Home » Neuralgia
04/13/2019Author:
Intercostal neuralgia is a neurological disease that occurs as a result of compression of the nerves or their damage, manifested in the form of severe pain. The feeling is so strong that it is compared to acute liver pain - the pain brings discomfort and interferes with leading a normal lifestyle.
The pathology is often so similar to the manifestation of a heart attack or acute gastrointestinal diseases that without instrumental and laboratory diagnostics it is sometimes impossible for even the most experienced specialists to distinguish it.
ul
Preventive measures
If back pinching occurs frequently, although it is not associated with a serious pathology, preventive measures will help.
- Hypothermia should be avoided. You should not be in drafts, go outside in the cold without warm clothes, or stay in a cold room for a long time.
- Try not to lift excessive weights. If this can be avoided, it is impossible, for example, when working as a loader, to do this, correctly distributing the weight load and without sudden movements. Wear a corset.
- Avoid injury, especially when playing sports. Wear a supportive corset.
- If you have a history of osteochondrosis or any musculoskeletal pathology, pathology, undergo preventive examinations, do home exercise therapy, visit the pool and follow all medical recommendations.
- Be sure to purchase and use an orthopedic or at least anatomical mattress for regular sleep.
Prices for orthopedic corsets and posture correctors
Any problems with posture, traumatic situations, eating disorders, deviations to an overly active or, on the contrary, static lifestyle, as well as winter sports can provoke an attack of pain due to a pinched back between the shoulder blades. Preventive measures taken in a timely manner will help you avoid this and lead a full, healthy life, without pain.
Video - Pain between the shoulder blades
Choose among the best clinics based on reviews and the best price and make an appointment
Show all Moscow clinics
Show all Moscow specialists
Prevention
To prevent pain, you need to monitor your health. A person suffering from angina or having had a myocardial infarction should regularly visit a cardiologist and take medications to stabilize the heart. It is important to exclude heavy physical activity, psychological stress and follow a diet.
To prevent pain under the left shoulder blade from appearing due to spinal deformities, you need to perform a special set of exercises and take anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs.
If pain is associated with gastrointestinal diseases, you must follow a diet and take antacids as prescribed by your doctor.
Diseases and pain are much easier and safer to prevent than to treat. Even if there are no health problems or discomfort, you need to regularly visit a doctor and undergo a medical examination. If pain does appear, you should not self-medicate, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Preventive measures involve self-monitoring of health status. The most important thing is to monitor your posture and perform a set of exercises designed to strengthen your muscle corset.
To preserve youth and beauty, and also to avoid the appearance of intercostal neuralgia:
- Do gymnastics regularly.
- Ensure healthy sleep, don’t worry about every little thing.
- Say no to smoking and alcohol.
- Eat right.
The development of intercostal neuralgia is prevented by daily exercises, kneading the body, self-massage, and proper nutrition. It is necessary to give your body adequate physical activity every day. Do not be in a draft or be exposed to hypothermia. The diet should contain foods rich in B vitamins.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nCHwV4Hd9Eg
Comprehensive treatment recommended by the attending physician, moderate physical activity, and a balanced diet relieve intercostal neuralgia. Preventive measures prevent relapses from occurring.
Causes
Pain in the shoulder blades indicates disorders in the body. Diseases of the organs and systems of the body lead to paroxysmal pain under the shoulder blade.
There are many reasons that cause discomfort in the shoulder blades:
- damage to the spinal cord or peripheral nerves;
- protrusion of the wall of the intervertebral disc (protrusion);
- intervertebral hernia;
- spinal or thoracic injuries;
- inflammation of the neck, chest or back muscles (myositis);
- diseases of the respiratory system (tuberculosis, pneumonia, pleurisy);
- diseases of the liver, kidneys, pancreas (pancreatitis);
- cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder);
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract (peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum);
- shingles;
- cardiac ischemia;
- benign or malignant formations in the spine;
- psychological problems.
Causes of pain between the shoulder blades with neuralgia
In rare cases, neuralgia develops on its own, without the influence of visible provocateurs. In 90% of situations, the condition is one of the signs of problems that already exist in the body.
It can accompany the course of an infectious or inflammatory process, or become a consequence of intoxication, the formation of a tumor in the spinal cord or along the course of a nerve. Most often, neuralgia with pain localized in the scapula area is the result of diseases of the thoracic spine . Scoliosis, osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernias and other common ailments lead to compression of nerve fibers by surrounding tissues. The result is a persistent pain syndrome, which, in the absence of specialized treatment, can torment for years and provoke the development of complications.
Some diseases cause nerve compression.
Diagnostic methods
Neuralgia under the scapula should be under medical supervision. When the first symptoms appear, you need to contact a specialist for diagnosis and treatment. First of all, sensitivity is established and the location of the pain syndrome is determined.
Diagnostic methods are as follows:
X-ray - this method will help assess the condition of the bones for injuries and damage.
- Myelography is a rare diagnostic method in which a special substance is injected into the spinal region.
- Contrast discography is a method of introducing a contrast agent into the intervertebral disc.
- CT scan.
MRI is the most effective way to obtain information about the condition of bones and tissues. The method has its contraindications. It cannot be used if there are metal formations in the body.
Neuralgia in the scapular area has many symptoms similar to other diseases. In this regard, a thorough examination of the patient is required to exclude their presence.
Differences from other pathologies are as follows:
- Cardiovascular diseases - pain in the heart area can occur with neuralgia of the left scapula. Patients often confuse pain with a heart attack. The difference between neuralgia and heart disease is that the heart pain will be constant, it subsides only after taking medications.
