How can I make sure my child is learning to develop certain cognitive abilities appropriate for his or her age? How does children's thinking work? And what are the main stages of a child’s cognitive development? Is it normal for my child to make mistakes in speech or thinking processes? Piaget's theory explains in detail the different stages in children's development. This article by CogniFIt Eva Rodriguez Weitz will help you get acquainted with this scientific theory and find out whether your child is developing according to his age. Let's resolve all your doubts together!
Piaget's theory: stages of development in children
Jean Piaget is one of the most famous psychologists in history. He was recognized in the scientific community primarily for his discoveries in the field of child psychology and the development of intelligence in children. Piaget devoted his life to studying the different stages of growth to understand how children's abilities develop in certain patterns of learning, thinking and cognitive development. This article describes Piaget's theory and offers an explanation of the various stages of child development.
Is your child restless and easily distracted? Check whether you are at risk of having attention deficit disorder with or without hyperactivity with the CogniFit ADHD neuropsychological test
!
What is cognitive impairment
It is important to understand what it is – cognitive deficit, cognitive impairment. The latter occurs due to certain disorders. These include:
- physical injuries;
- mental illness;
- diabetes;
- stroke;
- old age;
- oncology;
- infectious diseases (for example, meningitis).
Depending on the disorder, there are a variety of symptoms that cause cognitive (sensory) deficits, a condition in which the brain malfunctions (for example, memory loss).
Causes
Vascular diseases of the brain are considered one of the most common causes of cognitive impairment.
There a risk of developing abnormalities as a result of hemorrhagic damage, a multi-infarction condition, chronic cerebral ischemia or a strategic localized infarction.
Certain functions of the brain begin to work abnormally or completely lose themselves.
, numerous factors related to the negative impact of the external environment or the progression of specific pathologies can provoke cognitive deviations
factors can provoke cognitive impairment :
- progression of brain tumors,
- serious abnormalities in the metabolic system,
- neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimer's disease, etc.),
- insufficiency of blood supply to the brain,
- consequences of traumatic brain injuries,
- liquorodynamic disorders,
- alcoholism and drug addiction (in advanced stages of development),
- neuroinfections and demyelinating diseases,
- the result of serious hormonal imbalances,
- diseases of the central nervous system,
- consequences of infectious diseases,
- the result of pathologies associated with blood vessels,
- age-related changes in the body.
Why are cognitive disorders dangerous?
Impairment of one or more cognitive functions, such as deterioration in memory, attention, or the ability to think, causes the death of neurons in the brain and the connections between them. At first this manifests itself in the form of slight forgetfulness and absent-mindedness. Many people have had the experience of putting their keys in their pocket on autopilot, and then searching throughout the apartment, thinking that someone had hidden them. Soon these points become more and more obvious.
The brain needs to be trained: crossword puzzles, reading books, and arithmetic operations not with a calculator, but in your head, will help. If this is not done, the disease will progress, the brain will begin to miss new knowledge, “erase” those achievements that the individual could boast of several years ago.
Note! Every person is characterized by absent-mindedness, but forgetting the faces of relatives is a cognitive disorder.
It is important to pay attention to the person, especially children who have suffered a head injury. A number of “habitual” diseases, such as hypertension, can cause cognitive impairment. When working in an office, a person moves little, which means his blood circulation is impaired, he rarely goes out to breathe oxygen, which prevents the body from being saturated with it. This will soon lead to the initial stage of cognitive impairment.
Manifestations of cognitive impairment in children and methods of treating the disorder
Cognitive impairments in children create problems with learning and further socialization, and therefore require correction.
They manifest themselves in a disorder of perception and reproduction of information. This is caused by various diseases of the central nervous system, infections, and difficult childbirth. The main causes of cognitive impairment are organic brain lesions of varying severity. Factors leading to the formation of problems with cognitive abilities:
- Intrauterine infections.
- Birth and traumatic brain injuries.
- Maternal smoking and alcohol consumption during pregnancy.
- Past neuroinfections: meningitis, encephalitis.
- Disorders of the birth process.
- Deficiency of vitamins, macro- and microelements, unhealthy diet.
- Organic pathologies – hydrocephalus.
Intrauterine infections, such as chlamydia, herpes, rubella, can cause disturbances in the development of nervous tissue. The presence of such pathogens in mothers often leads to defective formation of the infant’s brain.
