A peripheral nerve disease of an inflammatory nature, characterized by impaired sensitivity, the appearance of painful sensations along the nerve, and muscle weakness, is called neuritis. Damage to the peripheral nerve trunk can lead to paralysis.
It is important to distinguish this disease from neuralgia. Neuritis is a disease whose development is caused by an inflammatory process, but neuralgia is a term that denotes painful sensations along the nerve trunk. Neuralgia, unlike neuritis, occurs due to a bruise or any other injury, while neuritis occurs due to inflammation.
What is neuritis?
Neuritis is an inflammatory disease of peripheral nerves, characterized by a decrease or complete loss of sensitivity, as well as motor disorders of the tissue innervated by this nerve.
It should immediately be noted that innervation is the supply of various tissues and organs with nerves, through which the central nervous system (CNS) provides them with sensitivity and motor function.
Neuritis can also cause the development of partial (paresis) or complete paralysis.
Most often, the optic, auditory, facial, trigeminal, radial and sciatic nerves are affected by the disease.
If the inflammatory process develops in one place, the disease is called neuritis, while damage to nerves in several places is called polyneuritis.
The main symptoms of neuritis (manifested at the site of inflammation) are decreased sensitivity, numbness, partial or complete impairment of motor function, and pain.
The main causes of neuritis are infections, trauma, tumors, hypothermia, poisoning, various diseases (osteochondrosis, arthritis, diphtheria and others).
Development of neuritis
Thanks to the nervous system, we can see, hear, smell, move, breathe, etc.
The collection of nerves in the body form the peripheral nervous system.
A nerve is a part of the nervous system, which consists of bundles of nerve fibers covered with a sheath, providing communication between the brain (cerebral, spinal) and other parts of the body, organs, and tissues.
There are also blood vessels inside the nerve.
The largest nerves are called nerve trunks, after which they branch significantly, and at the end points, control of the tissue/organ by the nervous system can be achieved with just one nerve fiber. The structure of the nerve may differ depending on its location.
The mechanism of development of neuritis is quite complex, but is caused mainly by disturbances in the nerves - metabolic and vascular processes, their injury, tumors, and infection.
These factors lead to the destruction of myelin and Schwann cells, which are involved in the transmission of nerve impulses along the fibers. With severe pathology, the axial cylinder is also destroyed. At the same time, the nerve fibers are not able to perform the function of transmitting nerve impulses from the brain to the tissues, which is why the latter are not able to perform their functions.
Neuritis, neuralgia and neuropathy (neuropathy) - difference
This is also an interesting question, since various sources combine these concepts, indicating the sameness of this disease. However, in clinical practice these concepts are separated, since the causes, localization, symptoms and further treatment regimen may differ slightly.
Let's consider the distinctive features of these concepts.
Neuritis is characterized by inflammation of the peripheral nerve itself, in which pronounced changes also occur. The inflammatory process involves the myelin sheath (contains myelin and is located inside the glial sheath of the nerve) and the axial cylinder.
Neuropathy (neuropathy) is a disease of peripheral nerves (most often nerve trunks) of a non-inflammatory nature, in which degenerative and metabolic damage to the nerves occurs. The causes of neuropathy are usually impaired blood supply, injury, and metabolic disorders. Symptoms of neuropathy are decreased sensitivity, decreased reflexes, and decreased strength. Neuropathy in psychiatry is diagnosed in the case of increased excitability of the nervous system with increased fatigue.
Neuralgia is characterized by inflammation of the peripheral nerves, but loss of sensitivity, paresis, paralysis and impaired motor activity in the innervation zone are not observed, nor are there any (or minimal) structural changes in the nerve itself. The main symptom of neuralgia is pain (often severe) at the site of innervation, decreased sensitivity. There may be autonomic disorders.
Neuritis statistics
According to medical statistics, neuritis most often occurs in older people, especially women.
Neuritis - ICD
Neuritis: ICD-10 - M79.2, ICD-9: 729.2; Neuropathy: ICD-10 - G60-G64;
Forecast
The prognosis of neuritis is extremely varied and depends on its etiology. If the harmful (most often infectious) cause has ceased to have its effect, a gradual restoration of the functions of the affected nerve always begins to appear.
The ability of the peripheral nerve to regenerate makes it possible for even severe neuritis to result in complete functional restoration.
However, more or less significant residual effects are not uncommon. Often the intensity of these phenomena directly depends on insufficiently energetic or incorrect treatment.
