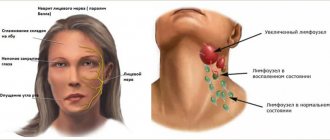
Main types of neuralgia and characteristics of pain
The damaged nerve generates pathological pain impulses, which are interpreted differently by the cerebral cortex depending on the location of the lesion. Classic neuralgic pain most often occurs when the trigeminal, occipital and glossopharyngeal nerves are irritated. Symptoms for intercostal neuralgia, neuropathic pain in the neck, lower back and limbs are more variable.
Trigeminal neuralgia and other facial pain syndromes
The symptoms of primary neuralgia are fully consistent with the classic picture described above. When the trigger zones are irritated, a sharp shooting throbbing pain occurs in half of the face, which is accompanied by limited mobility, change in skin color or lacrimation.
This is what pain with trigeminal neuralgia may look like from the outside
- Secondary neuralgia is characterized by damage to one or more branches, and not the entire nerve trunk. Most often, this is the mandibular, maxillary or infraorbital nerve. The painful sensation is less intense, the affected area is smaller. Spontaneous regression after cure of the underlying disease is characteristic. Residual symptoms respond well to simple analgesics.
- When peripheral nerve ganglia and small branches in the facial area are affected, specific symptoms arise; the eye, ear, jaw or group of teeth, as well as the head in the forehead area may hurt.
Read the full and detailed article about trigeminal neuralgia - Trigeminal neuralgia: causes, symptoms, treatment.
Intercostal neuralgia and other vertebrogenic syndromes
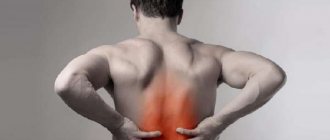
Intercostal, cervical, and lumbar neuralgia are most often symptomatic. The cause of pain is infringement of the dorsal roots of the spinal nerves at the exit from the spinal canal, which is why they are also called vertebrogenic. It occurs with a sudden movement or after a long stay in an uncomfortable position, and intensifies with a deep breath, coughing, sneezing, or changing body position. The intensity of the pain is described as severe or moderate, spreads to one or more intercostal spaces, and can be either unilateral or symmetrical. Sometimes it radiates to the upper abdomen, right hypochondrium, and in women to the mammary gland.
The photo shows the location of classic intercostal neuralgia
Intercostal neuralgia must be distinguished from referred pain, which occurs when internal organs of the chest and upper abdominal cavity are affected: the heart, lungs and pleura, liver, and lumbar neuralgia - from renal colic
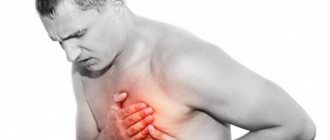
- Cardiac pain is intense, compressive, can intensify with inspiration, but does not depend on the position of the body. Accompanied by severe weakness, pale skin, and in severe cases, loss of consciousness;
- With pleurisy, the pain is more diffuse, felt in the entire half of the chest or radiates to the stomach (in the diaphragmatic form). Unlike intercostal neuralgia, the pain intensifies when the body is tilted to the healthy side and is accompanied by symptoms of intoxication: increased body temperature, headache, weakness;
- With renal colic, the pain radiates to the bladder and groin area, occurs acutely, but does not go away spontaneously, most often accompanied by general symptoms.
Read the full article about intercostal neuralgia - Intercostal neuralgia: causes, symptoms, treatment
This article provides general information about pain and types of neuralgia. The 2 main, most common types of neuralgia are presented with a brief description. For more complete information, see other articles.
Treatment methods
Several doctors can treat this disease at once. Typically, therapy is carried out by a proctologist, but sometimes the help of a gastroenterologist, rehabilitation specialist and psychotherapist is required.
Conservative treatment alone is not enough to eliminate symptoms. Therapy includes an integrated approach. In case of a disease of secondary origin, it is necessary to exclude the root cause (treat stool disorders and psychogenic disorders, engage in spinal therapy, do special exercises).
An integrated approach includes the use of the following treatment methods:
- physiotherapy: electrical stimulation, UHF, infrared radiation (necessary for relaxing tight muscles);
- injection anesthetics (novocaine blockades) - to relieve pain;
- massage to eliminate muscle tension and spasms;
- enemas with laxatives to soften the stool if the disease occurs due to hardening of the stool;
- Sedatives and tranquilizers are used to relieve anxiety.
Depending on the type of disorder that occurs, appropriate medication is used. If stool is abnormal, tablets are prescribed to normalize it; for psychogenic disorders, sedatives are indicated. In severe cases, muscle relaxants are prescribed to relax tight muscles.
Examples of medicines:
- to normalize sleep and calm: Donormil, Zopiclone, Phenibut, Corvalol, motherwort tincture, valerian extract;
- tranquilizers: Gidazepam, Diazepam, Mebikar;
- local painkillers: Anestezol suppositories, novocaine suppositories, Clonidine;
- laxatives: Duphalac, Guttalax, sea buckthorn oil, Microlax;
- for the treatment of hemorrhoids: Relief suppositories, Detralex tablets, Phlebodia.
Folk remedies are rarely used, as a rule, as part of complex treatment, as an addition to the main therapy. You can use herbal remedies to normalize stool and relax the central nervous system.
Forecast
The prognosis of the disease is unpredictable. In most cases, with timely consultation with a doctor, complications can be avoided, and relief occurs relatively quickly. Long-term treatment is required for some patient groups. In rare cases, therapy for the primary form does not help.
Some patients confirm the disappearance of pain, other patients do not note the effectiveness after the first course of treatment, relief occurs only after the second. The third group of patients is very difficult to cure.
Proctalgia with its symptoms disrupts normal life: patients cannot fully work and do normal activities.
Prevention
There are no specialized methods for preventing proctalgia. Basic measures should be aimed at maintaining a healthy and active lifestyle, as well as eliminating factors that increase the risk of disease:
- rejection of bad habits;
- normalization of nutrition;
- timely treatment of disorders of the spine, gastrointestinal tract, and nervous disorders.
Nausea and dizziness with osteochondrosis
Dizziness and nausea are usually manifestations of osteochondrosis affecting the cervical spine. Unlike other parts of the ridge, the cervical region is characterized by a thin structure. Many nerves and vessels are connected in the cervical area. This area of the spine is subject to constant stress, and even a slight displacement of the intervertebral discs can cause compression of the artery. In this case, the blood supply to the brain is disrupted, vision decreases, headaches and dizziness occur. The patient notes the occurrence of noise in the ears.
httpv://www.youtube.com/watch?v=embed/DVLCvQ_WhRU
If the pathology occurs in a progressive stage, the patient may experience nausea and even fainting.
Read: Diet for cervical osteochondrosis
In patients suffering from osteochondrosis, dizziness usually appears after the formation of hernias between the vertebrae or as a result of protrusions in the cervical spine. Due to compression of the vertebral artery, which supplies the brain, there is insufficient blood supply to the vestibular apparatus.
Patients complain of nausea most often in the morning. With osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, intracranial pressure may increase, resulting in vomiting and pain in the heart area.
