Hypochondriacal syndrome is a condition where a person worries too much about their health. He constantly “stabs, pulls, ache, shoots somewhere.” Very often unusual sensations occur (senestopathic type of syndrome): for example, numbness of a limb for a short period of time. Such “symptoms” greatly frighten a person, he imagines dangerous diseases, and he again and again turns to a doctor for advice.
Hypochondria is a disorder that affects both men and women after 35-40 years of age. Constant worry about your own health poisons your life, makes it difficult to concentrate on work and often leads to depression. As a result, a person actually begins to get sick, since emotional stress causes fatigue, insomnia, reduces immunity and disrupts metabolism. Therefore, like any mental disorder, hypochondria requires treatment from a psychotherapist.
What is senestopathy
Senesthopathy is a certain condition that is characterized by: unreasonable complaints of poor health, internal discomfort in the body or on the skin. The sensations are devoid of objectivity, the patient cannot accurately determine what and where it hurts.
- Etiology
- Classification
- Elementary
- Simple
- Psychosensory
- Interpretative
- Hallucinatory
An attack of senestopathy is a symptomatic manifestation of mental disorders and may be accompanied by hypochondriacal delirium and depressive states. A person with attacks of senesthopathy during neurosis constantly feels suffering that is not associated with internal anatomical pathologies and is of an abstract nature.
Senesthopathy occurs quite often in the overall picture of the underlying mental disorder. Diagnosed after examining the patient, listening to complaints and studying the medical history. Additional studies are ordered to differentiate from other diseases.
Treatment is conservative with subsequent observation by the attending physician. The prognosis is ambiguous: it all depends on the type and severity of the underlying disease.
Causes of senestopathy
Senesthopathy is an abstract psychological sensation, the projection of which is directed by the patient into the body. The pathology can manifest itself in episodic attacks, constantly, or as a state of acutely aggravated senestopathic crisis.
The cause of the deviation is a number of diseases:
- schizophrenia is a severe mental disorder that affects the functions of consciousness and behavior, causing an obsessive state;
- organic pathology of the nervous system - death of neurons in the brain or spinal cord, necrosis of tissues of the nervous system, leading to personality degradation;
- manic-depressive psychosis - a disease with periodic depressive and manic phases, the condition has intervals of enlightenment;
- neuroses - a group of functionally reversible psychogenic deviations;
- affective-delusional syndrome - a condition when the patient feels a mania of persecution or poisoning, delusions, hallucinations, and paranoia are often present;
- paranoia - obsessive state;
- paraphrenia - a severe degree of delusional syndrome, when a person exalts himself, often combined with hallucinations;
- drug addiction - behavioral changes caused by taking drugs;
- Alcoholism is a disease that occurs due to systemic consumption of alcoholic beverages.
There are many types of mental illnesses with signs of senestopathy. The condition requires careful analysis and differentiation.
Symptoms
Hypochondria, according to the symptomatic complex, is divided into several varieties:
- Astheno-hypochondriacal syndrome.
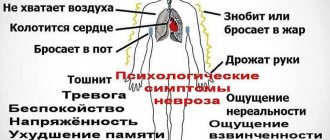
The person is convinced that he has a weak heart or blood vessels. Poor health is expressed by constant lethargy, lack of appetite, frequent headaches, darkening of the eyes, and increased sweating.
Astheno-hypochondriacal syndrome is also characterized by emotional “lethargy”: a state when you want to give up on everything, saying that nothing can be done, because “there is no health, and doctors still won’t help.”
Astheno-hypochondriacal syndrome is usually accompanied by a depressed mood: a person is often offended by loved ones, cries and feels sorry for himself.
- Depressive-hypochondriacal syndrome.
The symptoms are similar to the previous ones, but in a more severe form. Due to constant deep worries about his fragile health, a person becomes very irritated, falls into despair, commits inappropriate actions (prepares a will, writes complaints against doctors who “have committed negligence,” quits his job, threatens to leave the “ungrateful” family for whom he worked like a slave and lost his health).
A person often “plays for the audience” by demonstratively measuring his pulse or blood pressure, but at the same time he actually begins to feel very strong tachycardia or dizziness. Such a nervous disorder is dangerous because the person provokes real problems (heart attack or stroke).
