One of the most unpleasant and painful ailments these days is back neuralgia .
It occurs quite often among adults, children and young people. Pain occurs due to the nerve being pinched by the surrounding inflamed tissue, so most often this problem develops in narrow spaces between bones (for example, between the ribs on the back).
Usually, specialists are contacted with already advanced cases, which is fundamentally wrong.
You should see a doctor as soon as you start to notice pain in your back, rather than overusing painkillers and waiting for a miracle.
How to cope with a problem such as back neuralgia? Is there a number of activities that can relieve hateful pain?
Numbness of body parts after a stressful situation
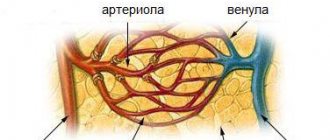
Numbness is a painful, uncomfortable tingling sensation, which is accompanied by a decrease in skin sensitivity, and less commonly, a disruption of the normal functioning of the joints of the fingers of the right or left foot or hands. Parts of the body become numb because a nerve is compressed or the blood supply to tissues is disrupted.
- no ability to move your toes or hands normally;
- feeling weak, dizzy;
- the bladder empties involuntarily;
- partially or completely unable to speak clearly or move adequately.
Numbness often affects a person’s limbs
Muscle pain often appears after training and excessive physical activity. It does not require drug treatment. Wandering pain in joints and muscles can be a manifestation of systemic neurosis. Muscle pain during neurosis occurs for no apparent reason.
In this case, patients at the Yusupov Hospital are advised by a psychotherapist. Constant muscle pain occurs due to intoxication during infectious diseases of a viral or bacterial nature.
There are muscle pains due to hormonal disorders in women and men. Aching muscle pain appears after heavy physical labor. Pain in the muscles of the neck, armpits, and groin bothers patients with immunodeficiency conditions (AIDS). Pain in all joints and muscles occurs simultaneously in patients suffering from systemic degenerative diseases of the nervous system.
Muscle pain may occur after the plate is removed from the collarbone. Pain in the neck muscles when turning the head is a manifestation of cervical osteochondrosis. Muscle pain under the left shoulder blade can occur with intercostal neuralgia or be one of the symptoms of myocardial infarction. The cause of pain in the trapezius muscle of the neck is osteochondrosis.
Muscle pain in the lower back is a sign of protrusion of intervertebral discs. It can be difficult to distinguish from kidney pain. Pain in the trapezius muscle on the left always alarms doctors, since it can be caused by osteochondrosis, myositis, or coronary heart disease. Pain in the pectoral muscle on the left may be a symptom of myocardial infarction. If a patient experiences walking muscle pain, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital conduct a comprehensive examination.
Sometimes wandering pain does not occur throughout the body, but in certain places. Pain in all joints and muscles simultaneously appears with arthralgia. This may be an independent disease associated with irritation of neuroreceptors in the synovial bursa of the joint or a harbinger of arthritis or arthrosis.
There are the following main causes of muscle-joint pain:
- joint injuries;
- viral or bacterial infections;
- neoplasms;
- disturbances in the functioning of the immune system;
- excess stress on joints and muscles.
Joint pain can be aching, sharp, or dull. It occurs in one or another joint. At the same time, patients complain of muscle pain. How to distinguish joint pain from muscle pain? Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital carry out a differential diagnosis of pain syndrome after receiving the results of instrumental and laboratory tests.
Pain in the gluteal muscle is typical for people who work at a computer and representatives of sedentary office professions, athletes, and cyclists. It can be different:
- shooting in the buttock;
- radiating to the gluteal region;
- sudden and acute.
The most likely causes of buttock pain are:
- osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral region;
- intervertebral hernia;
- lumbosacral radiculitis;
- injuries;
- tendinitis (inflammation of the tendon);
- rachiocampsis;
- hip arthritis;
- fibromyalgia.
For this reason, if pain in the buttock occurs, you can take a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug tablet orally, rub the buttock area with anesthetic ointment, and rest. In order to find out the cause of the pain syndrome and undergo a course of treatment, contact the Yusupov Hospital.
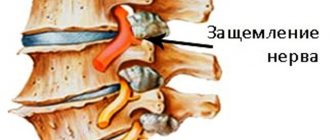
Wandering back pain has the same causes as painful sensations in the joints. In many cases, the culprit is arthralgia, associated with compression of nerve endings in one of the parts of the spine. When pinched, a circulatory disorder or spasm of the periarticular muscles occurs, which entails irritation of neuroreceptors and discomfort.