Rectal neuralgia: symptoms, treatment – Neurology
Bad feeling
Intestinal proctalgia often occurs in those people who have not previously been bothered by the digestive tract. The pain syndrome occurs unexpectedly with a sharp pain radiating to the perineum, peritoneum and coccyx. Proctalgia in women, symptoms of the pathological condition may appear at 35-55 years of age. Soreness in the anorectal area occurs due to muscle spasm.
Proctalgia in women has symptoms that may disappear after a bowel movement or taking a bath with warm water (sitz bath). The pathology proceeds long and debilitatingly until the development of enderophobia.
Proctal syndrome requires medical examination, diagnosis and effective therapy.
The patient must be examined by a proctologist with a digital examination of the rectal organ and instrumental examination.
The attack and its signs and how long it lasts
It is quite difficult for the patient to understand whether it is neuralgia or another disease.
A debilitating painful attack is usually accompanied by additional manifestations, such as redness and itching of the skin along the nerve trunk and in the area of its innervation. Gradually, the intensity of the pain syndrome may increase and become unbearable for the patient. Additionally, affected nerve structures disrupt the function of neighboring organs or systems.
For example, trigeminal neuralgia is accompanied by pain in the eye on the affected side, lacrimation, twitching of the upper eyelid, involuntary smacking of the lips, and numbness of the tip of the nose. Damage to the sciatic nerve can lead to cramps in the anterior lateral thigh muscles.
Many patients try to relieve pain with NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) or analgesics.
However, temporary elimination of symptoms does not completely solve the problem, and in the near future the attack may recur again.
Basic principles of treatment of proctalgia
If proctalgia is diagnosed, the patient is prescribed the following treatment methods to relieve pain attacks:
- physiotherapy (infrared irradiation via intrarectal laser, mud therapy, diathermy, electrical stimulation);
- so-called novocaine blockades (usually perisacral, retrorectal and epidural-sacral);
- massage of the coccygeal muscle, massage of the elevators of the anus in case of pronounced spasm;
- microenemas using novocaine or sea buckthorn oil;
- sedatives (sleeping pills, sedatives and tranquilizers).
The course of treatment usually begins with sanitation of the rectum with antibacterial components, which are often used as a measure for the treatment of latent proctosigmoiditis. Since primary proctalgia is often associated with the psycho-emotional state of the patient, the main goal of therapy is to create a favorable psychological background and avoid stress and tension. Various psychotherapeutic relaxation methods are often used. It happens that a consultation with a psychologist is required.
In addition to strictly following all treatment instructions, you must adhere to the prescribed diet, which helps normalize the digestion process.
The secondary type of proctalgia goes away when the main disease causing this disease is cured.
Symptoms of vagus nerve neuritis.
Very often, the vagus nerve is damaged precisely in those areas that are related to strictly defined anatomical parts of the body. Accordingly, the symptoms of the disease are also different. One of the main symptoms characteristic of vagus nerve neuritis is paralysis of the soft palate, due to which the patient begins to speak “through the nose” and swallowing disorder due to paralysis of the pharyngeal muscles. In addition, due to damage to the vocal cords, the timbre of the voice changes (becomes more hoarse) and breathing becomes difficult, and if the process is also bilateral, it can even lead to suffocation. Also, symptoms of vagus nerve neuritis include cardiac dysfunction. This disorder is affected by a change in the pulse, which can speed up (120-180 beats per minute) and slow down (up to 30-40 beats per minute). Stomach upset can also be considered characteristic of vagus nerve neuritis. At least, the development of a painful phenomenon is associated with this moment, which is known as a tabic gastric crisis and the essence of which is uncontrollable vomiting, accompanied by severe pain in the stomach. When the vagus nerve is pinched, a person may experience attacks of severe headache - migraine (a sudden and severe attack of headache localized in one point of the head)
Not all symptoms of vagal neuritis develop at the same rate. This is important not only in relation to various forms of neuritis n. vagi, but also in relation to various cases of other neurological diseases.
So, for example, paralysis of the soft palate during diphtheria in the first patient increases slowly and reaches its greatest intensity on the 3-4th day, while in the second the full picture of the same paralysis is established within just a few hours. On the other hand, a symptom such as a gastric crisis in a “tabika-syphilitic” develops extremely slowly, and often several months pass before the picture of this symptom develops completely and takes on a completely finished form.
The persistence of symptoms in which vagal neuritis manifests itself also appears to vary. For example, paralysis of the soft palate due to diphtheria in most cases proceeds well, and with timely and correct treatment disappears completely. On the contrary, paralysis of the vocal cords due to the same infection in certain cases, having reached the highest degree of its development, no longer shows any tendency to weaken, remaining unchanged for the entire subsequent life of the patient.
Pathology of the anus
Bleeding and prolapse of the mucous membrane through the anus often occur with hemorrhoids. The diagnosis is made by performing sigmoidoscopy.
Papillomatosis of the skin around the anus, fibroepithelial polyps and thrombosis of external nodes are relatively less severe situations, but can provoke a serious clinical picture. If necessary, patients are referred to a surgeon to remove these formations.
Prolapse of the rectal mucosa can be mistakenly regarded as prolapse of hemorrhoids. The diagnosis is made by making the patient strain as if having a bowel movement. Although unattractive, it is best to examine such a patient while sitting on the toilet rather than in the left lateral decubitus position.
Anal fissures sometimes cause unbearable pain
Diagnosis is carried out based on complaints and anamnestic data with a careful examination of the anal canal. Sometimes such a study must be carried out using anesthetics
Treatment of anal fissures is currently conservative. Less commonly performed are traditional sphincterotomy and the discredited method of stretching (digital dilatation) of the anus.
Abscesses in the anorectal area usually form when infection penetrates into the anal glands located along the dentate line. An acute inflammatory process can cause abscess formation and the formation of a chronic fistula. Anorectal abscesses vary in length; they can be peri-anal, ischiorectal, intersphincteric and supralevator.
Types of neuralgia
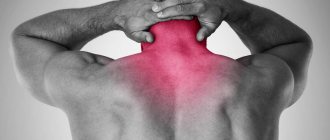
Acute and severe pain that appears in response to irritation of peripheral nerves is called neuralgia. It disrupts the function of the affected fiber. Depending on which plexuses are affected, neuralgia of the cranial, spinal or other nerves, for example, the femoral or sciatic, is distinguished. The main and most pronounced sign of pathology is burning pain along the nerve fiber. It is paroxysmal in nature and can increase significantly with physical activity. This pathology is also characterized by muscle spasms, a crawling sensation, numbness and increased sweating in the innervation zone. When the pathology is localized in the cervical region, dizziness and severe headache occur, and if the pathological process affects the thoracic region, then it becomes difficult for the patient to breathe.
Neuralgia, which negatively affects the functioning of the stomach, can be provoked by the following factors on the human body:
Diabetes mellitus may influence the development of symptoms.
- mechanical compression as a result of spinal osteochondrosis or arthritis;
- tumor process;
- hormonal imbalances;
- infectious agent;
- allergies;
- sudden and significant physical activity;
- diabetes;
- intoxication;
- injury;
- multiple sclerosis.
Trigeminal nerve damage
It is characterized by severe and sharp pain in the jaw and entire face, which significantly intensifies during touch or contact with clothing and air flow. Sometimes it spreads to the nose and eye area. It can be acute or chronic and causes disruption of facial symmetry. Patients often confuse this type of neuralgia with toothache. After an illness, a disruption in the functioning of the main facial muscles occurs.
