Radial nerve neuropathy is a chronic pathological process that results in gradual fiber atrophy. A person loses the ability to perform habitual actions with the upper limb. In severe cases, the hand is completely immobilized and it becomes impossible to make any movements at all.
In most cases, radial arm neuropathy is a secondary condition. It is based on any degenerative, inflammatory, traumatic or endocrine disease, which entails a disruption of the blood supply to certain sections of the nerve fiber. Among the most likely causes is compression (squeezing). For example, when using crutches, injury to the radial nerve in the axilla often occurs. This disease can also develop with enlargement of regional lymph nodes. When inflamed, they compress the surrounding soft tissues, including the radial nerve.
Neuropathy of the right radial nerve is more often diagnosed - this is due to the fact that for many people this is the “working” hand and it bears the bulk of the physical load when performing professional duties. Neuropathy of the left radial nerve can occur due to metabolic changes, endocrine disorders, after injury, use of crutches, as a result of the development of carpal tunnel syndrome, etc. This localization is no exception, but is not as common as on the right hand.
In this article, we propose to find out information about the main types of radial neuropathy and the reasons for its occurrence in completely healthy and young people. We will also tell you about the first signs of trouble and clinical symptoms. Information will be provided on the possibilities and prospects of treatment using manual therapy methods.
Causes of radial neuralgia and its treatment
Radial neuralgia is a disorder of innervation in any part of the right or left arm. The nature of the occurrence of reduced sensitivity of the nerve roots can be different, however, the degree of danger is always high. Thus, in the absence of complete and adequate treatment, sensory impairment becomes irreversible, leading patients to disability.
Causes of the disease
Radial neuralgia can be of various origins: post-traumatic, metabolic, compression or ischemic origin. The main reason is prolonged compression on a certain area of the arm. Compression can be caused by the following factors:
- sleeping in an uncomfortable position with severe fatigue, alcohol intoxication (the patient rested his arm);
- brain pathologies;
- formation of scar tissue between muscles after injury;
- humerus fractures;
- prolonged squeezing with a tourniquet;
- injections into the outer brachial region, especially in the presence of anatomy of nerve localization;
- pressure on the arm due to crutches.
Neuralgia can develop against the background of lead poisoning, acute intoxication with alcohol, food, poisons, or diabetes. Innervation often occurs during pregnancy, hormonal disorders, and acute inflammatory diseases of any nature.
How to treat pinching?
If the radial nerve is pinched in the arm, treatment depends on the severity of the lesion. As a rule, pinching can occur when there is too much pressure on it from surrounding tissues: bones, cartilage or muscles. This pressure causes pain, tingling and numbness in the hand.
When determining treatment, the doctor takes into account the source of the pinching and the location of the damage. Treatment of pinching caused by an infectious disease or intoxication is carried out with the help of medications. If the pinching is caused by an injury, for example, a fracture, immobilization of the arm and other measures are carried out to eliminate it. If the fracture is accompanied by a nerve rupture, the doctor will stitch it together.
Nerve damage caused by an external factor, for example, sleeping in an uncomfortable position, using crutches, or muscle activity, can be cured by eliminating the factor that provokes the disease. As a rule, treatment in this case is outpatient. A person is hospitalized only when the indications require the administration of potent drugs.
When treating pinching, you must follow all the doctor’s recommendations, especially those related to taking medications. Thus, non-steroidal drugs (to eliminate pain and inflammation), decongestants, vasodilators (to improve blood flow to the nerve), vitamin preparations and biostimulants are prescribed.
In addition to medications, physical therapy, massage, and physiotherapy (for example, laser radiation on the affected areas) are indicated. A bandage or scarf may also be useful to hang the arm on to provide relief to the patient.
Symptoms
The symptom complex directly depends on the localization of compression and the degree of compression of the nerve roots. Considering that the degree of compression of nerves has several types, the symptoms are also expressed in accordance with the type of pathology.
Type 1 severity
Nerve tissue damage usually occurs in the armpits on the right or left. The following symptoms are identified:
- with the arm in a straight position, extension of the hand is difficult;
- when the arm is raised, there is a drooping of the hand;
- numbness, tingling, paresthesia in the distal parts;
- impaired elbow reflex;
- partial numbness.
Type 2 severity
The lesion occurs as a result of prolonged compression of the arm during sleep, fixation during injuries, or improper application of a tourniquet. The symptoms are as follows:
- the forearm is mobile, extends, sensitive, the reflex is preserved;
- loss of sensitivity of the hand on the inside;
- constant goosebumps on the back of the hand;
- violation of extension of fingers and hands.
Type 3 severity
This type of compression is often caused by post-traumatic factors, and the symptoms are expressed by the following manifestations:
- pain with any physical activity;
- pain when straightening fingers;
- weakness and hypotrophy of the extensor muscles of the forearm.
