Description: Paresis: what is it, why are the manifestations of this pathology so dangerous? The fact is that pathology in the future can provoke not only paralysis, but also lead to death from asphyxia. Therefore, you need to consult a doctor in time, especially if discomfort or muscle pain was preceded by injury or inflammation.
Paresis is nothing more than partial paralysis. It can be called a certain inability to perform movements and actions due to serious damage to the central nervous system or peripheral nervous system. Doctors divide this type of pathology into 2 groups: organic (when there is a way to determine why the nerve impulse reaches the muscles irregularly), functional (associated with serious pathologies of the cerebral cortex).
Let's understand the concepts and manifestations
Lower paraparesis is extremely rare.
Only a few have ever heard of this type of disease. Be that as it may, knowledge about such disorders must be acquired by every attending physician, as well as by parents raising small children. This disease manifests itself in the form of a mild form of paralysis of the lower limbs. Symptoms may only appear in certain areas. The legs are never completely affected.
You need to understand that this disease is classified as very serious, but the intensity of its manifestation can be severe or have a mild form. At the same time, paraparesis is characterized by development in a wide variety of variants, which implies the need for individual courses of treatment.
When spastic paraparesis develops, the patient may not perceive tactile sensations in the affected areas. A person can receive physical injuries, as well as burns, but not feel anything. Therefore, such people always require special care and supervision. This condition can mostly occur as a result of damage to the spine in the thoracic region.
You can often hear the name “plegia” when referring to paraparesis. Such a replacement of concepts cannot be called correct, since plegia is a complete paralysis, which means the loss of the ability to perform targeted movements of a certain group of muscle tissues.
Paresis, in turn, implies only a partial loss of the ability to move, while the damaged tissues become flaccid and unable to bear the same loads.
Muscle strength and the number of active movements are thus significantly reduced. Depending on the location, the disease can be divided into several types:
- tetraparesis extends to all limbs;
- when triparesis , only three limbs may be paralyzed;
- paraparesis is characterized as a disease of both arms or legs;
- hemiparesis of one lower and upper limb;
- monoparesis paralyzes the muscle tissue of one limb.
Flaccid paraparesis is characterized by a state of relaxation and slight atrophy of the muscle tissue of the arms or legs without significant overexertion, as well as shortening. In this case, reflexes may gradually fade away.
Spastic paresis is characterized by a decrease in physical capabilities with accompanying muscle spasms, as well as tension.
How paresis of the limbs is treated and what it is – Psychological help
Paresis is a neurological syndrome accompanied by weakness of the legs and the inability to perform voluntary movements.
The disease develops when the nerve trunks of the brain and spinal cord are damaged, against the background of myopathies, neuropathies, and disturbances in the peripheral innervation of tissues.
Paresis of the lower extremities can affect one or both legs, cause muscle atrophy, or, conversely, be accompanied by selective hypertonicity.
Essence of the disease
Pathological processes arise due to dysfunction in the transmission of impulses to the distal parts of the limbs due to primary damage to the medulla or injury to the nerve trunks.
The cause of disruption of soft tissue innervation may be a disorder in the processes of excitation, agility, inhibition and balance in the cerebral cortex.
Depending on which neurons are affected, spastic, flaccid and mixed paresis are distinguished.
In the first case, the muscle tone of the lower extremities increases, hyperreflexia is noted, the patient makes fast, rhythmic movements caused by jerky contractions of a separate muscle group.
With peripheral paraparesis, patients are diagnosed with hypotension, lack of protective reflexes, and synkinesis. The mixed form combines the symptoms of the previous two.
Causes
The disease is caused by the following factors:
- intervertebral hernia;
- metastasis of malignant tumors to the brain and spinal cord;
- Guillain-Barre syndrome;
- stroke;
- rheumatoid arthritis of the cervical spine;
- myasthenia gravis;
- metabolic myopathy;
- polyneuropathy;
- radiculitis;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- cerebral palsy;
- neurosyphilis;
- plexitis;
- encephalitis;
- botulism;
- birth injuries;
- multiple sclerosis.
Paresis of the lower extremities is not an independent disease, but occurs when the motor pathway from the brain neuron to the peripheral nerve ending is disrupted. Damage to any area along this segment inhibits the transmission of impulses to the muscle, causing weakness in the legs and impaired mobility.