The information presented in this article is intended for informational purposes only and cannot replace professional advice and qualified medical care. If you have the slightest suspicion that you have this disease, be sure to consult your doctor!
Symptoms of neuritis
The first signs of neuritis:
- Feeling of pain at the site of the inflammatory process;
- Numbness of the innervated area;
- Tingling sensation.
Main symptoms of neuritis:
The main symptoms of neuritis depend on the type of nerve fibers affected - sensory, motor and autonomic, as well as on the cause and severity of the inflammatory process:
Inflammation of sensory fibers causes paresthesia (decreased sensitivity, goosebumps, numbness and tingling in the innervation zone), and a feeling of pain.
Inflammation of motor fibers is caused by impaired motor function (paresis - partial, paralysis - complete), weakening and/or atrophy of muscles, decreased or loss of tendon reflexes.
Inflammation of vegetative fibers is caused by local hair loss, skin depigmentation (the appearance of vitiligo), xeroderma, thinning and swelling of the skin, fragility of the nail plate, the appearance of trophic ulcers, increased sweating and others.
Additional symptoms of neuritis
The following symptoms are characteristic of different types of neuritis, and depend mainly on the location of the innervated area/organ/tissue:
Neuritis of the facial nerve (Bell's palsy) is an inflammation of the nerve responsible for the work of the facial muscles of one half of the face. Symptoms of facial neuritis are the appearance of weakness in the facial muscles, which manifests itself in the form of partial or complete absence of facial movements, as well as facial asymmetry, similar to the consequences of a stroke. With neuritis of the facial nerve, on the affected side, wrinkles on the forehead are also smoothed out, the eyelid is drooping, and the corner of the mouth is drooping.
Symptoms – signs and symptoms of nerve inflammation
The symptom complex of the disease in question will be varied. This is due to the location of the nerves - they can be found anywhere in the body, from the eyeball to the toes.
The complaints of patients will depend on the location of the neuritis:
- When the optic nerve becomes inflamed, abilities in the aspect of vision will be reduced/lost. The patient complains of pain in the eyes, a yellowish tint to the eyeball is noted.
- Errors in the functioning of the auditory nerve manifest themselves as hearing loss and can lead to deafness. If the disease in question has affected the nerves of the face, the patient experiences paralysis of the muscle tissue, the corner of the mouth droops, and there are no folds on the forehead. The eye is unable to close, the tongue becomes sensitive, taste may be partially/completely lost. Increased lacrimation may be present. If this phenomenon is ignored, total facial paralysis will actually develop.
- In case of mercury poisoning, a rash and plaque can be visualized in the patient’s mouth. In rare cases, body temperature rises and the sense of smell becomes dull.
- Inflammatory phenomena that occur in the nerve fibers of the limbs, cause tingling, numbness, pain, lack of
sensitivity. Procedures in the form of flexion/extension of the elbow and knee joints are accompanied by severe pain. If the nerves of the lower extremities are affected, errors in gait and partial/complete paralysis of muscle tissue may be visualized. The upper limbs regularly go numb, the patient confirms muscle weakness. When the ulnar nerve is damaged, it is difficult for the patient to clench his palm into a fist: the fingers are slightly splayed. If inflammation occurs in the radial nerves, then spreading your fingers is unrealistic.
- Inflammation of the nerve fibers of the vestibular apparatus is characterized by attacks of nausea and vomiting.
Rate
—
Causes of neuritis
Among the main causes of neuritis are:
- Injuries (various fractures, tears, cracks, bruises, electric shock, radiation exposure, etc.);
- Inflammatory processes in the body of various organs (otitis media);
- Tumors;
- Infection of the body - viruses (herpes zoster virus), bacteria and other pathological microorganisms;
- The presence of various diseases - diphtheria, measles, influenza, arthritis, osteochondrosis, kyphosis, scoliosis, lordosis, intervertebral hernia, atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension, vegetative-vascular dystonia, tunnel syndrome, allergies, thyrotoxicosis, diabetes mellitus, brucellosis, uremia, rheumatism, herpes , syphilis, malaria, leprosy, blood diseases;
- Dehydration of the body;
- Hypothermia of the body;
- Poisoning of the body - food, alcohol, drugs, chemicals;
- Hypovitaminosis (vitamin deficiency);
- Hereditary factors (features of body structure).
