Heart neurosis is most often a manifestation of general neurosis, that is, a disorder of higher nervous activity. In this case, there is no so-called organic or structural damage to the heart tissue, but pain in the heart area is present.
Neurosis is formed in people with a certain type of higher nervous activity who are prone to emotional lability, anxiety, and unreasonable worry. Often the cause of cardioneurosis can be found in childhood - these are children who grew up in conditions of overprotection, accustomed to obeying strong parents, who do not know how to make decisions on their own and defend their own opinions.
In adulthood, such individuals are extremely dependent on the environment, prefer to go with the flow and are in a constant state of fear of negative influences on their own lives. At the same time, the main concern in the life of such a person is his health, regardless of the presence or absence of reasons for concern. In the life of such a person, a so-called triggering moment arises, from which heart neurosis begins.
Intercostal neurosis and facial nerve neurosis: symptoms and treatment. Relieving muscle tension
Modern people are often exposed to various stresses, which are primarily caused by excessive and unbearable stress on the fragile nervous system. In turn, stress provokes neuroses , which can be accompanied by muscle tension.
Such tension must be relieved, but before you understand how this can be done, you need to understand what neurosis is.
Neurosis is a pathological condition that is accompanied by exhaustion of the nervous system, autonomic disorders and anxiety. This is a complex pathology that has various signs and causes.
Types of muscle neurosis
Neurosis occurs when two provoking factors - psychotrauma and a biological cause - coincide . The basis of muscle neurosis is the mechanism of repression. A person who is experiencing a neurotic state has a lot of negative experiences in his consciousness.
At the same time, a large amount of stress hormones are released into the body, which strain the muscles of the body. However, due to civilized restrictions, the necessary motor discharge does not occur, and instead of rushing into battle with offenders, an adequate civilized person swallows the insult and remains silent.
Such “useless” muscle tensions do not go away without a trace , and sooner or later they become the cause of muscle neuroses. Therefore, doctors recommend relieving negative energy, which puts muscles on alert, in the gym or by swimming and running.
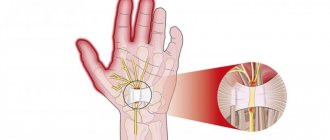
Since the higher nervous system is distributed throughout the human body, during neurosis a pinched nerve can occur, that is, muscle neurosis. Muscle neurosis can be as follows:
- Intercostal. It is otherwise called chest neurosis. In this case, compression of the endings of the intercostal nerves occurs, and the clinical picture that is observed is very similar to the signs of heart disease.
- Cervical.
- Facial and so on.
Intercostal neurosis
Intercostal neuralgia is diagnosed in people of different ages and both sexes. This is a rather unpleasant disease, however, it is not at all dangerous and is curable.
Important! Intercostal neurosis has a number of signs that are observed in cardiac pathologies. Therefore, it is necessary to consult a doctor in order not to miss the development of a serious heart disease.
The essence of the pathology under discussion is pinched nerves located between the ribs. The difference between thoracic neuralgia and heart pain is that the pain associated with this disease is constant and intensifies when turning, coughing, sneezing or any movement of the body.
Heart pain does not become more intense with an uncomfortable position, and is usually relieved by taking nitroglycerin or other cardiac medications. In addition, heart problems are often accompanied by pathological changes in blood pressure, as well as pulse rhythm disturbances, which does not occur with intercostal neurosis.
Diagnosis of intercostal neuralgia consists of the following measures:
- taking anamnesis;
- neurological examination, during which pain in the spaces between the ribs is determined;
- a blood test that reveals inflammatory processes in the body;
- ECG to exclude cardiac pathologies;
- fibrogastroduoenoscopy to exclude diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, which can also be felt as pain in the chest area;
- X-ray of the lungs to exclude pathologies of the pulmonary system.
Causes
Muscle spasms can develop due to stress , injury or excessive exercise. In addition, this condition is provoked by hypothermia, infections or lung diseases.