- Senesto-hypochondriacal syndrome.
The main sign of this type of hypochondria is a firm belief in the reality of those unusual phenomena that occur in the body: “electric” goosebumps throughout the body, inexplicable sensations under the scalp, a numb body, etc. The person experiences panic and may begin to convulse due to fear of unknown diseases. He demands that doctors conduct a full and comprehensive examination and urgently identify the disease, since his imagination paints the most unimaginable pictures of what can happen inside the body.
Senestopathic syndrome often occurs against the background of mild schizophrenia, which can progress. Delaying treatment is not recommended at all.
- Anxious-hypochondriacal syndrome.
With this variety, there is a particular greed for “terrible” news about various diseases. Having heard about another epidemic on some distant tropical island, a person frantically reads details in newspapers or the Internet about this “modern plague”, all the time listening to his body, looking for confirmation of the onset of the disease.
People with anxiety-hypochondriasis syndrome do not believe that their panic is unfounded. They are convinced that doctors and TV presenters deliberately deceive people to get sick and buy expensive medicines. Due to his impressionability, a person often suffers from colds with each “wave of flu”, as well as stomach disorders, every time he suspects food is not fresh.
Summarizing the above symptoms, we can say the following: any hypochondriacal syndrome is accompanied by an obsession with an illness that does not actually exist, and mistrust of doctors. Even when the therapist provides test results and examinations indicating the patient’s absolute health, the person doubts the qualifications of the hospital and looks for another doctor who will finally prescribe at least some treatment.
Classification
Senesthopathy has several varieties, the gradation takes into account the modality, localization of the projection, and the degree of severity of epicritic features.
Elementary senestopathy
The sensory modality is unclearly expressed without a specific localization. Projection is directed inwards and is intertwined with affective disorders.
Patients describe an anxious-depressive state as internal tension, they are overcome by a feeling of a tense string that is about to burst. There is fear and melancholy.
Often the patient complains of weakness, soreness of the whole body, lack of living space (“as if they ran over a roller”). This is observed with somatopsychic depersonalization.
Simple senestopathy
It is characterized by a clear sensory modality with specific pain and thermal sensations. Localization, scattered or limited to certain areas on the human body: side, head, hypochondrium. The disease with neurosis manifests itself quite often.
There is a gradation:
- Algic form. Rich in pain sensations of different shades (expansion, compression, breaking, drilling, eversion, cutting, aching sensations). Symptoms can be constant or paroxysmal. The patient may experience discomfort for several years.
- Thermal. I am haunted by a burning sensation: it burns under the shoulder blade, the whole body, the cheek freezes.
- Paresthesia. The patient is left with the feeling of “crawling goosebumps,” itching, numbness, and tingling.
- Physical heaviness, lightness of the whole body or individual parts.
Psychosensory senestopathy
It is diagnosed when a person feels a condition with a different direction (volume, size changes). Manifests itself in the following sensations:
- the stomach is tied into a knot;
- bursting in the chest;
- the brain swells;
- twists joints.
Interpretive senestopathy
Interpretations of the condition are varied: the brain freezes, the spleen itches. The following subspecies are distinguished:
- organotomic form - has a clear localization;
- associated form, when a large number of sensations are combined into one;
- a delusional form, when patients put forward a version of their condition that is very far from reality.
Hallucinatory senestopathy
Characteristic complaints of the patient are pain in a circle on the abdomen, as if they had hit the arm, leg, head, the brain is peeling off and disintegrating. Sound and taste senses may be added.
The last two varieties are often recorded in schizophrenia, when the patient’s condition borders on delusions, hallucinations, and fixation on sensations.
Development of the disease
As the disease progresses, pain migrates and discomfort manifests itself in various affected areas. At the same time, the intensity and duration of pain only increases.
In some cases, the manifestation of painful symptoms may be accompanied by gestures, such as rubbing the affected area or grabbing the head. The pain begins to migrate and at one moment it may appear in the head, and at another in the abdominal area.
Over time, delusional senestopathy develops and the disorder becomes intrusive. During the development of the disease, special somatic symptoms may appear in the form of thermal pain. The patient may feel the movement of foreign bodies or fluids in his body.
