There are several dozen different diseases associated with digestive disorders that pose a danger to human life. From this category of diseases, pathologies characterized by impaired eating habits should be distinguished. The danger of this group of diseases is rarely perceived properly, but it is important to understand that behind eating disorders there are problems associated with the psyche. In this article we will look at what bulimic neurosis is and talk about its dangers.
Bulimic neurosis, ravenous hunger, kinorexia, bulimia nervosa - a disease associated with an eating disorder that goes by different names
Description of the disease
Bulimia is a pathology of a psychological nature, manifested in the form of a deviation from the usual pattern of behavior.
The disease is accompanied by constant bouts of overeating that cannot be controlled. Several different terms are used in medicine to describe this disease. “Kinorexia,” “bulimic neurosis,” “bulimia,” and “bulimia nervosa” are the most common synonyms used as a diagnosis. The pathology in question is popularly called “wolf hunger.” According to experts, bulimic neurosis poses a serious danger to the life of the patient, since the amount of food consumed is several times higher than the level of nutrients necessary for the normal functionality of the body. It should be noted that the patient cannot control this process in any way, as he constantly feels hungry.
One of the most common methods of “cleansing the body” among patients with bulimia is artificially inducing vomiting after each meal. People often resort to using potent medications that have a laxative effect. It is important to note that such drastic methods are used several times during the day.
The cause of this behavior is mental disorders and disorders of the central nervous system. The danger of the disease in question is explained by the fact that a mental disorder prevents the patient from realizing that his actions are catastrophic for many internal organs and systems.
According to medical statistics, only one person out of several hundred patients manages to cope with the disease on their own. In order to be able to overcome his habits, a person must have an unbending will and a stable psyche. In the realities of the modern world, where every individual faces various stress factors every day, the presence of “iron nerves” is quite rare.
Bulimic neurosis is a consequence of a mental disorder and disruption of the central nervous system.
Many patients of psychologists say that an insatiable feeling of hunger gives rise to feelings of guilt and contributes to the development of depressive syndrome. The appearance of depression can provoke anorexia nervosa, which manifests itself in the form of a complete lack of appetite. Against this background, there is an increase in the level of neurasthenia and a disappearance of interest in life.
Bulimic neurosis: what is it and how to cope with it?
Bulimic neurosis is a mental disorder caused by a nervous pathology in which a person eats excessive amounts of food, and then tries to get rid of excess calories by inducing vomiting. Forms of the disease without inducing vomiting are also possible; in this case, overeating is followed by a period of fasting, severe food restrictions, and strict diets.
Symptoms of bulimic neurosis
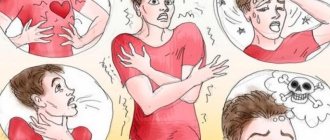
With this pathology, a person spends most of his time thinking about weight, figure, and nutrition. There is a panicky fear of weight gain and the appearance of fat deposits. A person is aware of the abnormality of his eating behavior, unlike patients with anorexia nervosa, and may worry about this.
A strong appetite arises, which the patient is unable to control. Because of this, a person overeats to the point of discomfort and pain. During an attack, the amount of food greatly exceeds that taken at other times.
After eating, a person induces forcible vomiting. Some patients prefer not to get rid of food in this way and punish themselves with grueling workouts and starvation diets.
Between attacks, they tend to count calories, the amount of proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
Patients often resort to using medications to avoid weight gain due to constant attacks. Laxatives and diuretics are used in large quantities. Enemas are used less frequently. Herbal teas or special supplements designed to control appetite and speed up metabolism can be used.
Treatment of bulimic neuroses
For treatment, you need to see a doctor and psychotherapist. The therapy is comprehensive: a psychologist helps to understand the causes of the problem, normalize the emotional state, and improve eating behavior; the doctor prescribes special medications.
Several options for psychotherapy are used. Cognitive behavioral therapy is often used. This method helps to identify destructive beliefs, replace them with new ones, and instill in the patient useful habits and behavior patterns.
Interpersonal therapy can help improve communication skills with others, which can help overcome low self-esteem, which often leads to bulimia.
Family psychotherapy helps improve family relationships and get rid of destructive communication patterns, which often cause pathology in adolescents.
Antidepressants are used among medications. You should take only those medications prescribed by your doctor, following the prescribed dosage. You should not prescribe medications on your own due to possible harmful effects on the body.
Forecast and prevention of the disease
Bulimia nervosa can be cured. The success of therapy depends on the patient's behavior. If a person refuses treatment or does not take prescribed medications, the pathology cannot be eliminated.
In this case, there is a high probability of death from liver or kidney failure. The disease may recur.
When the first signs appear, you should consult a doctor to avoid harm to the body.
To prevent the onset of the disease, you should get rid of existing mental disorders. It is recommended to work with self-esteem.
You should find something that interests you, a hobby, communicate with people in order to have other interests besides your figure, self-confidence.
Relatives should support the person, not criticize the figure, concentrate on the merits, so as not to create excessive importance of appearance and weight.
Source: https://eustress.ru/nevroz/bulimicheskij-nevroz
Causes and signs of the disease
The reasons why bulimic neurosis develops are not fully understood. Among the proven facts, this disease can be caused by disorders of the endocrine system, disorders of the central nervous system, as well as mental disorders. A number of researchers say that in childhood these people did not have enough parental love (or experienced excessive parental criticism of their appearance), and learned to “eat stress.” The following symptoms of bulimia neurotic are distinguished:
- attacks of uncontrollable appetite;
- the ability to consume huge portions of food at one time;
- lack of volitional control over food consumption;
- negative attitude and self-dislike (after an attack);
- desire to resort to forced cleansing of the stomach and intestines after an attack;
- mood swings, emotional instability.
The main symptom of bulimia nervosa is alternating uncontrollable attacks during which the patient eats an unlimited amount of food. You can understand what it is when a person, after a huge amount of food, tries to lose weight (goes on yet another strict diet, does grueling workouts) or simply empties the stomach of the food he has eaten, provoking vomiting, or taking laxatives.
The symptoms of kinorexia depend on the type of disease. There are three varieties:
- insatiable hunger that does not go away while eating and lasts until the bulimic attack ends;
- the need for constant, continuous food consumption;
- bouts of binge eating at night.
After all, a person is gnawing at a feeling of guilt, an awareness of his own inability to fight the disease, which can only aggravate the picture: depression begins, addiction to alcohol, drug addiction arises.
Particularly dangerous is the habit of alternating bouts of eating food with getting rid of it, causing vomiting. Constant exposure of the food mass, already mixed with gastric juice, to the esophagus and oral cavity leads to tissue damage by acid, inflammation of the esophagus and gums (gingivitis) occurs, and tooth enamel becomes thinner. If a person takes laxatives, the body becomes dehydrated and constipation occurs.