So, the reasons could be the following:
- poisoning;
- hormonal changes that provoked disorders in the spine, this phenomenon is often observed during menopause;
- multiple sclerosis;
- allergies;
- polyradiculoneuritis;
- osteochondrosis, arthrosis, hernias and other deformation processes in the chest area;
- aortic aneurysm, benign and malignant neoplasms in the pleural cavity;
- diseases of internal organs;
- physical stress;
- diabetes;
- chest injuries;
- awkward sudden movement;
- avitaminosis;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- prolonged incorrect body posture when working.
Symptoms
The most characteristic symptoms of neuralgia:
- periodic or non-stop pain in the ribs;
- muscle twitching;
- increased sweating;
- redness or paleness of the skin;
- increased pain when coughing and changing body position;
- pain in the lumbar region;
- fights when pressing on certain points of the thoracic spinal column;
- A feeling of numbness may occur at the site of damage to the nerve fibers.
Treatment
Treatment is as follows:
- Taking medications that can only be prescribed by a doctor, based on the intensity of pain and other factors.
- Physiotherapy. Prescribed for pain relief. This can be electrophoresis, thermal procedures, amplipulse, etc.
- Vitamin therapy. B vitamins are especially indicated, since they nourish nerve fibers.
- Physical therapy to relieve muscle spasms and relax muscles.
Important! Self-medication is absolutely excluded, since medications have contraindications, and all other methods of treatment should be prescribed after the acute syndrome has resolved and carried out under the supervision of a physician.
on this topic
An interesting video about intercostal neurosis - a description of the disease, and methods of treatment with a special patch.
Neurosis of the cervical spine
Cervical neurosis develops against the background of cervical osteochondrosis; if the cervical area of the spinal column is damaged, an intervertebral hernia, impaired blood flow and pinched nerve roots can develop.
In this case, the patient experiences various pain sensations that can radiate to the shoulder, back of the head, or ear.
In addition, with cervical neurosis, visual acuity may decrease, and signs of vegetative-vascular dystonia may appear:
- increased blood pressure;
- fever or chills;
- insomnia;
- nausea;
- weakness.
Cervical neurosis can manifest itself as pain in the heart and lungs.
Signs
:
- pain in the back of the head and in the temporal region;
- deterioration of the sensitivity of the tongue, which leads to deterioration of speech;
- pain in the upper limbs;
- numbness of fingers;
- stiffness in hand movements;
- pain in the liver area and under the shoulder blades;
- burning in the cervical region, as well as decreased sensitivity in the neck and shoulder.
The pain with cervical neurosis is dull and bursting.
To treat cervical neurosis, medications and massage are prescribed. The duration of treatment depends on the intensity of the clinical picture and the severity of the pathology. If the disease is advanced and the patient suffers from severe pain attacks, he may be prescribed potent medications, which are available in pharmacies only with a doctor’s prescription.
on the topic of cervical neurosis
We invite you to watch a short video about spasms in the muscles of the cervical spine.
Facial nerve neurosis
This is a unilateral lesion that is observed in the 7th pair of nerves located in the cranial region. These nerves regulate facial expressions on one side, so the main symptom of facial nerve neurosis is the absolute inability to control facial expressions in the affected area .
Prevention of muscle neuroses
Despite the fact that there are many ways to defeat neurosis and relieve muscle tension, doctors recommend trying to prevent the development of this pathology, because often the treatment of muscle neuroses is long and difficult.
To reduce the risk of muscle neurosis, you must adhere to the following principles:
- Reducing stress in everyday life.
- Proper working conditions, as well as strict adherence to work and rest schedules. In addition, during prolonged sedentary work, it is recommended to get up every hour and do simple gymnastic exercises to relieve muscle tone.
- Proper nutrition, providing the body with all the necessary vitamins and minerals.
- Active lifestyle, sufficient physical activity - walking and so on.
Water procedures are useful, and these include not only baths with essential oils, but also contrast showers. Contrast showers cope very well with a number of problems:
- nervous system disorders;
- initial stages of hypertension;
- VSD;
- low immunity and many others.