- Intercostal neuralgia is similar in symptoms to gastritis. With gastritis, pain will vary in severity. It intensifies when eating or when a person is hungry. In addition to pain, a person will be bothered by indigestion, nausea, vomiting. The condition will improve if you take enveloping agents. To exclude diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, an ultrasound of the internal organs is prescribed.
- Pleurisy and pneumonia are diseases in which pain is localized in the chest area. Pathologies are often confused with neuralgia, since the pain intensifies when coughing or sneezing.
Due to the fact that neuralgia under the scapula has many similar symptoms to other diseases, self-medication is unacceptable.
The nature of the treatment for pain under the shoulder blades will depend on the causes of its occurrence. If this is a symptom of diseases of the internal organs, then treatment should be aimed at eliminating them.
To eliminate the disease, various medications are used:
- Painkillers.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Ointments.
- Injections.
With the help of painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, it is possible to relieve pain and stop localized inflammation. Diclofinac, Ketonal, Ibuprofen, Movalis are used for therapy.
All ointments that can be used to treat a pinched scapular nerve should only be prescribed by a doctor, as they can cause an allergic reaction in the body. The most commonly used are Finalgon, Viprosal, and Carmolis.
The complex of treatment therapy for neuralgia includes:
It is imperative to strengthen the body; calcium and B vitamins are used for this.
How can the disease be treated?
Painful changes in nerve fibers can appear for various reasons:
- injuries;
- past infectious diseases;
- hypothermia;
- tumors;
- diabetes;
- osteochondrosis;
- atherosclerosis.
Burning, paroxysmal or chronic pain can occur in nerve fibers located throughout the body. Depending on the area of the lesion, neurites are distinguished:
- intercostal (gives in the area of the heart, chest, under the scapula);
- shoulder joint;
- post-herpes;
- lumbar;
- inflammation of the trigeminal (sensitive nerve of the face or trigeminal neuritis), sciatic, ulnar, occipital nerve;
- femoral;
- pterygopalatine node (pain affects the temples, neck, and sometimes spreads to the hands);
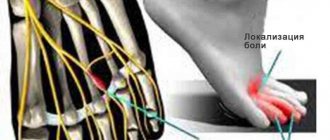
- neuroma of the foot (Morton's disease).
How to cure neuralgia as soon as its symptoms appear? The first is the correct diagnosis, because Under the guise of this disease, problems with the heart or blood vessels may be hidden, so it is important to be examined by a doctor for the presence of other diseases with similar symptoms. The main problem of the disease is severe pain that can make you unable to work, and the goal of getting rid of a disease such as neuralgia is to treat the pain syndrome with anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics. At the initial stage, the following may help:
- anti-inflammatory ointments with fir oil;
- acupuncture for local pain relief;
- warming compresses.
Drug treatment alone during an exacerbation may not produce the desired results. The complexity of a syndrome such as neuralgia means treatment must be complex, long-term and combined. The very first cure for neuralgia is painkillers: ointments, tablets, compresses, injections. In combination with pain relief, doctors prescribe medications:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Indomethacin);
- anticonvulsants (Carbamazepine, Baclofen, Phenytoin);
- muscle relaxants (Clonazepam, Sirdalud, Mydocalm).
Analgesics are often used to relieve the first signs of the disease. Ortofen and Diclofenac are not recommended for use as painkillers for neuralgia. Preparations with ibuprofen and nimesulide have the best effect on the source of pain. A common method of pain relief now is the fentanyl patch.
The most effective pills for neuralgia are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which not only relieve pain, but also relieve inflammation. Such tablets include Indomethacin, Ibuprofen, Sulindac, Ketorolac. All these medications are irritating to the kidneys and gastric mucosa, so their use should only be prescribed by a doctor after examination.
Ointment for neuralgia
To suppress unpleasant symptoms, an ointment for neuralgia will help, the effect of which is to:
- warming tissues and relaxing them;
- improving local blood circulation;
- increasing the elasticity of diseased ligaments;
- activation of local metabolic processes.
The ointments contain anti-inflammatory and analgesic components. Ointments based on bee and snake venoms are effective. Popular ointments that are used to relieve pain and inflammation are Viprosal, Finalgon, Apizartron, Myoton. The main effect is achieved by warming the tissues, improving blood circulation and dilating blood vessels.
Injections for neuralgia
What to do with neuralgia if you can’t use ointments, tablets, or they simply don’t help? Drugs for neuralgia that are used for injection are effective. For severe symptoms, analgesic injections are the best way to restore mobility and normal condition to the patient. Injections of Spazgan, Baralgin, Trigan are used. It is important to remember that an injection to numb an inflamed nerve should only be given by a doctor who knows human anatomy well.
During the period when acute pain subsides, it is effective to do acupressure, general or cupping massage to relieve tension in the muscles. Thus, massage for intercostal neuralgia, together with acupuncture, will help improve lymph flow, relieve muscle tension between the ribs, prevent muscle wasting and promote rapid recovery and restoration of mobility. Massage in combination with physiotherapy is effective - physical therapy, which is performed under the guidance of a doctor, will help cope with pain.
Intercostal neuralgia symptoms are marked by pain in the chest area that occurs
- when coughing;
- when sneezing;
- during physical activity;
- with a deep breath.