Any movement with type 3 compression is accompanied by pain. Clinical manifestations vary in intensity, which is associated with multiple factors.
To identify diseases, differential diagnosis is carried out to exclude inflammation of the radial nerve and neuritis.
Forecast
The recovery time for the radial nerve of the arm takes on average 1 – 2 months.
The duration of rehabilitation is determined by the patient’s age, the nature of the lesion and the characteristics of concomitant diseases. Post-traumatic neuropathy requires a longer recovery. To prevent neuropathy, you need to sleep in a comfortable position and give up bad habits. Persons whose profession involves frequent repetitive movements should regularly exercise and massage the upper extremities. It is also recommended to undergo a complete body examination every 6 months.
With timely treatment, it is possible to restore the functions of the radial nerve in 1-2 months. The timing and extent of nerve recovery largely depend on the depth and extent of its damage. In some cases, the disease becomes chronic and periodically worsens.
Diagnosis and treatment
The main diagnostic goal is to establish the sensory sphere and conduct functional tests that reliably determine the ability of the muscle structures innervated by the radial nerve. An important aspect is the neurological examination. The neurologist performs several tests:
- straightening and raising your arms;
- rotation, extension of the hands;
- finger mobility.
At the time of such actions, the patient’s reaction to the actions performed is assessed. Based on the data obtained, one disease is differentiated from another. Among instrumental diagnostic methods, X-ray is important.
The diagnosis is based on the patient’s clinical history. If it is severe, consultation with a cardiologist, endocrinologist, or therapist may be required.
Treatment tactics
Treatment of pathology is usually carried out at home. The treatment process necessarily includes a number of the following activities:
- drug course of therapy (antibiotics, vasodilators, anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers);
- vitamin complexes to improve general and peripheral blood circulation (capsules and tablets or injections);
- physiotherapeutic procedures to relieve pain and increase muscle tone.
Post-traumatic disruption of innervation requires immobilization of the limb, drug treatment and elimination of the consequences of atrophy. During treatment, a course of massage, electrophoresis, physical therapy and special exercises is required. Use traditional treatment methods at home without a doctor’s advice.
Radial neuralgia is a serious disease that requires immediate correction. Lack of therapy often causes irreversible changes in the general and peripheral system.
Treatment
Treatment of radial neuritis is determined in accordance with the cause that caused its development. So, if the disease appears due to infections, then the patient is prescribed antibacterial therapy, antiviral and vascular drugs.
For traumatic neuritis, the patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics. Treatment begins with immobilization of the limb, then decongestant therapy is prescribed.
In both cases, the patient is prescribed vitamins B, C and E. This is necessary in order to restore blood circulation.
Drug treatment of radial neuritis is used in combination with additional methods that make it possible to cope with the disease faster and more effectively.
So, the patient is prescribed physiotherapy:
- electrophoresis;
- phonophoresis;
- etc.
Their main goal is to restore sensitivity, as well as increase muscle tone. Usually they are not prescribed immediately, but at the end of the first week of treatment.
In addition, the following procedures apply:
In some cases, a neurosurgeon performs surgical treatment of radial neuritis. It is necessary if the patient continues to have pain and there is a risk of developing muscle atrophy.
The operation is performed when, with a long-term and adequate treatment package, there are no signs of recovery. When processes appear that indicate degeneration of the nerve, surgical treatment, which involves suturing, is also indicated.
In young patients, neuritis responds well to therapy. On the contrary, in elderly people with concomitant diseases, in the absence of adequate treatment, paralysis and the formation of contractures may occur. That is why you should not self-medicate, and when the first signs of illness appear, seek help from a doctor.
Exercises
Therapy for radial neuritis involves performing a certain set of exercises, which contributes to the rapid restoration of functions and lost muscle volume.
| First set of exercises: |
|
| Water gymnastics complex (must be performed in the bathroom): |
|
Each exercise must be performed at least 10 times. These complexes can be used after consultation with your doctor. They need to be done as carefully as possible, so as not to aggravate the course of the disease.
Folk remedies
There are various traditional medicines that promote a speedy recovery of the patient. It should be remembered that these recipes cannot completely replace traditional healing methods. They can only be used after consultation with your doctor.
Let's consider the most popular recipes of traditional healers:
| Propolis |
|
| Red clay |
|
There are other recipes that allow you to quickly recover from radial neuritis. For example, folk healers recommend rubbing the problem area with bear lard every day for a month.
Radial neuritis (ICD 10 code: G56.3) is a disease that can develop for various reasons. Specific symptoms make it easy to diagnose this disease.
One of the common neurological diseases of the upper extremities is radial neuritis.
