Neuralgia is a lesion of peripheral nerves, accompanied by intense pain in the area of innervation of a particular nerve. If symptoms appear, you should seek medical help immediately. The prognosis for early treatment is favorable. Neuralgia refers to severe shooting pain that occurs due to a damaged or irritated nerve. Neuralgia can affect any part of the body, causing mild to severe pain. Certain medications and surgical procedures can effectively treat neuralgia.
Severe neuralgia can affect a person's ability to perform everyday tasks and can affect their quality of life.
Neuralgia has many possible causes, including:
- infections such as shingles, Lyme disease, or HIV
- pressure on bone nerves, blood vessels or tumors
- other medical conditions such as kidney disease or diabetes
- aging
Definition of neuralgia
This disease is considered quite dangerous because it damages the nerve endings. This disease can damage the nerve in absolutely any part of the body, even in canals and narrow openings.
The patient will periodically suffer from sharp, burning pain in the area of innervation of the affected nerve. Loss of sensation or deterioration in motor activity is usually not observed.
This disease is classified into several forms and subtypes; doctors distinguish between neuralgia of the cranial, femoral and spinal nerves.
Herpetic
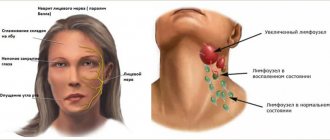
Nerve location diagram Herpes is a disease that is very difficult to treat. It may have complications that manifest themselves in the form of herpetic neuralgia. As a rule, this pathology affects people with weak immunity and elderly patients. The patient's ganglia of the dorsal roots of the spinal cord and peripheral nerve endings become inflamed. The main symptom of herpetic neuralgia is pain, which can cause discomfort to the patient for 5-6 months. For some it is sharp and burning, for others it is dull and pressing.
Causes of neuralgia
Before starting treatment for the disease, it is necessary to find out what triggered its appearance, otherwise after some time the disease may return again.
The main causes of neuralgia:
- excessive physical activity, which leads to injury to the nerve trunk;
- damage to the body by toxins (with long-term use of certain medications or alcohol abuse);
- hypothermia. Disturbs blood flow and leads to inflammation of the nerves;
- the presence of diseases of the musculoskeletal system or hip joint (spinal injuries, congenital bone anomalies);
- diabetes;
- swelling of soft tissues located near the nerve;
- aneurysms;
- peripheral vascular diseases leading to impaired blood flow.
It is almost impossible to identify the cause of the pathology on your own; for this you will have to undergo a special medical examination
Forms of neuralgia
This disease comes in only two forms:
- Primary. Pain response of a specific nerve, unrelated to any specific stimuli. In most cases, it is never possible to identify its original source (discomfort can be caused by stress, the release of adrenaline into the blood, or the presence of certain diseases). This pathology can be cured with an integrated approach; treatment should be aimed at suppressing painful sensations. The most common type is triangular neuralgia;
- Secondary. It is provoked by third-party pathologies, for example, aneurysms, inflammation or tumors. Treatment of this form is more difficult; first of all, the patient will need to get rid of the original source, and only then from the painful sensations. Secondary neuralgia is very dangerous, since in about half of cases it is a symptom of more serious diseases.
Classification
Systematization of the disease according to etiology is of practical importance. This principle underlies the determination of the most appropriate treatment tactics (conservative or surgical). According to the etiological aspect, trigeminal neuralgia is divided into two main forms:
- Idiopathic (primary). Caused by vascular compression of the trigeminal root, most often in the area of the brain stem. Due to the difficulties in diagnosing pathological vessel-nerve relationships, idiopathic neuralgia is assumed after excluding other causes of trigeminal pain syndrome.
- Secondary (symptomatic). It becomes the result of neoplasms, infections, demyelinating pathology, and bone changes. Diagnosed using neuroimaging and cranial tomography.
Symptoms of neuralgia in adults
The signs of this disease may differ slightly from each other depending on what type of pathology the person is faced with. But the main symptom of neuralgia is cutting pain, which can cause a burning sensation or lumbago.
Painful sensations usually affect not only the nerve itself, but also spread throughout the entire area that it can affect.
If a certain nerve is damaged, a person may experience pain:
- Teeth, left or right side of the face, eyes. Painful sensations in these areas appear with ternary neuralgia. The patient may also experience involuntary salivation and increased tearing of the eyes. If the injured nerve is located close to the surface of the skin, touching this area will provoke new attacks of pain;
- Back of the neck and back of the head. Such disorders occur with occipital neuralgia; in most cases, patients complain of shooting pain;
- Discomfort and tingling in the chest , increasing with inhalation and movement, indicate interfemoral neuralgia;
- Back leg. Pain in this area is a sign of sciatic neuralgia. Because it is very large and has many branches, the burning sensation can be very strong and the pain will spread to most of the leg.
Another sure sign of neuralgia is increased sweating and redness of the epidermis in the area of the affected nerve.
Take note! If any of these symptoms persist for a long time, and the pain does not go away even after taking anabolic steroids, do not delay a visit to the doctor
Neuralgia during pregnancy
This problem is very common and does not affect about 70% of women carrying a child. The main characteristic of this pathology is compression or irritation of the intercostal nerve.
The disease usually develops due to weakening of the protective properties of the body and accelerated growth of the uterus and fetus, which, when expanded, can put pressure on the ribs. Pain in this case most often occurs in the chest area, in most cases it is aching or pulling.
Signs of anemia during pregnancy:
- painful sensations will mainly occur after physical exertion, a burning sensation may radiate to the back, lower back or shoulder blades;
- a woman will periodically suffer from muscle cramps, and sometimes they can be very painful;
- the appearance of anemia;
- increased sweating;
- change in skin tone in the affected area. The epidermis may turn red or become almost porcelain.