Diagnostics
Bulimic neurosis is difficult to diagnose because there is no objective clinical picture. To find out the true cause of the disorders, it is necessary to conduct a differential diagnosis. This will help exclude pathologies from the kidneys, liver, pancreas and gall bladder, and gastrointestinal tract. The following examination methods are used:
- blood test (general, biochemical);
- electrocardiogram;
- fibrogastroscopy.
If no pathologies are detected, the patient is referred to a psychologist for testing. The basis for the diagnosis of bulimic neurosis is the presence of attacks of uncontrolled food intake every three days for three months.
Bulimic neurosis - what it is, causes, symptoms, stages, treatment
Bulimic neurosis can be eliminated if you approach the issue comprehensively. Only doctors can do this task. There are enough recommendations, and they are all aimed at normalizing mental balance. The disease is not a death sentence; treatment should be started at the first stage; in the future it will be more difficult.
What is bulimic neurosis?
Bulimic neurosis is a condition where a person eats a lot of food without control and constantly blames himself for it. Psychological imbalance and improper functioning of the central nervous system play a role here.
Due to the constant fear of gaining weight, the patient begins to take various methods to “cleanse” the body - most often this is inducing vomiting after almost every meal, taking various drugs that promote weight loss, laxatives, etc. All this is fraught with serious consequences.
Causes
Bulimic neurosis can appear due to both external and internal factors, namely when:
- Wrong eating habits.
- Constant dietary restrictions from parents.
- Improper functioning of the central nervous system.
- Problems from endocrinology.
- Psycho-emotional imbalance.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Suffered severe stress.
- Significant mental overload.
- Serotonin deficiency in the brain.
- Alcohol or drug intoxication.
This deviation is often noticed in women. The age category is usually 18-26 years. Also at risk are those who suffered from obesity in adolescence or earlier.
A bad environmental factor, a serious shock, or some kind of disorder can aggravate the situation.
Most often, attacks are provoked by scandals and any negative effects on the psyche.
Main symptoms and signs
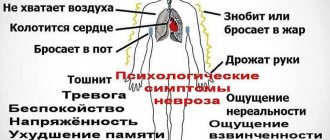
Symptoms of bulimic neurosis include:
- uncontrolled eating of food, up to the occurrence of painful sensations in the abdominal area;
- isolation;
- feeling of extreme hunger;
- lethargy;
- apathy;
- the desire to eat not only during the day, but also at night.
People with bulimic neurosis feel guilty after eating. They try to compensate for this by forcibly induced vomiting. This is how people try to lose weight. Grueling physical activity, taking laxatives, special herbs and teas for weight loss, and enemas are not excluded.
A person constantly thinks that he eats a lot, is not like everyone else, is gaining weight and wants to stop it, but cannot.
Stages
There are three stages of this disease:
- Initial. A person periodically overeats so much that he experiences abdominal pain, but such attacks do not occur very often. Usually the appetite wakes up in the evenings. This condition lasts about 6 months.
- Average. Overeating increases. Due to the constant feeling of guilt and reluctance to gain weight, the patient vomits after meals. If the body is strong, this can last from 2 or more years.
- Heavy. The patient's body is exhausted by violent methods of removing food. In this regard, in the severe stage of bulimia, the stomach is practically no longer able to digest food normally. Even small amounts of food cause nausea and vomiting. Severe problems appear with the gastrointestinal tract, nervous system, and also with the heart.
What can bulimia lead to?
With bulimia, the patient constantly overloads the stomach and overeats. Consequently:
- problems with the digestive system;
- interruptions in heart function;
- depression;
- load on the joints and the appearance of associated pathologies.
Due to systematic vomiting, the following may occur:
- enamel damage, caries;
- gum problems;
- inflammatory process of the esophagus;
- dehydration and cramps;
- impaired metabolism;
- constipation;
- dysfunction of all organs and systems.
And the most important thing is a feeling of weakness, instability of the nervous system. A person is no longer able to control himself. He becomes uncommunicative, rarely leaves the house, and problems appear in his personal life and at work. Any outside statements and hints are taken very seriously. The patient takes all the words of strangers to heart, which suppresses him even more.
Treatment methods
To recover, you will need complex therapy. Psychotherapy plays a special role, but medication cannot be avoided.
Important information It is possible to cope with the disease faster when not only the patient, but also his relatives take part in the therapy. All points are discussed with a specialist.
He will help you understand the causes of bulimia and tell you how to deal with the uncontrollable desire to consume food. He will convince you otherwise, focus on other points, and develop habits that will help you cope with the problem.
It is important that the family helps with this.
Antidepressants will be prescribed as medications. They will help stop bulimic neurosis. Such drugs as Prozac, Fluoxetine, Fluxen are advisable.
Personal attitude is also important. It is important to set yourself up for the positive, avoid stress and any nervous tension. It’s a good idea to find something interesting to do that will distract you. You can change something in your appearance or image, this will somewhat raise your self-esteem, mood and minimize attacks.
If during the examination any additional pathologies were identified, then their treatment is also necessary. If this is not done, poor health will overshadow the patient and, as a result, the progression of bulimia.
Dangerous treatments
The following methods of combating the disease are absolutely excluded:
- Absolute restriction in food. This is additional stress that will only make the situation worse. This is done gradually and only under the supervision of a doctor.
- Consumption of alcohol or drugs. This should be absolutely excluded during treatment.
- There is no need to look for those to blame. No excuses or slander to your loved ones about what they were forced to eat since childhood will help. This will only ruin your relationship with them and again have a negative impact on the body.
- Turning to alternative medicine. It is better not to waste time on healers and sorcerers, but to immediately consult a doctor, since wasting time can only aggravate the disease.
- Taking medications at your own discretion. No medications should be self-prescribed. Any medicine is selected individually, as is the dosage.
- Using weight loss products. It is important not to eliminate the accumulated mass using teas, decoctions, creams or tablets. You need to fight the root cause.
You can’t constantly think about your shortcomings, it will only unsettle you. All thoughts should be directed towards the positive.
Conclusion
Bulimia is a disease that occurs for neuropsychiatric reasons. Important information There is no point in fighting the problem on your own; this can only lead to the progression of the pathology.
Often his relatives also participate in the recovery of the patient, supporting and helping to fight neurosis. Not only drug therapy is important, but also psychotherapy, which is carried out by an experienced specialist.
2897 ratings
Source: https://nervy-expert.ru/neurology/nevroz/bulimicheskiy-nevroz/
Reasons for the development of kinorexia
Unfortunately, today there are many unresolved questions regarding the causes of the development of the disease. There are several proven theories related to the origin of bulimic neurosis. According to researchers, the development of the disease is provoked by the following internal factors:
- disruptions in the functionality of the central nervous system;
- hereditary factors;
- mental disorders;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system.
In addition, the development of bulimia is facilitated by chronic diseases that deplete the body and reduce the quality of the immune system. Often, additional reasons include systematic use of alcoholic beverages and drugs. A significant role in this issue is played by the level of stress resistance of a particular individual.