Intercostal
If the nerves of the cervical spine are damaged, the patient may experience cognitive impairment.
Occurs in the back or neck due to compression of nerve fibers by the vertebrae or other pathological effects. Symptoms depend on the location of the process. When the nerves of the cervical spine are damaged, severe headaches, dizziness and cognitive disorders develop. If the nerves in the chest are affected, the patient has difficulty breathing and attacks of shingles pain occur. When localized in the lumbar region, digestion is disrupted and the stomach hurts. The disease is also characterized by irradiation of unpleasant sensations along the nerves. Muscle spasm occurs, motor and sensory function suffers. Increased pain occurs with sudden movements or physical activity.
Glossopharyngeal nerve
The characteristic localization for the lesion is the innervation zone in the pharynx, tonsils and root of the tongue. Sometimes the discomfort spreads to the ears and lower jaw. In severe cases, pain may radiate to the neck and eyes. The pain is sharp and paroxysmal. Initially, it provokes dry mouth, and after the attack ends, it causes increased sweating and salivation.
Other types
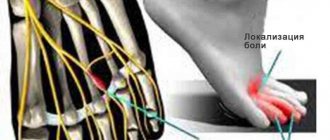
If the problem is in the sciatic nerve, then the pain can reach the feet.
With sciatic neuralgia, symptoms manifest as pain in the limbs, back, and are especially pronounced in the feet. The lumbago can also radiate to the chest area. In this case, spasmodic muscle contraction and weakness appear. Damage to the superficial cutaneous nerve in the thigh is characterized by a feeling of numbness and tingling. Neuralgia of the occipital nerve fiber provokes a piercing headache and pressing sensations in the eyes. Increased discomfort occurs when you move your head and radiates to the neck and chest.
Diagnosis and treatment of anorectal neuralgia
The disease is not classified as dangerous or developing, but it causes a lot of trouble. Occurs regardless of gender and age in approximately 6.5% of the population.
The main characteristic is uncontrolled contraction of the anus, as well as the rectum. Painful sensations spread to the peritoneum and lower back. Rectal neuralgia is not accompanied by mechanical damage to organs, being exclusively a problem of the nervous system.
At the moment, anococcygeus pain has not been sufficiently studied, but experts identify possible provoking factors:
- bruised tailbone;
- fracture (even an old one);
- nervous disorders in the muscle tissues of the pelvic and retroanal areas;
- pathological changes in the musculoskeletal system in this area;
- neuralgic diseases of the spine;
- problems in the intestines (hemorrhoids, fissures, etc.);
- organ prolapse;
- tense mental states;
- problems with bowel movements (frequent constipation, diarrhea).
Symptoms
The main indicator of the presence of a problem is severe pain in the rectum, interfering with normal life activities. These signs appear in:
- coccyx (called “coccydynia”);
- anus (anal neuralgia). Usually they have no prerequisites for their appearance.
- be a constant companion of the victim;
- occur suddenly and continue for any time, but usually no more than half an hour and at night.
The pain can be either dull or stabbing. Sometimes they are of such a nature that it is impossible to determine the exact location.
- spasms;
- burning in the tailbone;
- heaviness in the stomach;
- priapism;
- pale skin;
- increased sweating.
If the underlying disease is persistent cancerophobia, then the patient is indicated for surgical intervention due to organic factors.
Classification
Doctors identify several classification bases, each of which describes the nature of the disease:
- By location:
- in the coccyx area – coccydynia;
- in the anus - anorectal syndrome.
- Type:
- primary;
- secondary. It is a symptom of other diseases, mainly in neighboring organs (prostatitis, acute urethritis, problems “on the female side”, etc.).
- According to the nature of the manifestations:
- Night. The pain occurs at night and lasts for an indefinite period of time. Additional localization: in the perineum, pelvic floor.
- Spastic. Determined by the presence of gastrointestinal diseases and stool disorders.
- Anusolgia (“flying proctalgia”). It is distinguished from the nocturnal type by a known cause: back injuries, infectious diseases of the urinary system, and sometimes constipation.
Diagnostics
Anococcygeal pain syndrome is made as a diagnosis only after excluding the possibility of organic pathologies:
- problems with the intestines - hemorrhoids, anal fissures, etc.
- diseases of the reproductive system – endometritis, prostatitis, etc.
- rheumatological diseases – radiculitis, sciatica.
- neuralgia.
If the examination establishes that the cause of the painful sensations is not a disease of a certain organ, then a diagnosis of “ancoccygeal syndrome” is made.
The examination is carried out by a proctologist and gynecologist.
The proctologist determines the absence of:
- damage to the anus;
- foci of inflammation;
- injuries of the sacrum or coccyx;
- muscle spasm in this area.
A gynecologist is recommended for women to analyze the condition of the reproductive organs.
Laboratory tests are required. Standard procedures include:
- coprogram;
- feces for testing bacteria and the presence of blood in the composition;
- general urine analysis;
- gynecological tests for both sexes.
For a full diagnosis, consultations with a urologist, traumatologist, andrologist, neurologist, and psychotherapist are often necessary. Only after their conclusions does the attending physician make a final decision regarding the nature of the disease.
Treatment of vagus nerve neuritis with folk remedies
Traditional medicine suggests treating inflammation of the vagus nerve with the help of healing infusions and decoctions.
Here are the recipes for some of them:
- A tablespoon of meadow clover is poured into a glass of boiling water. Infuse for 20-30 minutes and strain. Take half a glass twice a day
- A tablespoon of thyme is poured with boiling water, about 250 ml, and left to steep for 15-20 minutes. The resulting decoction is filtered and taken one third at a time throughout the day.
- 50 grams of linden flowers are poured into 0.5 liters of white wine and allowed to brew for two weeks in a warm place. The resulting infusion is filtered and taken 3 times a day, 100 grams each.
- Fifty grams of thyme, pour 0.5 liters of white wine. Leave for a week in a dark place. This infusion should be taken ten drops in milk, four times a day.
For those who prefer aromatherapy, in addition to tinctures and herbs, we can also recommend making a special aromatic pad. For this you will need thyme, mint, lemon balm, several hop cones, lavender, rue, chamomile, bay leaf and oregano. You can sleep on this pillow, or just keep it nearby while you sleep.
To be honest, the treatment of inflammation of the vagus nerve with folk remedies seems to us rather dubious, and probably the only advantage of these methods is that all of them can be used at home.
Vagus nerve neuritis has a strong negative impact on the body, so patients need help in a medical facility.
(2 ratings, average 3 out of 5)
Michael
All about rectal fissures with hemorrhoids
Anal fissures with hemorrhoids, even small ones, can turn a person’s life into a series of suffering, pain and shame. It is not customary for us to talk about such problems, although hemorrhoids are the most common ailment of the colon.
Hemorrhoids are often accompanied by fissures in the anus
This is not just discomfort, but a serious illness accompanied by bleeding, so you need to discard the modesty that is inappropriate in this case and consult a doctor for help. Today for you - useful information about fissures in hemorrhoids - treatment, symptoms, causes, possible complications.