Causes
This pathology can be primary, that is, it occurs without special prerequisites, or secondary. In such a situation, the pain is explained by pathological changes in the neck area.
Secondary neuralgia develops under the influence of such factors:
- Osteochondrosis. This disorder, which can occur in the cervical spine, often provokes degenerative processes in the intervertebral discs. As a result, there is a disruption of the nerve roots located in the back of the head.
- Prolonged tension in muscle tissue of a static nature. It may be a consequence of a violation of the position of the body. This condition is provoked by prolonged use of the computer. It can also be the result of stress or heavy physical activity.
- Neck injuries. They can lead to compression of nerve endings.
- Hypothermia.
- Gout. This disease can lead to joint damage.
- Arthritis. This disease can affect joints located in the cervical region.
- Complex forms of viral pathologies.
- Oncological diseases. They can affect the brain or cervical spinal cord.
- Infectious pathologies. Diseases such as encephalitis and meningitis can lead to damage to nerve tissue.
- Endocrine disorders. Neuritis of the occipital nerve can be a consequence of diabetes mellitus.
- Autoimmune disorders. When such problems develop, the immune system negatively perceives nerve cells. Such diseases include lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis or.
- Inflammatory processes in blood vessels.
- Tuberculous spondylitis.
What are the symptoms of nerve irritation?
If the spinal column and spinal nerve roots are suddenly exposed to excessive force, acute radiculitis occurs, the main symptom of the disease will be vertebral neuralgia.
With degenerative and metabolic disorders, the process is chronic; pressure from an osteophyte, hernia, tumor or other formation is gradually exerted on the roots. Symptoms will gradually increase as the disease progresses.
It is worth understanding how radiculitis in various parts of the spine will manifest itself, since further diagnosis and treatment will depend on this. Inflammation of the roots of the cervical and lumbosacral regions, for example, will have a completely different clinical picture.
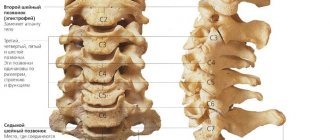
Diseases of the cervical spine are not uncommon, since this segment of the back is actively involved in holding the head when walking, running, sitting at a table, or working at a computer. The vertebrae in this part of the spine have a rather vulnerable structure, and at the same time they are in close interaction with important vessels and nerves.
If a spinal disease has led to inflammation of the nerve root in the cervical back, the following manifestations are likely to occur:
- Pain in the back of the head and neck, aggravated by exertion or prolonged immobile work.
- Pain in the shoulder blade, along the collarbone, in the area of the shoulder joint.
- Numbness, pain, loss of sensitivity in the hand. Radiculitis of the lower parts of the neck is manifested by disruption of the brachial plexus, which is responsible for the innervation of the upper limb.
- Loss of muscle strength in the arm.
- Headaches, migraines, dizziness are a sign of insufficient blood flow through the vertebral artery.
- Blood pressure disorders.
Most often, the disease manifests itself as neuralgia - pain at the exit site of the root and along the nerve fibers. Other signs appear if there is strong pressure on the nerve structures, or the inflammatory process becomes extensive.
The rarest form of radiculitis is damage to the thoracic region. The reason for this phenomenon is that a large number of vertebrae in the thoracic floor of the back take on part of the lost function, and the disease takes a long time to compensate.
In addition, in the thoracic region there are no such important structures as nerve plexuses or cauda equina, so only the spinal roots are involved in the process. Radiculitis of the thoracic region is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Pain in the thoracic part of the back, aggravated by exercise.
- Shootings along the chest, following the course of the ribs.
- Intercostal neuralgia can even mimic heart disease, occurring in the left side of the chest.
- Difficulty taking a deep breath due to chest pain.
Poor symptoms lead to the pathological process not being diagnosed for a long time. Dangerous diseases can be detected too late, so at the first symptoms you need to consult a doctor.
The most common location of radiculitis is the lumbosacral segment. This explains the large number of patients complaining of lower back pain.
The thing is that it is on the area of the lumbosacral floor that most of the load falls during active movements, lifting weights, and playing sports. Under the influence of these factors, degeneration occurs, which leads to aseptic inflammation of the nerve roots. Symptoms of lumbar radiculitis:
- Pain in the lower back after exertion, bending, standing for a long time, or lifting heavy objects.
- Shooting pain along the spine - in the buttock, thigh, and other parts of the lower limb.
- Impaired skin sensitivity in the leg, numbness, “crawling” feeling.