Many psychologists say that the reason for the presence of a tendency to various neuroses may be emotional trauma suffered in childhood. The lack of parental love, understanding and support affects the level of self-criticism, the decrease of which gives rise to various complexes. It is these complexes that are the main reason for the emergence of the habit of “eating stress,” which provokes the development of the disease.
Causes of bulimia
Often a person, without realizing his actions, eats up troubles with high-calorie foods, usually sweets. This attempt to sweeten the bitter pills of life is justified not only logically, but also biochemically: chocolate contains substances that promote the production of serotonin (also called the happiness hormone). Even in a state of deep depression, it is enough to eat a piece of a chocolate bar to improve your mood.
But with disorders of the nervous and endocrine systems, the patient is unable to stop - he absorbs a huge amount of high-calorie food. Therefore, another name for bulimia nervosa is ravenous hunger or kinorexia.
There is no clear expert opinion on the causes of bulimia. The development of the disease is influenced by internal and external factors. Internal ones include:
- nervous disorders;
- disorders affecting the endocrine system;
- genetic factor;
- mental illness.
External reasons prevail; they are the ones that form in a person a painful craving for food and a serious psychophysiological dependence. Psychotherapists formulate the underlying cause of eating psychosis in one word: loneliness. Moreover, it is not necessarily literal. Sometimes a person may feel lonely in a family when there is a lack of understanding and participation.
Fact! The vast majority of patients with bulimic neurosis are lonely people, often divorced, those whose loved ones have left, or widowed people experiencing the loss of a loved one.
External provoking factors include:
- stress;
- depression;
- constant mental overload;
- the presence of problems that a person is not able to solve;
- alcoholism and drug addiction;
- consequences of exhaustion.
Exhaustion can be a consequence of serious illnesses (for example, tuberculosis) or simply food restriction, forced or conscious. It is known that people who once experienced acute hunger eat a lot for the rest of their lives, trying to fill themselves up for future use. Although there is no longer a shortage of food.
A separate topic is strict diets and the desire to bring weight to a minimum level. Those who are drawn into such self-experiments alternate between periods when there is no appetite (they suddenly lose weight) with periods of attacks of ravenous hunger. The desire to lose weight at any cost can develop into anorexia.
Clinical picture
Symptoms of bulimic neurosis are often individual in nature. Many patients report experiencing intense shame and guilt due to their inability to moderate their appetite. It is these feelings that provoke attempts to induce vomiting or take a laxative. Then the circle closes, and all the above actions begin in a circle.
Some patients notice changes associated with increased food absorption. In this situation, even a slight weight gain can provoke emotional instability and the desire to withdraw into one’s own world. Lethargy and apathy force a person to plunge into voluntary isolation, avoiding communication with loved ones.
With bulimia, a person experiences constant bouts of hunger, which they try to suppress with high-calorie foods.
Experts distinguish three forms of the disease, each of which has its own characteristics:
- The first is that the feeling of irresistible hunger appears strictly in the evening hours.
- The second is a feeling of intense hunger that does not disappear even after eating a single meal.
- The third is constant eating that cannot be curbed or controlled.
Each of the above forms of the disease has only one common feature - attempts to artificially get rid of consumed foods.
Treatment methods for bulimic neurosis
There are several ways to relieve a person from the manifestations of this condition. Nominally, bulimic neurosis is treated:
- with the help of psychotherapy: communication with a specialist, regular sessions that stabilize a person’s emotional and mental state;
- with the help of medications: drugs act as an auxiliary component; they only complement the treatment, helping to alleviate the patient’s general condition.
There are also cases of self-healing, when a person recovers without the use of medications or the help of a psychotherapist. But such cases are rare; not many have been described in practice. For this reason, doctors recommend not to risk your health and to seek help when the first signs of bulimic neurosis appear.
Causes of pathology and what causes it?
The root of suffering lies in an unstable psyche and nervous tension caused by the current situation in a person’s life or provoked by past events about which a person is secretly or openly worried.
In an effort to reduce the degree of irritation, the patient drowns out the discomfort in the soul in a way suggested by the subconscious.
It, which records every single emotion in our lives, helpfully brings to the surface of memory encrypted memories of the bliss we experienced when gaining access to our mother's breast or a bottle of food.
This very connection “eating food = peace of mind” becomes the desired goal of many who are looking for a way to say goodbye to emotional torment in the most primitive, but effective, in the opinion of our subconscious, way.
Another factor that prevents you from adequately responding to problems: fear of frank dialogue with yourself and reluctance to act effectively under circumstances, the habit of postponing decisions or shifting them to others.
As a result, eating stress over and over again becomes a habit, from which the development of bulimia is just a stone's throw away.
- Bulimic neurosis begins with the absorption of various dishes and sweets in huge quantities at one time. A person eats repeatedly, and then immediately tries to get rid of the consumed food in various ways. This happens several times a day.
- The patient's self-image is deformed. He always sees himself differently from what he really is. Patients are overly concerned about their weight. They constantly complain about excess body weight, although it is normal.
Disorders gradually develop:
- Bulimic neurosis begins with the absorption of various dishes and sweets in huge quantities at one time. A person eats repeatedly, and then immediately tries to get rid of the consumed food in various ways. This happens several times a day.
- The patient's self-image is deformed. He always sees himself differently from what he really is. Patients are overly concerned about their weight. They constantly complain about excess body weight, although it is normal.
- The perception of food is distorted. The patient sees in it not a source of nutrients and energy, but a way to gain pleasure and relieve stress.
- Most often, the disease affects girls and women. Among representatives of the stronger sex, such a disease is rare. Statistics show that for every 9 sick women there is 1 man.
- Symptoms of the disease worsen in winter, when there is a lack of natural sunlight.
What are the dangers of bulimia?
- Repeated artificial vomiting leads to damage to internal organs.
- The esophagus suffers greatly, since the acidic contents of the stomach are constantly thrown into this muscular tube. This acid corrodes the walls of the esophagus, causing ulcers to appear. Symptoms of reflux occur - an inflammatory lesion of the esophagus. The sphincter between the stomach and esophagus is damaged. Tissue rupture may occur.
- Some nutrients do not enter the body. Therefore, hair begins to fall out, the structure of the nails is disrupted.
- The stomach contains hydrochloric acid. Tooth enamel cannot resist it. Therefore, over the years, the upper shell of the tooth is destroyed and caries develops.
- The parotid glands become enlarged and inflamed.
- Dehydration and kidney failure caused by vomiting occur.
- Dependence on laxatives occurs.
- Disruptions in the menstrual cycle occur.
- Patients suffer from abdominal pain and bloody vomiting.
- Characterized by sudden changes in mood and bouts of depression.
- As a result, a very difficult situation arises that may have a sad ending.
- Typically, patients hide in the toilet to induce vomiting, but loved ones do not notice this.
