Normal blood circulation in the brain is the basis of the life of the human body . Any circulatory disorders can lead to serious diseases and complications, including heart attacks and strokes. How is a violation of the venous outflow of the brain treated, symptoms and manifestations of this condition, how to avoid sad consequences?
Symptoms of disorders
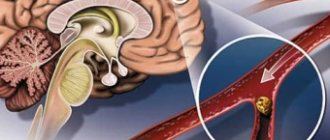
The venous drainage of the brain is a complex system , the functions of which are to supply neurons with oxygen and nutrients, remove toxins and maintain cranial pressure at a normal level.
The causes of difficulties in venous outflow are increased thrombus formation, abnormalities in the structure of the veins, thrombophlebitis, tumors and other diseases.
Symptoms of this condition include:
- dull pain in the head, which manifests itself in the morning, when trying to turn the head, after stress and physical exertion;
- dizziness, fainting, spots before the eyes;
- noise and ringing in the ears;
- insomnia, emotional lability (mood swings);
- weather dependence – deterioration of well-being due to fluctuations in atmospheric pressure;
- swelling of the face and hemorrhages in the conjunctiva in the morning;
- cyanosis of the skin of the face;
- memory loss;
- hand tremors, lack of coordination of movements;
- weakness or increased tone of certain muscle groups.
If a person has two or more symptoms, this means that the venous drainage of the brain is obstructed .
As the disease progresses, its manifestations worsen, and the development of psychosis, epilepsy and other serious dysfunctions of the nervous system is possible.
Traditional therapy
Treatment of obstructed venous outflow with folk remedies is impossible. Even at the initial stage of this disease. A patient with this diagnosis, one way or another, must undergo complex therapy, taking vasodilating painkillers and other medications.
Treatment with folk remedies is more likely to be preventive in nature or has healing power only in combination with all other methods of therapy.
It is believed that fresh nettle and grape juice helps in this case. It is also recommended to drink a decoction of walnut separating plates.
How is it diagnosed?
Diagnostic measures for poor venous outflow of blood to the head are aimed at identifying the main factor that interferes with normal circulation, the scale and localization of the pathological process.
- X-ray of the skull. Indicated for suspected head injuries, tumors and structural disorders in the brain.
- CTG. Computed tomography, as a rule, is performed together with vascular angiography to assess blood circulation, identify the consequences of injuries, strokes and other pathologies.
- MRI. The most effective diagnostic method, allowing to identify any disorders, including benign and malignant neoplasms, dilation and constriction of blood vessels, and other changes in tissues.
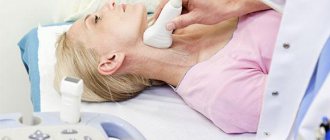
- Ultrasound. Ultrasound examination of the cervical vessels is performed to identify possible blockages, narrowings, or blood flow rates.
How to recognize complications
To identify circulatory problems and determine whether the problem is mild or severe, you will need to undergo diagnostic testing.
It includes the following procedures:
- visual examination by a neurologist or vertebrologist, filling out a complaint form;
- Ultrasound (ultrasound examination) of the vessels of the head and neck;
- CT or MRI (computer or magnetic resonance imaging) of the brain;
- angiography – examination of cerebral vessels using a special contrast agent;
- REG (rheoencephalography) – measurement of the resistance of brain tissue to electric current;
- fundus examination - small hemorrhages confirm increased pressure.
All these activities allow you to see where the vessels are compressed, examine the filling of arteries and veins, and study the movement of blood through them. To determine the stage of osteochondrosis, an x-ray of the spine is also prescribed.
How to improve churn?
With the development of symptoms of disorders of the venous outflow of the brain, urgent therapy is required , otherwise serious consequences may develop.
Self-massage
Massage of the collar area normalizes venous outflow and helps eliminate tension in the neck muscles. The best option is to carry out the procedure yourself several times a day, following the recommended massage technique and proper breathing (calm and deep). Massage each side with the other hand, starting with light stroking, then pressing on the points located above the shoulder blades. Next, clasp your neck with your fingers and perform spiral movements up and down along the points located on both sides of the spine, to the base of the head.
In order for the brain to function normally - without downtime and overload - the blood circulation in it must be fine-tuned to the precision of a clockwork mechanism. Therefore, in addition to the need for the influx of oxygen and glucose with arterial blood, which provides its nutrition, the outflow of venous blood from it is also of utmost importance, carrying everything that the brain not only no longer needs, but has become simply dangerous - poisons formed during “thought production” .
This is where the ever-present extraordinary wit of nature manifests itself, surpassing in the degree of simplicity and elegance of solving the problem all imaginable engineering ideas.
Basic treatment methods
To get rid of blood dyscirculation, an integrated approach is needed. Most often, doctors prescribe venotonics when there is a violation of the venous outflow of the brain. Such preparations supply the necessary vitamins and microelements to the capillaries, the walls of blood vessels become stronger and more elastic. But for a speedy recovery, you need to follow a diet and exercise.
Drug treatment
Pharmacies have a good selection of drugs that improve the condition of blood vessels. These medications not only help strengthen the arteries, but also normalize lymphatic drainage and are an excellent prevention of this disease. The most common and effective venotonics:
- Detralex. The drug is produced on the basis of natural flavonoids. The product has a beneficial effect on the cardiovascular system as a whole and helps to avoid pain and spasms. The big plus is that it prevents varicose veins.
- Vaso collected. Most often prescribed for chronic vascular diseases of the brain. Regulates metabolism and fights increased intracranial pressure. Doctors also claim that Vasobral eliminates insomnia and promotes overall well-being.
- Phlebodia 600 . The medicine has a complex effect on the walls of capillaries and is an excellent prophylactic agent.
- Troxevasin. Combined action drug. Available in the form of capsules and gel for external use.
The list of medications is huge, but you need to select them together with your doctor.
Physiotherapy
Numerous studies have confirmed that regular exercise also helps normalize venous outflow. But you can do therapeutic exercises only after consulting a doctor, and even better - under his supervision. If you choose a complex yourself or immediately start complex exercises, the effect on the capillaries will be even more intense, and their bending will increase.