However, it is contraindicated in the following cases:
- atherosclerosis;
- tendency to bleed;
- heart failure;
- skin diseases;
- tumors;
- tuberculosis;
- menstruation.
If it is impossible to relax on your own, doctors recommend seeking help from specialists - these can be psychotherapists, yoga therapists and others. It is also a good idea to take preventative massage courses from time to time.
How to relieve muscle tension during neurosis? It is very important to understand that any remedy that is aimed at relieving muscle tension will be ineffective if a person does not relieve moral or mental stress . Therefore, the basis of preventive measures to prevent muscle neuroses should be work with the psychological state of the patient.
Muscle neuroses are painful and very unpleasant manifestations that cause a person a large amount of pain and significantly reduce the quality of life.
It is not advisable to treat muscle neuroses on your own, since only a doctor can determine the cause of the disease, its nature and severity.
Drugs that are used to treat muscle neuroses can be prescribed from different groups, and an independent approach to choosing a drug can only aggravate the situation.
Source: https://psihiatr.me/nevroticheskie-rasstrojstva/nevrozy/myshechnyi-nevroz.html
Treatment of pathology
If you seek medical help in a timely manner, it is quite possible to overcome intercostal neurosis without all sorts of complications. Therapeutic therapy is based on pain-relieving medicinal compounds that help relieve muscle tension.
Most often, treatment and prevention methods include 7 very effective physiotherapeutic measures:
- electrophoresis with novocaine,
- magnetic therapy,
- a special technique called “Amplipulse”,
- physiotherapy,
- ultraphonophoresis,
- reflexology,
- UHF.
In addition to the above measures, acupressure, warming the spine with hot stones, hirudotherapy and acupuncture are introduced.
Intercostal neurosis: causes, symptoms and treatment of muscle spasm during neuralgia
Intercostal neurosis is compression of the intercostal nerves caused by injuries, compression injuries, inflammation, which is accompanied by acute burning or shooting pain in the ribs. The disease occurs in people of all ages, but is most common in adults.
The structure of the intercostal nerves contains sensory, motor and sympathetic fibers. The intercostal nerves form 12 pairs. They provide innervation to the chest, mammary glands, pleura (costophrenic), anterior abdominal wall, and peritoneum.
The sensory fibers of neighboring nerves connect, and thus cross innervation occurs (one area of the skin or muscle is innervated by the main nerve, as well as neighboring ones).
Causes of neurosis
The pain appears due to the fact that the nerves located in the intercostal space are compressed (pinched). The reasons for the development of pathology may be:
- posture disorders;
- osteochondrosis of any part of the spine;
- flick;
- strong physical activity;
- prolonged stress;
- injuries;
- being in a draft;
- the presence of a focus of infection in the body.
More often, pathology appears due to sudden movement. In this case, a pinched nerve occurs. It’s easy to find yourself in such a situation - sit at the computer for a long time in one position, and then sharply turn your body.
Intercostal neurosis can happen to anyone. Often pain in this area appears due to exhaustion of the nervous system or stress. The danger lies in being in a draft, including in a room with the air conditioner on. Often in hot weather, people do not notice drafts, which provokes nerve irritation and pain.
Disease Prevention
Intercostal neurosis can be prevented by treating emerging problems, diseases of the spine and preventing its curvature, timely treatment of injuries in the chest area.
Increasing the level of immunity will help to avoid herpes infection, which provokes neuralgia.
This can be achieved through sports, adequate physical activity, hardening, and a healthy lifestyle.
As a preventive measure, you should also reduce the amount of stress, reduce alcohol consumption, and normalize the level of physical activity.
Symptoms of pathology
Intercostal neurosis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- sharp pain between the ribs on any side of the body;
- increased discomfort when coughing, sneezing, turning the body;
- voluntary muscle twitching;
- numbness in the area around the affected nerve.
Often such neuralgia causes pain in the lower back or thoracic spine. Pain may also be felt under the shoulder blade.