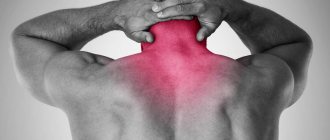
Sometimes patients feel as if a rib is caught on another rib. A person simply cannot take a deep breath due to the burning pain. In addition to localizing pain in the intercostal space, pain sensations can move along the diseased nerve, responding under the shoulder blade, in the neck, in the back, in the heart and lumbar region.
Sometimes the skin in the area of the pinched nerve becomes pale or red. The pain with intercostal neuralgia is constant, without attacks, burning.
This disease most often occurs in patients with osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, in middle-aged and elderly men and women whose lifestyle is associated with hypothermia and excessive physical exertion. It does not occur in children and newborns.
Clinical picture
When moving, bending, turning the body, symptoms intensify
To determine the source of neuralgia under the right or left shoulder blade, an important diagnostic step is to study the nature and frequency of unpleasant sensations. Interscapular neuralgia occurs with sudden lumbago, radiating to nearby areas: limbs, lower back, neck, armpits. The discomfort increases when inhaling and when turning the body.
The clinical picture differs depending on the primary process:
- The functioning of the liver, kidneys, and gall bladder is impaired. Spasms and inflammatory processes are accompanied by acute, cutting symptoms. If the gallbladder ducts are blocked, pain may occur in the intercostal space on the right, the scapular region, or the right half of the neck.
- Coronary heart disease develops, the condition of the spinal column, spinal cord, and digestive system organs is impaired. In such cases, the syndrome occurs paroxysmally only on the left or only on the right side. The pain radiates to the shoulder blade and lower back, accompanied by numbness and tingling. In gastrointestinal pathologies, the intensity of the symptom may depend on food and be seasonal when chronic inflammation is present.
- There is a history of trauma. A characteristic symptom is an increase in the intensity of the attack when moving the body. Edema, swelling appears in the area of injury, and possible damage to the integrity of the skin.
- The cause of pain in the shoulder blade is a psychological factor. The discomfort is acute or dull in nature, spreading to the lower back, limbs, and cervical region. The pain is supplemented by apathy or irritability, increased sweating, and anxiety.
- Herpes zoster develops. Painful symptoms appear around the circumference, covering the shoulder blades and thoracic region (ribs). The intensity of discomfort increases at night.
- The muscles are inflamed. Myositis is accompanied by pain in the scapular region, radiating to the anterior thoracic area, arm, neck, and lower back. Inhalation discomfort increases.
Nature of pain
To determine why pain occurs between the shoulder blades, you need to evaluate the characteristics and frequency of sensations. Interscapular neuralgia is characterized by sudden shooting pains that radiate to or above the shoulder blades. When the chest is filled with air, the pain appears suddenly and is felt stronger than when exhaling. Other features of pain can be identified depending on the disease:
- Gallbladder, liver and kidneys. With spasm or inflammatory processes in these organs, the pain occurs sharp, cutting and tearing. In case of blockage of the gallbladder, an unpleasant feeling radiates to the right hypochondrium, shoulder blade, neck, eyes and jaw. Inflammation of the kidneys is characterized by constant pain in the lumbar region.
- Coronary heart disease, diseases of the spine, spinal cord and gastrointestinal diseases. The pain is paroxysmal in nature. Most often, sensations occur on one side of the shoulder blade. Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are characterized by seasonality and increasing pain. Intercostal neuralgia and coronary heart disease are accompanied by tingling and numbness.
- Injuries. Pain increases during movements. Injuries that occurred within the last 7 days must be taken into account. Injuries are accompanied by swelling and edema.
- Psychological problems. Sensations in the area of the shoulder blades can be sharp or muted. The pain may spread to the lower abdomen, collarbone, neck or arm.
- Shingles. Pain syndrome appears in the area of the shoulder blades and ribs. The excruciating pain intensifies at night.
- Myositis. Pain sensations spread to areas of the neck muscles, shoulders and shoulder blades. May radiate to the left shoulder blade or sternum. Unable to take a deep breath.
If an unpleasant symptom occurs in the center of the chest, then the pathology is associated with the vertebrae in the thoracic region. With pathology of the pancreas, pain is present in the abdominal area and radiates under the shoulder blade. The sensations intensify every day.
Symptoms on the left side
Pain under the shoulder blades occurs for various reasons; based on their symptoms, the disease that is the cause of the discomfort can be diagnosed.
Acute
Occurs as a result of physical strain, including sudden lifting of a heavy load. It may periodically weaken, but even with a slight sudden movement it can resume. These are signs of herniated discs, angina pectoris or perforation of an ulcer.
Aching or pulling
They occur as a result of diseases such as pyelonephritis, osteochondrosis, tuberculosis, gastritis or inflammatory processes.
Dumb
Occurs at the bottom of the scapula with a return to the cervical region. If it periodically disappears and reappears, this is a sign of cervical osteochondrosis. The pathology may be accompanied by dizziness and numbness of the limbs.
It especially makes itself felt when you stay in the same uncomfortable position for a long time. Diseases that caused it: pleurisy, inflammatory processes of various types, pyelonephritis, tuberculosis, scoliosis.
Burning
These are manifestations that indicate serious diseases: spinal disc deformation, heart attack, angina. At the same time, the skin becomes pale.
Pressing
A feeling of squeezing occurs with vegetative-vascular dystonia or a pre-infarction state. Similar dysfunctions appear in ischemic heart disease and hypertensive crisis.
Stabbing
Indicates the development of pneumonia, intercostal neuralgia and osteochondrosis.
Constant
Accompanied by exposure to physical overload, tuberculosis, osteochondrosis, and the presence of tumors. Discomfort in the area of the left shoulder blade disappears, and with loads it increases, accompanied by a burning sensation.