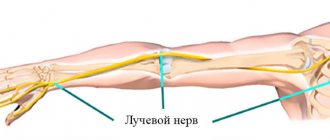
This nerve runs through the entire arm, originating just above the shoulder joint and ending in the first three fingers of the hand.
He is responsible for turning the hand with the palm up (supination), extension of the elbow and hand, and abduction of the first finger from the rest.
Due to the proximity of the radial nerve to the skin and the peculiarities of its anatomical structure, almost all people are familiar with some of the signs of this disease. For example, everyone knows the condition “overlying the hand” - numbness of the hand after prolonged squeezing during sleep. In a healthy person, this unpleasant symptom goes away within a few minutes, but in a sick person it will bother him for a long time.
The neurological disease in question can appear for several reasons:
- Infectious or inflammatory disease: influenza, typhus, pneumonia, measles, tuberculosis, herpes, rheumatoid arthritis. The basis of radial nerve neuritis is the inflammatory process that affects this nerve. In other words, bacteria and viruses act as causative agents of neuritis in this case.
- Traumatic damage to the radial nerve: fracture of the humerus or radius, dislocation of the shoulder or forearm, injuries to the ligaments and tendons of the arm joints, unsuccessful injection.
- Poisoning of the body with arsenic, lead, mercury, alcoholic beverages or other toxic substances.
- Compression (squeezing the nerve) is the most common cause of neuritis. Occurs during sleep due to an uncomfortable position of the arm (sleep paralysis), as well as when a tourniquet is applied to the arm to stop bleeding. The radial nerve may be compressed by the tumor. When using crutches, “crutch paralysis” is sometimes observed - compression of the nerve in the armpit. Prisoners experience "prisoner's paralysis" - compression of the radial nerve in the wrist area.
- Excessive overload of one of the muscles innervated by the radial nerve.
Some diseases can cause hearing problems. if prolonged and left untreated, it can lead to deafness.
Symptoms and treatment methods for facial neuritis are described.
general description
Radial nerve disease (neuropathy) (G56.3) is a pathological condition in which the radial nerve is affected. It manifests itself as difficulty in straightening the muscles of the forearm, wrist, fingers, difficulty in abducting the thumb, and impaired sensitivity in the area of innervation of this nerve.
Etiology of radial nerve neuropathy: compression of the radial nerve during sleep (deep sleep, severe fatigue, alcohol intoxication); humerus fracture; long periods of walking with the help of crutches; past infections; intoxication.
Why is this happening
The radial nerve can be affected during sleep when a person is fast asleep with his arm under his body or head. Often such a lesion may be preceded by alcohol intoxication followed by deep sleep. The patient usually complains of a feeling of numbness in the arm.
In what other situations can the radial nerve be damaged?
- when compressed by a crutch,
- when the humerus is fractured (shrapnel can also damage the nerve),
- while bandaging the arm with a tourniquet to stop bleeding,
- if the intramuscular injection is performed carelessly (this is especially true for situations where the radial nerve has an abnormal location).
Less common causes may be complications after various infectious diseases or intoxication with salts of heavy metals (mercury, arsenic).
Often the causes of nerve damage are diabetes, tuberculosis, and polyarthritis. Deficiency of B vitamins and folate also leads to the above-mentioned disorders. Long-term use of various medications can also have a toxic effect.
Clinical picture
Patients are concerned about pain and a tingling sensation, burning sensation in the fingers and back of the forearm, weakness in the muscles of the hand. Gradually, numbness of the back of the hand appears, adduction and abduction of the thumb is impaired, and extension of the hand and forearm becomes difficult.
An objective examination of the patient reveals:
- paresthesia and hypoesthesia in the area of the rear of the I, II, III fingers, the posterior surface of the forearm (70%);
- weakness in the extensor muscles of the hand and fingers, weakness of the supinator, brachioradialis muscle (60%);
- inability to abduct and adduct the thumb (70%);
- decreased carporadial reflex (50%);
- muscle atrophy (40%);
- the appearance of pain during supination of the forearm with overcoming resistance and in the test with extension of the middle finger (50%);
- pain on palpation along the radial nerve (60%).
Diagnostics
To verify the presence of this pathology, several functional tests are performed during a neurological examination to identify impairments in the motor function of the hand. The following signs clearly indicate radial nerve neuritis:
- if the patient presses both palms to each other and tries to spread his fingers, then on the sore hand the fingers will bend and slide along the palm of the healthy hand;
- with the sore hand lying on the table, palm down, a person will not be able to place its middle finger on the ring or index finger;
- in a standing position with arms down along the body, the patient will not be able to turn the hand forward with the palm on the affected side and move the thumb up;
- When the hands are positioned with the back of the hands lying on the table, the person is unable to abduct the thumb.
Diagnosis of radial nerve damage
- Electroneuromyography.
- X-ray or computed tomography of the elbow and/or wrist joint.
- Lateral epicondylitis.