If such symptoms occur, a pregnant woman should make an appointment with a specialist as soon as possible, who will rule out the possibility of heart problems and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Take note! Many women confuse neuralgia with heart disease, since both of these diseases manifest themselves in a similar way. That is why, if you suspect any of them, you need to sign up for a diagnosis. Self-medication is strictly contraindicated
Pathogenesis
The above etiofactors potentiate morphological changes in the sheath of the trigeminal nerve. Studies have shown that structural changes in the myelin sheath and axial cylinders develop 3-6 months after the onset of the disease. Local microstructural disorders provoke the formation of a peripheral generator of pathologically enhanced excitation.
Excessive impulses, constantly coming from the periphery, cause the formation of a central focus of hyperexcitation. There are several theories that explain the connection between local demyelination and the occurrence of a focus of hyperexcitation. Some authors point to the possibility of the emergence of transverse interaxonal impulse transmission.
Which doctor should I contact?
It is not possible to get rid of this disease on your own; treatment should only be carried out under the supervision of an experienced therapist or neurologist. At the first visit, the doctor will carefully examine the patient and listen to all his complaints.
To reveal the full picture, a patient survey is also conducted, which allows you to get answers to the following questions:
- How long ago did the pain begin?
- Have similar problems been observed in the past?
- Has the patient been hypothermic recently?
- Does the patient have problems with the spine?
- Is the patient taking any medications for a long time?
This survey will help the physician identify what exactly caused the development of the pathology, and this data will also be used to choose the most appropriate treatment method.
General
Nerve branches of the cranial area Symptoms and treatment of neuralgia are interrelated. If you notice the first signs of the development of such a disease, you should immediately contact a neurologist. Diagnosis of pathology begins with an initial examination of the patient and examination of his complaints. In order for the diagnosis to be as accurate as possible and the treatment to be effective, you need to undergo additional examination. Most often, doctors prescribe instrumental electroneurography, especially if the cause of neuralgia is injury. In addition, magnetic resonance imaging may be needed to detect intervertebral hernia, tumor, protrusion and other diseases.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of this disease is always carried out in several stages: anamnesis analysis and visual examination.
In addition, the patient will need to undergo some tests and undergo instrumental research methods.
More specifically, here's what diagnostics includes:
- Neuralgic examination and testing the sensitivity of the patient’s nerves;
- Electroneuromyography. Using it, you can determine how quickly the pulse travels along the nerve fibers, and signs of nerve injury are revealed;
- Angiography of cerebral vessels. Shows the presence of compression of the nerve by dilated vessels;
- Nerve biopsy. Using a very thin needle, a piece of the nerve is taken from the patient and examined under a microscope. This study is carried out only in extreme cases.
If there are difficulties in making a diagnosis, the patient may also be referred to a neurosurgeon.
Blockades for pain relief
For this form of neuralgia, alcohol blockades are used. The purpose of the method is to create a barrier between the affected nerve and the central nervous system, thus stopping the transmission of pain impulses, which helps relieve pain.
The blockade is carried out in a hospital setting and only by an experienced doctor. The injection is given at a point located directly next to the affected area of the nerve. This method allows you to instantly relieve pain, but the duration of the injection is limited and does not exceed two days, after which the pain syndrome returns.
If the procedure is performed incorrectly, the following complications are possible:
- bleeding;
- hematoma formation;
- nerve damage.
To relieve pain, a layer-by-layer injection with novocaine or lidocaine is given, and alcohol is used as a guide.
Treatment of neuralgia
Treatment of neuralgia should be comprehensive; doctors in most cases prescribe the following medications to patients:
- non-steroidal analgesics;
- painkillers;
- anticonvulsants;
- vitamins A, B, C and E.
In addition, warm compresses applied to the affected area will help speed up the treatment process. As for physiotherapy, it includes electrophoresis and ultra-high-frequency currents.
Advice from traditional healers
Treating neuralgia with recipes that people have used in the past has yielded positive results. An alcohol tincture of wild rosemary shoots helps relieve an attack. Rub the sore spot at night, using the product until the discomfort completely disappears.
Treatment of neuralgia with the leaves of indoor geranium (pelargonium) can reduce painful sensations. It is necessary to apply the raw material to an area of the skin where pain can be very severe.
During therapy, you can take medications based on medicinal plants that have anti-inflammatory and restorative effects. It is useful to drink a decoction of the herb St. John's wort, black elderberry flowers and birch buds. Quick relief can come from consuming a mixture that contains the following plants:
- fireweed leaves;
- oregano herb;
- linden flowers.
Traditional healers know whether it is possible to reduce pain by rubbing the inflamed area with herbal alcohol tinctures. Therefore, preparations made from montana arnica flowers and eucalyptus leaves are very popular. After completing the procedure, the affected area must be covered with a warm woolen scarf.
Prevention
In order to reduce the likelihood of developing this disease, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle and monitor your diet.
Here are some tips doctors recommend you follow:
- It is necessary to exclude all “harmful” foods from the diet; it should be based on vegetables, fruits, fish and dairy products;
- you need to eat 5 times a day in small portions;
- to improve immunity, you can take a course of multivitamins twice a year;
- It is strongly recommended to follow a daily routine, go to bed and wake up at approximately the same time;
- At least three times a week you need to take walks in the fresh air and do exercises in the morning.
Any form of neuralgia is a serious test for a person. To protect yourself from possible complications, you should never self-medicate, because incorrectly selected medications can only worsen the situation.
Each patient must remember that only an experienced specialist can provide real assistance in the treatment of this pathology.