Sharp
This discomfort is caused by intercostal neuralgia. It is most noticeable when inhaling.
Pulsating
They occur as a result of ischemic heart disease, hypertension, and stomach ulcers.
Pulling
Occurs in cervical osteochondrosis. They can occur with incorrect movements and uncomfortable postures.
Frequent
Occurs with lung diseases accompanied by coughing or sneezing.
Features of treatment
Depending on the pathology, the doctor is obliged to choose the right treatment. It is aimed at eliminating the underlying cause and prescribing appropriate medications. Additionally, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to relieve pain. Ointment with diclofenac or ketoprofen is used as a local anesthetic.
To strengthen the body, calcium and B vitamins are prescribed. Medicines that weaken muscle tone (muscle relaxants) will help reduce muscle spasms in the area of the shoulder blades. A rehabilitation course is carried out to eliminate neuralgia:
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- movement therapy (kinesitherapy);
- laser use;
- acupuncture;
- massage.
The use of folk remedies will help relieve discomfort. In some cases, it is possible to eliminate neuralgic pain forever. Apply compresses from burdock leaves, black radish juice, and flax seeds. Use ointments based on bee or snake venom. Baths with essential oils, sage infusion, and valerian root decoction are effective.
Rehabilitation
Subsequent treatment tactics include the following:
- UV irradiation of the right segment of the chest, electrophoresis.
- Acupuncture.
- Laser therapy.
- Osteopathy.
- Taking B-group vitamins in high doses. Vitamins restore the nerve sheath, making it more resilient.
As part of the rehabilitation period, the patient is prescribed ozokerite and paraffin applications on the right side of the chest, massages, mud therapy, baths with hydrogen sulfide and radon, swimming, and physical therapy.
Surgical treatment is carried out in case of detection of space-occupying formations, when they compress the nerve roots and cause pain. Traditional therapy is the main, but not the only way to eliminate a disease such as intercostal neuralgia. Treatment with folk remedies can also have a beneficial effect. However, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
Clinical picture
To determine the source of neuralgia under the right or left shoulder blade, an important diagnostic step is to study the nature and frequency of unpleasant sensations. Interscapular neuralgia occurs with sudden lumbago, radiating to nearby areas: limbs, lower back, neck, armpits. The discomfort increases when inhaling and when turning the body.
The clinical picture differs depending on the primary process:
- The functioning of the liver, kidneys, and gall bladder is impaired. Spasms and inflammatory processes are accompanied by acute, cutting symptoms. If the gallbladder ducts are blocked, pain may occur in the intercostal space on the right, the scapular region, or the right half of the neck.
- Coronary heart disease develops, the condition of the spinal column, spinal cord, and digestive system organs is impaired. In such cases, the syndrome occurs paroxysmally only on the left or only on the right side. The pain radiates to the shoulder blade and lower back, accompanied by numbness and tingling. In gastrointestinal pathologies, the intensity of the symptom may depend on food and be seasonal when chronic inflammation is present.
- There is a history of trauma. A characteristic symptom is an increase in the intensity of the attack when moving the body. Edema, swelling appears in the area of injury, and possible damage to the integrity of the skin.
- The cause of pain in the shoulder blade is a psychological factor. The discomfort is acute or dull in nature, spreading to the lower back, limbs, and cervical region. The pain is supplemented by apathy or irritability, increased sweating, and anxiety.
- Herpes zoster develops. Painful symptoms appear around the circumference, covering the shoulder blades and thoracic region (ribs). The intensity of discomfort increases at night.
- The muscles are inflamed. Myositis is accompanied by pain in the scapular region, radiating to the anterior thoracic area, arm, neck, and lower back. Inhalation discomfort increases.
Symptoms of the disease
Damage to the peripheral nerves, in which pain is concentrated under the scapula, is conventionally considered one of the types of intercostal neuralgia. Often the clinical picture of the condition is limited to pain, which has specific characteristics.
Features of pain syndrome with neuralgia in the scapula area:
- sensations are unilateral; bilateral localization is rare. If they are located strictly in the center, this almost always indicates damage to the vertebrae;
- pain occurs suddenly, resembles an electric shock, and rarely lasts longer than a few seconds. They are so intense that they force the patient to freeze; any movement of the body intensifies the symptoms;
- pain syndrome complicates the breathing process. As you inhale, the intercostal muscles stretch, which provokes an attack or its intensification. Because of this, the patient begins to breathe “shallow” so as not to strain the chest.
Depending on the cause of the condition and the extent of peripheral nerve damage, neuralgia in the scapula area can last from several days to weeks. Due to limited motor activity and frequent occurrence of pain, the patient’s general well-being suffers. His sleep and appetite are disturbed, irritability and signs of chronic fatigue occur.
The most effective recipes
- To eliminate the disease, it is recommended to use willow bark. Approximately 15 grams of crushed plant material is brewed with 250 ml of boiling water. The mixture is boiled for about 20 minutes over low heat. Then the broth should cool, filter it and drink 20 ml four times daily.
- Several petals of a simple indoor geranium are laid out on a piece of linen. A compress with leaves is applied to the affected side, bandaged and insulated. The pain should subside within two hours. The intensity of the procedures is 2-3 times a day.
- Garlic oil helps eliminate neuralgia. No more than 25 ml of oil is diluted in 500 ml of cognac or alcohol. The resulting essence should be lubricated on the forehead and temples, which helps eliminate attacks. The homeopathic effect is realized.
