Causes of cerebral palsy
The causes of cerebral palsy, depending on the time of exposure to the child, are divided into three groups:
- Intrauterine factors.
- Intrapartum factors (various problems during childbirth).
- Postnatal factors (pathological conditions that arise during the neonatal period - in the first weeks of life).
In most cases, when studying the history of a small patient, doctors discover not one, but several causes that could cause cerebral palsy. But there are also situations when it is not possible to find out exactly what factors provoked cerebral palsy. Therefore, researchers suggest that hereditary predisposition and gene mutation .
Signs of cerebral palsy
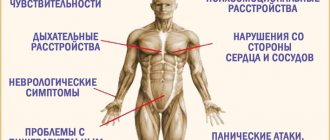
Signs of cerebral palsy can be different, it all depends on the age of the child and the form of the disease. Children with this diagnosis are always delayed in physical development. They begin to sit, crawl, stand and walk much later than healthy children.
One of the first signs of cerebral palsy in young children that can be observed is deviations in muscle tone; they can be either completely relaxed or very tense. Some signs of this disease do not appear immediately, but much later.
Signs of cerebral palsy:
- Visual impairment;
- Hearing impairment;
- Inability to navigate;
- Epileptic seizures;
- Delayed mental development;
- Inhibition of emotional development;
- Gastrointestinal dysfunction;
- Deviations in the functioning of the genitourinary system;
- Cramps.
For early diagnosis of this disease, it is necessary to show the baby to a neurologist regularly, without missing scheduled visits.
Features of the course of pregnancy and cerebral palsy
The fetal brain is the most vulnerable organ in the entire small body. A particular danger to nerve cells is oxygen starvation (hypoxia), infections, toxic substances, and radiation exposure.
Fetal hypoxia can occur in the following situations:
- If there is a threat of miscarriage, when the placenta detaches and bleeding occurs.
- For severe toxicosis and gestosis. These pregnancy complications appear because the mother’s body cannot get used to the new condition, and various pathological changes occur in it, including those that negatively affect blood circulation between the uterus and placenta.
- With placental insufficiency - dysfunction that leads to disruption of gas exchange between the blood of the mother and the fetus.
- For diseases of the mother, accompanied by vasoconstriction and low oxygen concentration in the woman’s blood. Such ailments include diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, systemic autoimmune pathologies, anemia, heart defects, and chronic lung diseases.
Serious damage and abnormalities in brain development can occur due to exposure of the fetus to infectious agents . The greatest danger in this regard are:
- Herpes viruses (including cytomegalovirus).
- Toxoplasma.
- Rubella virus.
All these infections can harm the fetus if a woman’s body encounters them for the first time during pregnancy, that is, this must be a primary infection or a serious exacerbation (for example, genital herpes, cytomegalovirus infection). If a woman has been sick for a long time and has antibodies to these pathogens, the risk of CNS defects in the fetus is minimal.
The cause of the development of cerebral palsy, as mentioned above, can also be the influence of toxic substances on the fetus . These include drugs that have a teratogenic effect (the ability to cause developmental defects in a child), drugs, and alcohol.
Intranatal causes of cerebral palsy development
During childbirth, the baby may develop acute hypoxia, which damages the brain. Leads to this:
- Premature placental abruption. The placenta loses connection with the uterine circulation, so the blood flowing to the baby is no longer saturated with oxygen.
- Difficult, protracted labor.
- Tight entanglement of the umbilical cord or prolapse of the umbilical cord loop, which disrupts blood circulation between the fetus and the placenta.
- Breech presentation of the fetus. When the head is the last to emerge from the birth canal, it compresses the umbilical cord, so if doctors hesitate and do not help the baby to be born as quickly as possible, severe hypoxia may develop.
In addition to oxygen starvation, cerebral palsy is caused by brain injuries sustained during childbirth.
Injury to the baby's head can occur if a woman has a narrow pelvis, if the baby is large or incorrectly placed in the uterus, if labor occurs rapidly or is induced by medications. A risk factor for the development of cerebral palsy is also the application of obstetric forceps (precisely because of the possibility of brain damage, this method of obstetrics is now practically not used), as well as squeezing the fetus from the mother’s abdomen.
Premature birth and cerebral palsy
Premature birth is considered the most dangerous for a child in terms of the development of cerebral palsy, since premature babies are most susceptible to brain damage such as hemorrhages and periventricular leukomalacia. Moreover, the smaller the baby, the greater the risk of developing postpartum complications (in particular cerebral palsy). For this reason, in many developed countries, where they have learned to successfully care for children with critically low body weight, the incidence of cerebral palsy in newborns is at a high level.
What can cause cerebral palsy after childbirth?
During the newborn period, the baby's brain remains very vulnerable. The following reasons can cause irreversible changes in the central nervous system:
- A severe hemolytic disease, in which a large amount of toxic bilirubin is formed in the newborn’s body, damaging the structures of the central nervous system.
- Infectious diseases complicated by meningitis or encephalitis.
- Head injuries.
Important: doctors do not include vaccinations in this group of causes, since there is no confirmed data on the connection between vaccination and the development of cerebral palsy.
How to minimize the risk of occurrence?
You can reduce the likelihood of pathology by adhering to the following recommendations:
- At least a year before pregnancy, completely stop drinking alcohol;
- Complete all vaccinations on time;
- Undergo a full examination for pathological processes in the body (hormonal, inflammatory, metabolic);
- During pregnancy, avoid stress and overload.