Dangerous treatments
Bulimia is a neurosis, and neurosis is a disease, so only a doctor with the appropriate specialty can treat it.
The list of harmful advice that people with bulimia hear includes:
- a volitional ban on food, which will become such stress for a person that the psyche will have to come up with an even stronger “shock absorption”, for example, alcohol or drugs;
- searching for those to blame: “my mother taught me to eat a lot” - perhaps my mother really did not contribute to the development of correct eating habits, but this information will not help in any way to get rid of food addiction, but resentment towards parents can become another source of stress;
- numerous hypnotic practices, ear piercing “at biologically active points,” healing mantras and other unscientific theories take a person with bulimia further away from solving the problem, aggravating his condition;
- taking medications that dull the feeling of hunger without a doctor’s advice. Firstly, they are harmful, and secondly, they have a limited duration of action - when the brain realizes that it has been “deceived”, it will demand even more food.
Recovery is real. You just need to believe in yourself.
Thus, bulimic neurosis is a disease that can be cured through a competent and professional approach, faith in one’s strengths and the desire to take life into one’s own hands, without yielding the reins to various addictions and neuroses.
Diagnostic methods
When it comes to neurotic disorders, diagnosing the disease has certain difficulties. Many practical techniques used to objectively assess the patient’s condition cannot be applied due to the fact that the clinical picture is weakly expressed. In order to establish an accurate diagnosis, a differential technique is used, which is based on the method of excluding diseases that have similar symptoms. These diseases include various disorders of the kidneys and digestive system.
In addition, to confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo an electrocardiography procedure, fibrogastroduodenoscopy of the duodenum and stomach, and also do a detailed blood test. Only after undergoing a thorough examination does a psychologist begin working with the patient. To confirm the diagnosis, special tests and survey methods are used to identify neurotic disorders.
In a situation with bulimia, a special questionnaire about the process of eating is used. This technique was developed by Canadian specialists. It is important to note that to confirm the diagnosis of bulimic neurosis, it is necessary to prove the presence of bulimic attacks at least twice within seven days, over several months.
It is possible that the first specialist should be a therapist who will issue a referral to specialized specialists: a psychologist, an endocrinologist and a nutritionist.
It is not difficult for a specialist to diagnose “bulimic neurosis”. Since the picture with food is typical, and the patient’s reasoning confirms the reluctance to eat a lot, the doctor has no choice but to suspect a pathological process controlled at the neurological level.
It is quite difficult for the patient to cope with such a situation. Additional influence is required at the psychogenic level.
In such cases, the physician faces several tasks:
Clinical laboratory blood tests, electrocardiography, fibrogastroscopy of the stomach and duodenum are used for diagnosis. It is necessary to exclude toxic poisoning, infectious diseases, and digestive disorders according to other schemes.
If no other organismic pathology is identified, such a patient is the object of the psychiatrist’s work.
Treatment methods
Since the causes of the development of bulimic neurosis are associated with malfunctions of the nervous system and mental disorders, the treatment of the disease should be carried out by specialists in the field of psychotherapy. Complex treatment of the disease involves the involvement of a neurologist and therapist in the process. In cases where there is a serious danger to the patient’s life, therapy for bulimia is carried out only in a hospital setting. Timely detection of symptoms of pathology at an early stage of development allows for outpatient therapy.
It is important to pay attention to the fact that if you have this disease, you are prohibited from using potent medications on your own. Uncontrolled use of many medications can significantly worsen the situation, since a weakened body exhibits increased sensitivity to the effects of drugs. That is why the treatment strategy and the list of medications used should be considered by a specialist on an individual basis.
Overeating and lack of satiety are the main characteristics of bulimia.
Many psychotherapists recommend that their patients visit a nutritionist. A specialist from this field will help not only to correctly compose a daily diet, but also to educate the patient about the processes occurring in the gastrointestinal tract. Also, thanks to this, the doctor can learn about the rules of safe food intake in the presence of the pathology in question. Based on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body, the doctor will be able to create a competent diet based on the required ratio of proteins, carbohydrates and fats in the diet.
The emphasis in drug treatment of bulimia is on drugs that have a calming effect on the nervous system. This category of medications includes appetite suppressants, sedatives, and antidepressants. Cognitive behavioral therapy plays an important role in complex treatment. This method is based on establishing the correct motivation associated with the process of eating.
In order to determine the strategy for this treatment method, it is very important to detect internal conflicts that provoke the appearance of the disease . It is possible to understand the nature of the disease by keeping daily records, in which the patient must describe all the emotions overwhelming him that arose before the feeling of hunger. It is also very important to indicate the situations in which hunger worsened, as well as the amount of food that was consumed to eliminate the attack.
It is very important to take full control of the nutrition process, for which monitoring the frequency of food intake is used. It should also be mentioned that the basis of psychotherapeutic treatment includes methods such as music therapy and color therapy. Music treatment involves daily listening to audio files that have a positive effect on the body. The sounds of living nature and classical music allow you to relax and forget about existing problems. Color therapy is based on the exclusion of brightly colored items from the patient’s wardrobe and interior. Many bright colors have a stimulating effect on the nervous system, which negatively affects the state of the psyche.
Bulimic neurosis syndrome is a mental illness caused by a disorder of the functioning of the central nervous system.
It is important to understand that therapy for neurotic disorders requires a long time and perseverance. Only the desire to get rid of the problem helps patients overcome the feeling of hunger. It is very important to promptly identify the presence of a problem, since at a certain stage of development, destructive processes become irreversible. Since the cause of the development of the disease “grows” from childhood, it is very important to approach the education process correctly. Only harmonious and trusting relationships between parents and children can reduce susceptibility to various mental disorders.
but on the other hand
After some time, when relaxation with a plate of food becomes a habit, other problems will arise:
- growing body weight;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- problems with the heart and blood vessels due to excess weight;
- psychological discomfort in situations where food cannot be taken (for example, at a lecture).
People around him notice that a person eats too much, and the problem becomes obvious to the person with bulimia himself. This creates new stress, but, unfortunately, the psyche already has an effective and reliable way to get rid of stress - going to the refrigerator. And now the brain needs to solve a new puzzle of how to cope with stress, when the way to get rid of stress is stress itself!
With bulimic neurosis, it is impossible to stick to a diet
This period is the most difficult for a person with bulimia. Numerous breakdowns, sworn promises to go on a diet, attempts to deceive the body by inducing vomiting, remorse for what they had done and a complete feeling of helplessness. This is precisely the range of emotions that a patient with bulimia feels, and telling him about proper nutrition, using radical methods with a locked refrigerator, or criticizing his appearance only means worsening the situation.
Symptoms
The main symptom is considered to be a pathological craving for food without reference to external factors that stimulate excellent appetite in ordinary people (PMS, great physical activity, prolonged exposure to the cold).
The patient absorbs food in abnormally large quantities; he does not care what he eats or what the food he eats tastes like.