- Folk treatment for intercostal neuralgia contains the following recipe: a simple hard-boiled egg. When hot, it is applied to the sore spot until it cools completely. When the egg becomes cold, the pain should go away.
- Horseradish may be no less effective. The crushed leaves of the plant are laid out on the right side of the chest and covered with a warm woolen scarf.
- Juice is squeezed out of one black radish fruit. When warm, it is rubbed along the nerve to treat intercostal neuralgia.
- It is also recommended to prepare a tincture of thyme. The plant relieves pain well, which is always accompanied by intercostal neuralgia. Treatment with folk remedies involves using the following recipe: ten grams of the herbal component is poured into 100 ml of alcohol. The mixture is infused for 24 hours, filtered and taken three times a day, 15 drops.
Signs of neuralgia
Many experts attribute pain under the scapula to intercostal neuralgia. Signs of neuralgia are:
The pain becomes stronger as you inhale and decreases as you exhale. This is due to the fact that when you inhale, the intercostal spaces, in which the segmental nerve endings are located, stretch, both on the right and on the left. Most often the pain is felt asymmetrically
It can be concentrated either on the right or on the left. It is very important to pay attention, if the pain is most felt in the middle, most likely this is a problem directly with the vertebrae, and the inflammatory process is already moving to the scapular region. Pain occurs when moving, breathing, abducting, spreading the shoulder blades, raising the arms, bending. Attacks of pain are caused by coughing and sneezing. The pain with neuralgia is sharp, but quickly disappears. It is of a shooting nature.
The person begins to independently adapt to the pain. Most often, such patients are characterized by “shallow” breathing, without deep breaths. They try to minimize the stretching of the chest. Patients limit any physical activity.
Diagnostic measures
Immediately before treatment, the doctor must make a correct diagnosis. This requires examination of the patient. Diagnosis of neuralgia includes:
- taking anamnesis;
- palpation of the affected area (chest);
- instrumental research.
In the latter case, an X-ray examination of the spine and chest, MRI or CT, and electroneurography may be required. If the pain is localized not on the right, but on the left, it is necessary to exclude heart pathology (heart attack and angina). For this purpose, an ECG is performed. Intercostal neuralgia may be infectious in nature, so a blood test for antibodies to the herpes virus may be needed. It is advisable to do a general blood and urine test if the pain affects the lumbar region.
Carrying out differential diagnosis is of great importance. The doctor must exclude the following pathologies: pleurisy, pneumonia, inflammation of the gastric mucosa, peptic ulcer, hepatitis. Pain with right-sided pneumonia most often occurs with the development of pleurisy. Pain during pleurisy is stabbing and localized on the affected side.
What can cause pain between the shoulder blades in the spine?
Painful sensations that occur in the interscapular region are most often a sign of spinal pathologies. These may be congenital or acquired conditions, the refusal of treatment of which will lead to an increase in the severity of the clinical picture.
Also, pain between the shoulder blades may indicate the following diseases:
- spinal cord pathologies;
- damage to peripheral nerves;
- intervertebral hernia;
- spinal column or chest injuries;
- myositis – muscle inflammation;
- damage to the respiratory system;
- diseases of the kidneys, pancreas, liver, gastric bladder;
- disruptions in the functioning of the digestive system;
- cardiac ischemia;
- herpes zoster;
- neoplasms in the area of passage of peripheral nerves or the spinal cord;
- disorders of a mental or psychoemotional nature.
Sudden pain in the area of the shoulder blades does not always indicate problems in the body. If the sensations are not pronounced and are not accompanied by other symptoms, they may indicate a muscle spasm due to an uncomfortable body position. Introducing a regimen of physical activity and observing the rules of hygiene at work and rest will prevent the return of pain.
Pinched nerve in the back and under the shoulder blade
When the nerve endings are compressed by neighboring vertebrae, protrusion, hernia or spasmodic muscle tissue, a pinched nerve occurs. This pathology is characterized by significant pain, which forces the patient to take any measures to alleviate his condition. This article will tell you what the dangers of a pinched nerve in the back and under the shoulder blade are and how to treat it.
Causes
A pinched nerve in the back can be caused by various reasons, namely:
- progressive osteochondrosis (is the main cause);
- rachiocampsis;
- physical activity, which consists of repeating the same movements of the body and arms;
- pregnancy (increase in weight and stress on the back and spine);
- excess weight;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- neoplasms on the vertebrae;
- injuries and diseases of the spine;
- genetic predisposition.
Curvature of the spine is one of the causes of pinched spinal nerve
Symptoms
The main symptom of a pinched nerve in the back is intense and burning pain, in some cases it becomes unbearable. Particularly acute pain is felt during movements, sneezing, laughing, coughing, and during night sleep. Discomfort and pain may be constant or intermittent. Also a sign of a pinched nerve in the back or under the shoulder blade is numbness in the limbs.
If the pinched nerve is localized under the scapula, the pain radiates to the arm and resembles “shooting”. In this case, you should pay close attention to the symptoms of pinching and seek help from a specialist. The signs of this pathology are similar to heart pain, symptoms of pneumonia, pleurisy or cancer.
If a patient has an attack of pain caused by a pinched nerve in the back, then he needs to provide first aid. To do this you need to do the following:
- Unload the back - lay the victim on a hard surface, for example, on a hard bed or floor, after laying a soft blanket over him. To relieve the load from the lower back, you need to place your legs at right angles to the torso (for example, if the patient is lying on the floor, then your legs can be placed on a chair);
- Give a pain reliever, for example, Ibuprofen or Analgin;
- To relieve spasms from muscle tissue, give the patient an antispasmodic drug, for example, No-Shpa. This will not only relax the muscles, but also relieve pain, and also activate blood circulation in the area where the pain is located;
- Call an ambulance.