Gonococcal, meningococcal, staphylococcal meningitis, viral encephalitis lead to swelling and death of nerve cells, which subsequently affects mental development.
Head injuries, including birth injuries, are the cause of many disorders: epileptic syndrome, cerebral palsy. In this case, a disorder of cognitive functions naturally occurs.
A deficiency of B vitamins during pregnancy and after birth can have an extremely negative impact on the formation of the brain and neural connections in it. Alcoholism in a pregnant woman leads to nutritional deficiency, as well as a direct toxic effect on nerve cells.
Hypoxia during childbirth is a common cause of cognitive disorders in children, as well as cerebral palsy and epileptic syndrome.
Identifying a cognitive disorder is not an easy task. An examination by a neurologist (newborns, infants) is required to study reflexes and muscle tone, and a conversation with teachers.
To detect severe disorders of brain formation, a thorough diagnosis should be carried out using methods:
- Echoencephalography or neurosonography in newborns.
- Electroencephalography.
- REG.
- Ultrasound examination of blood vessels - Dopplerography.
- Myometrium.
In case of severe disorders of cognitive abilities, patient correction is required for further socialization of children in specialized institutions.
If there are organic brain lesions, such as hydrocephalus, surgical treatment is necessary. To do this, a flexible tube is implanted connecting the ventricles of the brain with the abdominal cavity.
This helps remove excess fluid and improve liquor dynamics.
With a mild or moderate degree of cognitive decline, the prognosis of the disease depends on how carefully and regularly corrective work is carried out.
The following treatment is prescribed:
- Antihypoxic drugs (Mexidol, Reamberin, Mildronate).
- Angioprotectors: Actovegin, Solcoseryl.
- Vitamins: thiamine, methylcobalamin, folic acid, pyridoxine.
- Nootropic drugs: Noopept, Piracetam, Pantogam, Glycine.
- Spa treatment.
It is useful to read what dyslexia is: symptoms, causes, diagnosis and treatment.
Note to parents! Motor alalia in children: causes of pathology, main symptoms and effective treatment.
Information about what borderline mental retardation is: symptoms and treatment.
In case of motor hyperactivity, you should limit the use of stimulants - caffeine-containing drinks, spices with monosodium glutamate. With ADHD (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder), the need for physical activity increases. Sports sections and hobby groups will be a useful pastime and will direct energy in a constructive direction.
Conclusion
Impairment of cognitive functions is a complex problem that requires drug treatment, as well as pedagogical correction. Sometimes surgery is required. The prognosis depends on the severity of organic brain damage and the degree of mental impairment.
(45.00 out of 5)Loading…
How unpleasant it is to notice in yourself or loved ones a deterioration in the ability to remember information, the appearance of rapid fatigue, and a decrease in intelligence.
Such disorders in the functioning of the brain are called “cognitive disorders” in medicine. However, one should not despair. Adequate therapy is of great importance for people with this disease.
Modern medicine is able to provide proper treatment and achieve stable remission.
Cognitive functions are perception, intelligence, the ability to get acquainted with new information and remember it, attention, speech, orientation in space and time, motor skills.
Over time, a person begins to experience disturbances in everyday behavior due to disruptions in cognitive functions.
Isolated cases of forgetfulness are not a reason to worry, but if a person begins to regularly forget events, names or names of objects, then this may indicate disturbances in brain activity, then the patient needs the help of a neurologist.
The activity of the frontal lobes of the brain is associated with the perception of smells and sounds, with the emotional coloring of the surrounding world, it is responsible for experience and memorization.
If the disease affects the parietal lobes of the brain, then the patient loses the ability to purposefully perform actions, he does not distinguish between right and left, and cannot write or read.
The occipital lobes are responsible for the ability to see color pictures, analyze, recognize faces and objects. Changes in the cerebellum are characterized by inappropriate behavior and speech impairment.
What is a cognitive disorder and how does it manifest itself externally? These include severe fatigue during mental activity, the inability to remember new information, confusion, difficulty concentrating, and problems in performing purposeful actions.
It is often difficult for a patient to understand someone else’s speech or choose words to convey thoughts. An interesting fact is that this is a reversible process. With strong mental stress, the symptoms progress, and after a good rest they disappear. However, there is a need to visit a neurologist and therapist, who will conduct the necessary instrumental studies and prescribe tests.