Manifestations of neuritis can also appear during prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position - during sleep, at sedentary or other sedentary work.
Physiotherapy
In a clinical setting, undergo physical therapy - this will significantly reduce the number of medications used. During the treatment of an inflamed sciatic nerve, current, magnetic field, ultrasound - in a word, irritating active effects on the sacral region - are very helpful. For example, electrical neurostimulation acts on different areas of the skin with certain currents, which quickly relieves pain.
The problem of neuralgia cannot be considered solved after the acute inflammation is relieved. It is necessary to cure the underlying disease. You may be prescribed a spinal stretch, since some back diseases are associated with a reduction in the distance between the vertebrae. It is necessary to regularly hang on a wall bars or horizontal bar, or undergo a course of treatment using an augravity installation.
Problems with the spine are solved with the help of physical therapy and manual therapy. Typically, these measures are allowed by vertebrologists and neurologists with caution, subject to the necessary research. Find an experienced manual with a good history of recovery for his patients diagnosed with sciatica, only then begin active therapeutic measures.
Attention!
Use of materials from the site “
www.site
” is possible only with the written permission of the Site Administration. Otherwise, any reprint of site materials (even with an established link to the original) is a violation of the Federal Law of the Russian Federation “On Copyright and Related Rights” and entails legal proceedings in accordance with the Civil and Criminal Codes of the Russian Federation.
Neuritis is characterized not only by inflammatory processes, which are observed in one or more groups of nerves. Negative transformations occurring in the nervous tissue and nearby areas are associated with neuritis. The body's reaction is a partial loss of sensitivity and reflexes.
Types of neuritis
The classification of neuritis is as follows:
Type:
- Mononeuritis - the development of the inflammatory process occurs in one nerve;
- Polyneuritis - the development of inflammation occurs simultaneously in several nerves.
With the flow:
- Spicy;
- Subacute;
- Chronic.
By localization
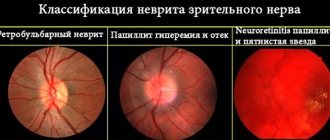
Optic neuritis – an inflammatory process develops in the optic nerve; divided into:
- Orbital (retrobulbar) neuritis - inflammation develops in the optic nerve located outside the eyeball - from the exit from the sclera to the chiasm.
- Axial retrobulbar neuritis - inflammation develops in the maculopapillary bundle of the optic nerve, which is often accompanied by optic nerve atrophy and vision loss.
- Interstitial retrobulbar neuritis - inflammation develops from the optic nerve sheath to the nerve trunk, deep down.
- Peripheral retrobulbar neuritis - inflammation begins with the optic nerve sheaths, then spreads along the septa to its tissue; proceeds to the interstitial type, with the formation of exudative effusion, accumulating in the subdural and subarachnoid space;
- Transversal neuritis - the inflammatory process spreads to the entire optic nerve, initially developing in the axial fascicle or in the periphery, and then affects other tissues;
- False optic neuritis is an anomaly in the development of the optic nerve, the clinical picture resembles an inflammatory process, while there is no atrophy of the optic nerve or visual dysfunction.
Axial neuritis - inflammation develops in the axial cylinders of the nerve fiber (axon).
Interstitial neuritis - inflammation develops in the connective tissue of the nerve, most often caused by autoimmune processes.
Parenchymal neuritis - inflammation initially develops in nerve fibers (axons and myelin sheath), after which it spreads to the connective tissue parts of the nerve.
Autonomic neuritis - inflammation develops in the peripheral fibers of the autonomic nervous system, accompanied by trophic disorders.
Ascending neuritis - develops mainly when the peripheral part of the arms and legs is injured, after which the pathological process from the periphery moves to the center of the nervous system.
Cochlear neuritis - inflammation develops in the cochlear part of the auditory nerve, the symptoms of which are tinnitus and decreased sound perception.
According to clinical manifestations:
Gombeau's neuritis is characterized by the disintegration of the myelin sheath of nerve fibers, while the axial cylinder remains intact.
Hypertrophic Dejerine-Sotta neuritis is characterized by hypertrophy of the sheath of nerve fibers, which initially leads to compression of the conductive part of the nerve, after which the nerve begins to gradually degenerate and lose its functionality.
Rossolimo neuritis is one of the forms of hypertrophic Dejerine-Sotta neuritis, characterized by a recurrent course and occurring mainly in childhood.