Fissure in the anus - symptoms, causes
The pathology consists of ruptures of various sizes in the mucous membrane of the rectum or a defect in the skin in the anus. A fissure by itself rarely occurs; more often it is a consequence of serious health problems; chronic and acute hemorrhoids are the most common cause.
Attention! The main symptoms of fissures in hemorrhoids are pain in the anus, rectal bleeding, spasms of the anal sphincter and prolapse of hemorrhoids. Blood from cracks is always scarlet in color
Bleeding occurs due to injury to damaged areas of the rectum with feces. The pain spreads to the entire perineal area, so cases of difficulty urinating are also common.
Blood from cracks is always scarlet in color. Bleeding occurs due to injury to damaged areas of the rectum with feces. The pain spreads to the entire perineal area, so cases of difficulty urinating are also common.
The symptoms are in a closed cycle: one problem provokes an increase in another. A slight pain in the anus is constantly present, but significantly intensifies with defecation. Severe pain causes muscle spasm of the anus, which again leads to painful sensations and prevents the healing of the mucous membrane.
Ointments for the treatment of hemorrhoids
Causes of anococcygeus syndrome
The main provocateur of ABS is considered to be a one-time or long-term injury to this area as a result of constant exposure, for example, when regularly sitting for a long time, or when shaking in a vehicle. This is about coccydynia. These include abnormalities in the structure of the spine, which contribute to the development of neurological and vascular pathologies.
Pain in the anorectal area occurs for the following reasons:
- Anomalies of the neuromuscular tissues of the pelvic floor, as a result of which the muscles contract by themselves;
- Descent of the perineum;
- Formation of areas of connective tissue, simply scars, after surgery in the anus;
- Subsequently, prolonged disturbance of stool, both in liquid form and in the form of constipation. Pain does not arise from defecation itself, but as a result of changes that have formed for this reason;
- Injuries after difficult childbirth;
- The habit of sitting on the toilet for a long time;
- The presence of diseases of the lower intestines, such as proctitis, anal fissure, hemorrhoids, sigmoiditis. Again, pain is not a direct reaction to these pathologies, but as a consequence of the resulting changes, therefore, at the time of the formation of the syndrome, the diseases can already be treated;
- Psychological factors that arise for various reasons.
Presumably, ABS occurs after prolonged pathological and traumatic situations that lead to disruption of the transmission of nerve impulses to the muscles. The result is involuntary spasms or constant tension, poor circulation and nutrition, which leads to pain. Psychological factors fuel this condition and provoke its continuation.
What is proctalgia
Proctalgia is a sharp pain syndrome in the anal area that occurs against the background of muscle spasm. The pain may radiate to other parts of the body: the tailbone, perineum or abdomen. In ICD-10, the disease is described in the section “Other functional intestinal disorders” under paragraph K59.4 - spasm of the anal sphincter.
The pathological condition develops regardless of gender. Office workers who spend a lot of time in a sitting position are most prone to it. The condition is aggravated if you are in the wrong position and on a hard surface.
When sitting for a long time, the muscles of the back of the thigh and buttocks are overloaded, and the sacroiliac joint suffers. Spasms often occur in adolescents, mainly at night.
Types of disease
Proctalgia in men and women is divided into two types:
- Primary – occurs against the background of psycho-emotional disorders and overload of the nervous system, which develop under severe stressful conditions.
- Secondary – the result of other pathological processes in the body that affect the appearance of muscle spasticity (which is typical against the background of the occurrence of proctological diseases).
Features of the course in women
Often the disorder has signs of coccydynia: pain is felt not only in the anus, but also in the rectum and tailbone. The pain is intense and protracted. Typically, attacks occur at night during sleep, during prolonged sitting and during bowel movements.
As it worsens, the pain radiates to the hip joint or perineum. Referred pain in the perineum often blurs the picture of the disease, which is why the patient may think that she has an exacerbation of cystitis. If the diagnosis is made incorrectly, treatment will not have an effect.
Proctalgia in women symptoms, types, signs, complications, diagnostics, drugs, traditional methods
Poor health
Intestinal proctalgia often occurs in those people who have not previously been bothered by the digestive tract. The pain syndrome occurs unexpectedly with a sharp pain radiating to the perineum, peritoneum and coccyx. Proctalgia in women, symptoms of the pathological condition may appear at 35-55 years of age. Soreness in the anorectal area occurs due to muscle spasm.
Proctalgia in women has symptoms that may disappear after a bowel movement or taking a bath with warm water (sitz bath). The pathology proceeds long and debilitatingly until the development of enderophobia.
Proctal syndrome requires medical examination, diagnosis and effective therapy.
The patient must be examined by a proctologist with a digital examination of the rectal organ and instrumental examination.
Types of proctalgia
Proctalgia in both men and women is recognized by two types:
- Primary – occurs against the background of emotional stress and nervous disorders.
- Secondary – occurs against the background of various pathological processes.
The secondary type of proctalgia is provoked by hemorrhoidal inflammation, fissures in the anal area, tumors, and Crohn's syndrome. Secondary proctalgia can be caused by an imbalance in the urinary and sexual spheres.
Proctalgia is recognized by type:
Pain syndrome
- Night - based on the name of the type of pathological syndrome, one can guess that a proctalgic attack occurs at night with characteristic varying pain in the form of spasms (proctological fugues). The pain varies in intensity and duration. This pain syndrome is felt in the perineal muscles and hip region.
- Spastic - manifested by problematic bowel movements in the form of constipation, diarrhea, imbalance in the digestive tract.
- Anusolgia - this type of proctalgia is also called flying proctalgia. If we compare it with night syndrome, then distinctive features are observed in the causes of the pathological condition. Anusolgia appears against the background of injuries to the sacrococcygeal region, inflammation of the urinary or genital area, and vertebral diseases. Constipation is often the cause of anusolgia.
Proctalgia symptoms and signs
Neuralgia from the rectum is recognized by certain signs and symptoms. The main symptom of the disease is a prolonged painful sensation (half an hour).
During an attack, the pain intensifies when relaxed, sleeping or sitting. The syndrome is felt by a sharp pain in the rectal organ, radiating to the perineum, to the coccyx, and hip joints.
Discomfort is also felt in the lower abdomen, gluteal area, and bladder.
When emptying, the pain symptoms subside. Attacks occur most often during sleep; if the patient wakes up and takes a standing position, the pain manifests itself less, and a sitting position, on the contrary, increases the pain.
Neuralgia from the rectum manifests itself not only at night; it can disturb peace during the daytime, but the duration of attacks is shorter. But the frequency of paroxysmal pain during the day is increased. With a long attack of more than 30 minutes, proctologists diagnose spastic proctalgia.
Sometimes a pathological phenomenon can be confused with impaired functioning of the urinary and reproductive systems. This is due to similar manifestations of pathological conditions.
Doctors have not confirmed the factors that caused proctalgia, since the condition is still being investigated.
Proctologists think that the female condition of intestinal spasms occurs against the background of psychosomatic diseases and neuralgic changes.
Features of proctalgia in women
Pain from hemorrhoids
Proctalgia in women is marked by coccygodine pain. Simply put, pain is felt not only in the anal area, but also in the coccygeal-sacral region and throughout the intestines.
