crunching in the back and joints over time can lead to dire consequences - local or complete restriction of movements in the joint and spine, even to the point of disability. People, taught by bitter experience, use a natural remedy to heal joints, which is recommended by orthopedist Bubnovsky... Read more"
If a person experiences spasms of the pectoral and intercostal muscles, he experiences a temporary decrease in inspiratory volume. Because of this, the presented syndrome is often confused with diseases of the respiratory system or pathologies of cardiac activity.
After the end of the attack of Crumpy, the patient experiences muscle fatigue; a local aching pain may persist for some time, which subsides without the use of anesthetic drugs.
Diagnostics
A diagnosis of crampy is made during an examination by a doctor. The doctor should invite the patient to walk around the office, after which he conducts a series of proprietary tests to diagnose the state of tissue contractility.
Source: https://tvoypozvonok.ru/sindrom-krampi-po-kakoj-prichine-svodit-myshcy.html
Anatomy of the pyramidal tract
The anatomy of the pyramidal tract is presented here. Here you see the supplementary motor area, the premotor cortex.
Pyramidal tract
These transformations transmit signals from the brain to motor neurons in the spinal cord. They innervate skeletal muscles and regulate voluntary movements.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is an unusual neurodegenerative disease! The ICD 10 code is G12.2.
All the worst things happen when a person doesn’t feel anything yet. At this preclinical stage, 50–80% of motor neurons die after a genetic failure occurs with the participation of environmental factors. Then, when 20% of resistant motor neurons remain, the disease itself begins.
What is benign fasciculation syndrome?
Fasciculation is a long word for muscle twitching. It doesn't hurt and you have no control over it. It's involuntary.
The type of fasciculation that most people are familiar with is eyelid twitching. It has its own names, including:
- eyelid spasm
- blepharospasm
- myokymia
Fasciculations can be a symptom for many types of conditions. They have about 70% healthy people. They are rarely a sign of a serious neuromuscular disorder.
However, because they are a symptom of some devastating disorders such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), the presence of lesions may be a sign that you should seek medical help. Doctors usually evaluate them carefully.
Benign fasciculation syndrome is rare. People with benign fasciculation syndrome may have twitching:
- eye
- language
- weapon
- big
- legs
- hips
- calves, which is especially characteristic
Some people also have muscle cramps with patches. People with this condition are otherwise healthy. There is no underlying disorder or neurological cause for these seizures and seizures. However, the symptoms can be bothersome both physically and psychologically. If the cramps are severe, they may interfere with daily activities such as work and work.
advertisingAdvertising
Symptoms
Symptoms of benign lesion syndrome
The main symptom of benign fasciculation syndrome is persistent muscle twitching, tingling, or numbness. These symptoms occur when the muscle is at rest. As soon as the muscle moves, the twitching stops.
Attacks most often occur in the thighs and calves, but they can occur in several parts of the body. The twitching may only occur occasionally, or it may occur almost all the time.
People often worry that the lesions are associated with a serious neuromuscular condition such as ALS. It is worth noting that lesions are not the only symptoms of ALS.
In benign fasciculation syndrome, the main symptoms are lesions.
In ALS, fasciculations are also accompanied by other problems such as worsening weakness, trouble grasping small objects, and difficulty walking, talking, or swallowing.
Causes
Causes of benign fasciculation syndrome
Benign fasciculation syndrome is thought to be caused by overactivity of the nerves associated with the twitch muscle. The cause is often idiopathic, meaning it is unknown.
Some studies have shown some connection between fasciculations and:
- stressful time
- injury
- anxiety or depression
- high intensity, strenuous exercise
- fatigue
- drinking alcohol or caffeine
- recent viral infection
- They are often associated with stress-related symptoms, including:
headache
- heartburn
- irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- changes in food
- Some over-the-counter and prescription medications can also cause lesions, including:
nortriptyline (Pamelor)
- chlorpheniramine (Chlorphen SR, Chlor-Trimeton Allergy 12 Hour)
- diphenhydramine (Benadryl
- beta agonists, used to treat asthma
- high doses of corticosteroids followed by lower doses to taper them
- AdvertisingAdvertising
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of benign fasciculation syndrome
The depression can be a symptom of several health problems. A serious neuromuscular disorder is not usually the cause. Other more common causes may include sleep apnea, hyperthyroidism (an overactive thyroid gland), and abnormal levels of calcium and phosphorus in the blood.
However, the lesions can be a sign of highly debilitating neuromuscular problems. For this reason, doctors are likely to evaluate them carefully.