By etiology (cause of occurrence):
Traumatic neuritis - the development of the disease is caused by nerve injury.
Occupational neuritis - the development of the disease is caused by a person’s professional activity - poisoning (chemical fumes, heavy metals and other substances), exposure to vibration on the body.
Infectious neuritis - the development of the disease is caused by infection of the body, infectious diseases.
Alcoholic neuritis - the development of the disease is caused by alcohol consumption, the effect on the body of which is the removal from the body of B vitamins, which are responsible for the functioning of the nervous system, as well as dead brain cells (the process of cell death occurs during alcohol intoxication).
Pathological anatomy
The pathological picture of mononeuritis varies, depending on whether purely inflammatory or degenerative phenomena predominate in one case or another. In the first case, during acute processes, the nerve trunks macroscopically appear swollen and reddened. Mainly in the perineural connective tissue, but often also in the endoneural connective tissue, inflammatory phenomena occur: hyperemia, edema, vascular thrombosis, hemorrhages, and round cell infiltrations are observed here. In later stages or in cases that are chronic from the very beginning, instead of these acute inflammatory phenomena, there is pronounced sclerosis of the connective tissue, which can sometimes lead to nodular thickenings clearly located along the nerve trunk (“neuritis nodosa”). This picture of interstitial inflammation is naturally mixed with the death of the nerve fibers themselves. To the periphery of such affected areas stretches an area of typical secondary (so-called Wallerian) degeneration of nerve fibers, often leading to secondary atrophic phenomena in the muscle.
On the contrary, in cases with a predominantly parenchymal-degenerative nature of the process, inflammatory phenomena in the peri- and endoneurium recede far into the background or are completely absent. The process comes down to degeneration of the nerve fiber with the breakdown of myelin. In mild cases, this process occurs only in the form of myelin disintegration over a certain extent, which is not accompanied by the death of nerve fibers and naturally does not lead to the development of secondary Wallerian degenerations.
All these educational-degenerative processes often depend not on the penetration of infectious pathogens into the tissue of the peripheral nerve itself, but mainly on its poisoning by toxins formed in the body due to the existence of infection in it.
Diagnosis of neuritis
Diagnosis of neuritis includes the following examination methods:
1. Electromyography;
2. Electroneurography;
3. Functional tests to identify motor disorders:
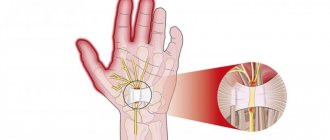
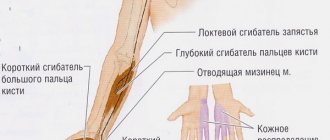
- to determine neuritis of the radial nerve: - the hand lies with the palm on the table, while the patient cannot place the 3rd finger on the neighboring ones; — the back of the hand lies on the table, the patient cannot move the thumb; - in a standing position, arms down, the patient cannot turn the affected hand with the palm forward, and also move the thumb to the side.
- to determine ulnar nerve neuritis: - the hand lies with the palm on the table, while the patient cannot cause scratching movements with the little finger on the table; — the hand lies with the palm on the table, while the patient cannot spread the fingers, especially 4 and 5; - the patient cannot completely clench his fingers into a fist, especially the 4th and 5th fingers; - the patient cannot hold a strip of paper with his thumb and index finger, since the phalanx of one of the fingers does not bend completely.
- to determine median nerve neuritis: - the hand lies with the palm on the table, while the patient cannot cause scratching movements with 2 fingers on the table; - the patient cannot completely clench his fingers into a fist, especially 1, 2, and partially 3 fingers; - the patient cannot oppose the thumb and little finger.
Therapeutic massage of the facial area
Treatment of the trigeminal nerve of the face at home is a set of measures, including drug therapy, massage and heating, aimed at relieving inflammation and normalizing the sensitivity of the facial apparatus. Self-therapy should be carried out only under the supervision of a doctor after an accurate diagnosis of the disease and initial treatment in a medical institution.
Treatment of the facial trigeminal nerve at home is effective through the use of massage, which must be done very carefully, since touching sensitive points can cause a wave of unbearable pain. It is recommended to massage the neck in a circular motion on the painful side, starting from the shoulders and moving towards the chin.
With mild and moderate forms of trigeminal neuritis (that is, with not very acute symptoms), the face can be massaged from the center to the outer part - along classic massage lines. To obtain a more effective result, it is recommended to use massage oil. You can prepare it yourself using bay leaves.