If a nerve is pinched in the back, it is necessary to avoid physical activity and drafts, and also maintain bed rest.
Diagnostics
A pinched spinal nerve is diagnosed using the following procedures:
- magnetic resonance or computed tomography - will show the presence of defects in the intervertebral discs and pathological curvatures of the spine and muscles;
- electromyography - determines defects in nerve endings that are responsible for muscle function. The procedure is carried out by inserting an electrode needle into the muscle tissue;
- examination of nerve endings for conductivity using tests to determine damaged nerves - electrodes are attached to the skin through which weak impulses are transmitted;
- manual examination;
- general blood analysis.
DETAILS: Analogs of Nimulid, how to choose gel and tablets cheaper and more effective
Treatment
Standard therapy for a pinched spinal nerve consists of the following steps:
- pain relief with oral medications or injections. In this case, the patient must observe bed rest and a special diet that does not allow the intake of salty, spicy and smoked foods;
- relieving inflammation with non-steroidal drugs that have an anti-inflammatory effect. Such drugs are available in the form of tablets, gels, ointments or injections;
- restoring the functionality of a pinched nerve through massages, manual procedures, physiotherapy, physical therapy, taking vitamin complexes, and acupuncture.
When treating at home, it is convenient to use medications produced in the form of ointments.
Warming ointments “Finalgon” and “Viprosal” relieve pain and activate blood circulation. Diclofenac, Betalgon, Carmolis, and Flexen ointments also effectively anesthetize and reduce inflammation.
Symptoms
Symptoms of intercostal neuralgia
The symptoms of intercostal neuralgia are very vague, in some cases there is a sharp, shooting pain in the chest, in others the pain is constant and does not allow you to breathe normally or bend over.
Diagnosis of shoulder joint mobility in intercostal neuralgia
Projection of vertebrae in the lumbar-thoracic region
Characteristic signs of intercostal neuralgia:
- Piercing pain in the chest, along the ribs (aching pain is characteristic of thoracalgia);
- During an attack, the patient freezes, movements cause increased pain, it hurts to take a breath;
- The attack lasts from several seconds to several minutes;
- Attacks of pain in the heart area with a certain frequency, without treatment, become more frequent;
- Intercostal neuralgia is preceded by a disease of the spine.
The pain usually occurs on one side. If the patient feels pain on the left, then the first thing he associates is with the heart (non-coronarogenic, vertebrogenic cardialgia). Taking nitroglycerin does not reduce the attack.
Dysfunction of the costovertebral joints: a-norm; b, c – variants of pathology.
Causes of intercostal neuralgia
Contrary to the general belief that osteochondrosis causes intercostal neuralgia, in practice this turns out not to be the case. Against the background of a decrease in the height of the intervertebral discs and their protrusion, the risk of reflex reactions increases, which contribute to a sharp infringement. Over time, trigger points are formed that cause chronic pain.
The second most common cause of intercostal neuralgia is dysfunction of the costovertebral joints.
Before embarking on any type of treatment, it is important to establish the underlying disease; intercostal neuralgia itself may be just one of many symptoms of more serious diseases. In most cases, the cause of pain is polysegmental osteochondrosis of the thoracic region, scoliosis, vertebral displacement (spondylosis), dysfunction of costovertebral joints, reflex reactions, myofascial pain syndromes, tumor diseases and others
Position of a person during an attack
How do patients with intercostal neuralgia complain:
- Lately, there has been a shooting pain in the left chest area, like the heart is grabbing;
- Electric shock pierces the whole body, nothing can be done, very strong pain and a feeling of fear;
- For no reason, unbearable pain appeared, like an electric shock; it was impossible to straighten up or take a breath;
- While sitting at work, I got a strong grip in my ribs and didn’t go away for a long time;
- I am suffering from aching pain in the area of the shoulder blade; I cannot take a full breath through my chest;
- Ribs hurt on the right/left, worsens with movement.
Treatment of intercostal neuralgia
Unfortunately, as statistics show, modern medicine is practically useless for this pathology, offering vitamin therapy, painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs (their prescription has recently been proven to be groundless) as the main treatment - the main cause is not eliminated, time is lost. At the same time, with traditional treatment, the period of drug rehabilitation lasts for months, years, the result may be inconsistent or absent altogether.
Anatomy of the intercostal nerve
Many thin nerve bundles extend from the spine, some of which pass between the ribs - these nerves are called intercostal nerves. The muscles responsible for inhalation and exhalation are attached to the ribs above and below; between them there is a thin intercostal nerve. During an attack, pain impulses travel along nerve fibers to the spinal cord and brain, and the person feels pain.
As a result of vertebral displacements, osteochondrosis, scoliosis, due to injury or sudden contraction of the intercostal muscles, the intervertebral nerve can be reflexively pinched. The resulting severe pain, usually of a shooting or pulling nature, often spreads throughout the chest.
Since pain cannot last forever, atrophy of the nerve root occurs, pain goes away, but the volume of breathing decreases, a feeling of heaviness and shallow breathing occurs. Over time, treatment of advanced intercostal neuralgia is more labor-intensive and requires considerable effort.