- Compression of the posterior interosseous nerve.
- Damage to the brachial plexus.
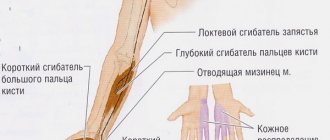
| Zone of cutaneous innervation of the radial nerve (2) | |
| “Dangling” hand with damage to the radial nerve |
Diagnosis of neuritis
Diagnosis of neuritis includes the following examination methods:
1. Electromyography;
2. Electroneurography;
3. Functional tests to identify motor disorders:
- to determine neuritis of the radial nerve: - the hand lies with the palm on the table, while the patient cannot place the third finger on the neighboring ones; - the back of the hand lies on the table, the patient cannot move the thumb; - in a standing position, arms down , the patient cannot turn the affected hand with the palm forward, or move the thumb to the side.
- to determine ulnar nerve neuritis: - the hand lies with the palm on the table, while the patient cannot cause scratching movements with the little finger on the table; - the hand lies with the palm on the table, while the patient cannot spread the fingers, especially 4 and 5; - the patient does not can completely clench the fingers into a fist, especially the 4th and 5th fingers; - the patient cannot hold a strip of paper with the thumb and forefinger, since the phalanx of one of the fingers does not bend completely.
- to determine neuritis of the median nerve: - the hand lies with the palm on the table, while the patient cannot cause scratching movements with the 2nd finger on the table; - the patient cannot completely clench the fingers into a fist, especially the 1st, 2nd, and partially the 3rd finger; - the patient cannot can oppose the thumb and little finger.
ul
Treatment of radial nerve damage
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamins.
- Physiotherapy, massage.
- Temporary limitation of physical activity on the arm.
- Novocaine and hydrocortisone blockades.
- Surgical treatment (used for compression of the radial nerve).
Treatment is prescribed only after confirmation of the diagnosis by a medical specialist.
Essential drugs
There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
- Xefocam (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug). Dosage regimen: for relief of acute pain syndrome, the recommended oral dose is 8-16 mg/day. in 2-3 doses. The maximum daily dose is 16 mg. The tablets are taken before meals with a glass of water.
- Tramadol (analgesic). Dosage regimen: IV, IM, SC in a single dose of 50-100 mg, possible repeated administration of the drug after 4-6 hours. The maximum daily dose is 400 mg.
- Ketoprofen (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug). Dosage regimen: IM - 100 mg 1-2 times a day; after pain relief, it is prescribed orally in a daily dose of 300 mg in 2-3 doses, a maintenance dose of 150-200 mg/day.
- Diacarb (a diuretic from the group of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors). Dosage regimen: adults are prescribed 250-500 mg once in the morning for 3 days, on the 4th day - a break.
- Milgamma (B complex of vitamins). Dosage regimen: therapy begins with 2 ml intramuscularly 1 time per day for 5-10 days. Maintenance therapy - 2 ml IM two or three times a week.
- Prozerin (inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase and pseudocholinesterase). Dosage regimen: orally for adults, 10-15 mg 2-3 times a day; subcutaneously - 1-2 mg 1-2 times a day.
Principles of disease treatment
Treatment is usually complex. It includes the following groups of drugs: antioxidants that improve microcirculation, anticholinesterase agents. Dehydration is also carried out, medications containing B vitamins are administered. Additionally, 2-3 weeks after the onset of the disease, physiotherapeutic treatment, exercise therapy, and acupuncture are prescribed. Psychotherapy, manual therapy, homeopathic medicines are included.
When a structure such as the radial nerve is damaged, treatment requires a long time, followed by a complex of restorative and rehabilitation measures.
If there is no good effect from the drug treatment, then radiotherapy is prescribed. If the cause of neuritis is a traumatic lesion, a suture may be necessary.
The main goal of treatment is the maximum possible stimulation of restoration of the structure and function of the nerve fiber. The complex of drugs used also depends on the cause that caused the development of the pathological process. If there is an inflammatory process, then antibacterial drugs are prescribed.
Symptoms of radial neuralgia
The radial nerve is a nerve of mixed type, which is responsible for the function of movement of the upper limb, for example: extension of the elbow joint and wrist, sensory inertia of the back of the shoulder and forearm, as well as the floor of the surface of the hand.
The causes of dysfunction of the radial nerve are different. Often, damage is caused by long-term compression, for example, when applying a tourniquet or due to a crutch, or injury to the radial nerve trunk. Sleeping on hard surfaces can also be a reason, when the patient puts his arm under his head or leans his body on it. Such a lesion (“sleep paralysis”) often occurs in the deep sleep phase, due to a person’s fatigue or state of alcohol intoxication. Radial neuralgia can also happen due to viral infections, diseases, toxic substances (alcohol).