100 grams of fresh or dried product must be filled with 0.5 liters of any vegetable oil, left for a week, strained and used as directed. If it is not possible to massage, it is recommended to lubricate the skin in the area where the trigeminal nerve is located with this product. Treatment at home, reviews of which are positive, is possible only after consultation with a doctor, which is necessary to avoid possible complications.
In older people, as we have already said, the trigeminal nerve becomes inflamed quite often. Treatment at home, according to patients, ensures a quick recovery. In particular, rubbing alcohol helps a lot. You need to take 50 grams of dried plantain raw material, pour it into a glass container and pour a glass of vodka.
Close the jar and leave the healing agent in a dark place for 7 days. The prepared solution should be rubbed onto the painful area. It is recommended to perform these steps before going to bed. Then you should tie a warm down scarf around your head, while trying to carefully wrap your face, and sleep in it until the morning. According to reviews from patients who have used this method, the facial nerve will restore its functions after approximately 6-10 treatment sessions.
In most cases, neuralgia is the result of hypothermia or drafts, since the peak incidence occurs in the off-season, September and March, when the deceptive sun is still (or already) warming and cold winds are blowing. Lack of headwear, clothing not appropriate for the weather and open windows contribute to inflammation of the facial nerve.
A sharp change in temperature causes a spasm of the vessels supplying the nerve, as a result of which it is compressed in the walls of the bone canal and swelling appears. Because of this, the supply of the nerve is weakened and an acute pain symptom appears. Modern neurologists have come to the conclusion that the etymology of this condition is also compression of the nerve by vessels or abnormally enlarged sclerotic plaques.
The cause of neuralgia may also be other reasons:
- Inflammatory processes (otitis, meningoencephalitis) occurring in the middle ear;
- brain tumors;
- injuries to the facial and temporal parts of the skull;
- inflammatory reaction after surgery;
- narrowing of the bone canal as a result of periodontal disease, caries or sinusitis;
- specific bone structure;
- hereditary factor;
- the result of a herpes infection.
If the true cause of neuralgia cannot be established, it is considered idiopathic.
Since inflammation of the facial nerve in most cases is associated with the off-season, special attention should be paid to prevention during this period. To do this, you need to take care of your immunity in a timely manner, avoid hypothermia, avoid drafts and direct exposure of the wind to areas of the face that have already suffered inflammation.
Remember, neuralgic pain of the facial nerve is one of the most severe and difficult to treat. Timely preventive measures will help you avoid an unpleasant condition and lead a full life.
Treatment of neuritis
How to treat neuritis? Treatment for neuritis depends on the type, cause and location of the disease, but usually includes the following:
1. Treatment of the root cause of the disease, i.e. disease or pathological condition that led to nerve disorders; 2. Drug therapy; 3. Physiotherapy. 4. Surgical treatment.
Treating the root cause of the disease
Accurate and thorough diagnosis for neurological disorders is very important, since treatment directly depends on this point. In addition, it is necessary to exclude secondary diseases.
Drug treatment of neuritis (medicines for neuritis)
Important! Before using medications, be sure to consult your doctor!
2.1. Relieving infection
Antibacterial and viral infections are the most common causative agents of various infectious diseases, accompanied by inflammatory processes, intoxication and decreased reactivity of the immune system. And due to the fact that nerve fibers penetrate all parts of the body, it costs nothing for pathological microorganisms to involve the nervous system in the inflammatory process.
Relieving the infection is generally considered more of a point of treating the underlying disease that led to the inflammatory process in the nerve.
Bacterial infections can be treated with antibiotics, while viral infections can be treated with antiviral therapy. In addition, the prescription of a specific antibiotic depends on the type of pathogen.
Antibiotics for neuritis: against staphylococcal infections - Amoxicillin, Vancomycin, Clarithomycin, Erythromycin, Oxacillin, Cephalexin, against streptococcal infections - Azithromycin, Doxycycline, Levofloxacin, Ceftriaxone ", "Cefotaxime", "Erythromycin".
Sulfonamides – antimicrobial drugs for neuritis: “Sulfanilamide”, “Sulfamoxol”.
Antiviral drugs for neuritis: interferon and its derivatives (Betaferon, Interlock, Laferon, Neovir, Reaferon, as well as gamma globulins.