Usually the discomfort is paroxysmal in nature. The pain intensifies and then subsides. If you press on several points located in the thoracic region, the pain will intensify significantly.
Often when a nerve is pinched on the left, the symptoms are much like pain in the heart area. The patient begins to fear for his health, which results in stress and increased pain against this background.
Neuralgia in the right side of the ribs can be mistakenly confused with pathologies of the lungs, since pain is felt precisely in this area. Often intercostal neuralgia has the character of “lumbago”, that is, the pain seems to penetrate the entire human body through and through, especially with sudden movement.
Externally, neuralgia is noticeable to the naked eye - the patient is tense, tries to limit the amplitude of his own movements, and if necessary, turn around, he slowly turns around with his whole body.
Such external features have one goal - to avoid accidentally making a sudden movement, which causes multiple increases in pain.
Which doctor treats intercostal neurosis?
At the first appointment, specialists will examine the patient. They will be able to immediately determine that the problem is not related to cardiovascular disease. The doctor will listen carefully to the patient’s complaints and also ask him several clarifying questions:
- How long ago did the first symptoms of intercostal neurosis appear? What is the nature of the pain?
- Have there been similar problems in the past?
- Has the person been hypothermic recently?
- Did you have problems with your spine?
- Does the person suffer from chronic diseases?
- Did he try to cope with the disease on his own?
The information received from the patient will help the specialist determine exactly what caused the intercostal neurosis. The data will also be used to develop a treatment program. It is always compiled by a doctor for the patient on an individual basis. In this case, attention is paid to the physiological characteristics of the patient, his general health and age are taken into account.
Regardless of the reasons that caused the spasm and the characteristics of the accompanying pathologies, drug treatment is used for intercostal neuralgia. Drugs are prescribed to relieve general symptoms and improve the patient’s quality of life.
physiotherapy
massage
In addition to treating intercostal neuralgia with medications, other methods are used, including massage, physical therapy and surgery. The choice of tactics depends on the disease that led to the syndrome. Therefore, before starting treatment, diagnostics are carried out using CT, MRI and other methods.
Therapy for intercostal neuralgia is often carried out at home. Treatment in a hospital is prescribed in the presence of severe complications. To relieve pain, ointments, tablets or injections of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used for intercostal neuralgia. For muscle tension, taking muscle relaxants is indicated.
When selecting medications, it is important to take into account the individual characteristics of the patient and the nature of the concomitant pathology. If pain is associated with the gastrointestinal tract, it is not recommended to take medications in tablet form. Such medications irritate the gastric mucosa, thereby increasing the intensity of general symptoms.
In the acute period, when the pain syndrome manifests itself most intensely, bed rest is recommended. Dry heat (heated sand in a cloth bag) must be applied to the sore spot. It is important not to overheat the problem area. Otherwise, as the skin cools, the intensity of the syndrome will increase.
This disease is certainly unpleasant and painful, but still not terrible.
- In order to reduce pain, painkillers are prescribed, such as Diclofenac, Nise, Nimesulide, Ibuprofen, Ketarol. And if this does not help, an intercostal anesthetic block is performed.
- Relieving muscle spasm. Muscle relaxants and anticonvulsants are prescribed.
- Taking anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Strengthening the nervous system, including taking B vitamins that improve the nutrition of nerve fibers and glycine. Sedatives that calm the nerves.
- Physiotherapy, medical massage, manual therapy, acupuncture, gymnastics.
On days 5 and 7, pain usually begins to subside.
But the main thing you must remember is that it is necessary to eliminate the root cause of the disease that caused neuralgia. Otherwise she will come back.
Risk group
The main risk group is office workers who spend long periods of time sitting at a desk. This body position leads to weakening of the back muscles, as a result of which any sudden movement can provoke neuralgia.
The disease often occurs in professional athletes due to excessive exercise.
The state of the nervous system indirectly affects the likelihood of neuralgia. Stress and anxiety weaken the nervous system, which is fertile ground for irritation, pinching and inflammation of nerves in different parts of the body.
