Causes
Natural wear and tear of spinal structures is the most common cause of myelopathy. As the body ages, the natural wear and tear of the spinal structures causes a process of degeneration. Degenerative changes affect the facet joints, intervertebral discs and ligaments.
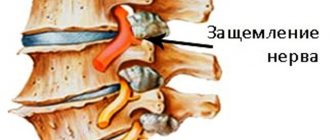
As intervertebral discs age, they begin to shrink and harden and begin to put pressure on nearby structures, including the cartilaginous surface of the facet joints. This adds stress to the joints and prevents them from working properly, which starts a cycle of degeneration. Intervertebral disc degeneration can also lead to a herniated disc, which can compress a nearby spinal nerve root or even the spinal cord, causing a range of unpleasant symptoms.
An intervertebral hernia occurs when a crack or tear appears in the weakened outer shell of the intervertebral disc, through which part of the gel-like contents of the disc (nucleus pulposus) is literally squeezed into the spinal canal under the influence of gravity. Typically, an intervertebral hernia is not so large and is not located in such a way as to compress the spinal cord. As a rule, with a hernia, only compression of the spinal cord root is observed. Symptoms of compression of the spinal cord root can also be very unpleasant and even disabling, but potentially this condition is much less dangerous and, in the vast majority of cases, can be easily treated with conservative methods. The spinal cord can only be compressed by a large hernia located in a certain position, often against the background of an existing spinal canal stenosis. Symptoms of myelopathy, despite the frequent absence of pain, are much more dangerous, since they are manifestations of loss of functions that control the spinal cord.
Read also…. Treatment of degenerative spinal stenosis
Degeneration of spinal structures can trigger the formation of bone growths (osteophytes), which can also compress the spinal nerve roots and sometimes the spinal cord. In addition, against the background of proliferation of vertebral bones, a narrowing (stenosis) of the spinal canal occurs. Since the spinal cord and the spinal nerve roots that extend from it are located just inside the spinal canal, the likelihood that a nerve or spinal cord will be affected increases.
Another common cause of myelopathy is injury, such as from sports, a car accident, or a fall. Such injuries often affect the muscles and ligaments that stabilize the spine. Injuries can also cause bone fractures and joint displacement.
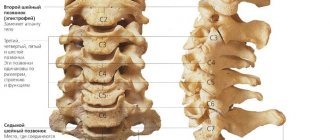
Myelopathy can also be caused by an inflammatory disease, such as rheumatoid arthritis, in which the person's immune system attacks the joints of the spine, usually the cervical region. Less common causes of myelopathy include tumors, infections, and congenital vertebral abnormalities.
Recipes from traditional healers
There are a lot of them. It is unrealistic to present even a small part in one article. Consider complex therapy with traditional methods:
- Every day for a long time, take 1 glass of warm milk in the morning and evening, adding 1 tsp. dead bees, alcohol tincture of propolis and honey. This is a real vitamin and mineral cocktail for the body.
- Spend at least 1 hour outdoors every day.
- Do self-massage of the neck-collar area and part of the thoracic region (wherever you can reach) daily.
- Every day, morning and afternoon, perform a simple set of exercises (see below).
- Every day before going to bed, lie on the Lyapko (or Kuznetsov) applicator for about 30 minutes.
- Ask your relatives to give you a honey massage of your entire spine every day.
- If your health allows, visit the bathhouse once a week, and after it, be sure to drink herbal tea.
Brief information about the disease
This term refers to damage to the spinal cord due to pressure on it due to something affecting the sensory and motor systems. It is not an independent disease. This is a complication that occurs due to pathological processes in the spinal membranes or in the spinal column.
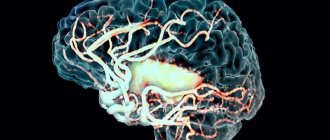
This complication is caused by disruption of the substance by pathological factors, such as compression of large blood vessels, as a result of which the nutrition of the nervous tissue is disrupted, and necrosis also develops. The longer this complication lasts, the more intense the blood flow changes.
Kinds
The classification of spinal canal myelopathy is divided into etiological types:
discogenic or spondylogenic(vertebrogenic myelopathy) - caused by diseases of the joints and intervertebral discs,
- cancerous (occurs against the background of an oncological neoplasm, its toxic effects and compression),
- ischemic (also known as dyscirculatory, caused by high cholesterol, thrombosis, vascular atherosclerosis, diabetes),
- post-traumatic myelopathy (characterized by varying degrees of damage depending on the damage caused by the injury to the integrity of the spinal canal),
- vascular myelopathy (epidural pathology develops as a result of open hemorrhage in the spinal cord following injury).