In addition to brutal appetite , bulimia is characterized by :
- Passion for methods that reduce the digestibility of what you eat.
Increased interest in diets against the background of normal or even low weight, vomiting immediately after the onset of insight and awareness of what happened, taking laxatives. - Attacks of shopping addiction in grocery stores immediately after experiencing stress.
- Periodic forays into fast food outlets for record periods of time.
- Systematic painful reactions to weight gain, leading to short periods of strict diets and subsequent obligatory breakdowns in the form of “attacks” on the refrigerator.
Indirect signs:
- change in diet;
- unexplained “melting” of prepared food;
- frequent visits to the bathroom;
- swelling of the glands behind the ear;
- wounds on the mucous membrane due to frequent contact with gastric juice.
Types of illness
The classification of bulimia is carried out taking into account the circumstances that helped develop the disease.
- Hereditary. Due to the repetition of the parental attitude, there is much more than is required to replenish the energy expended. In some cases, this occurs due to the body’s desire to obtain the necessary substances, of which there are very few in the “fuel” provided to it. The more useless the food, the larger volumes of food the stomach requires in order to extract from them at least the crumbs of useful microelements and vitamins. Sometimes the “uselessness” of food results from an endocrine or other disease that interferes with the normal absorption of food.
- Depressive. A decadent mood can contribute to the development of pathological appetite, be its consequence, or “coexist peacefully” with the problem.
- Transistor nervous. It develops in suggestible people, more often than not girls, who have learned from their friends about an “effective” way to eat as much as you want and not gain weight.
- Emotional. With a heightened perception of external stimuli and prolonged stress, a person cannot achieve relative calm until he empties the stomach at least partially by vomiting.
- Artificial.
Quickly becomes factual. A common occurrence for patients professionally engaged in activities that have strict weight requirements.
According to their preferences for ways to free themselves from food, bulimics are divided into:
- formed due to addiction to artificially induced vomiting after each meal;
- causing dependence on laxatives, with the help of which the patient tried to prevent the body from absorbing what he had eaten;
- which provoked a pathological passion for physical activity, which helps speed up metabolism and burn extra calories.
Diagnosis of bulimia
Since this disease does not have exact symptoms, only an experienced specialist can determine it. Initially, all patient complaints are taken into account. Next, the person is prescribed tests to rule out diseases with similar symptoms:
- ECG of the heart;
- General blood analysis;
- General urine analysis;
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy of the stomach.
After the doctor is absolutely convinced that the person has no other diseases, he is referred to a psychologist who, using certain tests, determines the presence of bulimia and its stage.
In this case, tests are not completely ruled out, since changes in the functioning of systems can be determined by a doctor even in case of bulimia. After a complete examination, the patient is prescribed treatment. Its duration ranges from 6 months to a year, depending on the person’s personal mood. There are also situations when recovery occurs very quickly; in this case, drug treatment can be partially stopped, depending on the physical condition of the person, but you still need to be observed by a psychotherapist for some more time.
How do you know if you have bulimia?
Doctors identify several manifestations of the disease described:
- attacks of uncontrollable appetite;
- the ability to absorb large portions of food at one time;
- lack of control over food intake;
- negative attitude towards oneself (after an attack);
- a great desire to independently cleanse the stomach and intestines after a seizure;
- constant and significant mood swings – emotional lability.
In order to determine the presence of symptoms of bulimia and carry out treatment according to a clearly established plan, the doctor needs to talk with the patient. Of course, there are currently many different tests that will help determine this disease. But the most basic thing in medical practice is the Canadian questionnaire of the patient’s attitude towards food, which can help the doctor identify bulimic neurosis.
True, doctors often do without this diagnosis, so you need to be extremely careful in choosing a specialist for the patient. As a rule, a psychotherapist deals with bulimic neurosis, because in the early stages it manifests itself only as a change in mental state.
In most cases, the doctor will need to ask his patient a number of essential questions on the basis of which he can prescribe medications. The doctor should find out:
- During what period of time did the patient begin to consume more food than usual?
- Was he limited to the usual portions or did he immediately have to increase them?
- How much food does the patient eat per day?
- Do any of your close relatives suffer from obesity?
- Does the person self-medicate by inducing vomiting and cleansing the intestines with a laxative.
If the disease has already begun to progress, then the patient needs to undergo examinations to exclude other diseases. To do this, he needs to conduct ECG studies, fibrogastroduodenoscopy, general and chemical blood tests. And only after ruling out the presence of gastrointestinal diseases, the patient is referred to a psychiatrist.
The patient can be treated on an outpatient basis or while in the hospital. Typically, patients with a severe form of the disease are admitted to the hospital. Based on statistics, the diagnosis of “bulimia” is made if attacks of the disease occur at least twice within three months.
In the initial stages of bulimic neurosis, the main emphasis is on psychotherapy. The specialist tries to identify traumatic facts from the patient’s life that led to the development of the disease and helps to find clues that will make it possible to reconsider his pathological beliefs. And in severe cases, when the patient’s physical health begins to suffer, he is prescribed medication.
Medications for bulimic neurosis are usually prescribed to restore the processes of inhibition and excitation in the human brain. The patient is also prescribed medications to improve the emotional background, sedatives, and appetite suppressants. With proper treatment, this pathology is reversible and amenable to therapeutic effects.
I have long heard about this remedy, I have long known that it is drunk not only to combat depression, but also to lose weight. I condemn this method, because after all, it is an antidepressant, and not some kind of MCC.
She herself had to contact him because of bulimia. I confess, I did not see a doctor, I diagnosed myself and prescribed medicine.
But I know for sure that this is bulimia - for a year now I have been inducing vomiting after acts of gluttony. If earlier I could still somehow control it, then in February-March I could no longer cope with it, I did it almost every other day.
There was an unrealistic craving for food. Therefore, after thinking it over carefully, I decided to try Fluoxetine.
I repeat, this was a deliberate decision.
Having bought fluoxetine without a prescription (lucky), I decided to take 60 mg, as stated in the instructions. 60 mg for the treatment of bulimic neurosis is what I need. I started with three tablets a day at once, although it seems to be recommended to gradually increase the dose. Apparently because of this, for the first three or four days I was bothered by severe nausea, and my body felt somehow different.
The capsules are standard size and easily pass down the throat.
My appetite has really decreased, but not only because of nausea. Due to chronic gastritis, I almost always experience nausea, so I managed to overeat with it, it didn’t really bother me.
But with fluoxetine, the psychological need disappeared, I experienced normal hunger. I started eating when I really wanted to.
If before I bought several packs of cookies and ate them a day, then after taking the drug, I began to eat much less. I can eat a few cookies and put the opened packet back in the cupboard without feeling the need to completely destroy it.
The first signs that help you suspect that you have the initial stage of bulimia:
- Any changes in mood cause wild hunger.