- Pain when pressing on the spinous process of the involved vertebra.
- Inability to stand for long periods of time.
- Pain when trying to straighten your back during an attack of neuralgia.
Radiculitis itself causes a lot of inconvenience, but it is also a manifestation of another disease. If the cause of neuralgia progresses, it may involve the nerve structure of the cauda equina, which is responsible for the innervation of the bladder and rectum.
How to recognize inflammation of nerve endings and the symptoms of this disease? The main symptom is pain, while neither the focus nor visible changes indicating the disease can be identified. The pain may worsen in the cold, during movement or at night, even with slight touch.
Symptoms of neuritis
The clinical picture of neuritis is determined by the functions of the nerve, the degree of its damage and the area of innervation. Most peripheral nerves consist of nerve fibers of different types: sensory, motor and autonomic. Damage to each type of fiber gives the following symptoms characteristic of any neuritis:
- sensitivity disorders - numbness, paresthesia (tingling sensation, “crawling sensations”), decreased or loss of sensitivity in the innervation zone;
- violation of active movements - complete (paralysis) or partial (paresis) decrease in strength in innervated muscles, development of their atrophy, decrease or loss of tendon reflexes;
- vegetative and trophic disorders - swelling, cyanosis of the skin, local hair loss and depigmentation, sweating, thinning and dry skin, brittle nails, the appearance of trophic ulcers, etc.
Typically, the first symptoms of nerve damage are pain and numbness. In the clinical picture of some neuritis, specific manifestations associated with the area innervated by this nerve may be noted.
Neuritis of the axillary nerve is manifested by the inability to raise the arm to the side, decreased sensitivity in the upper 1/3 of the shoulder, atrophy of the deltoid muscle of the shoulder and increased mobility of the shoulder joint.
Diagnostics
The diagnostic search for a doctor begins with a conversation and questioning of clinical symptoms, then the doctor will conduct an objective examination of the spine and specify neurological symptoms. Often, to determine the cause of the disease, a consultation with a neurologist may be required.
The next step is to examine the patient's tests. A general blood and urine test will allow you to exclude or confirm an infectious process. In case of aseptic inflammation of the roots, tests are not very informative. After laboratory testing, the patient will be referred for instrumental procedures. These include:
- X-ray of the affected part of the spine - excludes or confirms the pathology of bone formations, including spondyloarthritis, vertebral fractures, osteophytes, spondylolisthesis.
- CT and MRI are highly accurate methods that can detect the process at the initial stage. MRI perfectly detects vertebral pathology, therefore it is the best method for diagnosing osteochondrosis.
- X-ray contrast methods – myelography. Rarely used due to the risk of possible complications.
- Electromyography is an assessment of the conduction of electrical impulses during excitation of muscle fibers. It is used in the presence of symptoms from the upper or lower extremities.
- Cerebrospinal fluid analysis. Puncture is associated with certain difficulties and the risk of complications, so it is used if necessary, if infectious causes are suspected.
The listed list of studies changes depending on the data received and the doctor’s suspicion of the presence of a certain pathology.
Why does my stomach hurt from nerves?
When a person finds himself in a stressful environment, a malfunction occurs in the nervous system, which affects the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Changes occur in the digestive glands. The brain gives a signal to release cortisol and adrenaline - stress hormones - into the blood. Stress hormones affect each person differently. Some people lose weight and lose their appetite. Others, on the contrary, begin to eat a lot, filling themselves with a variety of taste sensations and avoiding thoughts of troubles. The result of uncontrolled undereating or excessive overeating is gastrointestinal disorders and cramps.
Among the causes that affect nerve pain in the abdominal area are:
- Feelings of fear or stress. This could be any situation related to the outside world. Fear of management or colleagues.
- Anxiety, excitement, worries. The child doesn’t listen, someone close to you gets sick, there’s trouble at work.
- Overexcitement or neurosis. Waiting for a long-awaited event, constant thoughts about something grandiose and resource-intensive.
Nausea, vomiting, acid reflux, diarrhea or constipation, gas formation begins. Symptoms can appear all together or separately.
Eating certain foods that can cause allergies can cause symptoms similar to those associated with nerve pain.
In this case, you need to pay attention to the following indicators:
- duration of illness;
- lack of lasting effect from standard drugs;
- persistence of pain.
The organs of the human digestive system can be severely damaged due to nervousness. Constant discomfort and increased sensitivity of the gastrointestinal tract lead to chronic abdominal diseases.