The pain lasts a long time and is marked by strong intensity. The symptom manifests itself during bowel movements, sleep or prolonged sitting. Additional symptoms for women include pelvic pain in the joints and perineum.
In terms of painful symptoms, the pathology is similar to inflammatory processes of the genitourinary tract (cystitis, vesiculitis).
According to medical observations, proctalgia most often affects the female body. The disease has a simplified name, I call it doctor’s disease, so the disease manifests itself to a greater extent in women who work mentally.
Diagnosing proctalgia
The diagnosis is established by a proctologist after carrying out the necessary research activities. Diagnosis of proctalgia is necessary to exclude other possible pathologies with similar symptoms.
A gynecologist refers a woman to a proctologist after examining the female reproductive and genitourinary organs.
A gynecological examination for proctalgia must be carried out, since the disease is often accompanied by additional proctological and genitourinary diseases.
At an appointment with a proctologist, the doctor examines the patient and conducts a digital examination of the rectal organ. This procedure is painless. If the doctor deems it necessary, sphincteromanometry of the urinary and genital areas is performed with testing of the sphincters (tone study).
Additional diagnostic measures are:
At the doctor
- laboratory blood test (detection of inflammatory processes);
- rectaromanoscopy – instrumental examination with a rectoscope;
- irrigoscopy - examination of the intestinal walls;
- colonoscopy – instrumental examination with a colonoscope (diagnosis of the intestine along the entire length);
- when no pathologies of the urinary tract are detected, the proctologist prescribes an additional examination with an ultrasound machine, as well as examinations by a urologist and gynecologist.
When no pathological changes are found in patients, but pain is present, proctalgia, the primary type, is diagnosed. Usually, before turning to specialists, patients have already tried to relieve painful symptoms on their own, so during a consultation with a proctologist, the patient should tell what measures he took and what results of treatment were noted.
Principles of treatment of proctalgia
To carry out therapeutic procedures to eliminate proctalgia, complex complex treatment is used.
Before prescribing a treatment regimen, the patient undergoes an examination by several highly specialized specialists: gynecologist, urologist, proctologist, gastroenterologist, psychotherapist.
In addition to the prescribed treatment regimen to eliminate the underlying disease that preceded the onset of proctalgia, drugs and procedures are prescribed to relieve painful symptoms, namely:
- physiotherapeutic effects - infrared beam treatment, mud, UHF, electrical stimulation with other procedures;
- medications in the form of injections (Novacaine);
- severe spasm of the puborectalis muscle is treated with massage;
- enemas with sea buckthorn oil, novocaine, collargol are prescribed;
- Sedatives and tranquilizers are recommended.
When the attack of pain is one-time without radiating to other pelvic organs, with a short duration, this is a benign indicator and requires therapy. A warm bath and massage can usually help.
Primary proctalgia is treated with psychotherapeutic methods using sedative medications. The patient needs to create a calm environment, without mental overload. Relaxation with relaxing procedures and a complete absence of stress is shown. Experts prescribe a special diet to normalize digestion and regulate the balance in the intestines.
It is not recommended to eat unhealthy foods, which include fatty, salty, spicy, smoked, sour foods, coffee, and alcohol. Doctors insist on quitting smoking. A healthy diet menu consists of fruits and vegetables, fermented milk products, cereals, soups and more.
Folk remedies are rarely used in the treatment of proctalgia. Basically, traditional medicine serves as additional manipulations to the main drug therapy. Herbal remedies are used to normalize intestinal function.
Prediction of proctalgia symptoms treatment
After therapeutic measures to eliminate proctalgia, patients have a different prognosis. Some patients confirm the effectiveness of treatment - the disappearance of pain. Some patients did not notice any effectiveness after the first course of treatment; relief occurs after the second course. The third group of patients is very difficult to cure.
Proctalgia with its symptoms disrupts normal life, patients cannot fully work.
Who is susceptible
Who is at risk for this disease?
The female body is most susceptible to proctological disease. Most often, women experience this syndrome between the ages of 30 and 65 years.
This group of patients suffers due to the psychoneurological direction of pain.
After patients contact a proctologist with complaints of attacks, the doctor often considers the symptoms as a sign of another disease, which often has nothing to do with the intestines.
The clinical picture of pain in male and female patients is no different. There are differences only when prescribing diagnostic measures. Symptoms of proctology are often confused with signs of ancoccygeal syndrome, and disturbing sensations in the rectal organ are attributed to pathologies of the reproductive system (endometriosis, salpingoophoritis).
Drugs
Help with medicines
If, after diagnosis, the patient has excluded the possibility of concomitant pathologies and neuralgia is detected, the proctologist prescribes symptomatic therapy using the following medications:
- drugs to improve sleep and calm the nervous system: Donormil, Valocordin, Valeriana forte, Sedasitron, Zoliclon;
- medications for pain relief - Anestezol, Clonidine, Salbutamol;
- tranquilizers – Diazepam, Gidozepam;
To relieve the pain of frequent attacks, novocaine blockade is used. With the help of the procedure, it is possible to quickly eliminate pain for a long time. However, doctors warn that it is not recommended to use such therapy often. As an alternative solution, pain relief can be carried out with microenemas with novacaine solution. Or sea buckthorn oil.
Folk remedies
To improve intestinal health and overall well-being, you can use folk recipes. You can improve intestinal function with a composition made from buckthorn. Crushed bark (2 tbsp) is poured with 200 ml of boiled water and kept wrapped for 30 minutes. The solution is taken one spoon twice a day
Traditional methods
Orange juice can improve intestinal function, but the juice must be freshly squeezed. Fresh orange juice is consumed twice a day, half a glass. Juice from mint leaves is good for proctalgia. Only young leaves are suitable for preparing medicine.
The product is taken at the rate of half a teaspoon of juice and 200 ml of water. After combining the two components, the solution is taken one time before meals. You need to take the product three times a day.
To improve the taste, you can add a spoonful of honey to a glass with the prepared composition.
Some patients recommend treatment with a remedy prepared from the rhizome of calamus. A composition is prepared from 3 tablespoons of raw materials and 400 ml of boiled water (cook over low heat for a quarter of an hour). After preparation, the medicine is filtered and drunk during the day in small portions.
To begin therapeutic measures, you must consult with your treating proctologist.
Source: https://proctoinfo.ru/vidy/u-zhenshhin/simptomy-zhenskoj-proktalgii.html
Symptoms
The main indicator of the presence of a problem is severe pain in the rectum, interfering with normal life activities. These signs appear in:
- coccyx (called “coccydynia”);
- anus (anal neuralgia). Usually they have no prerequisites for their appearance.
The pain may:
- be a constant companion of the victim;
- occur suddenly and continue for any time, but usually no more than half an hour and at night.
The pain can be either dull or stabbing. Sometimes they are of such a nature that it is impossible to determine the exact location.
Neuralgia is accompanied by:
- spasms;
- burning in the tailbone;
- heaviness in the stomach;
- priapism;
- pale skin;
- increased sweating.
Anorectal pain (neuralgia) adds the following zones to the painful areas described above:
- buttocks;
- vagina;
- hips;
- sacral region.
Most often occurs in women over 50 who suffer from:
If the underlying disease is persistent cancerophobia, then the patient is indicated for surgical intervention due to organic factors.