A common way to evaluate muscle cramps is electromyography (EMG). This test stimulates the nerve with a small amount of electricity. He then records how the muscle reacts.
Doctors can also evaluate overall health and risks for lesions with:
blood tests
- other nerve tests
- thorough neurological examination, including muscle strength tests
- a thorough health history, including mental health problems, physical symptoms from stress, and quality of life issues
- Benign fasciculation disorder is diagnosed when follicles are a common primary symptom and there is no other sign of a nerve or muscle disorder or other health condition.
Treatment
Treatment of benign fasciculation syndrome
There is no treatment to shrink benign lesions. They can decide for themselves, especially if a trigger is identified and addressed. Some people have had relief with medications that reduce nerve excitability, including:
carbamazepine (Tegretol)
- Gabapentin (Horizon, Neurontin)
- lamotrigine (Lamictal)
- pregabalin (Lyrica)
- Sometimes doctors prescribe a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, a type of medication used to treat depression and anxiety. Counseling can also help.
Cramps can be relieved by stretching exercises and massage. If the seizures are severe and no other medications help, doctors may prescribe immunosuppressive therapy with prednisone.
Doctors may try other treatments for severe muscle cramps that interfere with daily life.
Source: https://ru.medic-life.com/what-is-benign-fasciculation-syndrome-18328
Pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
If we talk about the pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, then first of all we must understand the following. There are various (largely unknown) genetic factors.
They are realized under conditions of selective vulnerability of motor neurons. That is, in those conditions that ensure the normal life-physiological functioning of these cells.
However, under pathological conditions they play a role in the development of degeneration. This subsequently leads to the underlying mechanisms of pathogenesis.
Motor neurons are the largest cells of the nervous system with long conducting processes (up to 1 meter). They need high energy costs.
Each motor neuron is a special power plant. It takes on a huge number of impulses and then transmits them to implement coordinated human movements.
These cells require large amounts of intracellular calcium. It is what ensures the functioning of many motor neuron systems. Therefore, the production of proteins that bind calcium in cells decreases.
Crumpy syndrome
At CELT you can get advice from a neurologist. Make an appointment
Initial consultation – RUB 3,200.
Repeated consultation – 2,000 rubles.
The frequency of muscle involvement is distributed as follows:
- muscles of the leg and foot;
- biceps brachii;
- extensors of the fingers;
- muscles of the trunk and diaphragm;
- submandibular
A distinctive feature of crampy is severe pain that occurs at the moment of muscle spasm, which stops when it ends. During spasm, the muscle becomes dense and sharply painful when touched. Every 10th person suffers from crampy on a regular basis.
Why does a cramp occur?
The causes are physiological (primary) and pathological (secondary). Relatively safe physiological causes are muscle strain, as well as temporary metabolic disorders.
In a healthy person, muscle cramps are provoked by the following factors:
- unusual long-term, high-intensity exercise;
- non-physiological muscle tension caused by diseases of the spine and joints of the limbs;
- alcohol abuse;
- insufficient sleep;
- smoking;
- violation of the temperature regime - overheating or hypothermia;
- water and electrolyte disturbances (excessive sweating in the heat, insufficient fluid intake, use of diuretics and medications);
Pathological causes of crampy are various diseases and conditions of the organs and nervous system. These include:
- diseases of peripheral nerves – radiculo- and polyneuropathy;
- Parkinson's disease;
- diseases of the central nervous system - spinal amyotrophy, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, consequences of poliomyelitis;
- multiple sclerosis;
- liver diseases, especially chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis;
- intestinal diseases, especially viral enteritis;
- kidney disease, especially chronic renal failure with uremia;
- muscle diseases – muscular dystrophies, metabolic myopathies;
- endocrine diseases - diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, decreased function of the parathyroid glands;
- growth and development of tumors, benign and malignant;
- iron deficiency in the body;
- obliterating diseases of the vessels of the lower extremities;
- heart failure accompanied by edema;
- pregnancy.
Diagnostic principles
Only a doctor can distinguish a physiological reaction from a pathological condition; it is impossible to do this on your own.
You should not worry only if cramps occur rarely, no more than once a month, and the cause “lies on the surface”, there is a clear connection with physical overload, profuse sweating or other “natural” reasons mentioned above. In all other cases, you need to see a doctor as early as possible to rule out diseases or adjust your medication intake. Particularly noteworthy are long, protracted convulsive contractions that are repeated.