2.2. Detoxification therapy
The waste products of pathogenic infectious agents in the body cause symptoms of intoxication (poisoning), which causes the patient to experience nausea, sometimes vomiting, a feeling of weakness and general malaise. This is also facilitated by the spread of microbes killed through the body due to the use of antibiotics or antiviral drugs.
To remove dead bacteria, as well as their waste products, detoxification therapy is used, which includes:
- Taking sorbents - “Atoxil”, “Polyphepan”, “Enterosgel”;
- Drink plenty of fluids, preferably with added vitamin C (ascorbic acid);
- The use of diuretics (diuretics) - “Diacarb”, “Furosemide”;
- In case of severe intoxication of the body, intravenous infusion of solutions of glucose, polysaccharides (“dextran”) and water-salt solutions, “Urotropin”.
2.3. Anti-inflammatory therapy
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and glucocorticoids (hormones) are used to relieve pain, as well as stop the inflammatory process in the nerves.
Among the drugs in the NSAID group are Ibuprofen and Nimesil.
Among glucorticoids one can o.
It is better to relieve high fever in children using water-vinegar based compresses.
For tunnel syndromes, medications are injected directly into the affected canal - “Hydrocortisone”, “Novocaine”.
If the cause of the inflammatory process is a violation of the blood supply to the nerve (ischemia), vasodilating drugs are prescribed - Papaverine, Eufillin.
2.4. Symptomatic treatment
Sedatives are prescribed to reduce the activity of the nervous system, which leads to a reduction or prevention of the development of muscle spasms - “Persen”, “Bekhterev’s Medicine”.
Additional intake of vitamins is required - B vitamins, vitamin E (tocopherol), vitamin C (ascorbic acid), vitamin PP (nicotinic acid), milgama, neurobion, neurorubin. Vitamin therapy is necessary to restore nerve function.
In addition, for neuritis the following can be used:
- Gravity treatment methods;
- Antihistamines;
- Angioprotectors and antiplatelet agents;
- Proteolytic enzyme inhibitors.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
Physiotherapeutic procedures for neuritis include:
- Plasmapheresis;
- Mud applications;
- Massage of the innervated muscles where the inflamed nerve is located;
- Hyperbaric oxygenation;
- Pulse currents;
- Ultraphonophoresis with hydrocortisone;
- UHF;
- Electrophoresis of novocaine, neostigmine and hyaluronidase.
Additionally, electrical stimulation of the affected muscles can be performed.
Special therapeutic exercise (physical therapy) also has a beneficial effect on the body. Exercise therapy (exercises) for neuritis directly depend on the location and type of the inflamed nerve.
The use of physiotherapy is prescribed on the 6-7th day of treatment for neuritis.
Surgery
Surgical treatment of neuritis is used for:
- traumatic etiology of this disease;
- lack of effectiveness of conservative treatment;
- no signs of nerve recovery.
What is the occipital nerve
Occipital nerves are peripheral branches of the nervous system, responsible for the timely receipt of impulses from the central parts of the brain to the organs and tissues that are located in the back of the head. There are two nerves that provide sensitivity to the skin in the back of the head:
- Large - located in the plexus of the 2nd pair of spinal nerves of the cervical spine, located between the first two vertebrae.
- Small - is a branch of the 2nd, 3rd, 4th pairs of nerves, passes in the lower part of the back of the head from the side, therefore it is often called the suboccipital.
Compression of the roots of these nerve processes leads to their irritation, the development of inflammation, a change in the frequency of impulses and the appearance of intense pain in the back of the head.
Treatment of neuritis with folk remedies
Important! Before using folk remedies against neuritis, be sure to consult your doctor!
Folk remedy for the treatment of auditory neuritis:
Propolis. Pour 40 g of crushed propolis with 96% alcohol and place in a dark place to infuse for a week, shaking it daily. After the infusion, you need to strain and add olive or corn oil to it in a ratio of 1:5. To use, shake the product, then soak a strip of gauze in it and place it in your ear for a day. The course of treatment is 10 times.
Golden mustache. Cut 1 large and 2 small leaves of golden mustache and pour 1 liter of boiling water over them, put on low heat and boil for 5 minutes. Then add the product to a thermos and leave it overnight to infuse. Strain the product and take it 1 teaspoon 3 times a day. The course of treatment is 2 weeks. By the way, the remaining raw materials can be added to the cream and lubricated with it on various wounds.