Radial neuritis - symptoms are determined by the location of the lesion itself. In turn, the clinical picture completely depends on the degree of damage. The higher the level of injury to the radial nerve, the more impaired the functioning of the upper extremities. Symptoms of neuralgia at the shoulder level may be as follows:
- The sensitivity of the skin in the area where the nerve is located is affected by a type of hypoesthesia (pathological decrease in sensitivity on the skin) - the back shoulder goes numb, as does the forearm, around the thumb, index and, sometimes, middle fingers.
- “Dangling hand” - this symptom manifests itself as a violation in the extension of the wrist joint (the victim extends the affected arm straight parallel to the floor, and the hand hangs downwards).
- It is impossible to straighten the forearm and also bend the arm at the elbow.
- The thumb cannot be retracted or straightened or connected to the index finger.
If the nerve neuropathy is in the middle third of the shoulder, you can rely on similar symptoms. However, at the same time, muscle performance is preserved - the forearm extends, there is no pain or discomfort in the back of the shoulder.
Motor function in the shoulder and forearm area is often not impaired. But sensitivity is lost from the back edge of the hand.
Neuropathy of the radial nerve branch is detected when the nerve is affected in the lower forearm or wrist area. The symptoms are as follows: decreased sensitivity in the fingers and hand, possible acute pain in the back of the thumb, which spreads to the shoulder and forearm.
Recommended reading
Popular articles
The success of a particular plastic surgery largely depends on how ... >>
Lasers in cosmetology are used for hair removal quite widely, so... >>
All women are advised to visit a gynecologist regularly. Often representatives of the beautiful... >>
It's no secret that Botox injections today... >>
A woman’s eyes are a reflection of her inner world. They express … >>
In the modern world, many are faced with such an unpleasant phenomenon as... >>
The modern woman has learned to appreciate her body and realized that in ... >>
in “Symptoms of radial neuralgia”
So is this neuralgia? This happens to me sometimes, I couldn’t even think about neuralgia, I kept racking my brains as to why this was happening...
Causes
This disease can develop due to various reasons. For example, one of the most common is compression of the nerve while a person is sleeping.
- All information on the site is for informational purposes only and is NOT a guide to action!
- can give you an ACCURATE DIAGNOSIS !
- We kindly ask you NOT to self-medicate, but to make an appointment with a specialist
! - Health to you and your loved ones!
Radial neuritis occurs due to excessive numbness of the patient’s arm while he takes a certain position and remains in it for a long time. Typically the upper limb is located either under the head or under the body.
Sleep should be very deep. This often happens when the sleeper is either very tired or intoxicated.
Neuritis of the radial nerve can develop due to its compression by a crutch. This is the so-called crutch paralysis.
The disease can occur if the crutches were incorrectly selected for height or they do not have a soft lining in the armpit area. Excessive compression of the radial nerve leads to the development of the disease.
The third cause of the disease is trauma, for example, serious damage to the humerus. It can also develop due to excessive compression with a tourniquet. In some cases, the disease occurs when a nerve suddenly contracts.
Traumatic cases of neuritis also include:
Quite rarely, the disease appears after previous infections: influenza, pneumonia, typhus, etc. Intoxication, for example, alcohol poisoning, can cause the development of radial neuritis.
Basic preventive measures include the need to avoid injury, hypothermia and infection.
What are the causes of damage to the radial, ulnar and median nerves?
The radial, ulnar and median nerves pass through narrow canals formed by bones, ligaments, tendons and muscles. Nerve tissue is very delicate and vulnerable. Often we detect nerve suffering even with slight narrowing or deformation of the nerve canal. Narrowing or deformation of the canals of the radial, ulnar and median nerves occurs:
- In case of injury (bone fracture, bruise, hemorrhage, sprain or wound); Often, when injured, the nerve is pulled into scarred tissue or compressed by a bone fragment; nerve injury can also be represented by a nerve bruise, partial or complete interruption.
- When squeezed in an uncomfortable position (tucked or pinned hand while unconscious or intoxicated, under anesthesia);
- With thickening and deformation of the elbow or wrist joints and ligaments , with chronic injury and overload of the joints, often associated with the type of activity (athletes, musicians, drivers, cooks, dentists, working with vibration and metalworking tools). Very often, such changes are facilitated by diseases of the cervical spine. These types of neuropathy are called tunnel syndromes of the ulnar, radial and median nerves (cubital tunnel syndrome, carpal tunnel syndrome) .
Stimulation electromyography of the upper limbs, electroneuromyography (ENMG) of the upper limbs / EMG of the hands
The function of nerves is to conduct electrical impulses from the brain to muscles and organs, and to the brain from sensory receptors in the body. Any damage to the nerve leads to disruption of the conduction of excitation along the nerve, which means disconnection of the affected part of the body from the brain.