Take the Attention Test! Find 10 differences! (click right here!)
Localized muscle-joint pain
Pain in the piriformis muscle occurs when the trunk of the sciatic nerve and the vessels that go with it are compressed in the infrapiriformis space. The main factor of compression is the spasmodic and altered piriformis muscle. Pathological persistent contraction of the piriformis muscle is accompanied by thickening of its abdomen.
The main symptom of piriformis syndrome is persistent and often treatment-resistant pain. Diagnosis of piriformis muscle syndrome consists of physical examination data and the results of additional instrumental research methods. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital include medicinal and non-medicinal measures in the treatment regimen for piriformis muscle syndrome.
In cases of persistent and severe pain and movement disorders, doctors at the neurology clinic perform a therapeutic blockade with local anesthetics and glucocorticoids. Rehabilitation specialists use the following techniques:
- massage;
- physiotherapeutic treatment;
- manual therapy using post-isometric and post-reciprocal muscle relaxation;
- reflexology based on acupuncture, vacuum and laser acupuncture.
The exercises, carried out with the help of a senior exercise therapy instructor, are aimed at relaxing the piriformis muscle and simultaneously activating its antagonists.
The causes of pain in the trapezius muscle are the following:
- working on a computer;
- passive lifestyle;
- problems with the cervical spine;
- arthrosis of the shoulder joint.
If pain suddenly appears, you should rest, avoid heavy loads and strain, and do a gentle warm-up. Every 1.5 hours, you can apply an ice pack to the trapezius area for 15 minutes.
Rehabilitation specialists recommend performing the following exercises for pain in the trapezius muscle:
- clasp the back of your head with your hand, which is located on the side of the painful area of the trapezius, and hold for several seconds;
- tilt your torso forward, lowering both arms;
- put both hands on the back of your head, take a deep breath, hold your breath for 5 seconds, press your head as close as possible to your hands (repeat the exercise 5 times).
Pain in the rhomboid major muscle occurs when the back muscles weaken. Many bodybuilders and weightlifters overwork their pectoral muscles and end up with a slouched figure. The force of an overworked pectoral muscle pulls the shoulders forward, and the subsequent stress on the rhomboid muscle weakens them, resulting in the development of pain areas.
Pain in the rhomboid muscle is felt along the inner edge of the shoulder blade. It does not depend on movement. An attack of pain can also occur during rest. A simple way to relieve stress points in the rhomboid muscle is to lie on the floor and place a ball between your shoulder blade and spine. For comfort, you need to rest your head on a thin pillow.
Do some stretching. Sit on a chair, lean forward and lower your head. Grab your opposite knees with crossed hands. Hold this position for 20 seconds. To prevent developing a slouched posture while sitting, lift your upper chest and lower your shoulder blades. Place the lumbar support on your lower back, slightly above your waist. A rolled towel works well for these purposes.
Inflammation of the occipital nerve
Inflammation of the occipital nerve leads to frequent headaches. Pain occurs in the back of the head and radiates to the front and sides of the head. Often, patients describe pain similar to what they experience with migraine. The scalp can also become very sensitive to various types of touch. For example, even when trying to comb your hair, unpleasant painful sensations occur.
By the way, with occipital inflammation of the nerve endings, doctors often encounter some difficulties. They are due to the fact that it is often difficult at this stage to distinguish inflammation from other causes that cause headaches. Therefore, the patient is obliged to describe all the symptoms present in as much detail as possible and honestly answer the doctors’ questions.
If headaches bother you constantly, you should immediately consult a specialist. In this case, taking exclusively painkillers, which the patient chooses at his own discretion at the pharmacy, is not enough. Doctors often conduct complex diagnostics, including computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.
If the inflammation does not require surgical intervention, the doctor will prescribe treatment aimed at relieving pain. Drug treatment is combined with physiotherapy procedures and massage. In addition, doctors recommend getting more rest. Additionally, a course of anticonvulsants and steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed.
Cases where surgical intervention is required to treat a disease occur less frequently. For chronic pain and lack of positive results from conservative treatment methods, surgery is indicated.
Treatment of inflammation of nerve endings
Some patients associate back pain exclusively with sciatica. However, the inflammatory process in the spine may be of a different location. The following structures may be affected by inflammation:
- Vertebral bodies.
- Intervertebral joints.
- Intervertebral discs.
- Ligaments of the spine.
- Back muscles.
- Spinal cord, nerve plexuses.
- Meninges.