- I want to eat away from everyone, whatever I can get my teeth into.
- Previously existing food preferences have evaporated, and even what previously caused stomach cramps is eaten.
- The idea of using laxatives or vomiting after a large meal seems like a delicious opportunity to eat whatever you want in whatever quantity you want.
If a person does not have any somatic pathologies, and the amount of food he absorbs is many times higher than the norm for his age, weight and lifestyle, it is logical to suspect neurosis.
Before talking about bulimia, you need to understand what neurosis is. Neurosis is a functional (that is, reversible) disorder of the nervous system when a person develops an internal conflict inside. “I don’t want, but I have to,” or “I can’t, but I want” - such situations happen in the lives of each of us all the time, but people prone to neurosis cannot resolve the internal conflict with the arguments of reason or a compromise with themselves.
Thus, a bulimic attack is a kind of “bridge” that allows you to bypass the internal problem. For example, the girl had not yet had time to reflect, when the thought arose in her head that her lover probably did not love her, that her new dress was making her look fat, and that her colleague would receive the desired promotion at work, when her brain helpfully gave her a false feeling of hunger. Now the girl doesn’t need to solve problems with her lover, dress and career ambitions right now, the main goal is to eat well!
You can “drown out” any troubles and stress only by eating a hearty meal.
After this hypothetical girl has a snack, she will experience a pleasant and blissful feeling - the parasympathetic part of the autonomic nervous system, which is responsible for peace, relaxation and digestion of food, turns on.
Worth seeing: Situation Neurosis
Thus, the pattern can be considered fixed. Eating brings pleasure, “turns off” all negative thoughts about problems, and relaxes.
Worth seeing: Depressive neurosis
Symptoms of bulimia
You can notice the presence of the disease in a person by constant eating, which is followed by bouts of remorse and feelings of guilt.
Symptoms:
- Frequent meals in large quantities;
- Frequent feeling of hunger that cannot be satisfied with the usual amount of food;
- Poor chewing of food, haste in eating;
- Vomiting after eating, caused artificially;
- Irritable or even depressed state, frequent mood swings;
- Anxiety, taking medications that cause vomiting and intestinal upset;
- Disturbances in the digestive system, poor digestion;
- Disease of the esophagus and pharynx due to frequent vomiting;
- Diseases of the teeth and gums as a result of the frequent presence of vomit and gastric juice in the oral cavity;
- Changes in weight, ranging from thin to obese;
- General malaise, drowsiness, fatigue.
Many people with bulimic neurosis refuse to admit it, citing fatigue, good or bad appetite, or fad diets. But in the most severe forms, the disease can lead to more global problems, such as kidney failure, disturbances in the functioning of the heart, changes in the balance of vitamins and minerals, due to the lack of time to absorb them from food. Therefore, if a person exhibits two or more symptoms of the disease, this is a reason to consult a doctor.
Factors that can provoke its development
An overly frequent and persistent “I want to eat” signal entering the brain indicates a person’s predisposition to an eating disorder. The following factors contribute to the development of the disorder:
- Belonging to the female gender. Most often, bulimia is diagnosed in girls and women.
- Age. Typically, the pathology manifests itself in girls 17-25 years old.
- Biology. If the patient's immediate family (siblings, parents, or children) are prone to eating disorders, the disorder may eventually develop in that person as well. Scientists do not deny the possibility of a genetic predisposition to bulimia. In addition, serotonin deficiency in the brain may play a significant role. Excess weight in a child or adolescent increases the risk of pathology in the future.
- Psychological and emotional problems. Mental instability, including anxiety disorders and low self-esteem, contributes to an increase in the normal “want to eat” signal. A person begins to overeat due to stress, a bad opinion of himself, having food in the refrigerator, suffering from diets, and simply out of boredom. In some cases, the situation is aggravated by psychological trauma and severe environmental pollution.
- Pressure from the media. On television and Internet channels, in fashion magazines, people constantly see many thin models and actors. The abundance of ideal figures in show business seems to equate slimness with success and popularity. However, it is still unknown whether social values are reflected in the media or, on the contrary, it is the media that guide public opinion.
- Work-related stress. Uncontrolled appetite is very common among professional athletes, actors, dancers and models. Coaches and family members often inadvertently increase the risk of developing neurosis in their athletes by encouraging young athletes to lose weight, maintain a low weight, and reduce food portions in order to improve the quality of their exercises.
An illness that forces one to seek solace by consuming incredible amounts of food is driven both by unresolved conflict situations from childhood and by problems that people have to face in everyday life.
Typical provocateurs:
- Strict upbringing that makes it difficult to relax even at home.
- Unhealthy eating habits, frolicking, for example, due to a hungry childhood or the experience instilled by adults of relieving stress with food.
- Specific working conditions that require you to maintain a certain physical shape at any cost.
Gymnasts, ballerinas, and fashion models are forced every day to resist gastronomic temptations for the sake of a slim figure. - Life under the radar of cameras: increased media attention and the inability to keep most of their personal lives secret from the public, along with problems at work and in their environment, have more than once caused celebrities to fall into the clutches of the disease.
Symptoms and characteristic manifestations of the disease
The first and most important sign is the appearance of attacks of appetite that a person cannot control. A person suffering from this disease can eat so much in one sitting that it surprises others. However, those who have bulimic neurosis cannot
control food intake using will.
After an attack, the patient experiences self-dislike, reproaches for incontinence and experiences other negative emotions. There is a desire to cleanse your body of food by vomiting or laxative, which causes a new attack.
Mood swings and instability in emotions are also common in people with bulimia. In such a situation, a person begins to “withdraw into himself,” becomes lethargic, and moves away from loved ones and friends.
What is bulimic neurosis? This is a condition in which at certain moments a person is so hungry that he cannot resist. At the same time, food consumption goes beyond all reasonable limits: it is eaten in quantities much greater than the physiological need. It happens that such attacks occur at night or last indefinitely while the signal from the brain operates.
At the end of it, the person seems to look at himself from the outside and regret what happened. The next stage in the manifestation of pathology is taking measures to prevent the digestion of the food eaten. It looks like artificially induced vomiting, use of laxatives and diuretics.
It is noteworthy that this stage lasts exactly until the onset of the next attack, the frequency of which can be quite impressive (several times a day).
The first and most important sign is the appearance of attacks of appetite that a person cannot control. A person suffering from this disease can eat so much in one sitting that it surprises others. However, those who have bulimic neurosis cannot control their food intake using their will.
What does this lead to?
Without treatment of the disease, the following problems arise:
- depression;
- changes in the psyche;
- problems with vision, hair, skin, nails;
- difficult to treat diseases;
- anorexia;
- fatality.
How dangerous is bulimia if it is not cured?
- A disorder of the nervous system and the development of preconditions that push towards addiction to alcohol and drugs.
- The digestive tract may lose the ability to absorb food so much that even medical professional correction will not help it and the person will die.
