The appearance of a headache is a clear hint that something is wrong in the body. Episodic (no more than once a month) and not too strong sensations should not cause concern and are most often the result of mental or physical overload. In other cases, it is important to establish the cause of the disease in order to know exactly what is happening. There are two large groups: primary headaches and secondary ones. Pain of the primary type is independent; it occurs in healthy people whose bodies have no pathologies. Secondary ones are the result of injuries, intoxications, and neurological diseases.
Secondary headaches
Out of a hundred people who go to the doctor complaining of a headache, only five suffer from some kind of organic disease. However, serious illnesses must be ruled out first. Almost all of them are somehow related to the functioning of the blood vessels of the brain.
Vascular disease of the brain.
A sudden headache in the back of the head is so intense that it can lead to vomiting and loss of consciousness. Happens when an aneurysm ruptures. The patient needs immediate hospitalization and treatment under the supervision of specialists.
Intracerebral hemorrhage, thrombosis.
Pain in the head can be both general and local. There is depression of consciousness, weakness in the arms and legs, impaired speech and coordination. May also be a symptom of ischemic stroke.
Arterial hypertension.
Pain in this disease most often occurs in the morning hours, from 5 to 8. It is localized mainly in the back of the head. A direct connection between increased pressure and the appearance of unpleasant sensations could not be identified; The only known pattern is that a headache occurs in the event of a sharp increase in pressure to values of 200/130 mm Hg. Art.
Temporal arteritis.
Systematic headaches in the temples and forehead against a background of low-grade fever in people over 60 years of age may be a sign of temporal arteritis. At the same time, weight loss is noted, and ESR values are increased in the blood test.
Increased intracranial pressure.
It can occur against the background of a tumor-like brain lesion, abscess, hematoma, and so on. The pain is at first episodic in nature, gradually becoming more frequent and turning into systematic attacks. Sometimes accompanied by vomiting, worsened by sneezing and coughing. Accompanied by visual impairment, memory loss, and a general change in behavior.
Tumor of the cranial fossa.
In this case, the headache occurs when you exert yourself - coughing, sneezing, laughing. Lasts from a few seconds to 2-3 minutes, during which it gradually fades away. It may be a consequence of abnormalities in the formation of the skull, but it can also mean nothing and be observed in a completely healthy person.
Disease of the cervical spine.
It is concentrated in the neck and back of the head, but can “radiate” to the arm, shoulder, forehead and temples. The intensity is moderate and increases with turning the head, staying in the same position for a long time, and palpating the neck muscles. It occurs as a result of neuralgia of the occipital nerves. Less than a third of patients also experience symptoms similar to migraine symptoms: dilated pupils, sweating.
Sinusitis, sinusitis.
Headache near the frontal and parietal region. Accompanied by feverish fever, purulent nasal discharge and general congestion. May be the result of an allergy or inflammatory process.
Temporomandibular joint syndrome.
With some types of malocclusion, headaches can be triggered by simple actions such as yawning, chewing, and opening and closing the jaw. The mobility of the joint is limited, sometimes the pain radiates to the lower jaw and temporal region.
Angle-closure glaucoma.
Headache in the area around the eyes, feeling of heat in the eye socket, blurred vision, nausea - with such symptoms, glaucoma should be excluded. To do this, you must first check the condition of the fundus.
Post-traumatic pain.
May occur for several months after a minor injury. Accompanied by confusion, fatigue, sleep disturbance and dizziness, intensified during physical stress. This pain can be described as dull, general throughout the head.
Infectious diseases.
When the temperature rises due to infectious diseases, a headache is always present. However, if other symptoms appear - depression of consciousness, repeated vomiting, neurological disorders - it is necessary to exclude brain abscess, encephalitis and meningitis.
Intoxication.
The pain is aching, throbbing; well known to those with caffeine addiction and those suffering from withdrawal symptoms. It intensifies with changes in body position, movement, and sharp sounds. Accompanied by increased sweating and nausea.
My head hurts when I get up or when I change position
A headache, or scientifically called cephalalgia, can indicate many things, and the real cause of discomfort does not always lie directly in the skull.
Neuroinfections, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, metabolic problems, in particular diseases of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus), pathologies caused by viruses (ARVI, flu, colds, etc.), tumors (malignant and benign) - this is only an incomplete list of circumstances that cause a very common phenomenon of cephalalgia. The reason is the fast pace of life: you have to get up early and go to bed late, so when you wake up, you feel some kind of malaise.