Classification
Based on the number of limbs involved, paresis is divided into:
- monoparesis - damage to one leg;
- paraparesis – paralysis of both legs;
- hemiparesis - impairment of motor functions of the arm and leg on the left or right side of the body;
- tetraparesis - damage to all limbs.
The development of monoparesis most often occurs with pathologies of the peripheral nervous system: muscle weakness spreads to the sections innervated by the pinched root. Hemiparesis has a central etiology and is diagnosed in diseases of the brain.
Signs of paraparesis of the lower extremities in adults often occur when the cauda equina is compressed by an intervertebral disc. In such cases, asymmetrical damage to the legs is observed, the disease causes intense pain, decreased sensitivity, urinary and fecal incontinence, and numbness of the perineum.
Tetraparesis is diagnosed in various myopathies, neuropathies, polymyositis, and poliomyelitis. The pathology develops acutely, causes paralysis of the respiratory system, and poses a direct threat to human life.
Depending on the severity, paraparesis is classified into mild, moderate, deep stage and complete paralysis (lack of mobility). Most often, hypotonia of one muscle or any group is diagnosed, or a certain part of the limb is affected (distal, proximal).
Symptoms
Clinical manifestations depend on the type of disease. With central paresis, there is an increased tone of some muscle parts of the pyramidal type, but there are no signs of malnutrition.
Deep motor reflexes are clearly expressed, while superficial ones are weakened, pathological flexion and extension reactions appear.
Characteristic is the appearance of friendly movements of the affected limb as a reaction to an action performed by a healthy one.
Increased tendon reflexes lead to causeless or induced clonus of the foot and buttocks. There is a dorsal extension-flexion of the thumb, a fan-shaped opening of the phalanges. Movements appear in response to external influence (pinch, injection).
What to do if a nerve is pinched in your leg?
With peripheral paraparesis, hypotension is observed up to a complete loss of muscle strength in the proximal parts.
Due to a violation of the nervous innervation, atrophy develops, the volume of soft tissues decreases, reflex reactions are weakened, and sensitivity decreases.
In rare cases, involuntary contractions of fibers may occur: a similar symptom is observed when the anterior horns of the spinal cord are damaged.
With spastic paresis, the patient cannot lift the leg or bend it at the joint, so the gait changes and the limb drags along the ground.
Patients suffering from flaccid paraparesis cannot move without additional support, since weakened muscles cannot cope with body weight. The limbs are in an unnatural position, coordination of movements is impaired.
Diagnostics
Establishing a diagnosis is not difficult; the doctor can easily determine the disease after an examination. Muscle strength is assessed on a five-point scale:
- 5 – all reflexes are preserved, muscle strength is normal, the patient is healthy;
- 4 – there is a decrease in strength, but the patient can make active movements, overcoming the resistance of the doctor’s hand;
- 3 – a person is able to perform habitual movements, but cannot cope with resistance;
- 2 – the patient does not overcome gravity;
- 1 – movements are minimal or completely absent.
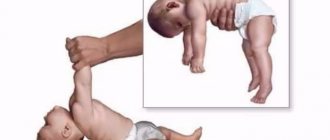
In the initial stages of the disease, the resistance test may not give the correct results; in such cases, the Barre test is additionally performed. The patient must hold the limb suspended for a long time; if the muscles weaken, the leg will begin to fall within the first 20 seconds.
Paraparesis of the lower extremities in children is diagnosed by pain localization. At the initial stage, children complain of discomfort, rapid fatigue, later their gait changes, paralysis and convulsions develop. The rate of progression of the disease is very high. Most often, the pathology occurs against the background of cerebral palsy or other diseases of the nervous system.
In case of brain damage, an encephalogram, a skull x-ray with contrast, and radioisotope research methods and electromyography are used.
Congenital paraparesis is diagnosed by decreased reflexes, low physical activity, hypotension or hypertonicity of the muscles of the lower extremities. Children have tremor of the arms and legs, increased excitability and other neurological disorders.
Treatment
Therapy for paresis is carried out comprehensively. It is important to identify the primary cause of the pathology in order to try to restore innervation to the lower extremities. To improve trophism, heat is applied to the legs, massage is performed, exercise therapy is performed, and hardware and robotic methods are used.
In case of bulbar, ascending paralysis, spinal amyotrophy of Werdnig-Hoffmann, the patient must be urgently hospitalized and provided with artificial ventilation, since paresis affects not only the limbs, but also the muscles of the respiratory tract.
Medicines
In case of paraparesis of the lower extremities, drug treatment is carried out to eliminate the primary disease, restore the functioning of the nervous and cardiovascular systems and relieve pain.
Antibiotics are prescribed for the treatment of infectious diseases. Angioprotectors and nootropics normalize blood pressure and blood supply to the brain.
When tumors, intervertebral hernias, or post-traumatic hematomas form, surgical intervention is required.
To maintain basic body functions and strengthen weakened tissues, patients are prescribed B vitamins and immunomodulators.
If spastic paraparesis of the lower extremities is diagnosed, skeletal muscle relaxants are prescribed: Sirdalud, Tizanil. These drugs relieve hypertonicity and reduce pain, and have a sedative effect in case of neuroses and increased excitability.
How to treat leg cramps in older people
Physiotherapy
Performing physiotherapeutic procedures can increase nerve conduction into weakened muscles and improve the effect of medications taken. People suffering from paraparesis of the legs are prescribed:
- UHF;
- impulse currents;
- electrophoresis with calcium and novocaine;
- microwave therapy;
- electromyostimulation;
- cryotherapy;
- thermal procedures: paraffin, ozokerite;
- UV irradiation.
During the recovery period, patients take mud, nitrogen-silicon, thermal, sulfide and radon baths. A course of physiotherapy is prescribed by the attending physician, taking into account the severity and type of disease, but not earlier than 2-3 weeks from the start of treatment.
Physiotherapy
After the patient is able to sit independently, special physical exercises begin to work out the muscles. A specialist teaches a person to stand and walk using mobile playpens, walkers, three-legged crutches, and a cane.
Later, the patient is taught to place the foot correctly; to do this, you need to climb the stairs or the trail. The course of exercise therapy lasts at least 2–3 months. The recovery period for paraparesis is quite long, so the patient must perform a set of exercises independently at home after discharge from the hospital for about 1.5–2 years.
As motor activity returns and general condition normalizes, you can visit the pool, jump on a trampoline, and jog. The speed of rehabilitation depends on the desire and persistence of the patient.
Massage
With the help of therapeutic massage, weakened tissues are restored. Procedures begin at 2–3 weeks. With central paraparesis, lightly stroking the muscles of the injured limb is performed, and in the area of the second leg, on the contrary, the muscles are kneaded more vigorously.
Massage is carried out every day, the full course is 10–15 sessions. Additionally, the doctor performs passive manipulations of the paralyzed limb.
Folk remedies
In addition to basic methods of therapy, alternative medicine recipes can be used. Treatment with masks made of natural clay, external alcohol rubs made from walnut shells, St. John's wort, thyme, and calendula help well with paraparesis of the lower extremities.
It is useful to drink freshly squeezed vegetable and fruit juices, decoctions of chamomile, yarrow, juniper, oak bark, marshmallow and dandelion root. Home treatment should be agreed with your doctor!
Operation
Surgical intervention is indicated for flaccid paraparesis and cerebral palsy, if other treatment methods do not produce results. The main indications for the procedure are changes in the shape and axis of the limb, neurogenic deformities, and reflex muscle contractures.
Types of operations:
- tendon-muscle plasty;
- capsuloplasty, tenodesis;
- corrective osteotomy, arthrodesis, limb lengthening.
In advanced cases, several techniques are combined. An important role is played by the implementation of rehabilitation measures in the postoperative period.
Prevention
To reduce the likelihood of developing paraparesis, it is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle, give up bad habits, and exercise regularly. It is important to promptly treat primary diseases, control blood pressure, avoid hypothermia and strengthen the immune system.
The prognosis for paresis of the lower extremities depends on the specifics of the primary disease, the degree of tissue damage and the compensatory capabilities of the patient’s body.
Cortical monoparesis is restored in a short time, rehabilitation for severe central hemiparesis, capsular or brainstem dysfunction lasts for several years, and very rarely it is possible to achieve complete remission.
With peripheral paraparesis, recovery occurs after 1–2 years.
Source:
Paresis of the limbs - symptoms and treatment
:
Paresis of the limbs is understood as a serious disruption in the functioning of the cerebral cortex and its parts responsible for ensuring human motor activity. The main symptoms of limb paresis are manifested by weakening of the muscular systems or mobility of the limbs.
The most common cause of limb paresis is a stroke. Treatment for limb paresis should begin as soon as the disease is diagnosed, otherwise loss of full motor function of the limb is possible.
Forms of limb paresis
5 gradations of paresis, based on muscle strength, which was identified during a neurological examination:
- 5 points - muscle strength is completely preserved (no paresis);
- 4 points - muscle strength is slightly reduced when compared with previously existing strength;
- 3 points - muscle strength is significantly reduced when compared with previously existing strength;
- 2 points - the muscle contracts in the absence of the ability to resist gravity (for example, a person bends his arm at the elbow lying on the table, but cannot do this if the arm is hanging down);
- 1 point - individual muscle bundles of the muscle contract unproductively (the entire muscle does not contract);
- 0 points - no muscle strength (presence of plegia, which is an extreme degree of muscle weakness. This condition does not belong to the concept of “paresis”).
Why does he take away his legs...
The most common cause of paraparesis of the lower extremities is considered to be damage to spinal tissues or myelopathy.
In this case, it is the cervical spine that is most often exposed to harmful effects. The very occurrence of myelopathy can be caused by the progression of osteochondrosis or spondylosis, as well as various injuries and pressure exerted by neoplasms. Typically, the result of exposure to such factors is lower paraparesis.
One of the common causes of the syndrome is trauma. Each injury can be either partial or expressed as a complete rupture of spinal tissue. In this case, compression of the spinal cord often occurs as a result of displacement of the vertebrae. This may cause partial paralysis.
An equally common causative factor is a neoplasm that can put pressure on spinal tissue in certain areas.
As a result, this can lead to a deterioration in the process of innervation conduction. Paraparesis in such a condition may not be developed in any case, and its progression can occur suddenly or gradually over a certain period of time.
Paresis of the facial nerve can be caused by diseases such as influenza, adenoviruses, herpes, rubella, chicken pox, and also CVM.
It should be borne in mind that such relationships have not been fully proven, so exceptions are possible. In most situations, accidents are the determining factors.
Possible reasons
There are many diseases and pathological conditions that can cause the development of paraparesis. The level of development of paresis (upper or lower) depends on the location of the pathological process. Several groups of lesions can be distinguished, which are accompanied by the development of paraparesis in both children and adults.
Compression lesions:
- spinal cord tumors;
- brain tumors;
- spinal injuries and traumatic brain injuries;
- abscesses, hematomas, cysts of the brain and spinal cord;
- intervertebral hernia;
- Duchenne-Erb and Dejerine-Klumpke paresis (obstetric paralysis in a child due to birth injuries);
- Arnold-Chiari malformation.
Injuries to the spine and spinal cord are the most common cause of lower paraparesis
Hereditary diseases of the nervous system:
- spastic familial paraplegia of Strumpel;
- X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy;
- degenerative diseases of the brain and spinal cord.
Infectious lesions:
- neurosyphilis;
- vacuolar myelopathy (AIDS);
- Lyme borreliosis;
- tropical spastic paraparesis;
- transverse myelitis.
Vascular lesions:
- occlusion (thrombosis, embolism, compression, reflex spasm) of the arteries of the brain and spinal cord;
- epidural and subdural cerebral hematomas;
- ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke;
- spinal cord stroke.
Other reasons:
You can also read:
Hypotonicity of muscles in a child
- Cerebral palsy in a child (cerebral palsy);
- atrophy of the cerebral cortex;
- multiple sclerosis;
- ALS – amyotrophic lateral sclerosis;
- radiation damage to the brain and spinal cord;
- vitamin B12 deficiency (funicular myelosis);
- metastatic lesions of the brain and spinal cord;
- damage to nervous tissue due to autoimmune diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjogren's syndrome);
- toxic myelopathies;
- idiopathic myelopathy;
- syringomyelia;
- traumatic hematomyelia;
- electrical injury;
- spinal ischemia;
- arteriovenous malformations;
- Guillain-Barre syndrome;
- sarcoidosis with damage to the nervous system.
Transverse myelitis complicates the course of a large number of diseases, both infectious and aseptic in nature, and can be the cause of upper or lower paraparesis
Clinical picture
Lower paraparesis is characterized by individual manifestations, which are a significant factor in the procedure for diagnosing neurological diseases. The main symptoms include:
- deterioration of sensitivity of the skin of the lower extremities;
- pain and swelling in the legs;
- weakening of muscle tissue;
- difficulty working the lower leg;
- sensations of discomfort during flexion and extension of the hip joint;
- worsening knee reflexes;
- while walking it is impossible to step on the heel normally;
- uncertain movement.
Such symptoms always appear very quickly and can have a long duration of action. In difficult situations, paraparesis in adults is combined with difficulties in the functioning of the pelvic organs.
In this case, a serious feeling of weakness in the muscles can be diagnosed, apathy is clearly expressed in the patient’s behavior, the person may hardly eat and sleep very poorly. In such situations, fever, mood swings, and disruption of normal bowel function often occur.
Due to the deterioration of the protective mechanisms in the human body, infection begins to develop at an accelerated pace.
In children's bodies, such diseases are often diagnosed after injury during childbirth. But there are cases when the diagnosis is determined incorrectly even in the real absence of a specific disease.
When the child becomes older, the established diagnosis must be confirmed or removed. Usually these issues are dealt with by a neurologist. In this case, several main degrees of paresis are determined:
- insignificant;
- moderate pathology;
- expressed;
- pronounced.
As the patient progresses to lower spastic paraparesis, tactile sensations deteriorate in the affected limbs. Therefore, patients with symptoms manifesting themselves in this way require special attention, as well as proper care. This condition mostly progresses when the spine in the chest area is damaged.
Lower flaccid paraparesis is the result of damage not only to the lumbar area, but also to the thoracic area.
Diagnostic features
In most cases, diagnosis is performed only by clinical methods without the use of additional technologies.
A comparative description of the muscle strength of the left and right extremities during the development of hemiparesis is derived. In this case, standard resistance testing procedures are carried out, and a classic testing technique called the Barre test is also used.
The essence of the procedure is the need to keep the limbs suspended for some time. If the paresis progresses, the outstretched limbs will slowly fall after 20 seconds.
To determine the factors causing the development of paraparesis of the limbs, the following hardware and laboratory testing methods are used:
- MRI of spinal and brain tissues, as well as CT diagnostics;
- analysis of the state of liquor fluid;
- electromyography;
- general blood test and testing using biochemical agents;
- electroneuromyography;
- determination of the amount of substance B12, as well as folic acid;
- identification of genetic predisposition or possible oncological tumors.
Features of the development of childhood paraparesis
With the general normal development of the child, you can notice that he walks on tiptoes. Naturally, this becomes a cause of serious concern for parents. If a child moves independently, this does not mean that he has paraparesis.
Walking on tiptoes may be due to the fact that only some groups of leg muscles may be in good tone, which is not in all cases a symptom of paraparesis. Most often, in such situations, doctors recommend massage, as well as performing therapeutic restorative physical exercises.
In the event of a disorder, restoration processes in the children's nervous system, due to its plasticity, proceed much more actively than in the developed organisms of adults.
Therefore, the results of any significant disorders, hypoxia and birth trauma may very soon cease to appear.
If paraparesis is diagnosed in a child, it is necessary to ensure continuous monitoring by a neurologist. Observation should be accompanied by drug treatment, as well as physiotherapeutic procedures and orthopedic examination. Acupuncture can significantly contribute to the positive effect of treatment.
Treatment and prevention
To treat paraparesis of the lower and upper extremities, an integrated approach is always necessary. It is mandatory to use treatment for the disease that provokes the syndrome, causing muscle weakness, as well as immediate intensive treatment of symptoms.
To make muscle tissue contract better, gymnastics and massage procedures are used. Over time, exercise requires more activity and increased stress on the muscles. In this case, each action performed must be strictly monitored by the attending physician.