Consequences for the body:
- From the psyche: neurosis develops into depression, which increases the pathological desire for food.
- Metabolic processes are deformed and endocrine diseases develop.
- The body may forget how to benefit from food and the person dies of hunger.
A detailed description of the unpleasant consequences of bulimia:
- Decreased general tone, decreased memory.
- Deterioration of teeth due to changes in color and strength of enamel under the influence of gastric juice.
- Red eyes due to systematic sessions of artificially induced vomiting, leading to rebooting of the blood vessels in the eyeballs.
- Parchment skin, peeling nails, hair loss.
- Convulsions, heart problems due to potassium deficiency, unstable water-salt balance.
- Hormonal cycle disturbances and subsequent “joys” in the form of early menopause, diseases due to problems with the endocrine system.
You can see this in the photos of some show business stars before and after the development of the disease.
Is it possible to die from bulimia? It may be hard for you to believe, but the disease already has its own reclaimed cemetery with victims.
Most often, these are girls and women - “bulimics”, since they are the ones who are more inclined to try diets on themselves and find ways to eat and not gain weight without much effort.
In advanced stages, bulimia can lead to various kinds of neurasthenia, loss of interest in life, and a disorder in a person’s social status. Mental disorders requiring hospital treatment and even death cannot be ruled out.
Under the influence of disrupted neurological impulse transmission chains, important vital systems of the body often suffer: cardiovascular, digestive. Acute heart failure and inflammation of internal organs are not excluded.
Causes of the disease
Overeating neurosis is a very difficult disease for a person, since he realizes that this can lead to more serious consequences, but cannot stop, and tries in every possible way to drown out the symptoms of constant hunger. The causes of bulimia cannot be clearly stated. Most often, this is a combination of several factors coming together:
- Disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system: severe nervous shock, resentment or disappointment, stress;
- The presence of a number of complexes in a person regarding a person’s appearance, especially weight;
- Mental abnormalities, loss of reality;
- Disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system, hormonal imbalances;
- Great mental and physical stress;
- Disturbances in the digestive system;
- Infections and long-term illnesses;
- Hereditary predisposition.
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy, or psychological counseling, is a discussion of the disorder and related problems with a professional therapist. According to research, the following types of psychological counseling are characterized by proven effectiveness:
- cognitive behavioral therapy, which allows the patient to independently identify unhealthy, negative beliefs and behavior patterns and replace them with more favorable opinions and habits;
- family therapy aimed at targeted parental intervention in the unhealthy eating behavior of a teenage child;
- Interpersonal psychotherapy that analyzes difficulties in close relationships and improves communication and problem-solving skills.
Course of therapy
Somatic pathologies
Before talking about bulimia caused by neurosis, you need to understand that an uncontrollable feeling of hunger can also occur with serious physical illnesses. For example, hyperfunction of the thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism) forces a person to absorb food in huge portions. Fortunately, a large amount of hormones produced by the thyroid gland “stimulates” absolutely all systems of the body, so the resulting calories are not deposited on the sides, but are safely burned.
Another common reason for a strong desire to eat a lot of calories is the use of hormones and glucocorticosteroids. Typically, a strong appetite during therapy is accompanied by a decreased metabolism, so a person recovers easily and quickly. Doctors warn their patients before starting hormone therapy that they will have to endure the feeling of hunger, relying on their own will - there are no other recipes.
Stages
- Initial. Attacks on the refrigerator are relatively rare, but are already marked by blackouts to the point where the stomach is no longer physically able to contain food. Duration up to six months.
- Average. After bouts of overeating, the patient increasingly uses forced methods to remove the consequences of his addiction to food. It can last for several years if the body is initially strong enough and tolerates the consequences of such behavior well.
- Heavy.
The body is exhausted by violent methods of removing food and the stomach is unable to properly hold what has been received; the patient suffers from severe attacks of nausea even after small snacks, indigestion, constipation, problems with the heart and nervous system. In some cases, people begin to resort to alcohol and drugs, trying to drown out unpleasant sensations in the body and trying to regain the ability to eat without subsequent rejection of food by the stomach. Without medication and professional psychological support, death is possible.
Signs of Bulimia Nervosa
Bulimia nervosa is an eating disorder in which attacks of uncontrollable hunger occur, there is no feeling of fullness, and a person loses control while eating.
This disease is accompanied by fluctuations in body weight.
Overeating is often replaced by attempts to rid your body of excess food. The patient begins to exhaust himself with hunger, provokes vomiting, drinks laxatives, and exercises vigorously.
Not all people suffering from bulimia are overweight; many maintain a slim figure, so it is difficult for others to guess that the person has serious problems. Most bulimics hide the presence of the disease.
Most often, young women suffer from the pathology, because ideal weight is extremely important for them. Even with a large amount of food eaten, the patient experiences a strong feeling of hunger. The disease is very painful because a person loses control over the amount of food he eats, and his personality suffers serious pathological changes.
Bulimia has two variants. Primary – the patient constantly feels hungry. The desire to eat food is no longer controlled, resulting in a person eating, eating and eating.
Bulimia resulting from anorexia. With anorexia, bouts of overeating also occur. The patient loses control of himself, eats a lot, and then tries to induce vomiting in order to cleanse himself of the hated food.
The stage of the disorder can be determined by the number of emetic procedures that the patient organizes for cleansing:
- If this happens 1-3 times a month, we are talking about the initial stage of the disease, which, as a rule, lasts no more than three years.
- If a person emptys his stomach 1-7 times in one day, we are talking about advanced chronic bulimia, which usually has a history of 5-7 years. However, this classification is considered conditional and may have deviations in any direction.
The disease can occur in people with nervous, mental disorders or problems with the endocrine system. The most common cause of bulimia is a feeling of uselessness, severe mental shock, emptiness, loneliness, loss of a loved one, separation.
In all these cases, the patient feels deeply unhappy, so he begins to “eat up” the melancholy, brightening up the negative moments with pleasant taste sensations.
When food brings another portion of positivity, a person begins to repent, as he realizes how harmful such behavior is for the body and for the figure in particular. The bulimic promises himself and his loved ones that this will not happen again, but he cannot restrain himself for long and everything happens again.
The understanding that he has no willpower provokes self-contempt and another attack of gluttony. A vicious circle from which there is no visible way out, and those around only aggravate the situation because they tell the patient that he is simply spineless.
Recognizing the disease is very difficult, since the patient often hides his problem from himself and others.
You can suspect bulimia nervosa based on the following symptoms:
- unconscious (compulsive) overeating that has become a habit;
- fluctuations in body weight;
- frequent use of laxatives and diuretics, inducing vomiting;
- eating alone at night;
- frequent trips to the toilet;
- swelling of the submandibular glands;
- destruction or discoloration of tooth enamel;
- stomach colic;
- bruising in the eyes;
- unhealthy skin color, dry hair and brittle nails;
- voluntary seclusion;
- depression;
- pathological concern about one's own weight;
- constant feelings of guilt and shame;
- inflammation of the esophagus;
- low self-esteem.