A sharp headache when standing up often occurs as a reaction to structural changes in the functioning of internal organs. In this case, consultation with a specialist is required to identify the deviation at an early stage.
Possible diseases and associated symptoms
When you get up, your head hurts; most likely, this is a sign of a certain illness. There is a list of common pathologies:
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia: some call this condition “brain fatigue” caused by excessive physical and emotional stress. Ladies are more prone to VSD. Their disorder occurs due to changes in hormonal levels during pregnancy and menopause. But VSD also often manifests itself in adolescents, since their nervous system is unstable. A small child is almost not susceptible to VSD.
Today, doctors all over the world are arguing whether VSD is an independent disease, because the pathology is not yet included in the International Classification of Diseases. It would be correct to call VSD – neurocircular dystonia. This syndrome is a combination of abnormalities in the functioning of the cardiovascular and nervous systems, but does not pose a threat to the patient’s life.
A characteristic sign of VSD is cephalgia. In this case, patients exhibit a malfunction in the production of the hormones endorphin and serotonin, because the brain parts of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus function with disturbances. As a result, a depressed and nervous state, sudden mood swings, and poor health.
Pain in the head when standing up, when a person gets out of bed in the morning (after waking up), differs with VSD in relatively low intensity, but the attack continues throughout the day. Patients complain of a compressive, encircling type of malaise.
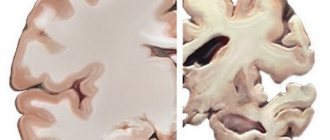
- Oncology: a person wakes up with a headache. Cephalgia is the first sign of a growing tumor in the brain. Gradually, severe vomiting is added, which does not bring relief, the pain intensifies, dizziness, possible loss of consciousness and sudden onset of convulsions, similar to epileptic seizures. The occurrence of a tumor is manifested by a feeling of discomfort in the area where the tumor is located: the frontal part, temples or back of the head. The intensity always increases with movements, for example, if you stand up suddenly, change your body position, sneeze or cough.
Pain in the head when standing up is, of course, not in itself a symptom of brain cancer. In addition, there are neurological abnormalities: decreased muscle tone, darkening of the eyes, numbness of the limbs. When cancer is discovered too late, the person can no longer speak normally, clearly, his gait has changed, and fainting often occurs.
If you suspect cancer, do not be afraid, you should consult a doctor. Anyone can get sick: the likelihood of a positive outcome directly depends on the stage at which the disease was detected.
- Migraine: a neurological disease caused by unstable vascular tone, when the initial narrowing is replaced by dilation of the arterial walls. The disorder always manifests itself in attacks, the frequency of which depends on the individual characteristics of the person.
Migraine sufferers complain that when I get up, there is a sharp pain in the head.
It begins to pulsate on the left or right, it hurts to walk, stand up, bend over, even a leisurely climb up the stairs gives off an unpleasant sensation in the back of the head or temple. Therefore, patients try to lie down more.
There is vomiting, fear of light and sound, and dizziness. Before the crisis begins, the so-called migration aura appears, which is expressed in:
- visual disorders;
- feeling of “goosebumps”;
- numbness of limbs, tongue;
- characteristic weakness on the right or left;
- aphasia.
- Colds: they are usually preceded by cephalgia. Pain in the head when changing position, chills, elevated body temperature, aching joints, weakness, nasal congestion and discomfort in the throat, sneezing, rhinorrhea. With the development of intoxication, cephalalgia worsens and the pain begins to get worse. More often it is localized in the forehead or in the back of the head.
The development of colds (acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections) is facilitated by hypothermia, pathogenic microorganisms (viruses), and infectious agents.
- Intracranial hypertension: increased intracranial pressure. Often, the disease is a consequence of brain damage, for example, after an injury or due to the onset of structural changes in organ tissue.
The cranial cavity is a limited space, as a result of which any transformations in the volume of its components inevitably affect the state of the brain; in fact, its compression begins. This process causes dysmetabolic changes in neurons.
Headaches with increased ICP often intensify when lying down or standing, since cerebrospinal fluid (cerebrospinal fluid), due to disruptions in circulation, begins to put pressure on the walls of the skull.
- Cervical osteochondrosis: a disease of the musculoskeletal system that primarily affects the intervertebral discs. Due to improper metabolism, bone and cartilage tissue gradually wear out and become more viscous. The process leads to gradual deformation of the discs. They begin to put pressure on the nerve roots located nearby, and also affect the blood vessels leading to the skull. Their compression negatively affects the state of the brain. The following symptoms appear:
- headache while standing;
- The sensitivity of the collar area, arms, and shoulders decreases;
- minor restrictions on motor activity in the neck area;
- "noise in ears;
- face goes numb;
- vision decreases;
- arms become weak;
- insomnia;
- shooting pain in the neck that radiates to the shoulder blades;
- When you turn your head, you can hear a characteristic crunching sound.