A pinched nerve occurs due to muscle spasm or hypertonicity and appears as a result of:
- posture disorders;
- staying in one position for a long time;
- heavy load;
- incorrect body position during sleep.
No one is immune from this disease, so it is important to recognize the symptoms in time and not delay a visit to a neurologist.
Diagnostics
In order to make a diagnosis, an experienced doctor simply needs to study the symptoms of chest neurosis and find out the person’s medical history. But sometimes the doctor may have doubts about making a diagnosis, in which case he will prescribe a diagnostic plan.
Such diagnostics will be of a differential nature, that is, its goal will be to exclude dangerous diseases. If all laboratory and functional tests for somatic pathologies of internal organs are negative, the diagnosis of “intercostal neuralgia” can be made without doubt.
- Laboratory tests of urine and blood to identify inflammation, functional organ failure, and infectious processes.
- Electrocardiogram of the heart to exclude pathology of the heart muscle.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity to identify pathologies of internal organs.
- X-ray examinations to exclude osteochondrosis or rib fractures.
Worth seeing: Autonomic neurosis
Source: https://neuro-orto.ru/bolezni/perifericheskaya-nervnaya-sistema/nevralgyya/mezhrebernyj-nevroz-simptomy-i-lechenie.html
Causes
In most cases, a pinched nerve is associated with muscle spasm or inflammation, which can occur for a variety of reasons. Let's look at the most common of them:
- Spinal injuries or chest injuries.
- Osteochondrosis.
- Some infectious diseases.
- Drafts.
- Lifting weights.
- Working in an awkward position.
- Sudden sharp movements.
- Severe hypothermia.
- Excessive physical activity.
- Prolonged stressful situations.
- Metabolic disease.
- Lack of vitamin B in the body.
- Diabetes.
Psychogenic chest pain: symptoms and treatment methods
Pain, shooting or uniform, in the chest area is a common symptom of vegetative-vascular dystonia, that is, a physical manifestation of an anxiety disorder.
Symptoms of nervous chest pain are as follows:
- the pain may be distributed throughout the chest and may not be severe, but long-lasting;
- can be sharp, shooting, piercing, radiating to the stomach;
- can be localized strictly in one place;
- you can feel how tense the muscles in the chest area are, sometimes their spasm is clearly noticeable;
- burning or numbness in the chest area;
- pressure on the chest and tightness inside it;
- feeling of fullness;
- migration of pain to the back and its return back.
Psychogenic chest pain can haunt an anxious person constantly, or it can be a rather rare episode in his life. At the same time, the same individual may have periods in life when pain in the chest does not go away, or there may be periods of calm that last days, weeks, months.
Chest pain can complement other symptoms of VSD or manifest itself in splendid isolation. They can begin after some stressful event or before it, or they can come as if out of nowhere.
Painful sensations tend to intensify at the moment when the neurotic person is not busy with anything, for example, he went to bed and felt fully himself. Quite often, increased pain in the chest area is observed after eating, especially a large meal.
Since chest pain can indicate very serious, life-threatening conditions, the diagnosis of “psychogenic pain” should never be made on your own. Only after you have been examined and found to be physically healthy can you relax and look for neural causes of your pain.
Muscle strain
Since with anxiety a person is in a state of “fight and flight,” his muscles become more toned. If anxiety passes quickly, then the muscles relax safely. But if the feeling of anxiety remains for a long time, the muscles also cannot return to normal.
Such muscle strain very often leads to pain in various areas of the human body. Including in the chest.
Abdominal discomfort
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is often associated with phenomena such as bloating and increased gas production. The gases accumulated in the intestines distend the abdominal cavity, it begins to prop up the lungs and heart from below, and this leads to chest pain.
The second reason why the abdomen is a source of discomfort in the chest area is referred pain.
Excitement and nervous trepidation very often cause discomfort in the stomach. It’s not for nothing that the British call this condition “butterflies in the stomach.” So these “butterflies” very easily fly from the stomach to the chest.