The main difficulty in treating the disease is that the person refuses to acknowledge the problem. Therefore, diagnosis and treatment of bulimia nervosa in the early stages is very difficult and sometimes impossible.
Many patients believe that this disorder does not require medical intervention; it is enough to just pull yourself together and show willpower. However, bulimia is a disease, which means it should be treated by specialists.
This can be monotherapy, that is, the use of one method, or complex treatment, in which two or even all three areas are used.
But before treatment begins, the patient must be carefully examined and the factors that provoked the pathology identified. In turn, the causes of the disease are divided into two types: physiological and psychological.
Physiological causes are hormonal disorders or organic damage to the parts of the cerebral cortex that are responsible for receiving satiety signals. However, bulimia very rarely develops this way.
The main causes of the disease should be sought in the psycho-emotional state of the patient. It can be:
- childhood psychological trauma;
- consequences of improper upbringing;
- serious experiences;
- an inferiority complex that was instilled in childhood by peers or parents.
I see the goal...
A mild form of the disorder can be cured by the work of a good psychologist. Chronic bulimia must be treated with medication. But the best results can be achieved by combining all three techniques.
Medicines for the treatment of bulimia nervosa are antidepressants that have a calming effect on the patient and reduce the number of attacks.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BDQmBt1sqGE
Psychotherapeutic treatment consists of a course of sessions conducted by a professional psychologist and auto-training. Such therapy is necessary to change the patient’s attitude towards himself and to increase self-esteem. Without this, it is impossible to defeat the disease.
The course of psychotherapy also involves independent work on oneself, which includes:
- recognition of the problem;
- self-confidence;
- reducing demands on oneself;
- awareness of the real needs of your body and following them;
- ability to withstand stress;
- rejection of the cult of food;
- active entertaining leisure time.
After completing this course, a person’s view of food and its place in life will radically change.
No way without diet
The principles of dietary nutrition are based on:
- on compliance with the diet;
- on a gradual reduction in the volume of portions;
- replacing fatty and high-calorie foods with vegetables and fruits;
- on eradicating the habit of “eating” stress.
Help in defeating bulimia will be provided by decoctions and infusions prepared at home. These drugs should suppress appetite, calm the nervous system and correct the functioning of the digestive tract.
The first place that suffers from bulimia nervosa is the stomach. Frequent vomiting and constant tension of the organ provoke a number of chronic gastroenterological diseases. The following pathologies can result:
- indigestion;
- gastritis;
- mechanical damage to the mucosa;
- stomach or intestinal ulcer;
- esophageal carcinoma;
- stomach rupture;
- internal bleeding, which can cause the patient's death.
The main symptom of bulimia nervosa is alternating uncontrollable attacks during which the patient eats an unlimited amount of food. You can understand what it is when a person, after a huge amount of food, tries to lose weight (goes on yet another strict diet, does grueling workouts) or simply empties the stomach of the food he has eaten, provoking vomiting, or taking laxatives.
The symptoms of kinorexia depend on the type of disease. There are three varieties:
- insatiable hunger that does not go away while eating and lasts until the bulimic attack ends;
- the need for constant, continuous food consumption;
- bouts of binge eating at night.
After all, a person is gnawing at a feeling of guilt, an awareness of his own inability to fight the disease, which can only aggravate the picture: depression begins, addiction to alcohol, drug addiction arises.
Particularly dangerous is the habit of alternating bouts of eating food with getting rid of it, causing vomiting. Constant exposure of the food mass, already mixed with gastric juice, to the esophagus and oral cavity leads to tissue damage by acid, inflammation of the esophagus and gums (gingivitis) occurs, and tooth enamel becomes thinner. If a person takes laxatives, the body becomes dehydrated and constipation occurs.
Diagnostics
Bulimic neurosis is difficult to diagnose because there is no objective clinical picture. To find out the true cause of the disorders, it is necessary to conduct a differential diagnosis. This will help exclude pathologies from the kidneys, liver, pancreas and gall bladder, and gastrointestinal tract. The following examination methods are used:
- blood test (general, biochemical);
- electrocardiogram;
- fibrogastroscopy.
If no pathologies are detected, the patient is referred to a psychologist for testing. The basis for the diagnosis of bulimic neurosis is the presence of attacks of uncontrolled food intake every three days for three months.
What is the nature of the symptom
Unfortunately, bulimic neurosis often turns into an uncontrollable process. It is of the nature of a neurogenic disease. The body develops special regulatory mechanisms that cause pathological foci of excitation in the brain.
What are the risk factors for developing bulimia? These include:
- hereditary factor;
- frequent alcohol and drug intoxication;
- psycho-emotional experiences and stress;
- uncontrolled use of a number of medications;
- hormonal problems;
- mental disorders.
Forecast and prevention of the disease
People starting treatment need to eat more foods rich in vitamins and minerals. As a result of constant cleansing of the body, their percentage in the body is reduced. The lack of minerals and trace elements can lead to more severe diseases, which can only be eliminated with the help of medications.
The patient is recommended to exercise. It will be better if the loads are not very heavy and take place on positive emotions.
This could be swimming, cycling, fitness or just walking. 30 minutes a day will be enough.
With proper and regular treatment, a person’s recovery is almost one hundred percent. But, nevertheless, the patient is recommended to remain under the supervision of a psychotherapist for some time to prevent recurrence of the disease.
Treatment
Complex treatment of bulimia nervosa is based on psychotherapy sessions, and medications are used to consolidate the results. The psychotherapist, in the process of communicating with the patient, must restore the correct motivation for proper food consumption: eat exactly as much as is needed to maintain vital functions.
At this stage of treatment, the participation of a nutritionist is necessary, who will tell you how to correctly create a diet, which foods to exclude (spicy, salty, stimulating the appetite). It is recommended to keep a diary in which you note the hours you eat, the amount of food, and your feelings. This helps you focus on solving the problem. If necessary, medications are prescribed to suppress appetite (anorectics).
Important! It is necessary to distinguish between anorectics and dietary supplements! Independent use of the former is unacceptable, since they have an impressive list of contraindications and side effects.
In drug therapy, plant-based sedatives (Valerian, Motherwort), Glycised (contains the amino acid glycine), and antidepressants (Zoloft, Neurofulol) are used. These drugs cannot be combined with alcohol. In severe cases (major depression, alcoholism), the patient is sent to a hospital, where treatment is carried out under the strict supervision of a narcologist and psychiatrist.
Physiotherapeutic procedures have a strengthening and healing effect:
- massage (especially recommended for overweight);
- gymnastics;
- hardening and water procedures (water aerobics);
- long walks in the fresh air.
Additionally, alternative medicine methods (acupuncture, yoga exercises, Chinese qigong breathing exercises) may be prescribed.