Osteochondrosis is caused by staying in an incorrect position for a long time, for example, when you have to sit on an uncomfortable chair, hypothermia ("blown" in a draft), if a person sharply turns his neck, and constant lifting of heavy objects.
- Hypertension: a disease characterized by high blood pressure: 139/99 mm Hg. Art. and higher. The disease occurs in the brain, affecting the central nervous system. Communication with vessels that do not receive the necessary impulses regarding contractions or narrowings is disrupted. Consequently, the body’s normal response does not occur during a stressful situation.
Hypertension can be primary, when it occurs as if by itself, and secondary, when it is a complication of the underlying disease (disease of the adrenal glands, narrowing of the aorta, etc.).
Symptoms:
- aching cephalgia. Discomfort is more felt in the occipital region;
- increased heart rate, shortness of breath;
- “noise” in the head;
- tremor of the upper extremities;
- restless sleep;
- legs and arms swell;
- attacks of nausea.
exhausted young Man in bed with coffee, water and tablets suffering hangover and headache
Diagnostics
It is worth noting that complaints when a person says that he has a headache when I get up cannot always be regarded as a manifestation of a serious illness. It happens that the reason lies in excess or lack of sleep, changes in weather conditions, uncomfortable posture and other phenomena that have nothing to do with the functioning of internal organs.
Therefore, only a doctor after an examination can clearly answer the question: why does your head hurt when you get up? Neuroimaging methods, ultrasound manipulations and other testing options show the state of the brain:
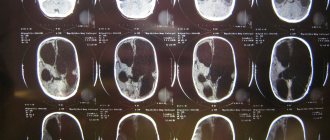
- computed x-ray tomography: the most accurate method for diagnosing pathologies of organs and systems in the human body. Today, CT scans are often used to determine any abnormalities in the functioning of the brain. The technique is, firstly, safe, and secondly, very accurate. With its help, tumors and other neoplasms in the skull are detected, and any problems with blood circulation in the cerebral vessels or depression of the central nervous system are established. After the procedure, the doctor receives a clear image of the bones, meninges and arteries.
To conduct a CT scan, a special device is required - a tomograph. The procedure is performed either with or without the introduction of a contrast agent, and no anesthesia is required. The patient is in a supine or lateral position.
The person must lie still throughout the examination and cannot sit or rise. It is for this reason that CT scans are not always recommended for young children or people with mental health problems.
For these categories, CT scans are performed under general anesthesia;
- Magnetic resonance imaging: an alternative to CT when x-rays are contraindicated. Most often, MRI is used to determine the location and size of tumors in the skull, to check the state of the brain before and after surgery, and to understand why a person experiences headaches and fainting. MRI actually gives the doctor a complete picture of the state of all brain structures;
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the cervical spine: with VSD, as a rule, changes in blood flow and increased arterial tone are detected;
- examination of the cerebrospinal fluid: a spinal (lumbar) puncture is required: fluid is taken from the lumbar region for analysis. In this way, intracranial hypertension and neuroinfections are established;
- echoencephalography: examination of blood vessels using ultrasound. The non-invasive method has almost no restrictions or contraindications; it is often prescribed. Moreover, the procedure is very informative and gives a complete picture of the condition of the cerebral arteries and the speed of blood flow. Thanks to manipulation, it is possible to confirm or refute the presence of tumors, abscesses, cysts, hematomas, and to identify probable pathological processes in the tissues of the brain and ventricles. The method significantly facilitates the diagnostic process, and also allows you to monitor the patient’s recovery over time and determine whether there is a positive effect from the prescribed treatment;
- Doppler ultrasound of the vessels of the brain and neck (USDG): the study is not hazardous to health and does not cause discomfort. The procedure has no contraindications; it is allowed even for infants and pregnant women. The manipulation reflects the condition of the valve apparatus, veins, arteries, the speed and direction of blood flow, the degree of narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels, and places of compression. Doppler ultrasound is prescribed for suspected osteochondrosis or arterial hypertension;
- intraventricular monitoring of ICP: normal for an adult in a supine position is ICP at the level of 7 -15 mm Hg. Art. The indication for treatment is a rise to 20 mm Hg. Art. If such numbers begin to increase significantly, it means that urgent measures need to be taken.