Diagnostics
It is impossible to diagnose proctalgia based on the patient’s complaints alone; one way or another, a set of examinations should be carried out that will exclude organic damage to the rectum.
It is important to clarify the anamnesis (history) of the pathology. It is often revealed that patients with proctalgia suffered:
- diseases of the urinary system;
- disorders of the genital organs;
- proctological pathology.
It also happens the other way around - proctalgia precedes the mentioned diseases, patients who have developed such pathologies indicate previously observed pain in the rectum.
Proctalgia is one of the pathological conditions in which additional studies should be carried out as widely as the diagnostic capabilities of the clinic allow. These are physical, instrumental, laboratory methods.
Physical examination findings will be as follows:
- when examining the anus, in some cases the external sphincter will be spasmed;
- during rectal examination (digital examination of the rectum) there is no pain, spasm of the levator muscles may be observed.
The instrumental methods used in the diagnosis of this pathology are as follows:
- sphincteromanoscopy – measurement of the tone of the rectal sphincter;
- rectoscopy - examination of the inner surface of the walls of the rectum using a rectal mirror;
- sigmoidoscopy - examination of the rectum and final parts of the sigmoid colon using a sigmoidoscope;
- colonoscopy - examination of the large intestine along its entire length using a colonoscope;
- irrigoscopy - an X-ray examination of the large intestine, in which a contrast agent is injected into it, after which a series of X-ray images are taken;
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs (ultrasound) – it can be used to determine the presence of a pathological process in a particular organ, its location, size, tissue characteristics;
- diagnostic laparoscopy - during this examination, a laparoscope (a type of endoscope) is inserted through a small incision in the abdominal wall, and the abdominal and pelvic organs are examined.
To exclude urological diseases, a consultation with a urologist is indicated; for gynecological diseases in women, a consultation with a gynecologist is recommended.
Among the laboratory methods used in the diagnosis of proctalgia are:
Source: https://medspina.ru/prichiny/anorektalnaya-nevralgiya.html
Pain in the rectum
There are several causes of pain in the rectum.
- Cracks in the anus. This is the most common cause of pain in the rectum. Symptoms of a fissure are severe, sharp pain, streaks of blood in the stool. Seven percent of patients complain of diarrhea, and twenty-five percent of constipation. The doctor will easily detect the crack during the examination. Acute fissures are treated with hot sitz baths three times daily and an emollient laxative. Chronic fissures are often treated surgically.
- Paraproctitis. This disease is characterized by inflammation of the anal glands, which are located in the anal sinuses. A sign of paraproctitis is constant pain in the rectum of a pulsating nature, accompanied by an increase in temperature. When examining the rectum under local anesthesia, the doctor will find an area of compaction. Paraproctitis is treated surgically.
- Thrombosis of hemorrhoids. Areas of the rectal venous plexus dilated according to the varicose type are called hemorrhoids. Internal hemorrhoids are located above the rectal-anal girdle and are innervated by autonomic nerve endings. The external nodes are located above this belt and are innervated by the spinal nerves. Internal hemorrhoids do not bother the patient, but thrombosis of external nodes causes severe pain in the patient. The main complaint of a patient with hemorrhoidal thrombosis is the appearance of a very painful lump in the anal area, which could be preceded by constipation or diarrhea. The doctor, under local anesthesia, will set the prolapsed internal hemorrhoid and prescribe the appropriate procedures.
- Haemorrhoids. Hemorrhoids are varicose areas of the venous plexus in the rectal area. The main signs of hemorrhoids are blood from the rectum after defecation, pain in the rectal area, subjective sensation of a lump in the anal area, itching. The diagnosis of hemorrhoids will be made by a proctologist, excluding other diseases that cause bleeding. Hemorrhoids have been treated conservatively for quite a long time. For treatment, suppositories, ointments, and a special diet are used. If the disease has progressed significantly, surgical treatment such as hemorrhoidectomy, sclerotherapy, and ligation of hemorrhoids is necessary.
Comments on this post: 1
Treatment
The effectiveness of therapy is determined by:
- completeness of the examination;
- correct diagnosis;
- correct identification of the root cause.
Treatment is carried out in 3 areas:
- Etiological. They try to rid the patient of the factors that provoke the disease.
- Pathogenetic. If possible, the development of the problem is slowed down.
- Symptomatic. First of all, pain relief.
A popular method is physiotherapy:
- laser radiation;
- UZ;
- UHF;
- mud treatment;
- massage.
Local preparations include suppositories, microenemas with painkillers and anti-inflammatory substances.
Since a common cause is an unstable psychological state, consultations with specialists in this field are often prescribed.
Analgesic methods
Treatment of pain, especially of unknown origin, is one of the areas for study in modern medicine. There are medical institutions all over the planet that are engaged in the prevention and relief of their patients from syndromes of this kind.
Doctors prefer not narcotic drugs, but various analgesics:
- Novocaine blocks nerve transmissions;
- local anesthesia relieves pain;
- hot applications relieve discomfort.
Cortisone has now proven its own ineffectiveness and the harm it causes to patients.
Placebo is applicable for psychogenic origin of the syndrome.
Sedatives and tranquilizers are prescribed for those suffering from:
- depression;
- anxiety;
- neurotic conditions.
Surgical intervention
Indicated in the most extreme cases if:
- coccydynia appeared only due to the injury;
- there is a separation of the tip of the coccyx.
In this situation, the operation is called extirpation. During the procedure, the coccyx is fixed at the sacrum.
Intercostal neuralgia with osteochondrosis
Intercostal neuralgia is pain that occurs as a result of compression of the roots of the intercostal nerve and spreads throughout the chest. Typically, intercostal neuralgia indicates the development of thoracic osteochondrosis. The condition occurs with constant or paroxysmal pain, and numbness, tingling or a burning sensation may occur.
httpv://www.youtube.com/watch?v=embed/H52cAXO1qSU
In addition, intercostal neuralgia is accompanied by:
- increased sweating;
- pallor or, conversely, redness of the skin;
- contraction and twitching of muscles.
In some situations, pain due to osteochondrosis can radiate to the back, shoulder blade, and cardiac area. Typically, the pain increases after changing position, when walking, coughing or sneezing, or deep breathing.
Intercostal neuralgia can also develop with the following diseases:
- Angina pectoris.
- Myocardial infarction.
- Mitral valve prolapse, etc.
The onset of the disease develops in the form of an acute muscle spasm that occurs after physical activity, sleeping in an uncomfortable position, unsuccessful movement, or working in an awkward position. Often, intercostal neuralgia can occur as a result of hypothermia, being in a draft, after a cold, stress, or chest injury.
Read: Neck massage for osteochondrosis at home
Treatment of intercostal neuralgia primarily depends on the root cause of the disease. When choosing a treatment method, the doctor takes into account various individual indicators of the patient. Painkillers and ointments are not effective in the fight against this disease.
It is necessary to understand that nausea, dizziness, pain, intercostal neuralgia are only manifestations of spinal osteochondrosis. That is why the underlying disease that caused the above symptoms should be treated.