In the elementary type of pain disease, unpleasant sensations do not have an exact localization; they are projected onto the person’s internal sensations.
In rare cases, the disease may be isolated and not accompanied by nervous and mental disorders. As the disease progresses, patient complaints may take on a peculiar character.
At the very beginning of the disease, a person develops simple senestopathies, which may have the nature of complaints about somatic pathology. Over time, sensations become more complex and bizarre, with unusual localization.
In a patient, the first signs of senestopathies are simple and static in nature, but with the development of the disease they acquire a more complex form, become mobile and migrating, but their projection is not disturbed.
Elementary senestopathy does not have a clear localization. It is projected onto the area of a person’s internal sensations. Patients with manic depression describe it as “constant internal tension,” “freezing inside.”
Simple senestopathy has sensory varieties (pain, burning, parasthesia). It is projected onto the area of the patient’s corresponding sensitivity zone. Senesthopathy in humans can occur in any part of the body; a specific location is not typical. Very rarely, senestopathy can be isolated, most often accompanied by mental or nervous disorders.
In some cases of this disease, a person does not have comparative characteristics and terms in describing his “strange” sensations; it is during this period that senestopathic delirium or delusional senestopathy occurs. This means that the patient’s thinking has been replaced by delirium. The persistent and intrusive nature of the manifestations of senestopathies does not give a person peace. They do not allow him to be distracted by household chores and do his job.
With this disease, patients may experience pathological thermal sensations (“burning”, “freezing”), fluid movements inside the organ (“transfusion”, “vascular thrombosis”, “gurgling”). Some patients complain of sensations of movement or movement of tissues (“separation”, “turning over”). Complaints can be of a peculiar nature: “I have drilling-tearing pain.”
As a rule, senestopathies are localized in the head, brain, and very rarely in the chest, upper and lower extremities.
This disease is characterized by symptoms of migration of sensations. Senesthopathy can be permanent or epizootic in nature, sometimes manifesting itself in the form of seizures and attacks.
Senestopathic crises are acute, with a vivid clinical attack, and can be accompanied by panic attacks and autonomic disorders. During a crisis, a patient experiences fear and displays expressive postures and defensive gestures.
Symptoms of senestopathy
The symptoms of senestopathy are unusually rich in color with uncharacteristic manifestations for common somatic pathologies. The patient's complaints are emotionally charged and cause great distress. The patient cannot relax, is extremely collected and fixated on his condition, believing in the truth of the suffering he is experiencing, bordering on imminent death from “brain rupture,” “cessation of blood flow to the organs,” and others.
The projection of sensations is borderline fantastic (stomach itches, blood vessels pulsate). When describing the symptoms experienced, sensations of skin sensitivity are transferred to the internal organs: itching, burning, freezing.
Attacks of false illness can be episodic or constant, accompanied by fear of going crazy and panic. As the condition worsens, the complaints intensify, and it is much more difficult to stabilize the patient.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made after a conversation with the patient, studying the medical history, listening to complaints with a detailed description. Additional studies are carried out to exclude the presence of pathology:
- Ultrasound of the head, chest;
- MRI of neck and head vessels;
- CT;
- radiography.
Instrumental studies are needed, since paresthesia is a consequence of vascular and neurological pathologies. Paresthesia in neurology is localized on the skin, and in case of problems with blood flow, sensations appear due to exposure to cold or severe physical exertion.
Treatment of senestopathy
Therapeutic measures will depend on the cause of symptomatic manifestations:
- for depression and neuroses, tranquilizers and antidepressants are prescribed;
- for psychoses, antipsychotics are prescribed.
The most commonly prescribed drugs are:
- Teraligen is an antipsychotic that belongs to the group of antipsychotics and has antispasmodic, antihistamine, and serotonin-blocking effects. The drug has a hypnotic effect with sedative and antiemetic properties. In acute psychotic disorders it is ineffective. The medicine is well tolerated and can be prescribed to children and adolescents.
- Eglonil is an antipsychotic, has a moderate antidepressant and stimulating effect. Helps eliminate apathy and depression. The peculiarity of the drug is its selective effect on the hypothalamus with the suppression of excessive excitation. This substance is not retained in the body and is excreted through the kidneys. Eglonil is used for schizophrenia, depression, and migraines.