Intraventricular ICP monitoring allows you to see changes in readings over time. The manipulation is carried out in the sterile conditions of a medical facility, since it involves the introduction of a sensor for measurements;
- electroencephalography (EEG) of the brain: during the procedure, electrical signals from the discharges produced by neurons are recorded. Measuring biopotentials makes it possible to establish the smallest transformations in brain tissue, and the tomograph does not always detect them. EEG is indispensable for differentiated diagnosis, distinguishing neuroses, psychiatric disorders, and vegetative paroxysm. At the time of the examination, special sensors are installed on the patient’s head. The person is in a sitting or lying position.
To be able to answer the question as accurately as possible: why there is pain in the head when sitting or when standing up, a number of laboratory tests are required:
- blood biochemistry and CBC (general analysis). The methods make it possible to identify inflammatory processes in the body (which means that there is a focus of infection somewhere if the ESR and leukocytes are exceeded), and show the level of various substances (hemoglobin, glucose, cholesterol). However, for vascular pathologies such studies are not of great importance. The data shows the condition of the blood in general;
- General urine analysis: indirectly confirms urinary tract ailments, indicates abnormalities in kidney function, how metabolic processes are going in the body, what the dynamics of recovery are. The presence of glucose, protein, and increased acidity in the urine - all this indicates a possible disease and requires a detailed examination;
- coagulogram: test for blood clotting. Elevated levels indicate a tendency to form blood clots, while decreased values indicate a high likelihood of bleeding. A complete assessment of the coagulogram indicates vascular pathologies, heart and liver problems.
neurologist Lidiya Rashidovna Magdoteva
Source: https://umozg.ru/simptomy/bolit-golova-kogda-vstayu.html
Primary headaches
This type of pain is the most common; it includes periodic attacks (migraine, cluster pain) and episodic ailments (tension headache). Treatment is mainly symptomatic and aimed at alleviating the ailment.
Migraine.
Acute throbbing pain on one side of the head, worsens with any movement. Combined with photophobia, noise intolerance, nausea and vomiting. A distinctive feature is a specific “aura” that appears before the pain itself (disturbed vision, tingling in the limbs and numbness).
Cluster pain.
It occurs predominantly in men, is localized in the forehead and temples, is usually one-sided and extremely painful. Attacks last from 10 minutes to 3 hours and occur mainly at night. They occur in series: for example, every day for 2 weeks, then a break for several months or even years. Today, the mechanism of formation of such pains has not been studied; they appear and disappear for no apparent reason, and are resistant to the effects of analgesics.
Tension headache.
People of any age can suffer from tension headaches, but most often the ailments begin after the 25th birthday. The pain in the head itself is of moderate intensity, duration ranges from 10 minutes to 2 days. It does not worsen with physical activity, is localized in the back of the head or forehead, is bilateral and has a pressing nature. Constant use of caffeine, analgesics, anxiety and depression contribute to the transition of the malaise to a chronic form.
Treatment methods
To find out how to treat a secondary type of headache, you will have to undergo a full examination by a doctor - to eliminate unpleasant sensations, you need to competently influence the underlying disease.
In case of pain of the primary type, it is necessary first of all to exclude all factors that can provoke the appearance of malaise:
- give up smoking and alcohol;
- reduce coffee consumption;
- do not overdo physical activity.
The dose of analgesics should not be large; it is recommended to take no more than 2 tablets per day for 3 days. Massage is extremely useful, as tension headaches can be cured without the use of medications. For pain caused by fatigue or overexertion, it is often enough to provide the body with quality rest.
Traditional medicine
If intense spasms appear in the head, you can use unconventional recipes, but only after consulting a doctor.
The most common folk remedies that will help eliminate pain on the right side of the head:
- Fragrant mint. Drink the decoction in small portions. You can also inhale its vapors.
- Geranium. Apply a plant leaf to the location of unpleasant discomfort and cover your head.
- Beets, onions. Painful sensations can be neutralized with juice from fresh vegetables. Moisten the bandage and apply to the problem area.
- Broadcasts. The best remedy against sudden spasms.
- Pepper patch. Allows you to quickly relieve pain.
- Lavrushka. For headaches, take a glass of decoction throughout the day.
- Massage of the cervical spine. It helps not only in the treatment of spasms, but is also used to prevent pathological conditions.
Aromatic mint can be taken in the form of a decoction, or you can inhale the vapors