Therefore, if the radial, ulnar or median nerve suffers, the following are possible:
- Decreased strength and weight loss of arm muscles
- Decreased sensitivity (numbness).
Causes
The neurological disease in question can appear for several reasons:
- Infectious or inflammatory disease: influenza, typhus, pneumonia, measles, tuberculosis, herpes, rheumatoid arthritis. The basis of radial nerve neuritis is the inflammatory process that affects this nerve. In other words, bacteria and viruses act as causative agents of neuritis in this case.
- Traumatic damage to the radial nerve: fracture of the humerus or radius, dislocation of the shoulder or forearm, injuries to the ligaments and tendons of the arm joints, unsuccessful injection.
- Poisoning of the body with arsenic, lead, mercury, alcoholic beverages or other toxic substances.
- Compression (squeezing the nerve) is the most common cause of neuritis. Occurs during sleep due to an uncomfortable position of the arm (sleep paralysis), as well as when a tourniquet is applied to the arm to stop bleeding. The radial nerve may be compressed by the tumor. When using crutches, “crutch paralysis” is sometimes observed - compression of the nerve in the armpit. Prisoners experience "prisoner's paralysis" - compression of the radial nerve in the wrist area.
- Excessive overload of one of the muscles innervated by the radial nerve.
Some diseases can cause hearing problems. Acoustic neuritis, if prolonged and untreated, can lead to deafness.
Symptoms and treatment methods for facial neuritis are described here.
The inflammatory process in the ganglia leads to ganglionitis. Read about the symptoms of this disease in the following article.
Diagnosis of neuropathies of the ulnar, radial and median nerves
The most successful treatment for neuropathy is treatment directly at the point of nerve damage. For successful treatment, your treating doctor will find out:
- At what exact point is the nerve damaged (compressed); this helps us provide targeted treatment;
- What exactly led to the nerve suffering (trauma, scar, compression);
- The degree of nerve suffering (complete or partial damage, the presence of a recovery process, the presence of complete death of the nerve, etc.).
Often, to establish the cause of nerve pain, a detailed neurological examination is sufficient , during which the strength of the muscles controlled by the nerve, the possibility of certain movements, sensitivity, the presence of pain points and seals along the nerve are assessed. Auxiliary diagnostic methods are electroneuromyography, radiography and computed tomography.
Electroneuromyography allows you to assess the speed and volume of impulses along the nerve, detect the location of damage/compression, and determine the prognosis for recovery. Electromyography helps us evaluate the effect of certain types of treatment and choose the most suitable ones. The Echinacea clinic uses a modern computer electroneuromyograph.
X-ray and computed tomography of the joints will provide complete information about the deformation of the joints and bone canals of the nerves, the causes and points of nerve compression.
Treatment of neuritis
How to treat neuritis? Treatment for neuritis depends on the type, cause and location of the disease, but usually includes the following:
1. Treatment of the root cause of the disease, i.e. disease or pathological condition that led to disturbances in the nerve; 2. Drug therapy;3. Physiotherapy.4. Surgery.
Treating the root cause of the disease
Accurate and thorough diagnosis for neurological disorders is very important, since treatment directly depends on this point. In addition, it is necessary to exclude secondary diseases.
Drug treatment of neuritis (medicines for neuritis)
Important! Before using medications, be sure to consult your doctor!
2.1. Relieving infection
Antibacterial and viral infections are the most common causative agents of various infectious diseases, accompanied by inflammatory processes, intoxication and decreased reactivity of the immune system. And due to the fact that nerve fibers penetrate all parts of the body, it costs nothing for pathological microorganisms to involve the nervous system in the inflammatory process.
Relieving the infection is generally considered more of a point of treating the underlying disease that led to the inflammatory process in the nerve.
Bacterial infections can be treated with antibiotics, while viral infections can be treated with antiviral therapy. In addition, the prescription of a specific antibiotic depends on the type of pathogen.
Antibiotics for neuritis: against staphylococcal infections - Amoxicillin, Vancomycin, Clarithomycin, Erythromycin, Oxacillin, Cephalexin, against streptococcal infections - Azithromycin, Doxycycline, Levofloxacin, Ceftriaxone ", "Cefotaxime", "Erythromycin".
Sulfonamides – antimicrobial drugs for neuritis: “Sulfanilamide”, “Sulfamoxol”.
Antiviral drugs for neuritis: interferon and its derivatives (Betaferon, Interlock, Laferon, Neovir, Reaferon, as well as gamma globulins.
2.2. Detoxification therapy
The waste products of pathogenic infectious agents in the body cause symptoms of intoxication (poisoning), which causes the patient to experience nausea, sometimes vomiting, a feeling of weakness and general malaise. This is also facilitated by the spread of microbes killed through the body due to the use of antibiotics or antiviral drugs.