Techniques for eliminating intercostal neuralgia. Clinic of Doctor Ignatiev
Treatment of intercostal neuralgia at the Clinic of Dr. Ignatiev, Kyiv
{SOURCE}
Neuralgia of the brachial nerve (plexus, joint) of the hand: symptoms and treatment
Neuralgia caused by muscle tension is a frequent and quite common phenomenon, especially in older and elderly people.
The disease is insidious, develops quickly, becomes chronic, and there is a risk of serious damage to the nerves themselves, which ultimately affects the functioning of the joints.
The causes and main manifestations of the pathology, stages of development, modern methods of differential diagnosis and treatment of neuralgia of the brachial nerve, or as it is also called - the shoulder joint of the arm or plexus, will be discussed in the article.
What it is? ICD-10 code
Anatomically, the nervous system is the most important component of the human body ; it is responsible for the coherence and consistency of the work of other organs and vital systems.
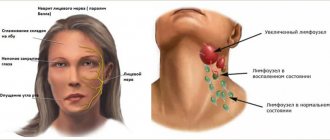
There are some pathologies that are directly related to damage to the nerve trunks - these are various neuralgia (occipital, trigeminal, external femoral nerve).
Brachial neuralgia - spasms of the shoulder muscles , pinching and damage (in clinical cases) to the peripheral nerve processes or roots of the brachial plexus.
The plexus of nerves emerges from the cervical spine and is located at the level of the joint (at the junction of the clavicle, the process of the scapula and the head of the humerus). This plexus then branches throughout the arm.
The essence of the interaction between the nervous and muscular systems is simple - the branches of the brachial plexus send electrical signals to the muscle, which contracts under the influence of this signal. Any movement is a muscle contraction.
With neuralgia, the inflammatory process only compresses, but does not damage the nerve fibers.
According to the international classification of diseases (1999) - ICD-10 - the disease is assigned the code: G54.0, denoting diseases of the nervous system, class No. 6. This pathology can also be classified as class M, No. 13 (diseases of the musculoskeletal system), depending on the root cause of its origin. If the diagnosis is “blurred”, specialists use coding M79.2 (subsection of unspecified neuralgia).
Clinical picture: manifestations and symptoms
Most often, brachial neuralgia develops unilaterally, on the right side.
If the disease is caused by hypothermia or is a consequence of influenza, ARVI, acute respiratory infections and other infections , it manifests itself in an acute form:
- pain in the shoulder and neck appears immediately;
- accompanied by general weakness and fever;
- temperature rise is possible.
For injuries:
- pain increases gradually;
- the pain subsides over time;
- slight stiffness when moving the arm and shoulder;
- partial numbness.
The duration of attacks varies - from 2-3 seconds (shooting pain) to several hours (dull, aching, obsessive).
In the advanced stage:
- constant pain (discomfort both during the day and at night);
- sweating;
- redness and severe burning of the skin;
- tearfulness;
- convulsions are possible.
General symptoms:
- muscle spasms (periodic involuntary twitching, sometimes lasting 1-2 minutes);
- as the disease develops, swelling of muscle tissue is observed;
- aching constant pain of an exhausting nature occurs;
- attacks of unbearable, burning pain occur spontaneously, periodically.
It is difficult to independently determine the original source, since it can hurt and radiate in different areas.
Possible patient complaints, depending on the affected area:
- Bottom form – severe pain is concentrated in the inner surface of the shoulder and forearm area, manifests itself when moving.
Partial loss of sensitivity is possible (the nerve fibers of the plexus are responsible for tactile and temperature sensitivity).Impairment of fine motor skills and decreased muscle tone (difficulty forming fingers into a fist or holding small objects) are also possible.
- Upper form – pain above the collarbone, radiating to the forearm area. Sensation is lost in the outer part of the forearm. The mobility of the arm is limited, a sharp cutting pain occurs when moving, it is difficult to bend the arm at the elbow and straighten the shoulders.
- The total form is the most dangerous; the general symptoms include fever, drowsiness, weakness, possible nausea and lack of appetite. This type of neuralgia often occurs against the background of poisoning and weakened immunity.
In an advanced state, the pain syndrome becomes excruciating, spreads to the area of the shoulder blade and chest, and radiates to the back.
Diagnostics
The first thing the patient needs to do is contact a neurologist or kinesiologist . Only a specialist can make a presumptive diagnosis and find the cause of inflammation based on:
- initial examination taking into account complaints and characteristic manifestations of the disease;
- medical history (lifestyle, activity, concomitant diseases, etc.).
A biochemical blood test is required, revealing:
- leukocyte count;
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate;
- blood protein ratio;
- exclusion of anemic condition.
To exclude other diseases and pathological neoplasms (stomach ulcer, renal pathologies, heart failure, vertebral hernia, etc.), the patient is prescribed additional differential diagnostics:
- MRI is a modern method that studies the structure of the vertebrae and tissues and detects neoplasms.
- Electroneuromyography - using myographs, the condition of the muscles and peripheral nervous system is studied (conductivity of the electrical impulse, the exact location of the affected area).
- X-rays monitor the displacement of the vertebrae, the presence of bone growths that clamp the nerve endings.
- Ultrasound allows you to assess the condition of blood vessels, and examines the movement of blood (to exclude vascular pathologies).
- In clinical cases, a spinal cord puncture is performed (the presence of harmful microorganisms causing pathology).
Features of therapy
The choice of treatment methods and techniques is directly related to the cause of the disease.