Diet
If you review your diet, venous circulation in the vertebrobasilar and carotid basins will normalize on its own, and the intracranial outflow of cerebrospinal fluid into the transverse sinuses will also decrease. To achieve a positive effect, the patient needs to give up:
- flour products. Buns, cakes and other baked goods are strictly contraindicated;
- smoked meats;
- pickling;
- canned food;
- soda;
- fast food.
The basis of the diet should be foods rich in fiber and polyunsaturated acids. The greatest amount of these substances is found in:
- fresh vegetables;
- nuts;
- linseed oil;
- berries;
- sea fish.
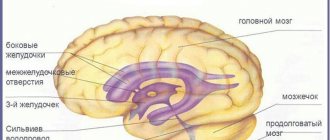
Features of the structure of the venous outflow system
The venous drainage system of the brain differs from that in other organs in that the veins do not accompany the arteries here. It is formed in the form of a ring structure that has numerous anastomoses with the extracranial venous network, and also uses the formations available in the brain for its needs, which provides considerable benefits.
Firstly, the “outflow pipe” of the brain is indestructible. It is formed not by soft tubules, but by sinuses - canals that pass epidurally - between two sheets of crescent-shaped protrusions formed by the dura mater cerebri and creating the internal skeleton of the skull.
Sickles - like partitions inside a walnut - divide the internal space of the skull into several large chambers, not completely isolated from each other (and in the common “bedroom”, each lobe of the brain has its own personal “cradle”).
At the same time, they serve as stiffening ribs - “rafters”, providing protection for the cranial roof from threatening pressure from the outside.
Veins of the brain
Secondly, the existing system of sinuses, which uses the free edges of the falxes - partitions between the lobes of the brain - does not require the laying of any additional communications. This aqueduct-like architecture provides this structure with enviable compactness.
The large (sagittal) medullary falx has an even greater resemblance to the aqueduct. It forms a sinus not only on the lower, free edge (inferior sagittal sinus), but also on the upper one, attached to the bones of the skull roof from the inside (superior sagittal sinus).
The inferior sagittal-sagittal sinus, “climbing” onto the “ridge” of the cerebellar tentorium, forms a short straight sinus. The communication of the latter with the superior sagittal sinus and two oblique horizontal parieto-occipital (transverse) ones, which receive paired temporal sinuses, forms a “cross” called the sinus drainage, or sphincter of Herophilus; its component is also the occipital sinus.
In addition, the system also includes:
- sigmoid sinuses - paired (available on both sides), serving as a continuation of the transverse ones, into which the lower stony sinuses flow;
- superior petrosal sinuses flowing into the transverse ones;
- cavernous sinus is an extensive “delta” around the sella turcica (from the confluence of paired sphenoid-parietal sinuses and formed with the participation of transversely passing intercavernous sinuses - anterior and posterior), having anastomoses with the venous plexuses of the outer base of the skull.
The sigmoid sinuses, in turn, become the beginning of the internal jugular veins.
Venous sinuses are collector lines where blood is collected and discharged from veins of normal structure, both superficial and deep.
Superficial structures (cortex and white matter of the brain) are served by short cortical veins of the subdural and subarachnoid spaces:
- superior anastomotic vein of Trolar;
- dorsal superior cerebral vein;
- superficial middle cerebral vein;
- inferior anastomotic vein of Labbe.
The path of blood from the deep zones of the brain (in particular, from the thalamus and basal ganglia, tissues that form the walls of the ventricles and choroid plexuses) lies:
- into the internal cerebral veins - paired veins, each of which is formed by the merger of the septal vein, which collects blood in the area of the septum pellucidum, and the thalamostriatal vein;
- into the veins of Rosenthal (also paired).
These two pairs of vessels behind the splenium of the corpus callosum discharge blood into the galenic (greater cerebral) vein, from where it, bypassing the straight sinus, enters the sinus sphincter of Herophilus.
The largest part of venous blood from the surface of the brain collects in the superior sagittal sinus, where it moves along it from front to back, while blood from the deep parts of the brain receives the straight sinus. The drainage from the transverse sinus occurs into the sigmoid sinus located on the same side, below the jugular foramen it becomes the internal jugular vein.
Exercises to help improve venous drainage
In some cases, when venous outflow is impaired, simple and accessible exercises can help. Sometimes it is enough to work on your neck to get rid of pain within a few weeks. In this case, exercises to improve venous outflow can be done several times a day, without particularly disturbing your rhythm of life. They will take about ten minutes to complete.
The purpose of the exercise is to improve venous outflow from the head. You need to sit on a chair, resting your hands on the back. The muscles of the legs and arms are relaxed, the head is thrown back freely. Try sitting in this position for a minute. Breathing is free and deep. After you finish the exercise, walk a little and repeat it twice.
The exercise can be performed standing or sitting. The main thing is to relax and lower your head to your chest. As you inhale, begin to lift your head up, looking at the ceiling. Then stretch your neck, as if an invisible thread is pulling you up. When you lower your head, exhale. The exercise is repeated up to eight times depending on how you feel.
The exercise is performed in a relaxed state. Start drawing an imaginary figure eight using the top of your head. One circle to the left, the other circle to the right. Breathing is free, the body is relaxed. The exercise is repeated up to six times.
Sit straight on a chair and clasp your fingers under your chin. While exhaling, tilt your head down, pressing on it with your palms and the back of them. As you inhale, tilt your head back, resisting the movement with your palms placed on the back of your head. The exercise is repeated up to twelve times. It is not recommended to hold your breath.
These exercises help a lot with asymmetry of venous outflow, as it often occurs when the neck is incorrectly positioned or pinched in the cervical spine. These four common exercises can bring a lot of benefits.
Yoga classes are good for improving venous outflow. In this practice there are many asanas aimed at strengthening blood vessels and improving blood flow. In addition, specific breathing through the larynx during exercise helps pump air, which in itself increases blood flow.
Running is great for improving overall blood flow. Considering that running is not accessible to everyone, you can start with regular long-distance walking. It’s good if walking and running are done in a place with clean air and beautiful views of nature. This will have a double effect.
Some argue that lifting weights can not only help prevent venous dyscirculation, but also cure it. Most likely, those who affirm this postulate mean the early stages of the disease, when everything is not yet advanced. In any case, before you start practicing physical activity, consult your doctor.
What about the bathhouse? In a bathhouse, a sharp change in maximum heat and cold has a strong effect on the blood vessels. Yes, blood flow increases, but if the vessels are weak, then harm can be done to the body. Still, the bathhouse is more suitable for prevention, as a means of pumping blood and strengthening the vascular system.
Dyscirculation: when venous outflow is obstructed or impaired
The venous network of the brain is a reflexogenic zone with a high level of nervous organization, responsible for the course of the most important physiological processes that must ensure the constant blood supply to the brain.
“Dis-” means that the process is upset and out of control. When it comes to a circulation disorder, this indicates a more or less significant metabolic imbalance in the brain:
And also about the increase in hypoxia and hypercapnia, venous and intracranial pressure, which leads to the development of cerebral edema.
The disorder of venous outflow goes through 3 stages along its path.
- In the latent stage, there are practically no complaints, no clinical symptoms are manifested.
- The period of cerebral venous dystonia is characterized by paraclinical changes; symptoms are few and do not interfere with life.
- A detailed picture of venous encephalopathy requires the intervention of a specialist, because it is already expressed by persistent organic microsymptoms.
According to the authoritative opinion of M. Ya. Berdichevsky, disturbance of venous outflow exists in two main forms:
- In the primary form , there is an increase in venous tone disorder; the basis for the development of venous discirculation is chronic nicotine or alcohol intoxication, hypertension or hypotension, venous hypertension or endocrine pathology, hyperinsolation or head injury.
- In the stagnant form, disruption of the flow of venous blood from the skull is caused by mechanical reasons, which leads first to a slowdown in venous circulation, then to stagnation of venous blood, and ultimately to cerebral edema.
Causes of obstructed blood flow
Poor blood flow can be caused by:
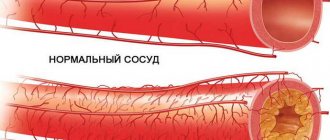
- Chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system (arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis);
- Skull injuries and their consequences, spinal injuries and osteochondrosis (mechanical compression of blood vessels);
- Endocrine diseases;
- Consequences of strokes;
- Infectious diseases with vascular thrombosis;
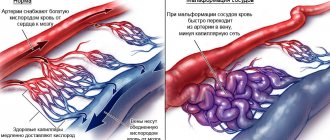
- Congenital features and developmental anomalies (malformations, collaterals);
- Medicines with long-term and uncontrolled use (vasodilators, hormonal contraceptives, nitrates);
- Emergency conditions (sunstroke or heatstroke).
In addition to etiological factors, there are also provoking factors: alcoholism, obesity, tobacco smoking, chronic or excessive stress, unfavorable working conditions (high and low temperatures), physical stress.
Mechanism of dysgemia development
Disruption of the venous outflow of the brain and its pathogenesis are currently continuing to be studied. At this stage, it is generally accepted that dysfunction occurs due to inadequate regulation of blood inflow and outflow. When the outflow is difficult once, this is physiological, but when the situation repeats, the body tries to adapt, which means the veins dilate and the valves stretch. The elasticity of the vascular wall is lost. Over time, these processes become irreversible.
There are several classifications of the disease.
Classification according to the form of manifestation (1989), proposed by M. Ya. Berdichevsky:
- The first form (primary): venous outflow is difficult due to impaired venous tone. Occurs in traumatic brain injury, diseases of the cardiovascular system, emergency conditions, acute intoxication
- The second form (stagnant): the reason for its development is mechanical. Due to the duration and severity of the process, the functions of the organ are disrupted.
According to the violation of the outflow of venous blood, the stages are divided as follows:
- Latent. Minimal number of symptoms. A person lives a full life.
- Cerebral venous dystonia. Full clinical symptoms. Quality of life is reduced.
- Venous encephalopathy. Violations at the micro and macro level. Specialized assistance is required.
Interim and final results
Venous circulation disorders may have the following variants:
- venous stagnation;
- encephalopathy of venous origin;
- hemorrhages of venous etiology;
- thrombosis of veins and sinuses;
- thrombophlebitis.
Some authors adhere to the classification of E. Z. Neimark, which distinguishes both the failure of cranial venous structures, and disorders of the function of main-type veins and disorders of combined genesis, dividing each type of disorder into:
- acute and subacute , including variants of the occurrence of venous hematomas and hemorrhages (intracerebral, as well as intrathecal) due to thrombosis of either intracranial veins or sinuses, as well as due to phlebothrombosis of the veins and sinuses, or their phlebitis, or thrombophlebitis;
- chronic cases caused not only by hypertensive and atherosclerotic encephalopathy, but also by venous encephalopathy.
Chronic venous insufficiency (in the form of encephalopathy) can occur in the form of symptom complexes leading to the development of a number of pathological conditions of the brain and nervous system:
- astheno-vegetative;
- pseudotumor-hypertensive;
- psychopathological;
- stroke-like;
- polymorphic.
And it can cause:
- bettolepsy;
- syndrome of terminal and preterminal seizures.
Blood stasis in the lungs
Venous congestion in the lungs is observed when the heart muscle is insufficient, when the outflow of blood from its left parts is obstructed. Passive venous hyperemia of the lungs develops. Blood fills the capillaries of the lung tissue, increasing the pressure in them. A similar picture can be observed with right ventricular hypertrophy.
The air space of the alveoli is reduced due to the protrusion of capillaries into the alveolar space. Violation of the permeability of the walls of small capillaries leads to the release of fluid into the alveoli and intercellular space.
Venous congestion in the lungs is expressed as an increase in their size and increased tissue density. The patient develops symptoms of increased interpleural pressure, and the suction force of the chest cavity is reduced.
Reduced elasticity of the lung tissue leads to disruption of the drainage function of the lymphatic system. The chronic course causes the proliferation of fibrous tissue and even greater compaction of the lung tissue.
There are many areas of the brain - there are no less reasons to hit them!
The localization of the zone of brain damage, its nature and depth depend on the causes of the development of venous discirculation, and the symptoms expressing it also “dance” from them.
Frequent reasons for disorders of the venous outflow from the brain include:
- pulmonary, or cardiac, or pulmonary-heart failure;
- compression of strategically important extracranial veins, such as the internal jugular, innominate, superior vena cava;
- malignant or benign tumors of the skull and brain;
- TBI;
- thrombosis of the veins or sinuses of the brain;
- craniostenosis and dropsy of the brain, leading to compression of the veins;
- asphyxia of newborns;
- as well as a suicidal or violent reason - hanging.
Most often, this occurs due to thrombosis of veins of varying depths or venous sinuses of the brain (and the clinical manifestations of phlebothrombosis will not differ in any way from those with thrombophlebitis).
Stages and forms of discirculation
If a person is healthy, blood circulates freely throughout the body, supplying the tissues with the necessary substances and components: glucose, protein, oxygen. When the transfer process is completed and the nutrients are absorbed, the outflow of blood begins. In the body, the vertebral and jugular veins and emissaries are responsible for this process.
With certain pathologies, venous dysfunction appears - deterioration and slowing of blood outflow from the brain. Today in international medicine there are three stages of this disease:
- latent stage. Dysfunction of the cerebral venous outflow is minimal, symptoms are completely absent;
- standard disorders (stage II). Signs of the disease begin to appear and become more pronounced. Most often, patients ignore the symptoms and continue to lead their previous lifestyle;
- encephalopathy . The state of health deteriorates significantly. Organic changes become so severe that professional help is required.
Depending on the symptoms and nature, the pathology can also be:
- primary. Usually develops with serious head injuries, alcohol abuse and blood pressure problems;
- stagnant _ Venous outflow is difficult due to mechanical compression of the vessels.
Particulars and nuances: symptoms and signs
The clinical picture of thrombosis of superficial cerebral veins usually combines neurological symptoms with characteristic signs of inflammatory, especially infectious, damage (with hyperthermia, an “inflammatory” reaction in the blood and cerebrospinal fluid).
Often the disease “debuts” with a headache with nausea and vomiting, impaired consciousness (almost always with psychosomatic agitation), which serves as a background for the development of focal brain symptoms (paralysis or paresis of the limbs, aphasia, generalized or focal seizures), the usual lability of which is explained by the movement of action from initially affected venous trunk to the adjacent one.
The ongoing studies end with demonstrating evidence of the symptoms described above: detection of hemorrhagic strokes in one or both types of brain matter, subarachnoid or intracerebral hemorrhages, a picture of ischemia and cerebral edema; Lumbar puncture ends with obtaining hemorrhagic cerebrospinal fluid.
In the vast majority of cases, thrombophlebitis of the veins of the surface of the brain accompanies the postpartum period.
The emphasis should be on the occurrence of brain symptoms against the background of the existence of previously identified active foci of inflammation or thrombophlebitis of the extremities, on the appearance of brain symptoms both after an abortion and in the postpartum period, as well as after processes in the middle ear, in the nasal sinuses and after infectious diseases .
The general picture of venous sinus thrombosis, accompanied by a violation of the venous outflow of the brain, is quite typical:
- severe headache;
- characteristic “meningeal signs”;
- pronounced swelling of the skin of both the facial and scalp;
- hyperthermia;
- varying degrees of change in the state of consciousness (from soporosis to coma).
When examining the fundus, the phenomena of stagnation and edema are clearly visible. In the blood test - leukocytosis, in the cerebrospinal fluid (transparent or xanthochromic) - mild pleocytosis. Focal neurological symptoms suggest the location of the involved sinus.
Manifestations of the most commonly observed thrombosis of the sigmoid sinus, complicating purulent mastoiditis or otitis, are characteristic pain and swelling of the skin and soft tissues of the mastoid region, with increased sensations both during chewing movements and when turning the head in the direction opposite to the one where the process developed, accompanied by significant septic phenomena.
If the process spreads to the jugular vein, symptoms of damage to nerves IX, X and XI occur on the side of the localization of the lesion.
What is the manifestation of cavernous sinus thrombosis, which is a common consequence of purulent inflammation on the face, in the orbital area, in the ears, and in the sinuses?
The appearance of undeniable signs of difficulty in venous outflow in combination with clearly manifested symptoms of the inflammatory process in the form of:
- periorbital edema or swelling of the eyelids;
- chemosis;
- increasing exophthalmos;
- congestive picture of the fundus with signs of optic nerve atrophy.
It is also possible that:
- external ophthalmoplegia (due to involvement of the III, IV, VI cranial nerves);
- ptosis;
- disorders of pupillary reactions;
- dullness of the cornea;
- pain in the forehead and eyeball (due to involvement of the superior branch of the trigeminal nerve);
- Sensory disorders in the area of the exit of the supraorbital nerve.
Drugs that improve venous outflow of blood from the brain
The consequence of cervical osteochondrosis (COX) is a violation of venous outflow in the brain area. Timely seeking medical help, modern and accurate diagnosis of the disease, its treatment, and compliance with preventive measures will help prevent serious consequences.
Causes
The reasons may be:
Venous discirculation of the brain is usually accompanied by headaches. Very often, patients complain of noise in the head and ears, pain when taking a lying position, or when tilting the head.
Such pain is the first sign of the onset of the disease. However, many patients confuse the pathology with ordinary fatigue.
By supporting the head in a comfortable position, the muscles of the neck and face are subject to tension, blood circulation is disrupted and, as a result, pain occurs.
Symptoms of tension headaches are:
- Pain in the neck upon palpation;
- pain in the temples, forehead;
- heaviness in the eye area
- weakness, nausea;
- labored breathing;
- decreased appetite;
- bad dream.
Factors associated with the occurrence of tension headaches are an improperly organized daily routine, weather dependence, long-term use of analgesics and tranquilizers, alcohol consumption, general fatigue, and emotional stress.
What is the threat of the disease?
Venous discirculation is conventionally divided into 3 stages:
- Latent. Accompanied by minor symptoms such as moderate headache, poor sleep. Often the patient refers to fatigue and does not consult a specialist.
- Cerebral dystonia. This stage is accompanied by an increase in the intensity of headaches, vomiting, insomnia, and fainting may occur.
- Venous encephalopathy. The onset of this stage means that some processes may become irreversible: vision and hearing deteriorate, and epileptic seizures occur. Urgent medical attention is required.
Options for the development of the disease can be:
- Hand tremors;
- epilepsy;
- VSD (vegetative-vascular dystonia);
- muscle tissue atrophy;
- hydrocephalus;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- coma;
- stroke.
Symptoms
The first signs of venous stagnation in the brain, as a rule, appear before the disease reaches its apogee. Symptoms to watch out for:
- When tilting or turning the head, the headache intensifies;
- there is noise in the head and ears;
- vision and hearing deteriorate;
- fainting occurs;
- legs and arms become numb, their sensitivity decreases;
- swelling appears on the entire face and on the eyelids in particular;
- frequent dizziness;
- sleep disturbance, insomnia;
- memory problems;
- speech disorder;
- sudden changes in mood, causeless anger, irritability.
In addition to the above, other unfavorable symptoms may occur, such as metabolic disorders. You should not neglect your health; it is better to get examined immediately.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out using modern methods, such as:
- Computed tomography of the brain (CT);
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain (MRI);
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the neck and brain;
- Angiography;
- X-ray of the skull (if there is injury or suspicion of it).
The same diagnostic methods are used for adults and children.
Depending on the complexity of the disease, one or more methods are used to detect impaired venous outflow in the brain. A referral for examination can be obtained from a general practitioner and neurologist, or you can contact a paid diagnostic center.
The methods used to identify the disease will help to understand what stage the disease is at and what the future treatment prognosis is.
More details about the diagnosis here:
Treatment methods
Depending on the speed of the disease and the patient’s well-being, the following treatment methods may be prescribed:
- Medicines;
- physiotherapy;
- massage of the collar area and back;
- physical therapy (physical therapy);
- acupuncture;
- special diet.
Treatment is carried out using one of the listed methods, or in combination.
In addition to taking medications, physical therapy can help you feel better. A general practitioner or neurologist may prescribe:
- Electrophoresis;
- Valerian masks;
- Magnetotherapy;
- Laser therapy;
- Electrical stimulation.
Medication and physical therapy can be prescribed in combination.
Massage of the collar zone is prescribed to a patient with venous stagnation quite often. Massage is prescribed only in the absence of acute inflammation, otherwise this procedure can become extremely painful and harm the patient’s health.
Massage helps improve blood circulation, relieve muscle tension, and eliminate pain. It is advisable that the procedure be performed by an experienced massage therapist or chiropractor. The massage course lasts no more than 10 days.
Self-massage is also possible, 2-3 times a day: light stroking in the direction from the base of the neck to the head. Circular movements are also made from bottom to top to improve blood flow.
Therapeutic exercise is prescribed to a patient if there is a violation of the outflow in the brain, if there are no other contraindications and acute pain symptoms are relieved with the help of medications. Exercise therapy is aimed at strengthening the neck muscles and is initially performed in a sitting position to avoid dizziness and fainting.
Effective exercises to improve blood flow include:
- Smooth circular rotations of the head;
- tilts back and forth, left and right;
- turns the head and neck left and right.
REFERENCE. A course of exercise therapy can be taken at a specialized medical center, where a physical therapy doctor will select the necessary set of exercises, because to improve well-being it is necessary to strengthen the entire body as a whole.
Vertebrogenic headache (cervicocranialgia) is associated with the presence of SCH. The muscles of the neck and back are subject to tension and therefore pain occurs.
The causes of vertebrogenic headaches can be severe physical exertion, injuries to the back muscles, and as a result, protrusions, prolapses or hernias in the intervertebral discs.
The main symptom of vertebrogenic headaches is a noticeable limitation of movements of the head or neck, as well as pain that occurs when palpating areas of the neck.
Treatment is achieved with medications, and after acute symptoms are relieved using the above methods of restorative treatment.
The course of therapy is prescribed by a neurologist or vertebrologist.
IMPORTANT INFORMATION! Massage for cervicocranialgia can lead to a deterioration in well-being and is prescribed only at the rehabilitation stage.
Prevention
Even in the absence of symptoms and complaints, you need to follow several rules for the prevention of venous stagnation:
Conclusion
Violation of venous outflow as a consequence of cervical osteochondrosis is common.
This is due to heavy physical or office work, bad habits, lack of sufficient physical activity, and poor lifestyle in general.
First of all, you need to reconsider your habits in order to avoid adverse consequences. If the disease has already been identified, it is necessary to competently approach the choice of treatment method and not neglect preventive measures.
Source: https://golovnoj-mozg.ru/preparaty/preparaty-uluchshayushhie-venoznyj-ottok-krovi-iz-golovnogo-mozga
How is VDC treated: treatment methods
During the period when the disease has just begun to manifest itself, it is enough to adjust the work and rest schedule.
If the venous outflow disorder persists, you should seek help from a specialist - a neurologist, who will recommend drug treatment appropriate to the condition.
For the most effective assistance, both the general condition of the patient and its particulars are assessed (for example, with concomitant varicose veins, it would be advisable to use antiplatelet drugs, for example, aspirin).
Most often, when the venous outflow of the brain is impaired, the use of venotonics is recommended:
- normalizing blood circulation;
- improving vascular function;
- giving veins elasticity;
- strengthening the walls of blood vessels;
- promoting their adequate permeability;
- relieving swelling;
- preventing the development of inflammation and fighting existing ones;
- increasing the tone of the body.
All this can significantly improve the “standard of living” of the cerebral veins.
This group includes: Anavenol, Venoplant, Aescusan, Venen-gel and others.
To enhance the resistance of the vascular wall, periodic injection courses of Nicotinic acid and Pyridoxine are used.
To eliminate brain symptoms, nootropic drugs taken in long courses are used: Phenotropil, Glycine.
Among non-drug treatment methods, courses of massage and self-massage (carried out after training with a specialist) are highly recommended, especially in the neck area.
How to treat outflow disorder?
Seeing a doctor at the stage of moderate manifestations allows you to prescribe timely therapy and adapt the patient’s life to the altered blood flow in the brain.
In general, the following should be provided:
- refusal of too strenuous work, night shifts;
- limiting physical activity;
- stopping smoking and drinking alcohol;
- inclusion of vegetables and fruits in the daily diet, limitation of heavy and spicy foods, salt, seasonings;
- normalization of sleep with evening walks, tea with mint, herbal sedatives such as valerian, motherwort, lemon balm (ready-made drug Novo-Passit).
Among the choice of drugs, the doctor prescribes a course of use:
- venotonics (Detralex, Venoruton, Aescusan drops, Phlebodia 600);
- diuretics, which are indicated for severe symptoms (Lasix with Eufillin intravenously), for continuous use - Diacarb according to the scheme;
- to prevent thrombosis, anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents are recommended (Warfarin, Thrombo Ass, Cardiomagnyl);
- Prodectin, Piracetam, Stugeron, Cortexin, Cerebrolysin help improve the functioning of brain cells.
Preventing problems
No less than in treatment for already developed pathology, the body also needs to prevent the problem of venous outflow - regular self-diagnosis.
An urgent examination by a neurologist and an ophthalmologist is necessary, with the necessary studies being carried out when:
- dull headache that gets worse with head movements;
- swelling of the lower eyelid;
- cyanosis of the cheeks, lips, nose;
- buzzing in the head with maximum manifestations in the morning;
- pronounced weather dependence;
- fainting, or dizziness, or blurred vision, not to mention mental disorders and epileptic seizures.
Measures to prevent disorders of the venous outflow from the brain also include maintaining an optimal work schedule, sleep and wakefulness, taking care of proper nutrition, and eradicating habitual intoxications and other harmful traditions from your life.
Other valuable methods of influencing the body in order to improve its condition are:
- various relaxation techniques;
- use of herbal medicine;
- taking a contrast shower;
- use of yoga.
Symptoms
Many of us take periodic headaches very lightly, but this is wrong. Dizziness and headache are among the first symptoms of this terrible disease. Most patients describe the same clinical picture: it is difficult to wake up in the morning, a dull headache immediately appears after sleep, spots in the eyes, getting out of bed is accompanied by dizziness, the body feels wobbly. In a horizontal position, the condition worsens sharply, numbness and tingling in certain parts of the body occur. Such people sense weather changes and pressure changes in advance.
If these symptoms are ignored, over time the face takes on a characteristic appearance: it becomes bluish, the nasolabial triangle swells, and the eyelids seem constantly swollen. Vision deteriorates significantly due to swelling of the optic nerve and dilated veins of the fundus. Patients often experience fainting. In severe cases, the psyche suffers, the person loses orientation in space, and sometimes epileptic seizures occur. During periods of exacerbation, a person cannot get out of bed, severe headaches and nausea occur. All these complaints clearly indicate that the venous outflow is impaired.
Survey
Patients diagnosed with venous dyscirculation first contact a cardiologist. A competent specialist, having assessed the symptoms, history of life and illness, genetic predisposition, will prescribe a consultation with a neurologist (this is the main specialist in this field) and a number of necessary studies:
Such patients should also be observed by an ophthalmologist. Changes in the fundus indicate obstructed blood flow .
And without consequences!
Those who do not take care of their health, or who continue to stubbornly cling to their old habits and lifestyle (if the diagnosis has already been established), risk losing not only their health, but also their life.
After all, a cerebral hemorrhage, the cause of which may be venous dysgemia (the same as dyscirculation), can lead to both a wheelchair and a place in the cemetery.
Relatively “benign” consequences are aphasia, mental disorders, the appearance of convulsive seizures and the development of paralysis or paresis in the limbs.
Today, not a single person can insure himself against a sudden deterioration in health or the appearance of any diseases of varying severity. It just so happens that the body is vulnerable, and with every year of life it becomes more sensitive and weaker.
One of the serious and complex diseases is a violation of venous outflow, which can appear in absolutely every person of different age categories.
Brief disturbances in venous circulation were observed by everyone, as they can occur during normal everyday activities.
Short-term symptoms appear during a sharp turn of the head, singing, coughing, defecation, or during light physical exertion.
Causes
To prescribe effective treatment, doctors need to find the origins of the disease. Experts assure that the primary form most often develops due to a deterioration in the tone of the veins in general. Pathology can also be caused by factors such as:
- severe traumatic brain injury with the formation of internal hematomas;
- the formation of benign and malignant tumors, leading to compression of capillaries;
- receiving ischemic or hemorrhagic strokes with further cerebral edema;
- alcohol abuse and constant smoking;
- long-term intoxication with chemicals;
- blood pressure problems;
- underdevelopment of the vascular network in brain tissue.
A distinctive feature of the congestive form of the disease is that venous outflow is disrupted due to mechanical obstacles. In the absence of timely treatment, the pathology will begin to progress and in the future may lead to a weakening of blood flow in general, which will negatively affect human health. The main reasons for the development of this form of the disease are:
- blockage of vascular channels;
- neoplasms in the cervical spine;
- chest injury;
- spinal hernia;
- Disc displacement;
- cervical osteochondrosis.
Violation of venous outflow can be caused not only by pathologies, but also by the influence of external factors. In this case, discirculation usually does not last long and goes away on its own, the person is not bothered by any consequences. It can be called:
- constant physical stress and fatigue;
- being upside down for a long time;
- holding your breath for several minutes (impaired venous outflow - an occupational disease of divers and singers);
- strong cry (especially in a child);
- coughing attack.
What is this disease?
Violation of the venous outflow of the brain is a serious and dangerous problem that can lead to disability and death.
In order to correctly determine the severity of the disease, it is necessary to carefully examine the characteristics of the venous vessels, their ability to withstand heavy loads, etc.
Human vessels have several characteristic features:
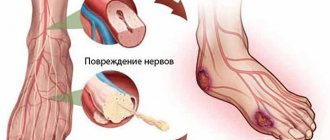
- The wall of the vein in the brain does not have a valve apparatus. Due to this structure, blood flows freely in both directions. This can cause the rapid spread of various bacteria and infections through the veins, which enter the sinuses, pores on the face and eyes.
- Almost all vessels in the brain have their own individual location and are not located next to arteries
- Venous sinuses act as intermediate collectors for cerebrospinal fluid and blood. These elements are connected by separate branches.
Experts distinguish two types of veins: superficial and deep. The former are located in the pia mater of the brain and are responsible for collecting blood from various parts of the cerebellum and hemispheres.
The deep veins are formed from the subcortical ganglia and white matter nuclei.
In addition to these types of veins, the brain also contains emissary and diploic veins. They are necessary for the normal flow of sufficient blood into the sinus system.
Diagnosis of venous discirculation in cervical osteochondrosis
Venous discirculation in cervical osteochondrosis requires careful differential diagnosis. Clinical symptoms present with obstructed venous outflow through the vertebral veins can occur with a number of other pathologies. In particular, it is necessary to exclude brain tumors, acute cerebrovascular accident, cerebral aneurysm, etc.
If the outflow through the vertebral veins is difficult, diagnosis begins with a visit to a vertebrologist. The specialist examines the patient and conducts a series of diagnostic functional tests. Then, as necessary, he can prescribe additional examinations:
- Doppler scanning of the blood vessels of the brain and neck;
- examination of the fundus vessels (performed by an ophthalmologist);
- MRI of brain structures and cervical spine;
- X-ray of the cervical spine in several projections;
- EEG of the brain, etc.
After an accurate diagnosis is made, treatment begins. It can be carried out using conservative methods and surgery (in advanced cases).
The main causes of impaired venous outflow
Deterioration of blood flow can occur either independently or in conjunction with other brain diseases. This factor is the main one when choosing a treatment method and its prescription.
Another reason for such disorders may be the formation of thrombophlebitis in the brain, the appearance of blood clots in the sinuses, and also due to congenital anomalies (irregularly sized veins, etc.).
A similar pathology can occur against the background of diseases such as:
Cases of mechanical compression in the cranial cavity:
- tumor of the neck and brain;
- severe head injury;
- severe swelling and displacement of bones;
- thrombosis at the level of the jugular vein;
- for bronchial asthma;
- due to suffocation.
As is known, venous outflow is associated with arterial circulation. For example, due to increased pressure, there may be an increase in the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid inside the skull directly into the sinuses.
To eliminate tension in the venous system in this case, an antihypertensive treatment complex should be used.
In addition, strokes can cause severe swelling of the brain, which will result in impaired blood flow in the veins. Hematomas strongly compress the vessels, which leads to a deterioration in the outflow of blood in the areas of hemorrhage.
Causes of circulatory disorders in the brain
Obstructed venous outflow of the brain can be caused not by one specific cause, but by several predisposing factors. But what exactly they are, scientists are still studying.
- First of all, it is a closed craniocerebral injury. Usually a 1st or 2nd degree concussion.
- If venous outflow is difficult in a child, or more precisely in a newborn, then most likely this is a consequence of birth trauma. After all, it is known that the skull of a newborn human is very fragile in the first months of life, and the crown is covered only by a thin layer of skin and cartilage.
- Hematomas that disrupt the flow of blood from any part of the brain can be the result of strokes or atherosclerosis.
- The venous outflow of the head is obstructed if a tumor begins to grow in the brain. As it increases, it first compresses thin vessels and then thicker veins.
- Veins can be affected by a variety of pathologies. This may be thrombosis, atherosclerosis and vascular insufficiency. Moreover, blockage of blood vessels with blood clots or atherosclerotic plaques can be either partial or complete.
- Obstructed outflow can be a consequence of an infectious disease of the maxillary cavities - meningitis, sinusitis, sinusitis.
- When a person's venous outflow on the left is obstructed, one half of the brain suffers. This may mean injury to the cervical vertebra: protrusion with subsequent pinching of the nerves. This condition most often paralyzes only one side of the vascular system of the head. And if an intervertebral hernia in the neck or swelling of the muscles on it occurs on the right side, then venous outflow on the right is difficult.
- Various diseases and critical conditions of the respiratory system can lead to obstruction of outflow. This could be asthma, allergic suffocation, hanging head down for a long time, prolonged crying of a small child. Even musicians who play wind instruments are at risk of developing a dangerous syndrome.
- This pathology may be a congenital defect resulting from connective tissue dysplasia, or otherwise Marfin syndrome.
MORE ABOUT: Cholesterol 7: what to do? Normal cholesterol levels by age
If venous outflow is obstructed, not everyone knows what this means for the body. As the issue unfolds, a person begins to monitor his current condition more closely so as not to miss the first signs of pathology.
Signs and symptoms of venous outflow disorders
This disease is common and occurs in people of different age groups.
It has been well studied, so changes in venous outflow are identified promptly and quickly.
The main symptoms include:
- constant headache;
- frequent vomiting and nausea.
Also, along with these symptoms, there is a high temperature and slight swelling of the face . With severe and advanced brain damage, the patient may fall into a coma.
The development of the disease in most cases is accompanied by the presence of:
Signs of impaired outflow of venous blood in the superficial veins are combined with neurological disorders.
Inflammation is observed, the temperature rises, and headaches become more frequent. In some patients, consciousness may be impaired, paralysis of the limbs may occur, and epileptic seizures may occur.
With deep vein thrombosis, patients end up in a more serious condition. Some go into a coma. Signs of dysfunction of subcortical and stem structures appear. In this case, professional doctors keep the patient under constant observation, monitoring the development of symptoms.
With thrombosis of the venous vessels, the disease causes swelling of the facial tissue, frequent headaches, fever and impaired consciousness. The main and most obvious symptom of impaired blood outflow of venous vessels is a change in the color of the cerebrospinal fluid (becomes completely transparent).
There is also thrombosis of the sigmoid sinus, in which the patient experiences pus, otitis media, soft tissue swelling, and pain when turning the head, bending over, or chewing. This type of blood flow disorder is the most common.
With infectious thrombosis of the sinuses and veins in the brain, purulent meningitis, brain abscess, encephalitis, etc. can develop. That is why, when the first signs of the disease appear, you should consult a doctor to identify a violation of the venous outflow.
Prevention and exercise
Prevention depends on the type of human activity. For example, if you have a sedentary lifestyle, you should get up from your chair every hour and do a light workout. In addition, impaired venous outflow manifests itself as a consequence of the underlying disease, so it is this that should be prevented. For example, to prevent heart failure, you should normalize your diet and quit smoking.
There are exercises that help improve blood flow and drainage to the brain, which should be performed at least once a day:
- Sit on a chair or armchair and straighten your back. Now slowly move and tilt your head back and hold it in this state for 3-4 seconds, then return your head to the reverse position. Repeat 10 times.
- Standing or sitting position. Try to stretch your neck upward. The exercise consists of 10 repetitions.
- Sitting or standing position. Try to mentally imagine an infinity sign and describe it with the top of your head. Repeat 5 to 10 times.
Source: sortmozg.com
Types and stages
Difficulty in venous outflow is divided into 2 types:
- 1. Primary form. This type is determined by a noticeable disturbance of blood circulation in the brain cavity, which appears due to severe changes in venous tone. Such a disorder may be the result of a serious head injury, alcohol intoxication, or hyperinsolation. Also, the primary form of the disease is caused by hypotension or hypertension, endocrine system disorders, etc.
- 2. Stagnant form. This type appears when venous outflow is mechanically obstructed. Such changes are critical, as they lead to the destruction of the entire mechanics of the blood circulation process. In this case, surgical intervention and complex treatment are mandatory.
Stages of the disease:
- Latent. At this stage, the main symptoms practically do not appear and the person may not even suspect that he is developing venous discirculation
- Cerebral dystonia . At this stage, primary paraclinical disorders and changes begin. A person can continue to live his usual life at a normal pace, but the first symptoms are already noticeable.
- Venous encephalopathy. This stage is accompanied by the development of microsymptoms of the organic type. It is at this stage that a person needs qualified help to avoid serious violations.
Possible complications
Complications of this pathology are individual for all age categories. So, if the disease appears in a newborn, if left without proper treatment, it can lead to a delay in his physical and mental development.
MORE ABOUT: List of foods for weight loss, what can you eat and what is prohibited on PP?
If an adult leaves the disease without treatment, he may develop hypertension, hypoxia, and discircular encephalopathy. All these conditions lead to heart attack and stroke, and, consequently, death.
Diagnostics
In order to accurately identify a violation of the venous outflow of blood, it is necessary to take several tests and consult a doctor. The patient usually undergoes an MRI.
Only this study provides an accurate and detailed picture of the state of the circulatory system of the brain and the performance of blood vessels.
Not every city has an MRI machine, so you should prepare for the fact that this procedure will force you to leave your usual habitat for some time.
Symptoms of cerebral venous circulation
In such cases, conservative treatment and observation are carried out by a neurologist, and the possibility of surgical treatment is determined by an angiosurgeon. Hello! Impaired venous outflow leads to increased intracranial pressure, which may cause your symptoms.
Hello, I'm 14 years old. The doctor wrote me a diagnosis of obstructed venous outflow from the deep veins of the head on the right. Good afternoon, I have a question: according to Doppler, I have a conclusion: signs of angiodystonia in the form of moderate vasospasm in the carotid basins with venous discirculation!
Treatment
Often, when such pathologies appear, patients are found to have varicose veins. In this case, in parallel with the main treatment, drugs and medications that can thin the blood are prescribed.
In some cases, mainly in the early stages of the disease, massage is highly effective in patients. It is carried out in the area of the shoulders and neck. You should not prescribe such procedures on your own, as they are effective only if prescribed by a doctor after a thorough examination and diagnosis.
In the case of self-treatment with massage, the body may experience a reverse reaction, and such a procedure will cause serious harm and aggravate the development of the disease.
Quite often, doctors recommend slightly increasing and diversifying physical activity. For example, gymnastics will provide quick improvements, but it is worth setting the dose of exercise correctly. Swimming is also a good way to improve blood flow. Almost all swimming pools have massage therapists and trainers who work with people with similar disorders and diseases.
For successful, and most importantly quick treatment and restoration of venous outflow of blood in the brain, you should eliminate bad habits from your life.
These include smoking, excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages, eating fatty and heavy foods, and visiting fast food restaurants.
In order to achieve blood thinning, sometimes it is enough to reconsider your diet. For example, in such cases it is recommended to eat more vegetables, fruits and herbs, and drink grape or nettle juice more often.
According to professional doctors and medical statistics, more than 75% of all diseases, including impaired venous outflow in the brain, are caused by poor diet and lifestyle. As preventive measures, you need to regularly exercise, exercise, and visit the pool.
Basic drugs to improve blood circulation
Nowadays you can find almost any drug in pharmacies. The range of drugs that improve venous blood flow is simply huge.
Drugs for such purposes are in different price categories, so anyone can afford such drugs. For example, venotonics show positive dynamics.
In general, these are drugs that are a preventative measure. They are able to strengthen blood vessels, normalize their permeability, reduce fragility and remove swelling.
Also, taking venotonics leads to strengthening and improving overall venous tone and eliminating inflammation.
Among the most popular and widespread such drugs are the following:
- gel or cream Aescusan, Gerbion or Venoplant . These preparations are made on the basis of horse chestnut. Their cost is moderate and affordable to everyone;
- Antistax capsules or gel . This medicine also contains horse chestnut and grape leaf extract;
- preparations based on Gingobilob extract (Ginkor-fluorine) .
Whatever the medications, you should start taking medications only after a doctor’s prescription. Self-treatment can have a detrimental effect on the course of the disease and increase symptoms.
Also, self-medication is sometimes simply ineffective due to incorrect identification of symptoms.
Diagnosis of the disease
An accurate diagnosis is determined by daily magnetic resonance imaging. Particular attention is paid to changes in the fundus. Due to dysfunction of the oculomotor, abducens and trochlear nerves, paralysis of the eye muscles is likely.
Pain in the eyeball and sensory disturbances in the supraorbital nerve are also noted. In this case, Doppler and rheoencephalographic studies are required.
After diagnosis, treatment is prescribed by a neurologist. At the same time, you can contact a vascular surgeon if you have problems with the veins in your legs and a tendency to thrombophlebitis and thrombosis.
A neurologist usually prescribes the following drugs: - “Tanakan” - this medicine improves the flow of venous blood and strengthens the walls of the veins, making them more elastic;
— “Phlebodia 600” is very effective in patients with encephalopathies accompanied by cerebral venous disorders. The drug reduces noise in the head, frequency and severity of headaches;
Depending on the pathology of the disease, the doctor may prescribe additional medications.
To improve overall blood flow, physical exercises are recommended: morning exercises, swimming and athletics. Therapeutic massage in the neck area, performed by a professional massage therapist, gives very good results.
It is necessary to give up bad habits: drinking alcohol, energy drinks and smoking. Diversify your diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, herbs and completely eliminate fast food products. Nettle and grape juices are very useful.