To remove dead bacteria, as well as their waste products, detoxification therapy is used, which includes:
- Taking sorbents - “Atoxil”, “Polyphepan”, “Enterosgel”;
- Drink plenty of fluids, preferably with added vitamin C (ascorbic acid);
- The use of diuretics (diuretics) - “Diacarb”, “Furosemide”;
- In case of severe intoxication of the body, intravenous infusion of solutions of glucose, polysaccharides (“dextran”) and water-salt solutions, “Urotropin”.
2.3. Anti-inflammatory therapy
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and glucocorticoids (hormones) are used to relieve pain, as well as stop the inflammatory process in the nerves.
Among the drugs in the NSAID group are Ibuprofen and Nimesil.
Among glucorticoids one can o.
It is better to relieve high fever in children using water-vinegar based compresses.
For tunnel syndromes, medications are injected directly into the affected canal - “Hydrocortisone”, “Novocaine”.
If the cause of the inflammatory process is a violation of the blood supply to the nerve (ischemia), vasodilating drugs are prescribed - Papaverine, Eufillin.
2.4. Symptomatic treatment
Sedatives are prescribed to reduce the activity of the nervous system, which leads to a reduction or prevention of the development of muscle spasms - “Persen”, “Bekhterev’s Medicine”.
Additional intake of vitamins is required - B vitamins, vitamin E (tocopherol), vitamin C (ascorbic acid), vitamin PP (nicotinic acid), milgama, neurobion, neurorubin. Vitamin therapy is necessary to restore nerve function.
In addition, for neuritis the following can be used:
- Gravity treatment methods;
- Antihistamines;
- Angioprotectors and antiplatelet agents;
- Proteolytic enzyme inhibitors.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
Physiotherapeutic procedures for neuritis include:
- Plasmapheresis;
- Mud applications;
- Massage of the innervated muscles where the inflamed nerve is located;
- Hyperbaric oxygenation;
- Pulse currents;
- Ultraphonophoresis with hydrocortisone;
- UHF;
- Electrophoresis of novocaine, neostigmine and hyaluronidase.
Additionally, electrical stimulation of the affected muscles can be performed.
Special therapeutic exercise (physical therapy) also has a beneficial effect on the body. Exercise therapy (exercises) for neuritis directly depend on the location and type of the inflamed nerve.
The use of physiotherapy is prescribed on the 6-7th day of treatment for neuritis.
Surgery
Surgical treatment of neuritis is used for:
- traumatic etiology of this disease;
- lack of effectiveness of conservative treatment;
- no signs of nerve recovery.
ul
Treatment of damage to the radial, ulnar and median nerves at the Echinacea clinic
When it is clear where, how and why nerve compression occurs, local treatment in the form of physiotherapy, therapeutic blockades, massage, and manual therapy becomes much more effective. Therefore, treatment in our clinic begins with finding out the cause and location of nerve damage .
The main goals of treatment for nerve compression:
- Remove nerve compression. To do this, we use powerful resorption therapy: we use enzymes that resolve and soften scar tissue, bone and cartilage growths (Karipazim enzyme, etc.), massage, and injecting medications directly into the site of nerve compression. Sometimes, to release the nerve, manual therapy and massage of the areas of compression of the ulnar, median and radial nerves (cervical spine, elbow, wrist joints, etc.) are sufficient.
- Accelerate healing and restoration of the nerve. To do this, we use modern medications that help restore the nerve freed from compression and scarring.
- Restore muscle function and volume. Special exercises, electrical stimulation of muscles, and physiotherapy are used here. The rehabilitator will tell you in detail and show you how to perform rehabilitation procedures at home.
Radial nerve neuropathy, how to treat damage to the radial nerve?
Radial nerve neuropathy is a pathology accompanied by painful symptoms; it is dangerous due to paralysis of the affected limb. Compression of the nerve ending, the presence of concomitant diseases, and physical overexertion lead to the development of the condition.
The therapy is selected in a comprehensive manner and lasts about 3 months. If you fully comply with medical recommendations, the prognosis is favorable.
In order to successfully neutralize motor impairment of the hand, it is necessary to familiarize yourself with modern methods of therapy, recovery, and relapse prevention.
Drug treatment
Therapy of neuropathy of the radial nerve of the arm using various groups of drugs is one of the main stages. The duration of treatment is on average 2 weeks. The dosage for each day is determined by the doctor individually.
- Non-steroidal drugs to relieve inflammation. Ibuprofen and Diclofenac are widely used.
- Antibacterial drugs. They suppress the activity of bacterial microflora that provokes inflammation. Erythromycin and Cephalexin are widely used.
- Decongestants – Hydrocortisone, Diprospan.
- Vasoconstrictors are also prescribed that increase blood flow to the diseased area - Papaverine, Eufillin, Istenon.