Hyperventilation
This is one of the most common bodily problems that anxious neurotics encounter, because it is quite difficult to worry and not lose your breath.
The connection between hyperventilation and chest pain is as follows. Hyperventilation leads to contraction of blood vessels, and this, in turn, can cause pain, including in the chest, where the vessels are very large.
Self-hypnosis
All anxious patients with manifestations of vegetative-vascular dystonia, that is, symptoms of physical anxiety, are focused on the state of their health and pay excessive attention to it.
However, some neurotics achieve aerobatics in these actions. And they feel pain when there is none at all. And especially often they feel it in the chest, because the heart is there, and it is not healthy for them, therefore, it must hurt.
How to get rid of psychogenic chest pain?
Complete elimination of painful sensations in the chest area is possible only when the anxiety goes away. That is, for this it is necessary to get rid of anxious, anxious-phobic neurosis and other similar conditions. It is not simple. It may take years to return to normal life. Therefore, it is important to know how to relieve chest pain here and now.
And for this you need to take the following actions.
First of all, you should understand what causes you pain most often: whether it comes from the abdomen, from a muscle, from frequent breathing. Once you understand this, you can try to reduce the pain by addressing its trigger.
If your chest hurts from hyperventilation
Use the same methods that are used to eliminate a panic attack caused by hyperventilation. And also learn how to breathe correctly by studying these instructions.
If chest pain comes from the abdomen
Try to review your diet and exclude from it those foods that cause increased gas formation and flatulence.
If your chest hurts due to muscle spasm
Use muscle relaxation techniques for complete relaxation. Pay especially close attention to exercises for the back, abdomen and shoulders.
You can also learn how to do an exercise to relax your stomach and solar plexus. This will help you not only eliminate excessive muscle tone, but also normalize your breathing.
Carrying out diagnostics
To determine or confirm the diagnosis, a set of diagnostic measures is carried out, which include laboratory and instrumental methods. These include:
- An appointment with a doctor, during which an anamnesis of the disease is collected, the time of onset of the first pain, its duration and intensity, the presence of injuries and lifestyle are specified.
- Neurological examination.
- Urine and blood analysis.
- An ECG, which will confirm or exclude the presence of heart disease.
- An X-ray used to examine a patient's lungs.
- Ultrasound examination of the heart.
What is the standard of first aid for a hypertensive crisis?
- Causes of the crisis
- First aid: how to act?
- Standard for emergency medical care for hypertensive crisis
A hypertensive crisis is a dangerous condition of a person when his blood pressure (blood pressure) rises sharply due to one reason or another and is accompanied by painful symptoms of an attack. It is dangerous when blood pressure increases by 30-50 ml Hg at once. column, became higher than 180/120 or increased to a value that is individually intolerable to a person.
It is important to suppress the symptoms of an attack in time and prevent complications from developing, including stroke and myocardial infarction. Therefore, there is a standard for providing first aid for a hypertensive crisis, which must be immediately put into action.
Causes of the crisis
What can cause an attack of high blood pressure? With age, due to poor diet and lifestyle, the walls of a person’s blood vessels become thicker, causing the blood pressure on them to increase, resulting in increased blood pressure and symptoms of chronic hypertension.
For some older people, normal blood pressure will already be more than 120/70. Here it is appropriate to talk about a person’s “working” pressure - this is an individual blood pressure norm that is normal (non-dangerous) for a particular person at a certain age, that is, does not cause painful symptoms and attacks.
A crisis, on the contrary, like a sharp surge in pressure, is very dangerous. To carry out emergency medical care, the doctor must identify the causes of the hypertensive crisis. It could be:
- Stopping taking medications to constantly maintain normal blood pressure in case of chronic hypertension (the person forgot to take a pill or reduced the dose of the medication).
- Stress and chronic nervous tension.
- Sudden changes in weather conditions, changes in air temperature for weather-sensitive people (for example, before a cold snap, blood vessels constrict and pressure rises).