It is very important to follow the doctor’s instructions, undergo prescribed examinations, tests, and tests in a timely manner. This will allow timely identification and elimination of pathologies that can provoke cerebral palsy.
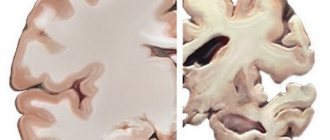
Mechanisms of development of cerebral palsy
The fundamental difference between cerebral palsy and other paralysis is the time of occurrence - this is the perinatal period (the period from the 22nd week of pregnancy to the seventh day of the child’s life). Pathological effects on the brain that occurred during this period of time lead to disruption of the extinction of postural reflexes characteristic of newborns - changes in muscle tone and posture when changing body position.
From a physiological point of view, the interaction between the central nervous system and muscles is as follows: in response to any irritation and changes in body position, the brain potentiates and sends signals along the nerve fibers to the muscles, causing contraction or relaxation of the muscle fibers. In this case, everything goes smoothly - one muscle group contracts, and the other (antagonists) relaxes or vice versa. Only thanks to such clear interaction does a person move normally. With cerebral palsy, connections between the central nervous system and muscles are disrupted, so patients cannot fully control their body .
In addition to motor activity and coordination, the child’s speech suffers . If the nuclei of the cranial nerves are affected, patients have problems with swallowing, vision, and facial expressions. In the most severe cases, brain damage that causes the development of cerebral palsy also becomes a cause of intellectual impairment .
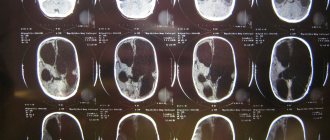
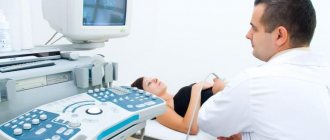
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of cerebral palsy in the first stages consists of an examination by a doctor using special tools.
If deviations are identified in the child’s development, then there is a need for additional diagnostic methods:
- Encephalography evaluates the functionality of brain biocurrents. Using electrophysiological studies, muscle potentials and the condition of peripheral nerves are studied.
- The patient also needs to be shown to doctors of other specializations , an ophthalmologist, an otolaryngologist, a psychiatrist, an epileptologist and an orthopedist, to identify the full clinical picture of the disease and the extent of damage to the baby’s body.
Based on the data obtained, the patient is prescribed treatment and rehabilitation measures.
Forms of cerebral palsy
We recommend reading: - Signs, diagnosis and treatment of cerebral palsy - Rehabilitation of children with cerebral palsy
There are five forms of cerebral palsy:
- Little's disease (spastic tetraplegia). This is the most common form of the disease, especially among premature babies. With it, the child’s lower limbs become immobile, but the arms are rarely affected. Impaired movements in the legs are caused by spasticity (persistent muscle contraction), due to which the limbs do not bend or straighten at all. As the child grows, deformities of the joints and spine occur, but this does not mean that the pathology is progressing.
- Hemiplegic form. It is characterized by immobility of one half of the body and spasticity, as with the first form of cerebral palsy.
- Atactic form. Its development is associated with damage to the frontal lobes of the brain and cerebellum. In such patients, discoordination of movements of different muscle groups, lack of coordination, tremors, speech and intellectual disorders are noted.
- Dyskinetic form . Most often occurs due to severe hemolytic disease of the newborn. The main signs are involuntary movements, sudden changes in muscle tone and body position, and impaired facial expressions. The intelligence of such patients, as a rule, does not suffer.
- Spastic tetraplegia is the most severe form of the disease, in which almost complete paralysis of the limbs is accompanied by constant convulsive seizures, impaired intelligence and speech. Some patients are diagnosed with microcephaly.
A separate form is distinguished , in which patients show signs of several forms of the disease at once. The task of doctors in such cases is to identify the leading syndrome and direct all efforts towards its correction.
Zubkova Olga Sergeevna, medical observer, epidemiologist
10, total, today
( 171 votes, average: 4.61 out of 5)
Perinatal encephalopathy: symptoms and treatment
Carpal tunnel syndrome (tunnel syndrome): symptoms and treatment
Related Posts
Will not be accepted into kindergarten or school
Ksenia Kovalenok, chief medical officer. Photo: Deacon Andrey Radkevich
There is no need to confuse the diagnosis of cerebral palsy and disability. The status of a disabled person is given in case of certain limitations in life activity and the need for compensatory actions and adaptations, but with cerebral palsy such restrictions may not exist.
In mild cases, cerebral palsy may only show up as some odd movements or gait patterns. This will always be at least a little noticeable from the outside, but it may not interfere with life in any way; the child will run, jump and study in a regular school.
In this case, the diagnosis of cerebral palsy is not removed - cerebral palsy is incurable. But the status may change.
Some parents are hesitant to register a disability for their children, fearing that this will close the “doors to a normal life” for the child.
“Certified disability is simply state support in difficult times, when a child is born into a family who is not entirely healthy,” explains Ksenia Kovalenok, “who requires a special approach and needs help in special institutions. This status gives more rights and easier access to necessary services.”
There is no need to be afraid that a child will not get into kindergarten or school, because this is determined not by status, but by the child’s capabilities and abilities. By law, in Russia any child must have access to educational
But learning does not mean that the child will study mathematics. Special education teachers will come to a difficult child’s home. Unfortunately, not everyone understands that even the most difficult children can learn something and all children need communication and communication.”