Taking antidepressants improves mood, reduces melancholy, lethargy and apathy. The feeling of anxiety and restlessness is leveled and lubricated. The patient gets rid of irritability, mental activity increases. Medicines in this group include Milnacipran, Pyrazidol, Mirtazapine.
Tranquilizers - anti-anxiety drugs (Seduxen, Afobazol, Amizil, Phenibut and others). There are many types of drugs:
- new generation products;
- daytime;
- with a pronounced hypnotic or anticonvulsant effect - components contribute to forgetting states of anxiety, tension and fear.
In addition to conservative treatment, psychotherapy sessions may be prescribed.
Treatment
Senesthopathy is treated by doctors, psychotherapists, and psychiatrists. Therapists rule out diseases of internal organs, psychiatrists determine the degree and type of disorder, psychotherapists conduct special sessions with patients.
- Neuroprotectors, antidepressants, sedatives, and tranquilizers are used according to indications.
- Much attention is paid to the proper organization of sleep, work, nutrition, as well as strengthening procedures (vitamin therapy, gymnastics, massage, relaxing baths, etc.)
- In the chronic course of senestopathy, a course treatment plan is developed using relaxation therapy, medications, hypnosis, auto-training, and active recreation.
Thus, senestopathy is a change in perception and its transmission to the brain. The disorder often accompanies organic, neurological or psychiatric diseases. Treatment of senestopathies is complex, with a combination of drug correction of symptoms and psychotherapy.
Romanovskaya Tatyana Vladimirovna
Possible complications and prevention
Frequent, prolonged attacks with constantly worsening symptoms can be considered a complication of senesthopathy.
Preventive measures will consist of timely detection and treatment of the underlying disease. If a person has a family history of mental disorders, the child may be at risk. You should be careful when hormonal changes occur in the body and avoid stressful situations.
Causes
Among the main reasons for the development of hypochondria, doctors identify: hereditary factors, brain diseases and emotional shocks experienced in recent times.
In the first case, hypochondriacal disorder may arise due to a genetic predisposition. Usually in a child its presence becomes noticeable already at the age of 5-6 years. The kid worries about trifles, doubts his decisions and actions, is overly impressionable and suspicious.
The second group includes abnormalities in the functioning of the brain. The patient receives incorrect impulses sent by internal organs. Because of this, the patient experiences disruption of the entire nervous system. A person begins to think that he is terminally ill and does not understand why doctors refuse to treat him.
It is also possible to identify emotional causes of the syndrome:
- Excessive family attention to the health of the sick person. While still a child, the baby can get used to the idea that he has health problems. As a result, already in puberty, a real hypochondriacal syndrome begins to form.
- Severe stress. Negative emotions reduce a person’s immunity, which means they can provoke the development of various diseases. The patient does not understand that the malaise that appears is only the embodiment of his thoughts. Hypochondria appears.
- Media influence. Intrusive advertising of various medications, television programs about human health and articles in information magazines cause a person to worry about the state of his own health. Elderly people are especially susceptible to this effect. After watching another story about a new flu epidemic or some dangerous disease, they immediately begin to look for symptoms of the pathology in themselves. And quite often they are found, but they are completely fictitious.
Many scientists believe that the disorder is a manifestation of the self-preservation instinct. At the same time, psychotherapists call the deviation “inability to be sick.” Quite often, due to excessive attention to an invented problem, patients forget about real-life ailments.
Elderly people are at particular risk. Adolescents are also susceptible to pathology due to their vulnerable psyche not yet fully formed. Deviation also occurs in patients with neuroses, psychoses and delusions.
What to do?
If you think you have Senesthopathy
and the symptoms characteristic of this disease, then doctors can help you: psychiatrist, psychologist, psychotherapist.
We wish everyone good health!
Diseases with similar symptoms
Paresthesia (overlapping symptoms: 4 of 12)
Paresthesia is a specific type of sensitivity disorder, accompanied by a large number of unpleasant sensations. In almost all cases, the pathology is of a secondary nature, that is, it is formed against the background of other ailments.
Did you like the article? Share with friends on social networks: