According to the observations of doctors, neuralgia of the back is one of the most insidious pathologies. It does not pose a direct threat to life and health, occurs frequently, and is usually treated at home or on an outpatient basis. Because of all this, patients often ignore the discomfort or try to cope with it on their own. Some people mistake the pain syndrome characteristic of the condition for signs of heart pathology and proceed to completely inappropriate treatment. Despite the absence of the need for hospital treatment, neuralgia is a dangerous disease in terms of complications and relapses. Most often, the disease affects the back, which significantly reduces the patient’s quality of life for a long period.
The disease is dangerous in terms of complications and relapses.
What is neuralgia
From a medical point of view, there is no such disease as “back neuralgia”. It is rather a syndrome that manifests itself as persistent pain as a result of a negative effect on the endings of the peripheral nervous system. The provocateur of pain is compression or irritation of the fiber, its deformation as a result of the influence of surrounding structures. At the site of a pinched nerve, inflammation of the tissues adjacent to it and their swelling are often detected.
In fact, signs of problems or increased risk factors can be noticed much earlier. If you take the necessary measures at this stage, the occurrence of attacks of pain can be prevented.
Possible consequences
Initially localized pain in one of the areas of the back quickly affects all its parts. Continuous and intensified attacks can greatly complicate a person’s quality of life:
- sleep is disturbed;
- performance decreases;
- stiffness of movements appears;
- muscle weakness is present.
Pain when inhaling prevents you from receiving the required amount of oxygen, which leads to hypoxia. The risk of inflammation in the intervertebral tissues increases, which can cause herpes, herpes zoster and other infectious diseases. Without treatment for neuralgia of the back, a person may develop neuritis, which can lead to motor impairment and paralysis.
Classification of the disease
Neuralgia of the back, like other forms of the disease, can be classified according to a number of characteristics. Firstly, the origin of the disease is primary (typical) and secondary (symptomatic). Primary neuralgia is rare and develops independently, not being a symptom of another pathology. It happens that doctors take months and years to treat typical neuralgia of the back, after which the source of the problem is discovered, and the condition begins to be called secondary. Symptomatic pathology is not considered a separate disease, but a syndrome against the background of a somatic or psycho-emotional disorder.
The disease occurs against the background of a psychoemotional disorder.
Depending on the type of course, spinal neuralgia can be acute or chronic. In the first option, the clinical picture develops suddenly, manifests itself clearly, and is characterized by sharp, burning, excruciating pain. Chronic disease does not cause such severe discomfort. It is often accompanied by constant aching sensations in the affected area of the nerve, which can become aggravated under the influence of external factors.
Based on the type of localization, back disease is informally divided into cervical, thoracic and lumbar forms of neuralgia. Symptoms of the disease most often occur as a result of damage to the roots of the vertebral nerves due to osteochondrosis, scoliosis, and intervertebral hernia. Cases of direct impact of surrounding tissues on the nerve are recorded much less frequently. Painful sensations can radiate to different parts of the back and internal organs, so it is better to entrust the diagnosis to a professional. The quality of treatment will largely depend on the correct identification of the source of the problem.
Prevention
Taking preventive measures can reduce the risk of intercostal neuralgia, as well as speed up treatment if it has already appeared
Therefore, it is worth paying attention to the basic rules of prevention and special gymnastics
Basic Rules
Simple recommendations help reduce the risk of neuralgia, fight it if a person is already sick, and also improve the general condition of the body, allowing you to avoid many different diseases.
Just follow the rules:
- Treat your spine in a timely manner;
- Improve your immunity, take care of your health;
- Try not to get too cold;
- Allow sufficient time for breaks during work;
- Eat right, give up bad habits.
Such rules are especially important for people of retirement age, as well as those who suffer from chronic diseases associated with the spine.
Gymnastics
Special gymnastics shows high effectiveness against thoracic neuralgia
In most cases, it is able to affect even the underlying cause, which makes it very important for general therapy
Therefore, it is recommended to pay special attention to it
- Lie on your back, begin to pull your legs one by one towards your chest, bending your knees. Additionally, you should try to reach your knees with your forehead.
- Roll over onto your stomach with your arms stretched forward. Raise your upper body upward, bending your back.
- Sit on a chair, clasp your hands behind your head, lean forward. After this, stand up and additionally bend or turn 90° with your entire torso.
- Lying on your back, stretch your legs and bend your arms at the elbows perpendicular to the floor. Tightening your chest muscles, slowly move your arms up and down.
- Stand up straight, spread your arms straight to your sides. Using the abdominal and chest muscles, rotate both sides of the body in the shoulder area.
Such exercises can only be performed when you feel normal, because... during an exacerbation, they will not provide any help and will harm the body.
Causes of the development of neuralgia of the back
No one is immune from neuralgia of the back, but it rarely occurs in children and adolescents. Women are at increased risk for the condition during pregnancy due to physiological changes in the body. The disease can also accompany menopause and menopause. Men are no less at risk for peripheral nerve damage, which usually occurs due to physical exertion, hypothermia, or refusal to exercise. Most often, older people suffer from pathology - their bodies change with age, the situation is aggravated by the presence of somatic diseases and lack of physical activity.
Older people's bodies change as they age and they are more susceptible to illness.
The main reasons for the development of neuralgia:
- back or spine injuries;
- decreased muscle tone and volume as a result of lack of physical activity;
- scoliosis, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine and other parts of the spinal column;
- tumors, intervertebral hernias, scars, cysts and other formations that create pressure on nerve roots and endings;
- past infections (tuberculosis, herpes, meningitis, encephalitis);
- exposure to a draft, sudden or prolonged hypothermia;
- excessive stress on the spine, including due to improperly designed sports training;
- abuse of alcohol, medications;
- influence on the body of poisons, toxins, salts of heavy metals;
- multiple sclerosis and other autoimmune diseases affecting the brain;
- vitamin B deficiency;
- intoxication of the body, for example, as a result of a serious illness;
- disruptions in the functioning of the heart, decreased functionality of blood vessels due to atherosclerosis, leading to problems with blood supply to the spine and nerves;
- chronic stress;
- hormonal imbalances (diseases of the pancreas and thyroid glands);
- general decrease in immunity as a result of physiological or pathological reasons.
The cause of the disease may be damage to the spine.
The action of each of these factors negatively affects the muscles or nerves.
The disease does not necessarily occur in people with these conditions, but they are at risk. Any careless movement, coughing or sneezing can lead to the development of pain.
Symptoms and methods of diagnosing the disease
The main symptom accompanying back neuralgia is pain. Depending on which nerve is affected, it may have different localization.
The intensity and characteristics of the manifestation are influenced by the type of damage to the nervous tissue, the neglect of the process, and the patient’s susceptibility.
In any case, discomfort occurs suddenly and intensifies with movement and palpation of the problem area. Symptoms are often supplemented by general weakness and increased sweating.
Features of the clinical picture depending on the location of the problem:
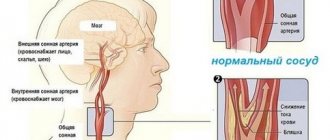
- cervical region - sharp, burning pains that cover the back of the head, spread to the neck, radiate to the eyeballs, areas behind the ears, and lower jaw. Usually concentrated in one half of the head, but can also be bilateral. Any movement leads to a shot in the affected area. The symptom is often accompanied by dizziness, nausea, lacrimation, numbness of the skin and decreased sensitivity of the fingers on the side of the problem;
- thoracic region - intense, girdling pain, in most cases on one side. It radiates to the arm, shoulder blade or internal organs. The clinical picture is much like heart problems, which is why patients start taking heart medications. Symptoms may be supplemented by surges in blood pressure, changes in heart rate, redness or paleness of the skin in the problem area;
- lumbar region - pain is often accompanied by muscle spasms and swelling. This increases the severity of the clinical picture of neuralgia in the lumbar region and additionally causes tremors and muscle weakness. The skin over the site of nerve damage is usually red and painful on palpation. In advanced cases or severe cases of neuralgia in the lumbosacral spine, symptoms persist even in the supine position.
If the disease is localized in the chest, pain appears in the arm.
The pain syndrome characteristic of the condition can be observed in a number of somatic diseases and neurological disorders. If alarming symptoms appear, you should consult a therapist or neurologist. It is important not only to exclude more serious causes of pain and confirm neuralgia, but also to establish its cause. For this purpose, in addition to examination and questioning, the patient must undergo an X-ray, CT or MRI of the affected part of the spine. A blood test is required to identify the presence of infection or inflammation in the body.
ethnoscience
If you do not have the opportunity to consult a doctor at the first symptoms of thoracic neuralgia, you can use folk remedies to alleviate the condition at first. But remember that with their help you can only temporarily relieve pain, but will not eliminate the main cause of its occurrence. Therefore, the main task is to complete the examination course as quickly as possible and receive qualified help.
So, what traditional medicines can help you? Perhaps the most popular and effective remedy is pepper patch. Before applying it to the painful area, it must be degreased with alcohol and wiped dry. You should wear the patch until you feel warmth spreading throughout your body.
Another good way to relieve chest pain involves the use of turpentine. Pour one hundred milliliters of boiling water into a container and add one hundred grams of turpentine. Stir the mixture thoroughly, then soak gauze or a soft cloth in it, wring it out lightly and apply it to the sore spot. Place film or compress paper on top and cover with a terry towel.
Treatment of back neuralgia
The fight against the clinical picture of the condition is almost always carried out at home or on an outpatient basis. A correctly selected list of drugs and manipulations allows you to quickly relieve inflammation in tissues, accelerate the restoration of nerve fibers, and improve metabolism. Despite the absence of a direct danger to the patient’s life from neuralgia, it must be treated by a professional. Self-medication does not always give the desired result, leads to the development of complications, and delays the moment of recovery.
Drug treatment
The fight against neuralgia is rarely complete without the use of medications. They are selected by the doctor taking into account the severity of the pain syndrome and other symptoms and causes of the condition. A comprehensive approach is required; their effectiveness depends on the correct adherence to the neurologist’s prescriptions. Against this background, it is not enough to get rid of the pain; it is also necessary to stop inflammation, improve metabolic processes, and improve blood flow in the affected area.
Treatment should be selected by a specialist.
Drug treatment options for neuralgia:
- oral administration of medications - the list of tablets for various forms of neuralgia usually includes analgesics, NSAIDs, anticonvulsants, antispasmodics, muscle relaxants. Additionally, the doctor may prescribe sedatives and antidepressants. Regardless of the causes of the pathology, the patient is recommended to take a course of B vitamins. They are prescribed in the form of tablets or injections;
- local use of drugs - pharmacies offer ointments, creams, gels and patches for treating the affected area with neuralgia. These products act on the problem area in a warming or cooling manner. The result is not only pain relief, but also a general improvement in the condition of muscles and nerves;
- blockades for pain relief - injections of painkillers for neuralgia are prescribed in cases where other approaches do not bring relief. Most often, Novocaine or Lidocaine is used for these purposes. The blockade must be performed by a medical professional.
Timely initiation of drug therapy makes it possible to relieve the pain syndrome in 1-2 days, and over the next 3-4 days, remove the patient from an acute condition. After this, the doctor can extend the period of use of medications or prescribe other medications to the patient. To increase the effectiveness of the approach, it is recommended to supplement it with physiotherapy, folk remedies, and massage.
Lidocaine is often used to relieve pain.
Exercises, massage, exercise therapy for back neuralgia
Such methods of influencing the affected area are often used after the end of the acute period and in order to prevent relapses. The doctor must individually select a list of manipulations that are acceptable and useful in a particular case. The range of procedures largely depends on the patient’s age, his response to drug treatment, and the location of the peripheral nerve lesion.
The maximum effect is achieved by an integrated approach consisting of swimming, massage, and exercises.
It is better to entrust any options for manual treatment for neuralgia to a professional. Careless actions against this background can aggravate the problem and provoke the development of complications.
Traditional methods of treatment
Alternative medicine offers a lot of effective remedies for back neuralgia. Before using any of them, you should consult your doctor to avoid negative consequences. Particular care must be taken with procedures that involve heating the affected area.
Before using alternative medicine, you should consult a doctor.
Examples of the most effective folk remedies for neuralgia:
- tea with lemon balm and mint - take a teaspoon of both components, pour 300 ml of boiling water over them and leave for five minutes. The composition is drunk like regular tea, you don’t even need to strain it;
- yarrow infusion - steam a tablespoon of the mixture with a glass of boiling water, leave in a warm place or thermos for at least an hour, strain. The infusion is taken three times a day before meals, a tablespoon;
- ointment with Vaseline for back neuralgia - you need to prepare a thick decoction based on lilac buds, strain. Then mix the composition with Vaseline, taking 3 parts of the latter to 1 part of the liquid. It is recommended to treat the painful area with this ointment twice a day;
- medicinal baths are warming procedures during which decoctions of chamomile, lemon balm, mint, oregano or burdock are added to the water.
The above techniques can be used as a therapeutic or prophylactic agent. Persons at risk for back neuralgia are recommended to use them every 2-3 months to reduce the likelihood of damage to peripheral nerves.
Baths are taken with various medicinal plants.
No need to treat joints with pills!
Have you ever experienced unpleasant discomfort in your joints or annoying back pain? Judging by the fact that you are reading this article, you or your loved ones are faced with this problem. And you know firsthand what it is:
- inability to move easily and comfortably;
- discomfort when going up and down stairs;
- unpleasant crunching, clicking not of your own accord;
- pain during or after exercise;
- inflammation in the joints and swelling;
- causeless and sometimes unbearable aching pain in the joints...
Surely you have tried a bunch of medications, creams, ointments, injections, doctors, examinations, and, apparently, none of the above has helped you... And there is an explanation for this: it is simply not profitable for pharmacists to sell a working product, since they will lose customers! It was precisely this that Russia’s leading rheumatologists and orthopedists jointly opposed, presenting a long-known effective remedy for joint pain that actually heals, and not just relieves pain! Read an interview with a famous professor.