Subsequent stages of treatment include exercise therapy courses, water treatments, physiotherapy, as well as electromyostimulation and the use of magnetic fields, acupuncture, individual massage procedures, and acupuncture.
Remarkable results continue to be demonstrated by the use of various psychotechniques and various trainings designed to improve the psychological state of patients.
Surgery is used extremely rarely. For the most part, such measures are necessary to eliminate diseases that cause paraparesis.
Water procedures are considered one of the most effective methods of preventing paresis of the upper and lower extremities.
Therapy
It is necessary to determine the source of the disease and select the most effective means to eliminate it. Additionally, restorative treatment is selected to reduce the risk of the consequences of a neurological syndrome. Complex therapy will speed up recovery and return a person to a normal active life.
Patients are prescribed medications to improve nerve conduction, tissue trophism and normalize muscle tone. Medicines are used to eliminate weakness in the legs. The general treatment regimen for paraparesis of the lower extremities in adults and children includes the following medications:
In the first days of treatment, the patient is prescribed injections. After a while, the remedies are in tablets. It is important to follow your doctor's prescriptions, since many medications have side effects.
If there is no positive result after conservative treatment, patients are offered surgery. The risk of complications always remains. But sometimes surgery is the only treatment that can restore sensitivity and function of the legs. After surgery, patients need time to recover. The rehabilitation course also includes the use of physical therapy.
The operation is prescribed for patients with flaccid paraparesis and cerebral palsy, if the shape and axis of the limbs change. The same applies to neurogenic deformities and reflex muscle contracture. Taking into account the patient’s condition and the damage caused by pathological processes, doctors select the most suitable method of operation:
- tendon-muscle plasticity,
- corrective osteotomy, arthrodesis, limb lengthening,
- capsular plastic surgery, tenodesis.
In difficult situations, surgeons use several techniques at once.
Therapeutic exercise helps to quickly recover from an illness. Even the simplest movements help restore the nervous response due to irritation of proprioceptors in the area of the muscular-articular apparatus. Exercises prevent the formation of contractures, maintain muscle tone, and stimulate neurotrophic processes.
The doctor will tell you what paraparesis is. He will take into account the course of pathological processes and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. Exercises should be done slowly, gradually expanding the volume and increasing the load.
Set of classes:
- Lie on your back. As you inhale, raise your right leg, and as you exhale, lower it. Perform similar movements with the left leg.
- Lying on your back, imitate swimming. Perform movements with the lower limbs using the breaststroke technique.
- Bend and straighten your legs at the knees.
- Take turns drawing circles in the air with your feet. Perform exercises while lying on your back.
- Pull your feet towards you or turn them in different directions. Can be performed with both legs at once or in turns. It is allowed to lie on your back or sit.
- Bend one leg at the knee and press it as tightly as possible to the chest. Stay in this position for a while. Straighten the limb and repeat the exercise with the other leg.
- Lie on your back. Take turns bending and straightening your toes, spreading them out. It is important to maintain consistency.
Exercises are performed slowly, in a calm state. If your health deteriorates, you should stop exercising. For some exercises you can use additional equipment. Exercise therapy lasts no more than 20 minutes; for weak patients, 10 minutes is enough. The exercises are repeated 3-4 times.
Along with physical therapy, patients are recommended to attend massage treatments, after which blood circulation is restored and muscles are strengthened. Sessions help prevent degenerative changes. The massage is carried out by 2 specialists at once, starting from the feet and gradually moving to the hips.
Rehabilitation helps restore lower limb function. Physiotherapeutic procedures increase the conductivity of nerve impulses. Not only the muscles are strengthened, but the effect of the medications taken is also increased. Patients with paraparesis of the lower extremities are prescribed the following therapeutic procedures:
- impulse currents,
- UHF,
- microwave therapy,
- cryotherapy,
- warming up with heat,
- electromyostimulation,
- electrophoresis with the addition of calcium and novocaine,
- irradiation with ultraviolet rays.
During the recovery period, patients are also recommended to attend medicinal baths. Physiotherapy is prescribed by a doctor. The specialist takes into account the severity of the disease, the degree of spread of pathological processes. In most cases, the rehabilitation period begins no earlier than 2-3 weeks after the start of therapy.