- Chronic interruptions in the functioning of the heart and blood vessels.
- Overeating (abuse of salty foods and liquids, fatty foods, especially at night) or excessive alcohol consumption.
- Head injuries.
- Smoking.
- Kidney failure (urolithiasis).
- Malfunctions of the endocrine system (problems with the thyroid gland, diabetes mellitus).
- Constant physical activity or, on the contrary, spontaneous fatigue due to a sedentary lifestyle.
- The period of menopause in women can also provoke sharp jumps in blood pressure.
- Complications during pregnancy.
First aid: how to act?
If you experience symptoms of a hypertensive crisis for the first time, do not prescribe treatment for yourself: call a doctor immediately. Only a physician can correctly assess your condition to make a decision on treatment.
The best thing you can do is take a horizontal “reclining” position and calm down, otherwise the pressure will increase even more (perhaps take a sedative). Then you need to wait for the ambulance to arrive.
If attacks are frequent and similar symptoms are habitual, then the patient or his relatives should have a clear action plan to cope with the crisis on their own:
- Provide the patient with peace, eliminate noise in the room, unbutton tight clothes;
- If necessary, give the patient a sedative tablet (valerian, corvalol);
- You need to take a pill that lowers blood pressure, which should always be in the first aid kit (captopril, corinfar, capoten, captopres, clonidine);
Important! It is not recommended to sharply reduce blood pressure; if blood pressure is 180/120 or lower, you first need to take 1 of 4 parts of the tablet, and after half an hour - another quarter, and so on. In general, this process can take 3 hours. If there are no blood pressure pills available, you can take 2 No-Spa tablets along with sedatives.
- Take a diuretic (furosemide);
- When bleeding from the nose, apply cold to the bridge of the nose, and tampons with peroxide into the nose and let the blood drain;
- If the symptoms of an attack do not go away or blood pressure does not decrease, then call an ambulance.
Standard for emergency medical care for hypertensive crisis
- Conducting diagnostics by a doctor, identifying causes and symptoms;
- Blood pressure measurement (normal in both arms, followed by monitoring every 15 minutes);
- Pulse measurement, cardiogram, their control and comparison with previous results;
- Prescribing medications that lower blood pressure (depending on the diagnosis based on determining the type of hypertensive crisis);
— Uncomplicated (worsening of the condition due to chronic hypertension).
- Hospitalization or recommendations for patients left at home.
In case of complicated crises, the patient must be hospitalized, and in uncomplicated crises, they look at the situation. If the pressure has not decreased in an hour or two, then you also need to monitor the patient’s condition in the hospital.
A hypertensive crisis requires immediate action. Only timely and correct medical care for the patient can have an effect and prevent complications from developing.
Signs (symptoms) of the disease
Intercostal neuralgia manifests itself with the following symptoms:
When such symptoms appear, intercostal neurosis can be difficult to distinguish from pathology of the heart or lungs. Therefore, it is extremely important to undergo high-quality medical diagnostics; you must take an x-ray of the lungs and be examined by a cardiologist, and have a cardiogram done. Only if specialists rule out diseases in their profile, then the treatment of intercostal neurosis will be carried out by a neurologist.
Folk remedies
In the treatment of intercostal neurosis, folk remedies have proven themselves well as an auxiliary therapy. But it is important to remember that traditional medicine is not recommended for use without consulting your doctor because of possible allergic reactions.
There are a large number of recipes that can be used for various manifestations of this pathological condition. Let's look at the most common of them:
- Calming agents. These include plants that have a sedative effect - mint, motherwort, chamomile, valerian.
- The anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect is achieved with ointments based on honey and pepper. Applying a cloth soaked in a hot saline solution to the source of pain may also help.
- There are many positive reviews regarding medicinal baths. When adding various herbs, it has a relaxing and anti-inflammatory effect on the body. Sage, lavender, and eucalyptus have proven themselves well in this regard.
It should be remembered that traditional medicine only complements the main treatment.