| Agitation | |
| ICD-10 | R45.1 |
| ICD-9 | 308.2308.2 |
| MeSH | D011595 |
Agitation
agitation
has the same origin ) - motor restlessness, often occurring with strong emotional arousal, accompanied by feelings of anxiety and fear [1]. The cause may be catatonia, alcoholic delirium, outbursts of despair during melancholic depression, anxious depression [1], mixed depression [2] and some other mental disorders. A person in this state becomes extremely fussy and is able to perform only simple automated actions. He develops a feeling of emptiness and lack of thoughts, the ability to reason and establish complex causal connections between phenomena is impaired.
This condition is accompanied by autonomic disorders
: pallor, rapid breathing, palpitations, sweating, trembling of hands, etc. appear. Agitation is assessed as a prepathological condition within the boundaries of the psychological norm.
Agitation is observed with affective tension caused by severe stress, as well as with many mental illnesses (for example, catatonic schizophrenia, anxiety neurosis, agitated or involutional depression). Agitation can also occur with alcohol and drug (for example, amphetamines) poisoning, exogenous and endogenous toxemia.
When treated with antipsychotics, agitation must be carefully differentiated from akathisia, a side effect of antipsychotics that is similar in clinical manifestations to agitation. Misdiagnosis of akathisia as agitation can lead to an increase in the dose of antipsychotic medication, as a result of which akathisia worsens[3].
Causes of agitation
Sometimes the emotional state of human subjects can be considered as a symptomatic manifestation of individual pathological processes. With such symptoms, it is necessary to carry out corrective drug and non-drug therapy. The conditions under consideration also include agitation, which is qualified by doctors as intense emotional arousal, giving rise to a number of unpleasant manifestations. Sometimes the state of agitation is absolutely natural, but in other circumstances it can act as a “bell” signaling the presence of quite dangerous pathologies.
It should be understood that the described disorder does not develop in a vacuum. It is provoked by external factors and internal reasons.
So what is agitation in medicine? This term refers to the excited state of an individual, accompanied by motor restlessness, fear and anxiety. Speech anxiety may also occur. In principle, agitation is considered a natural response of the body of human subjects to tension caused by severe stress. In other words, the described condition is detected under the influence of stressors or psychological trauma. In some individuals, the phenomenon in question appears as a result of severe fright or sudden changes in the environment surrounding the person. In addition, this condition is sometimes inherent in people whose work activity is dangerous to the individual’s life.
Among the external factors that provoke agitation, in addition to the effects of stressors, one can highlight increased physical stress, accumulated fatigue, and excessive mental stress that persists for a long period. Attacks of the affective state in question are often caused by pharmacopoeial drugs, consumption of high doses of alcohol-containing drinks, caffeine, and dependence on psychotropic substances.
Since the state of agitation can be a manifestation of an illness, a number of ailments can be identified that are internal factors that give rise to emotional overexcitation:
- infectious diseases;
- intoxication;
- endogenous depressive moods;
- Alzheimer's disease;
- anxiety neurosis;
- worsening senile changes that occur in the individual’s psyche, for example, with dementia;
- catatonic schizophrenia;
- senile decline;
- bipolar disorder.
In addition to the above, the described condition can also be provoked by endocrine ailments, advanced vitamin deficiency, and vegetative-vascular dystonia.
In psychiatric science, agitation is considered a serious problem that occurs in extreme circumstances. An individual, being in a similar state, is at risk of displaying aggressive behavior towards the environment and himself.
With a pronounced anxious depressive state, an individual often causes damage to other people's property. In addition, this disorder in patients is often the main cause of injury to medical staff.
Mental disorders are considered a rather big scourge of modern society, since every year more and more human subjects are exposed to these disorders.
In psychology, agitation is considered a disorder generated by a strong surge of emotions, which is accompanied by strong fear and anxiety, manifested in unconscious speech and motor excitation.
What is agitation and why does it occur?
Agitation – (Latin “set in motion”) is a psycho-emotional state characterized by uncontrollable fear, excitement, speech and motor restlessness. People in a state of agitation are not able to control their behavior, speech and emotions, they scream, run, make many unnecessary movements, their actions and words may seem inadequate, devoid of logic and meaning.
It is quite difficult to say exactly what agitation is. According to psychologists, this condition is borderline - between physiological norm and pathology. If agitation occurs periodically - as a reaction to very strong stress, then, most likely, these are personal characteristics of a person that are not related to psychopathology.
Agitation can occur at any age; such attacks occur in both children and adults. In children, attacks of agitation can occur during infectious diseases, accompanied by an increase in body temperature or during strong emotional experiences, even positive ones.
There are 2 groups of reasons for the development of agitation:
- Severe stress: fear, psychological trauma - agitation occurs as a mental reaction to shock, passes quickly and does not require treatment or medication. Also, overstimulation of the nervous system can cause fatigue, chronic lack of sleep, excessive consumption of drinks containing caffeine or pharmacological drugs that cause stimulation of the nervous system.
- Somatic and mental illnesses - agitation occurs as one of the symptoms of the disorder.
This condition can be caused by:
- Infectious diseases
- Intoxication
- Anxiety neurosis
- Depression
- Psychoses
- Schizophrenia
- Alzheimer's disease.