A set of diagnostic procedures may include, if necessary, not only general clinical tests, but also electroneuromyography, studies of the function of the heart, thyroid gland, kidneys and other organs. ENMG outside an attack can reveal signs of primary muscle pathology and disruption of muscle innervation; high-frequency and amplitude potentials are recorded during muscle contraction.
It is known that cramps occur more often in people with “thick” calves or some hypertrophy of these muscles. Researchers attribute this to the large amount of myoglobin in them (the so-called “red muscles”).
It is interesting that among peoples who spend a lot of time squatting and thus constantly straining their calf muscles, cramps are observed much less frequently.
However, prolonged stay in this position can lead to pinching of the peroneal nerve.
Treatment rules
Crumpies themselves do not pose a threat to life or health. However, they are extremely painful and cause a lot of trouble.
The symptoms accompanying cramps are varied, so the efforts of the doctors at the CELT clinic are aimed at identifying the underlying disease.
Treatment of this disease, as well as the abolition of excess medications, can quickly improve health outcomes.
Emergency relief for pain relief consists of passive stretching of the contracted muscle or voluntary active contraction of the antagonist muscle. So, when there is a cramp in the calf muscle, you need to stand up, leaning on the irritated leg, and when the muscles of the fingers contract, straighten them with your hand.
To prevent cramps after physical activity, you need to raise your legs high from a lying position. In this position, venous outflow improves and the likelihood of convulsive contraction decreases. If electrolytes are lost through sweat or diarrhea, potassium and magnesium supplements are recommended.
Physiotherapy is used as an auxiliary method, in particular the following methods:
- physical therapy aimed at general strengthening of muscles;
- contrast water procedures, massage and hardware types of physiotherapy.
If the effect of physiotherapeutic procedures is insignificant, the doctor may prescribe medication.
Prevention
Giving up bad habits, streamlining your lifestyle and nutrition are the basic principles of prevention. Along with this, moderate physical activity is useful - walking or exercising on an exercise bike.
It’s good to do simple muscle stretching exercises in your free time.
At any time of the year you need to drink a sufficient amount of clean water - 30 ml per kilogram of weight in the cool season and 50 ml in the hot season.
For those who experience frequent cramps, it is advisable to reduce the consumption of drinks containing a lot of caffeine and stop smoking. When sleeping, you need to cover yourself warmly, especially keep your feet warm.
The best prevention of cramps, as well as other disorders, is an examination that can be completed at the CELT multidisciplinary clinic at any time.
Make an appointment via application or by phone +7 (495) 788-33-88
Source: https://www.celt.ru/napravlenija/nevropatologija/zabolevanija/sindrom-krampi/
Epidemiology of motor neuron disease
If we talk about the epidemiology of motor neuron disease, the number of new patients per year is about 2 cases per 100,000 people. The prevalence (the number of patients with ALS at one time) ranges from 1 to 7 cases per 100,000 people.
As a rule, people from 20 to 80 years old get sick. Although exceptions are possible.
Average life expectancy:
- if ALS disease begins with speech impairment (with bulbar onset), then they usually live for 2.5 years
- if it begins with some kind of motor disorders (spinal onset), then this is 3.5 years
However, it should be noted that 7% of patients live longer than 5 years.
Benign crampy-fasciculation syndrome: causes and symptoms
Benign crampy-fasciculation syndrome
- persistent muscle twitching, tingling or numbness in one or more muscles. Muscle twitching is usually not a cause for concern, but a person should see a doctor to avoid serious complications.
Benign crampy-fasciculation syndrome
is rare and may be confused with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Wikipedia
(ALS), which is also known as Lou Gehrig's disease.
What is benign crampy-fasciculation syndrome?
Most people experience muscle twitching, common examples include eyelid twitching or leg spasms. Muscles contain motor units—groups of muscles and nerve fibers that work together.
Fasciculations occur when one or more motor units begin to move on their own and escape the control of the brain, resulting in unexpected movements.
Benign crampy-fasciculation syndrome
causes chronic muscle twitching that can last for long periods of time.
Causes of benign crampi-fasciculation syndrome
Benign crampy-fasciculation syndrome
It is rare and its exact cause is still unknown. One theory is that it is a reaction to a viral infection. The fasciculations themselves can have a variety of causes, including the use of certain substances or medications, especially allergy medications.
Drugs that can cause fasciculations:
- beta-agonists;
- chlorpheniramine;
- dimenhydrinate;
- diphenhydramine;
- nortriptyline;
- methylphenidate;
- pseudoephedrine.
The twitching usually goes away when the person stops taking the medications.