- Anticholyesterase medications that restore the conductivity of the radial nerve fiber. These include Phosphacol, Pirofos, Neuromidin.
- B vitamins to stimulate the restoration processes of damaged tissues.
- Vasoactive agents – nicotinic acid, Pentoxifylline. They normalize metabolic processes.
- In case of acute poisoning of the body, they resort to detoxification. The procedure is carried out by administering intravenous injections with solutions of Glucose and Sodium chloride.
- In case of endocrine disruption, hormonal agents are indicated.
Post-traumatic injury to the median nerve is treated by regenerating the limb after a fracture. Bone repositioning and other procedures are used to stimulate the restoration of the previous skeletal structure. Acupuncture, magnetic therapy, and massage are widely prescribed. Usually 10-15 sessions are enough to get a lasting result.
When is surgery necessary?
In case of nerve injury, it is very important to decide in a timely manner whether conservative or surgical treatment is advisable. The answer to this question can be obtained after conducting needle myography, which will answer the question of what is the degree of damage to the nerve and whether it has a tendency to recover. If during this study it turns out that at least partially the nerve is preserved, we carry out active conservative treatment, after which we must repeat the study to make sure that the treatment had an effect . If, during needle myography, it turns out that the nerve is completely damaged and its restoration is impossible, we resort to the help of a neurosurgeon who suturing the nerve or releasing it from significantly narrowed canals. Then we perform the entire range of restoration procedures.
Types of neuritis
The classification of neuritis is as follows:
Type:
- Mononeuritis - the development of the inflammatory process occurs in one nerve;
- Polyneuritis - the development of inflammation occurs simultaneously in several nerves.
With the flow:
- Spicy;
- Subacute;
- Chronic.
By localization
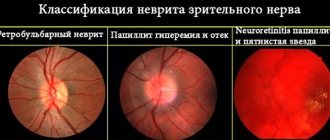
Optic neuritis – an inflammatory process develops in the optic nerve; divided into:
- Orbital (retrobulbar) neuritis - inflammation develops in the optic nerve located outside the eyeball - from the exit from the sclera to the chiasm.
- Axial retrobulbar neuritis - inflammation develops in the maculopapillary bundle of the optic nerve, which is often accompanied by optic nerve atrophy and vision loss.
- Interstitial retrobulbar neuritis - inflammation develops from the optic nerve sheath to the nerve trunk, deep down.
- Peripheral retrobulbar neuritis - inflammation begins with the optic nerve sheaths, then spreads along the septa to its tissue; proceeds to the interstitial type, with the formation of exudative effusion, accumulating in the subdural and subarachnoid space;
- Transversal neuritis - the inflammatory process spreads to the entire optic nerve, initially developing in the axial fascicle or in the periphery, and then affects other tissues;
- False optic neuritis is an anomaly in the development of the optic nerve, the clinical picture resembles an inflammatory process, while there is no atrophy of the optic nerve or visual dysfunction.
Axial neuritis - inflammation develops in the axial cylinders of the nerve fiber (axon).
Interstitial neuritis - inflammation develops in the connective tissue of the nerve, most often caused by autoimmune processes.
Parenchymal neuritis - inflammation initially develops in nerve fibers (axons and myelin sheath), after which it spreads to the connective tissue parts of the nerve.
Autonomic neuritis - inflammation develops in the peripheral fibers of the autonomic nervous system, accompanied by trophic disorders.
Ascending neuritis - develops mainly when the peripheral part of the arms and legs is injured, after which the pathological process from the periphery moves towards the center of the nervous system.
Cochlear neuritis - inflammation develops in the cochlear part of the auditory nerve, the symptoms of which are tinnitus and decreased sound perception.
According to clinical manifestations:
Gombeau's neuritis is characterized by the disintegration of the myelin sheath of nerve fibers, while the axial cylinder remains intact.
Hypertrophic Dejerine-Sotta neuritis is characterized by hypertrophy of the sheath of nerve fibers, which initially leads to compression of the conductive part of the nerve, after which the nerve begins to gradually degenerate and lose its functionality.
Rossolimo neuritis is one of the forms of hypertrophic Dejerine-Sotta neuritis, characterized by a recurrent course and occurring mainly in childhood.
By etiology (cause of occurrence):
Traumatic neuritis - the development of the disease is caused by nerve injury.
Occupational neuritis - the development of the disease is caused by a person’s professional activity - poisoning (chemical fumes, heavy metals and other substances), exposure to vibration on the body.
Infectious neuritis - the development of the disease is caused by infection of the body, infectious diseases.
Alcoholic neuritis - the development of the disease is caused by alcohol consumption, the effect on the body of which is the removal from the body of B vitamins, which are responsible for the functioning of the nervous system, as well as dead brain cells (the process of cell death occurs during alcohol intoxication).
ul