It is believed that this condition occurs more often in people whose nervous systems are weakened. Predisposing factors may be vitamin deficiency, metabolic disorders, vascular pathologies, head injuries, decreased immunity, poor nutrition, physical inactivity, and so on.
Symptoms of agitation
The emergence of agitation marks a number of different manifestations, but often the individual himself does not notice their presence.
The literal translation of the word agitation is excitement. Therefore, a characteristic manifestation of the pathological condition in question is the occurrence of motor disinhibition or speech anxiety. In addition, the individual may experience trembling of the limbs, excessive sweating, and increased heart rate. The listed manifestations are often accompanied by rapid breathing. In a state of agitation, the dermis becomes pale in color.
In psychology, agitation is a behavioral defect consisting in the uncontrolled transition of affective tension into motor restlessness. It is a concomitant symptom of various mental illnesses, for example, anxiety neurosis, involutional depression, catatonia.
When the state in question occurs, the individual “meets” a feeling of absolute absence of thoughts, his head seems empty. The patient becomes unable to reason sensibly or identify complex causal relationships.
Agitation is accompanied by a feeling of fear and anxiety, turning into speech disinhibition or motor restlessness. An individual in such a state is forced to perform unconscious motor acts of the same type. In addition, he is characterized by fussiness. The patient can only perform simple automated operations.
Agitation is determined by the presence of the following signs. The individual's behavior changes when the violation in question occurs, but he himself is not aware of it. Speech disinhibition, fussiness in motor acts, hand tremors, pallor of the dermis of the face appear, sweating increases, and the heart rate increases. In this case, the individual is in a hyperexcited state.
Particular attention is paid to the emergence of a state of agitation against the background of Alzheimer's disease, since depressive moods, hallucinations are added, behavioral disorders intensify, and a person is drawn to wandering.
If the disorder in question is a symptom of other ailments, then it is often accompanied by attacks of spontaneous shouting of swear words and motor tics.
Signs of agitation in depressive states are somewhat different from those given above. This illness manifests itself as a combination of various symptoms characteristic of ordinary depression (apathy, dream disorder, depressed mood) and those inherent in agitation. First of all, people suffering from agitated depression develop causeless anxiety. They begin to worry about loved ones and their health. Patients have a premonition of something bad. The speech of such patients changes; they reproduce the same phrases that convey their excitement. Often this comes to the point of endless repetition of just a few words. Behavioral changes are also noted. It is difficult for an individual to sit in one place. He has to constantly move.
Symptoms and diagnostic methods
Agitation has clear symptoms, but the patient himself usually does not notice them. The first thing that may appear in a person is speech anxiety.
Speaking quickly and indistinctly, he has difficulty formulating his thoughts. Added to this phenomenon is trembling of the fingers or sudden movements of the entire hand. At the same time, there is an increase in heart rate and breathing. The patient is sweating heavily and is in undisguised emotional excitement.
If the disease has passed the initial stage, the patient will complain of a feeling of devastation and difficulty concentrating. The disease does not allow us to draw up cause-and-effect relationships and think logically. In this case, fear, panic and fussiness arise.
A person has difficulty expressing thoughts, and cannot write at all due to trembling hands. He can perform only the simplest actions and requests, but as the disease worsens, his activity will be reduced to sleep and meals.
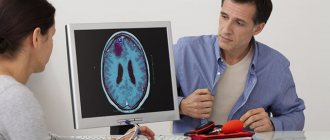
Diagnosis and treatment should be carried out by a psychiatrist. In addition, you will need to consult a neurologist and, possibly, a narcologist. Currently, there are accurate and rapid methods for diagnosing mental disorders. In order to determine the diagnosis and correctly plan the treatment, the specialist will need to collect an anamnesis, namely:
- visual inspection;
- monitoring pulse and blood pressure;
- general blood, urine and biochemical analysis;
- hormone analysis;
- MRI of the brain.
This will allow the doctor to determine the severity of the disease and state that it is agitation, and not, for example, akathisia, which is similar in symptoms. Based on the information collected, a treatment plan will be developed and specific medications will be selected. The specialist will also decide whether the patient needs hospitalization.
Treatment
Agitation is considered a prepathological condition and requires mandatory treatment. With the help of medication and psychotherapy, you can completely get rid of this condition. Even if the cause of agitation is stress or overwork, treatment is mandatory. This condition can not only provoke the development of other psychopathologies, but is also potentially dangerous for the patient himself and the people around him. Modern anxiolytics and antidepressants have a pronounced therapeutic effect and a minimum of side effects.
In treatment they use:
- Antidepressants - modern drugs do not cause drowsiness, addiction or other side effects. But when taking them, it is important to remember that the effect of use will be noticeable only after 3-8 weeks. Therefore, these drugs are used for long-term treatment, and not to relieve “acute” symptoms.
- Anxiolytics – anti-anxiety drugs are also used to treat agitation. Their use is recommended for severe fear, anxiety, and restlessness.
- Antipsychotics or neuroleptics help quickly get rid of the symptoms of agitation. They are indicated for severe agitation, aggression, delusions and hallucinations.
In complex treatment, psychotherapy is mandatory - it helps patients cope not only with the manifestation of the disease, but also with the side effects of the drugs used in treatment.