Muscle twitches can be the result of an injury or symptoms of anxiety or depression. They can sometimes be associated with other stress symptoms such as irritable bowel syndrome, heartburn and headaches.
Some people who are deficient in certain minerals, such as magnesium or calcium, may also develop muscle twitches.
Fasciculations may be associated with other factors, such as:
- physical exercise;
- alcohol consumption;
- smoking;
- fatigue;
- caffeine consumption.
Symptoms of benign crampi-fasciculation syndrome
The most common symptom of this condition is muscle twitching in the thighs or lower legs.
The twitching is most noticeable when the body is at rest. After some time, the person may also experience muscle pain and a feeling of weakness. More than 70% of people experience benign crampy-fasciculation syndrome
. These people may also experience numbness and muscle cramps. The symptoms may be due to stress and anxiety.
Other symptoms of fasciculation:
- itching and trembling in the muscles;
- sudden rapid contractions or involuntary muscle spasms;
- muscle stiffness;
- general weakness.
- anxiety symptoms such as a lump in the throat, headache, or shortness of breath.
Diagnosis of benign crampi-fasciculation syndrome
During the diagnosis, your doctor will check your tendon reflexes and ask about your medical history and stress levels.
Most diagnostic tests are aimed at ruling out other more serious diseases, such as multiple sclerosis or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
If the doctor thinks a person has a serious condition, they will order blood tests and electromyography (EMG) to rule out nerve damage.
Treatment of benign crampi-fasciculation syndrome
There is currently no treatment for this condition. Doctors may prescribe medications to reduce twitching or seizures. Some anti-inflammatory drugs or muscle relaxants may help people with pain and inflammation. If a blood test reveals a mineral deficiency, a person may use supplements.
To reduce anxiety, your doctor recommends:
Meditation, yoga or soothing music.
Spend time with your pet.
Eat a healthy diet rich in whole foods and nutrients.
Probiotics, which are found in foods such as sauerkraut, kimchi, miso and kefir.
If symptoms persist, get worse, or affect a person's quality of life, they should see their doctor to discuss treatment options.
Benign crampy-fasciculation syndrome
Both lateral and amyotrophic syndrome have the same symptoms, but they are different disorders.
A key symptom of ALS is muscle atrophy. The affected muscles atrophy and shrink over time. This means that a person with ALS feels weaker. With benign crampi-fasciculation syndrome,
muscle atrophy does not occur.
Although muscle fasciculation occurs in both cases, it is more common in benign crampy-fasciculation syndrome
. Muscle twitching occurs during rest, but stops when a person begins to work the muscles. In ALS, the twitching may start in one place, but will often spread to other muscles nearby.
If a person experiences persistent muscle twitching and has not been diagnosed, they should see a doctor to rule out any other possible causes.
Literature
- Beetz A. et al. Psychosocial and psychophysiological effects of human-animal interactions: the possible role of oxytocin //Frontiers in psychology. – 2012. – T. 3.
- de Carvalho M., Swash M. Origin of fasciculations in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and benign fasciculation syndrome //JAMA neurology. – 2013. – T. 70. – No. 12. – pp. 1562-1565.
- Filippakis A. et al. A Prospective Study of Benign Fasciculation Syndrome (S45.007). – 2020.
- Foster JA, Neufeld KAMV Gut–brain axis: how the microbiome influences anxiety and depression //Trends in neurosciences. – 2013. – T. 36. – No. 5. – pp. 305-312.
- Hoge EA et al. The effect of mindfulness disorder meditation training on biological acute stress responses in generalized anxiety //Psychiatry Research. – 2020.
- Thoma MV et al. The effect of music on the human stress response //PloS one. – 2013. – T. 8. – No. 8. – P. e70156.
Source: https://medicalinsider.ru/news/dobrokachestvennyjj-sindrom-krampi-fascikulyacii-prichiny-i-simptomy/
Instrumental methods for diagnosing ALS
During the diagnosis, your doctor will check your tendon reflexes and ask about your medical history and stress levels. Most diagnostic tests are aimed at ruling out other more serious diseases, such as multiple sclerosis or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. If the doctor thinks a person has a serious condition, they will order blood tests and electromyography (EMG) to rule out nerve damage.
Instrumental diagnostic methods are designed to exclude diseases that are potentially curable or have a benign prognosis.
Electromyography for diagnosing ALS
There are two methods for diagnosing ALS:
- Electromyography (EMG) - verification of the generalized nature of the process
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain and spinal cord to exclude focal lesions of the central nervous system, the clinical manifestations of which are similar to those of the onset of MND