Qualified specialists will help you differentiate between diseases and choose the optimal treatment.
What treatment can be given for inflammation of nerve endings? To eliminate the symptoms of the disease, medications are used: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac, Nise, Movalis, etc.), glucocorticoid hormones (dexamethasone, prednisolone, etc.), B vitamins and other drugs.
Is it possible to cure inflammation of nerve endings without drugs? Our nervous system produces its own painkillers - endorphins and enkephalins; a person can initiate or enhance their synthesis. In addition, special gymnastics can relieve muscle spasms, improve blood supply to the source of inflammation and eliminate pain.
There are also other methods and techniques to combat pain and inflammation. You can learn more about them at a special course at the M.S. Center. Norbekov "First health course." Wellness courses will teach you how to restore physical health, increase immunity, launch regeneration processes, and normalize your emotional background.
Treatment of neuritis
Therapy for neuritis is primarily aimed at the cause that caused it. For infectious neuritis, antibacterial therapy (sulfonamides, antibiotics), antiviral drugs (interferon derivatives, gamma globulin) are prescribed. For neuritis resulting from ischemia, vasodilators are used (papaverine, aminophylline, xanthinol nicotinate); for traumatic neuritis, the limb is immobilized. Anti-inflammatory drugs (indomethacin, ibuprofen, diclofenac), analgesics, B vitamins are used and decongestant therapy is carried out (furosemide, acetazolamide). At the end of the second week, anticholinesterase drugs (neostigmine) and biogenic stimulants (aloe, hyaluronidase) are added to treatment.
Decompression. In the absence of signs of nerve recovery or the appearance of signs of its degeneration, surgical treatment is also indicated, which consists of suturing the nerve; in some cases, nerve plastic surgery may be required.
Rheumatoid arthritis pain
In patients diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis, muscle pain subsides somewhat after performing active movements. Pain syndrome often accompanies people in the first half of the day, especially in the morning. By the evening the pain subsides, and in the morning everything repeats again. At a late stage of the disease, the pain does not subside even at night.
Rheumatoid arthritis causes poor circulation, joint deformation and muscle atrophy. A person becomes not only incapacitated, but subsequently will not be able to take care of himself, since the joints lose their mobility. Rheumatologists at the Yusupov Hospital establish an accurate diagnosis using modern diagnostic methods:
- determination of rheumatoid factor in the blood;
- radiography of joints;
- general and biochemical blood test;
- computed tomography.
Doctors puncture the joint and collect synovial fluid for microscopic examination, and perform a biopsy of the nodules. Timely diagnosis of the disease allows rheumatologists at the Yusupov Hospital to provide adequate therapy. The earlier it is started, the more effective the treatment regimen and the lower the risk of complications.
The treatment of rheumatoid arthritis is based on the principle of providing rest to the affected joints, since additional stress leads to increased inflammation and pain. Sometimes patients are prescribed bed rest for a short time with several joints immobilized. To do this, rheumatologists in the therapy clinic apply splints to the affected areas.
The treatment regimen includes modern drugs that are highly effective and have a minimal range of side effects:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- long-acting drugs (penicillamine, sulfasalazine, plaquenil and gold compounds);
- glucocorticoid hormones;
- immunosuppressants (azathioprine, methotrexate and cyclophosphamide).
Drug therapy is combined with therapeutic exercises, physiotherapy, exposure to high and low temperatures (cryotherapy). Sometimes surgery may be required. Water procedures are very effective when, during exercise in the pool, the joints actively move, but do not experience stress.
Make an appointment with doctors by calling the Yusupov Hospital. Highly qualified specialists will determine the cause of pain in the joints and muscles and provide comprehensive treatment and rehabilitation.
Symptoms
The main manifestation of this pathology is headache, which has certain features:
- Discomfort appears suddenly and increases significantly when turning the head or touching the occipital nerves.
- Usually the pain is localized only on one side, although sometimes a bilateral process is diagnosed.
- The pain is usually felt in the back of the head, lower neck or behind the ears. It can also be felt in the eye and eyebrow area.
- Unpleasant sensations occur when touching the scalp.
- The pain resembles a lumbago, and it also disappears suddenly.
- A person has a high sensitivity to light sources.
When the lesser occipital nerve is affected, the discomfort is usually localized behind the ears, so the diagnosis is often misdiagnosed. If the large nerve is affected, pain occurs in the back of the head. In addition, symptoms of inflammation of the occipital nerve often include pain in the eye area.