SUBSCRIBE TO SITE UPDATES
Causes
The reasons depend on the type of disease :
- Nocturnal primary proctalgia develops exclusively during sleep with varying degrees of pain, depending on the strength of the muscle spasm. The pain often radiates to the muscles of the pelvis and perineum. Usually develops against the background of an overloaded nervous system with an unstable psycho-emotional state.
- The spastic form occurs against the background of a problematic act of defecation, when the patient suffers from constipation or diarrhea. The root cause lies in gastrointestinal disorders.
- Volatile proctalgia (anusalgia) occurs against the background of a concomitant disease. Refers to a pathological condition of the secondary type. Anusalgia manifests itself against the background of previously suffered injuries to the sacroiliac joint, injuries to the spine and coccyx, and diseases of the genitourinary area. It is often caused by chronic constipation.
What to do
Neuralgia can be treated using medications and surgical methods. Conservative therapy consists of using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of ointments or intramuscular injections. Widely used drugs in this group are Diclofenac and Ibuprofen. If such measures are ineffective, it is worth resorting to surgery and eliminating the compression of the nerves in the area of narrowing of the channels through which they run. There is no need to treat the stomach itself with neuralgia with medications. The doctor will recommend using soothing infusions and decoctions of chamomile, mint, calendula, which normalize peristalsis and the stomach begins to function normally.
httpv://www.youtube.com/watch?v=embed/XxfL5t3fmkU
LiveInternet LiveInternet
Knitting. Hat with a honeycomb pattern. Dolgova Yulia Knitted.
Delicious crispy sauerkraut in brine Sauerkraut according to this recipe turns out very well.
Homemade adjika recipe. Raw adjika without canned tomatoes and bell peppers.
The secret of women's health and youth - point San Yin Jiao The secret of women's health and youth.
When you look at this tiny “hut”, you can’t believe that inside there is a stylish two-room apartment.
— Applications
- Blog catalog The
blog catalog allows you to organize the blogs of people and communities into categories, allowing you to quickly find the necessary and interesting blogs among the huge number of blogs on the site li.ru - Postcards
Reborn catalog of postcards for all occasions - I am a photographer
Plugin for publishing photos in the user's diary. Minimum system requirements: Internet Explorer 6, Fire Fox 1.5, Opera 9.5, Safari 3.1.1 with JavaScript enabled. Maybe it will work - always no analogues at hand
^_^ Allows you to insert a panel with an arbitrary Html code into your profile. You can place banners, counters, etc. there - TV Guide
Convenient weekly TV guide provided by Akado TV Guide.
Diagnostics
If there are signs of inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, you need to visit a gastroenterologist. During the initial examination, the doctor collects an anamnesis to establish a preliminary diagnosis - records the patient’s main complaints, the presence of congenital and chronic pathologies, conducts an external examination and palpation of the abdominal cavity. Diagnostic methods are the same for adults and children, but they try not to prescribe studies that involve radiation for young children and pregnant women.
Clinical tests:
- coprogram - allows you to identify the presence of pathologies in the lower intestines;
- examination of stool for the presence of blood impurities;
- biochemistry to exclude the presence of malignant tumors;
- clinical blood test - the presence of an inflammatory process is indicated by a high level of ESR and leukocytes;
- bacteriological analysis of stool.
Fecal analysis will help identify the cause of intestinal inflammation
In addition to tests, the patient is prescribed instrumental diagnostics - gastroscopy, sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy, biopsy, endoscopy. The methods allow us to identify the location and degree of pathological changes.
Treatment of coccydynia
Coccydynia is a very “individual” disease that can have a wide variety of symptoms and occur differently in different patients. In the treatment of coccydynia, an integrated approach is necessarily used - in parallel with classical medicine, physiotherapeutic procedures are used - rectal darsonvalization, ozonation of the anal canal (if the cause of coccydynia is an inflammatory process), UHF therapy, mud therapy and applications.
In some cases, surgical treatment is used - coccygectomy, which involves removal of the coccyx, but for the operation there must be appropriate indications - for example, if conservative treatment is carried out for quite a long time and does not bring effect. However, remember that the final decision regarding the treatment method for anococcygeus pain syndrome is made by your attending physician, based on the results of the examination, medical history, your examination and indications.
There is no need to endure pain if you notice symptoms of coccydynia, because the disease, if not treated, can seriously worsen the quality of your life - you will have to give up communication with work colleagues, relatives, children, just acquaintances and friends, i.e. To. any movement during coccydynia will cause you suffering. Just one visit to a proctologist is enough to diagnose and begin quality treatment that will return you the joy of movement and self-confidence. Throw away shame, fear and apprehension - your health and your everyday well-being are at stake.
Gives to the stomach with osteochondrosis
Almost all organs of the peritoneum are connected to the nerve endings of the thoracic spine. Patients suffering from thoracic osteochondrosis most often note the formation of pain radiating to the abdomen.
Abdominal pain with osteochondrosis is distinguished by the following symptoms:
- non-diffuse pain;
- pain is localized in the area of innervation of the affected area;
- pain occurs and also intensifies after the slightest movements or when turning, as well as coughing;
- pain is felt at the level of muscle tissue;
- usually the pain is one-sided, constant, dull or aching.
Pain in the abdomen in people suffering from osteochondrosis limits and impedes their movements. Usually the pain radiates to the stomach with such lesions of the ridge:
- in case of damage to the mid-thoracic nerves, pain is observed in the stomach;
- if the pathology is localized in the 8th and 9th roots, then the pain forms in the area of the duodenum;
- if osteochondrosis affects the 7th, 8th, 9th thoracic roots on the right, then pain is felt in the hypochondrium on the right.
Read: Exercises for osteochondrosis of the thoracic region
Cervical and thoracic osteochondrosis, in addition to abdominal pain, can provoke problems with stool, impaired intestinal motility, and pathologies of gas formation.
Soreness in the stomach
When the spine is affected by osteochondrosis, patients often experience pain in the organs of the digestive system. Often such stomach pains are mistakenly diagnosed as gastroduodenitis.
Infringement of the spinal root in the vegetative part of the ridge causes spasm or irritation of the nerve. The result is heartburn and nagging pain. Over time, pain in the digestive organ becomes constant.
Stomach pain caused by osteochondrosis is easily differentiated from gastric disorders: pain due to pathologies of the spine increases with the slightest movements or turns.
Pain in the lower abdomen
Typically, pain in the lower abdomen is caused by pathology progressing in the lumbar region. If the disease affects the thoracic area of the spinal column, then pain is felt on the right in the abdominal area. The symptoms resemble those of appendicitis, but without an increase in body temperature. In addition, pain in the lower abdomen is similar to manifestations of gastritis and colitis.
Osteochondrosis in this case is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- heartburn and nausea;
- feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium;
- cramps and bloating;
- stabbing pain in the right lower abdomen;
- constipation occurring with nagging pain;
- pain in the epigastric zone.
Read: How to treat osteochondrosis at home
It is very difficult to independently distinguish pain syndrome due to osteochondrosis from pathologies of the digestive organs. It is recommended to consult a specialist in a timely manner to avoid the development of complications.
AskDoctor.ru – Worried about anorectal pain and how to get rid of it – AskDoctor
No. 44 701 Neurologist 06/11/2017
I am worried about anorectal pain. It occurs in the afternoon. Feeling of the presence of a foreign body, distension, pressure on the anus. There is no discharge or bleeding. Defecation occurs normally once a day.