There are other types of myelopathy , from the name of which you can guess the nature of their occurrence: metabolic, intoxication, inflammatory, radiation.
Treatment
Conservative treatment
Although the best treatment for most patients with myelopathy is surgical decompression of the spinal cord, for those patients in whom symptoms of myelopathy are mild, waiting with constant monitoring is more appropriate. If the symptoms of myelopathy are mild, the doctor may recommend a set of exercises to strengthen the spine and increase its flexibility, various massage techniques, as well as medications aimed at relieving pain, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). In our experience, to treat myelopathy it is necessary to reduce the size of the disc herniation, especially in the case of spinal canal stenosis, since neck operations in case of stenosis lead to more frequent complications and often disable the patient. The use of hirudotherapy will help relieve inflammation, swelling and reduce pain. Hirudotherapy, unlike steroid hormones, has no side effects and is more effective.
Read also…. Intervertebral hernia of the cervical spine
Surgery
The main goal of surgery for myelopathy, as already mentioned, is decompression of the spinal cord. The doctor may choose a laminotomy with a lateral approach (through an incision in the back). With this operation, it is possible to remove part of the vertebral bone tissue that is compressing the spinal cord and, thus, freeing up space for the spinal cord. However, this procedure may not be suitable for all patients as it may lead to instability of the spinal segment and the development of kyphosis. The doctor may also use an anterior approach during cervical spine surgery, which will allow him to see and remove osteophyte or herniated discs that are putting pressure on the spinal cord. During the procedure, your doctor may also perform a spinal fusion (fusion of a spinal segment using a bone graft) to reduce the risk of complications after surgery.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis
To prevent thoracic osteochondrosis and symptoms, treatment and preventive measures are thought out in advance. Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is characterized by bone dystrophy and degeneration. With thoracic osteochondrosis, the composition of the elements of the spine, ligaments, and cartilage changes and is destroyed. The disease causes atherosclerosis, pneumosclerosis, prostate dysfunction and infertility.
- We advise you to read: diagnosis of osteochondrosis.
First, osteochondrosis affects the bones, then the cartilage and muscles. In young people with osteochondrosis of the thoracic region, the musculoskeletal system ages without having time to mature and develop.
Known symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, characteristic of various stages of development of the disease:
- Pressure in the back or chest that interferes with breathing;
- Difficulty turning (tilting) the body;
- Periodic sensations of body numbness;
- Reduced temperature of the lower extremities;
- Itching and burning sensation in the extremities (often in the legs);
- Brittle nails;
- Problems with gastrointestinal tract functions;
- Impaired functioning of the genital organs (decreased potency);
- Nausea;
- Heartburn;
- Migraine-like headache;
- Intercostal neuralgia;
- An unpleasant feeling in the anterior part of the peritoneum;
- Pain in the left side of the sternum, reminiscent of heart pain;
- Reflex tension in the back and chest;
- Acute pain at the level of the liver and gall bladder;
- Sometimes shingles.
Diagnostics
To detect the cause of the disease, assess the degree of damage to the spinal canal and paravertebral tissues, and determine the likelihood of the consequences of myelopathy, the specialist uses magnetic resonance and computed tomography , electromyography, biochemical blood tests, cerebrospinal fluid culture, PCR, and x-rays.
Based on the results of laboratory tests and recommendations of an oncologist, vertebrologist, surgeon, neurologist and other specialists, myelopathy therapy is prescribed by the attending physician.
Clinical manifestations
Regardless of the etiofactors, during the formation of the pathological process, the patient may experience the following clinical picture:
- Reflex dysfunction.
- Reduced sensitivity.
- Low grade fever
- Dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
- Painful syndrome in the damaged area radiating to the intercostal and sternal area.
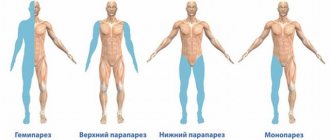
- Paresis and paralysis of the arms and legs.
Algia in the thoracic spine has been observed for several weeks. It has a pronounced and vivid characteristic, intensifying at the moment of deep breaths and bending of the body. In some cases, intensification of the pain syndrome at night may be observed, followed by regression in the morning.