At the first stage, brachial neuralgia can be treated conservatively:
- analgesics (Ibuprofen, Tempalgin, Ketoprofen) are prescribed to relieve pain and inflammation;
- for severe pain, injection blockade with Novocaine is used;
- to reduce swelling, diuretics (Veroshpiron) are prescribed;
- anti-inflammatory ointments are used (Fastum-gel, Viprosal);
- only after the swelling has been removed can you use warming gels (Capsicam, Finalgon), they restore the functioning of muscle tissue;
- antibiotics are prescribed according to indications;
- to fix the arm, special splints and bandages are used;
- support of the body is required (B vitamins).
The therapy lasts 2 weeks; with proper treatment, the patient returns to a full life quite quickly.
In the absence of positive dynamics, surgical methods are recommended:
- neuroexeresis;
- neurotomy;
- tractotomy.
Application of acupuncture
After general treatment, the specialist recommends undergoing a recovery course (electropheresis, massage, mud baths, etc.)
Acupuncture – a combination of reflexology and acupuncture – impact on biologically active points (a complex of acupuncture, massage and warming).
The peculiarity of the method is that tissue restoration occurs faster, the risk of complications and recurrence of the disease is reduced.
Possible complications, prognosis and prevention
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, the prognosis is always positive.
Self-medication or ignoring the first symptoms can lead to complications:
- neuralgia of the brachial nerve takes on a chronic form and becomes fixed;
- the disease degenerates into plexitis (the nerve fibers of the brachial plexus are damaged);
- risk of developing Horner's syndrome (affects the eyeball);
- significant damage to the nerve plexuses leads to loss of sensitivity and decreased mobility;
- in critical cases, paralysis of the arm and complete muscle atrophy are possible.
It is known that preventing a disease is easier than completely eradicating it.
Prevention:
- prevent hypothermia of the body;
- exclude situations of injury (ice, moderate sports activities);
- timely treatment of viral infections;
- balanced diet (vitamins, meat, dairy products);
- Hardening, sports and a healthy lifestyle strengthen the immune system and resist any viruses and infections.
In conclusion, brachial neuralgia should be treated immediately . Only in this case is a complete recovery guaranteed without complications or relapses.
Source: https://nerv.guru/zabolevaniya/nevralgiya/vidy-n/plechevogo-nerva.html
Features of treatment
Depending on the pathology, the doctor is obliged to choose the right treatment. It is aimed at eliminating the underlying cause and prescribing appropriate medications. Additionally, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to relieve pain. Ointment with diclofenac or ketoprofen is used as a local anesthetic.
To strengthen the body, calcium and B vitamins are prescribed. Medicines that weaken muscle tone (muscle relaxants) will help reduce muscle spasms in the area of the shoulder blades. A rehabilitation course is carried out to eliminate neuralgia:
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- movement therapy (kinesitherapy);
- laser use;
- acupuncture;
- massage.
The use of folk remedies will help relieve discomfort. In some cases, it is possible to eliminate neuralgic pain forever. Apply compresses from burdock leaves, black radish juice, and flax seeds. Use ointments based on bee or snake venom. Baths with essential oils, sage infusion, and valerian root decoction are effective.
Symptoms in pregnant women
The birth of a long-awaited baby is the most pleasant and bright event in a woman’s life. But it is precisely at this time that the woman’s body is subject to serious stress.
Pregnant women most often experience intercostal neuralgia with the following symptoms:
- Severe pain of varying strength, from mild to the most intense, radiating to the area of the shoulder blades and lower back.
- A common cause of neuralgia in women in an interesting situation is herpes zoster. A characteristic symptom is rashes, acne on the skin.
Here you can read more about the cause of back pain in the shoulder blade area and its treatment.
Causes of the disease
Some people associate the appearance of neuralgia with osteochondrosis. But not in all cases, intercostal neuralgia appears against the background of spinal curvature. There are a number of ailments that entail compression of nerve endings.
So, the appearance of intercostal neuralgia can be provoked by:
- Advanced osteochondrosis, kyphosis, spondylitis.
- Diabetes.
- Hormonal imbalance during menopause.
- A disease called aortic aneurysm.
- Ailments of allergic origin.
- Diseases that involve damage to the nervous system.
- Injury during active sports.
- Vertebral displacement. This phenomenon is notable for acute back pain.
- Scoliosis. Against this background, curvature of the spinal column is possible, which provokes the progression of the disease.
Read about shoulder blade pain here.
A significant cause of compression, spasm or pinching of the vertebrae can be uncontrolled loads during sports, lifting heavy loads, and sudden movements. To eliminate the possibility of this unpleasant situation occurring, start your gymnastics with a warm-up. This way the risk of injury is minimized.
In addition, intercostal neuralgia can appear as a result of:
- Excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- Prolonged exposure to cold, hypothermia;
- Lack of vitamin B;
- Exposure to stress, depression;
- Wearing tight underwear.
Traditional methods
In the absence of complications, conservative methods successfully cope with pinched nerve endings, and painful manifestations completely go away, after which you can begin therapy with traditional methods. For this, tools such as:
- treatment with ointments;
- taking a bath;
- use of infusions.
To treat pinched nerve endings, ointments prepared from natural ingredients are widely used. To prepare the ointment, you need to grind the bay leaf and juniper needles until smooth. Add a little melted butter to the mixture. The resulting product is applied to the damaged area. The ointment helps relieve pain and helps relax muscles.
Special medicinal infusions are also widely used for therapy. Such products are used for internal and external use. Wormwood infusion is used as a pain reliever. To do this, you need to infuse wormwood inflorescences and rub them into the damaged area. For internal use, yarrow herb is suitable, which needs to be brewed and taken 1 tbsp. l. 4 times a day.