Folk remedy for the treatment of facial neuritis:
Calamus and nutmeg. Chew calamus root and nutmeg on the sore side.
Mumiyo. To prepare a product from mumiyo, you need to dissolve 0.2 g of mumiyo with 1 teaspoon of honey in a glass of milk. You need to drink the product in the morning on an empty stomach and in the evening before bed. The course of treatment is 25 days; if necessary, the course can be repeated after a 10-day break.
How does the dental nerve treatment process work?
The occipital nerve, inflammation of which is provoked by irritation of its root, has increased sensitivity. When structural disturbances appear, the fibers in the roots begin to send impulses of increased frequency, which cause pain.
The inflammatory process of the dental nerve refers not only to painful sensations in the tooth, but also to infection of the entire pulp, which contains a tangle of nerve endings. Dentists call this disease pulpitis. It occurs due to infection of the inside of the tooth by microbes and foreign elements.
Pain due to nerve inflammation
The infection process is accompanied by very strong and sharp pain. You can understand that pulpitis has formed in a tooth by pressing on the tooth. After physical touch, the painful pulsating sensations intensify significantly. Pain can also occur with sudden temperature changes.
If the infection that appears is not taken care of in time, pulpitis can develop into periostitis. This disease is most often characterized by the spread of germs and bacteria to the gums and tissues around the tooth. Unlike periostitis, pulpitis does not contribute to swelling of the gums and the formation of abscesses on the periodontal tissues.
If a nerve in a tooth becomes inflamed, and there is a tangle of nerves in the pulp, then a person immediately experiences painful sensations, and when they appear, they need to contact a dentist as soon as possible in order to be able to keep the tooth alive. First of all, the dentist looks at the condition of the nerve.
We suggest you read: When the upper teeth come out after the lower ones
The tooth is preserved using a procedure called conservation. If the nerve is dead, the doctor completely cleanses the tooth cavity using antiseptic and anesthetic pads. In addition, the doctor installs temporary medications that remain in the tooth for about a month, thereby strengthening it.
It is necessary to contact a dentist as soon as possible in order to be able to keep the tooth alive.
After treatment has been carried out, bacteria has been eliminated and the tooth has been strengthened, the dentist places a permanent filling made of strong materials. If the work is done well, the tooth will not be disturbed for a very long time.
In particularly extreme cases, doctors decide to completely remove the tooth.
How does the dental nerve treatment process work?
Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, treatment at home which is aimed at getting rid of the inflammatory process and maintaining a weakened immune system, can be treated with medicinal herbs. You need to mix 100 grams of lavender flowers and 150 grams of St. John's wort herb. The resulting mixture must be poured with boiling water (1 tbsp.
spoon per 1/2 liter of liquid), leave for 15-20 minutes, then filter. Take the resulting tea warmly twice a day, 200 ml, until the alarming symptoms disappear. In the home treatment of facial nerve disease, chamomile tea will also help, for the preparation of which one spoon of dry raw material needs to be brewed with boiling water in the amount of 1 cup.
It is necessary to take it into your mouth and hold it for a while without swallowing.
Possible consequences
In the absence of appropriate treatment, the pain begins to progress. The occipital nerves are destroyed. In addition to permanent pain, you can get such a serious complication as blindness.
Intense pain occurs when inflammation of the occipital nerve transforms into neuropathy. At the same time, nearby soft tissues become sensitive and receptive even without moving the head. The neck may become deformed.
Eliminating the consequences is more difficult than treating the underlying disease. It is not always possible to correct a crooked neck. Often a person becomes disabled.
In what cases is surgery indicated?
In cases where the pain is chronic or there is no positive dynamics with conservative treatment, doctors recommend surgery.
There are two types of surgical intervention:
- Stimulation of the nerves in the back of the head. Wiring is connected to their ends, through which current pulses pass, relieving pain. In the painful area, the patient feels vibration or a feeling of heat spreading. Such an intervention has a big advantage. It does not cause side effects and causes minor mechanical damage to the body. This procedure interferes with the transmission of pain impulses from nerve cells to the brain. After achieving remission, it is necessary to treat the cause of the disease, since this technique is classified as symptomatic.
- Microvascular decompression is performed using microsurgical devices. It helps to deactivate the compression of the nerves. The essence of the operation is to correct the blood vessels that put pressure on the nerve endings. This causes pain relief.
If surgery does not have the desired result, the patient is re-examined. However, such cases are extremely rare.