The proctologist performed a manual examination and rectoscopy. 5 hemorrhoidal nodes measuring 0.4-0.8-1 cm were discovered. She underwent irrigoscopy.
Diagnosis: Chronic combined hemorrhoids of the 2nd degree in the phase of unstable remission. Dolichosigma. The doctor prescribed Posterizan Forte ointment 2 times a day in the rectum No. 10, Detralex according to the regimen for up to 1 month, diet, hygiene. Removal of hemorrhoids is recommended. I was treated conservatively. But the anorectal pain returns periodically.
I saw a neurologist. Neurologist's diagnosis: Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, polydiscosis. Protrusion of L3 – S1 IVD. Vertebrogenic lumbodynia with mild muscular-tonic manifestations. Coccydynia syndrome. Sop. Asthenic neurosis. Treatment: 1. Dona 2 im No. 6.2 times a week, then teraflex for 2 months. 2. Vit. Gr. B 3. Milgamma topically at night 4.
Duloxetine 30 mg 1 drop. At night - 3 weeks. 5. Bellataminal 0.5 tab. Overnight – 1 week. Got treatment. There have been improvements. The pain went away for several months. But then she began to return periodically again. This is especially felt after lunch, in the afternoon.
Tell me, is this pain related to hemorrhoids or neurology? And is it possible to adjust the treatment? With uv. Svetlana.
Sulzhenko Svetlana, Moscow
subscribe to answers 2 ANSWERS
neurosis scheme protrusion intestine
ANSWERED: 06/11/2017 Nikolashina Olga Moscow
0.0 doctor therapist
Hello, conservative treatment is currently considered preferable; indications for surgery have been narrowed. The treatment regimen prescribed is good; it is necessary to add mukofalk granules in addition to the diet for a long time.
it changes the composition of the intestinal microbiota, promoting the formation of stool, which, filling the rectal ampulla during defecation, promotes the drainage of hemorrhoidal sinuses, thus gradually restoring their normal functioning.
Anorectal pain is sometimes referred neuropathic pain, with lumbar osteochondrosis, when the pudendal nerve is involved.
Thank you Clarifying question
Rate the answer:
ANSWERED: 06/11/2017 Panigribko Sergey Kovrov
0.0 doctor dermatovenerologist
Hello, most likely both neurology and hemorrhoids. If you allow, I will give recommendations from practice. Be sure to massage the lumbosacral region, voltaren gel after the massage.
Naklofen 1 capsule per day, neuromultivitis, ddt for the lumbar region. For hemorrhoids - sitz baths with a decoction of oak bark, flax seed, chamomile, then edas 203 ointment at least three times a day.
Avoid constipation, spicy foods, alcohol, and physical activity.
Thank you Clarifying question
Rate the answer:
...Have a question for the doctor? OR DECODE THE ANALYSIS
Related questions:
Date Question Status
| 25.01.2016 | Anorectal pain Hello! It started with constipation and the presence of bloating, pressure, and the feeling of a foreign body in the anal canal. Previously, bowel movements were regular, once a day. I contacted a proctologist. Finger examination and rectoscopy (18 cm examination). Diagnosis: chronic internal hemorrhoids of 2-3 degrees. Anterior rectocele 1-2 degrees. Prescribed Detrolex (course) and proctoglivenol and proctosan suppositories for 3 weeks. I underwent irrigoscopy. Dolichosigma. Minor inflammation of the small intestine. In addition to the appointed... | 0 ANSWERS |
| 30.01.2016 | Anorectal pain Hello! It started with constipation and the presence of bloating, pressure, and the feeling of a foreign body in the anal canal. Previously, bowel movements were regular, once a day. I contacted a proctologist. Finger examination and rectoscopy (18 cm examination). Diagnosis: chronic internal hemorrhoids of 2-3 degrees. Anterior rectocele 1-2 degrees. Prescribed Detrolex (course) and proctoglivenol and proctosan suppositories for 3 weeks. I underwent irrigoscopy. Dolichosigma. Minor inflammation of the small intestine. In addition to the appointed... | 1 REPLY |
| 11.06.2017 | I am worried about anorectal pain. I am worried about anorectal pain. It occurs in the afternoon. Feeling of the presence of a foreign body, distension, pressure on the anus. There is no discharge or bleeding. Defecation occurs normally once a day. The proctologist performed a manual examination and rectoscopy. 5 hemorrhoidal nodes measuring 0.4-0.8-1 cm were discovered. She underwent irrigoscopy. Diagnosis: Chronic combined hemorrhoids of the 2nd degree in the phase of unstable remission. Dolichosigma. The doctor prescribed Posterizan Forte ointment 2 times a day directly... | 1 REPLY |
| 05.06.2017 | Maybe I was prescribed the wrong treatment? Good afternoon! I am 45 years old. I have been suffering from hemorrhoids for several years now. There was no pain before. But for the last six months, during morning bowel movements, pain has appeared and the nodes have begun to fall out, and sometimes severe bleeding has appeared. The knots go away by themselves somewhere in the middle of the day, and the pain disappears. Recently I found the strength to go to a proctologist because the pain intensified and bleeding began to scare me. At first he prescribed neoanuzole suppositories in the morning and evening, but the bleeding resumed three days later. Then he prescribed Detrolex for... | 2 ANSWERS |
| 01.05.2015 | Severe pain in the lymph nodes. Hello! I have been experiencing severe, sharp pain in the groin lymph nodes for three years now. Occur periodically. The pain is throbbing, sharp. They can appear quite suddenly, like shooting. I woke up a couple of times at night from acute pain. The lymph nodes are not enlarged, there is no redness. He suffered from the Epstein-Barr virus. Also, over the past 5 years, a couple of times I have experienced severe, sharp pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the rectum. The pain was so severe that they called an ambulance and they gave me a nosh-pa injection. I'm suffering about... | 0 ANSWERS |
Source: https://SprosiDoktora.ru/go/44701/
Classic pain due to neuralgia
- Seizures. Pain occurs suddenly in response to a stimulus that should not cause it, or for no reason at all. With primary true neuralgia, the attack lasts several seconds and stops spontaneously. With secondary changes in the nerve fiber - from several minutes to several hours, pain can persist in the interictal period.
- High intensity - the first attack is felt as a lumbago, an electric shock in the innervation zone of the affected branch, then it is perceived as stabbing or burning. With symptomatic neuralgia, the pain is less intense, but longer lasting; in the interictal period it is a dull aching pain.
- Constant localization. With each attack, the zone of manifestation of painful sensations remains unchanged, it corresponds to the area for the innervation of which the affected nerve is responsible.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary from case to case and are characterized by sudden onset and suddenness . It often has “volatile” manifestations that rapidly increase and disappear abruptly.
The pain may last for several hours, and taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs does not improve the disease. The pain is stabbing, during which spasms are felt. For some people, pain occurs only during bowel movements if the stool is problematic.
In women, symptoms may resemble an exacerbation of certain genitourinary diseases , for example, cystitis. If a man has a spastic attack that radiates to the perineum, he may confuse it with an exacerbation of prostatitis. In any case, only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis, so you should not self-medicate.