When the functioning of several processes deteriorates beyond the normal range of the patient's age, but does not reach the level of dementia, we can speak of a moderate impairment. According to medical statistics, such symptoms can occur in 20% of people over 60 years of age.
However, most of these patients develop dementia within the next five years.
In 30% of people, the disease progresses slowly, but if a disorder of several cognitive functions occurs in a short period of time, then urgent consultation with a specialist is necessary.
Severe form
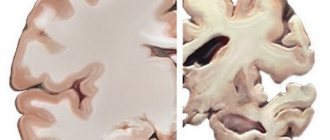
The prevalence of dementia is observed in elderly patients, and it is usually provoked by Alzheimer's disease. AD is a brain disease associated with the death of acetylcholinergic neurons.
Its first signs are loss of memory, constant forgetfulness of life events.
At the next stage of progression of pathological changes, disorientation in space begins, the person loses the ability to express his thoughts, speaks nonsense, becomes helpless in everyday life and may need help from loved ones.
Often, severe impairment of cognitive functions is provoked by cerebrovascular insufficiency, then memory for life events may remain good, but intelligence suffers.
Patients stop distinguishing and seeing similarities between concepts, their thinking slows down, and difficulty concentrating appears. In addition, the person experiences an increase in muscle tone and a change in gait.
If such signs occur, a neuropsychological examination is prescribed.
Causes
Violations are divided into two types: functional and organic. Functional disorders are provoked by emotional overstrain, stress, and overload. They are typical for any age and when the causes are eliminated, as a rule, they go away on their own. However, there are times when the doctor decides to use drug therapy.
Organic disorders are provoked by changes in the brain under the influence of a disease. As a rule, they are observed in old age and are stable in nature. Modern medicine offers productive ways to solve this problem, allowing you to get good results. The following reasons for violations can be named:
- Insufficient blood supply to brain cells. This includes diseases such as cardiovascular pathology, stroke, hypertension. A person must monitor his blood pressure, maintain optimal sugar and cholesterol levels.
- Age-related brain atrophy or progressive Alzheimer's disease. In this case, the symptoms of the disease increase gradually over many years. Adequate treatment will help improve the patient’s condition and stabilize symptoms for a long time.
- Metabolic problems.
- Alcoholism and poisoning.
- Cardiovascular failure.
In children
The practice of childhood neuralgia shows that cognitive deficits appear as a result of diseases affecting the nervous system of a small patient.
This could be, for example, a birth injury or intrauterine infection, or congenital metabolic disorders in the child’s nervous system.
Types of violations by degree of complexity
Deterioration of brain performance is caused not only by injuries and meningitis. Stroke causes cognitive problems that can lead to dementia. The risk of experiencing a stroke is determined by the presence of the following ailments:
- Hypertension (especially if its duration is over 5 years);
- Atherosclerotic diseases;
- Heart diseases;
- Diabetes (due to damage to nerve cells);
- Asymptomatic microstroke.
People are used to improving their health at home
Note! A microstroke is a blood clot that enters a small blood vessel in the brain. It does not cause sudden attacks, and the person will not lose motor or speech ability. Maybe the cheek will become numb, but the individual will not attach any importance to this.
Modern people rarely go to doctors, preferring to use the Internet search and prescribe self-medication. Later, they completely “get used” to various symptoms that should be paid attention to. As a result, the risk of cognitive disorders increases significantly, manifesting itself in the form of depression, asthenia, and chronic fatigue.
Mild cognitive impairment
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is not obvious because it goes unnoticed by others. Moreover, MCI is not diagnosed, since the analyzed indicators are within acceptable limits, and if they deviate, then only slightly. The individual himself notices that his behavior, reactions and thought processes are reduced.
Note! The first signal about the possible presence of MCI is a slowdown in the speed of habitual actions.
The quality of an individual’s activity remains the same, but more time is spent on its implementation. The same goes for thought processes. If a person usually remembers the necessary information quite quickly, then in the presence of MCI this process slows down. Forgetfulness is often observed, it is difficult to concentrate on one task, or it becomes more difficult to switch between several tasks.
If this occurs with age, then it is considered natural. However, if an individual increasingly notices such behavior in himself, it means that the process is proceeding too quickly. Modern diagnostics will reveal the root cause of MCI, namely the connection with pathologies or an unhealthy lifestyle (stress, physical and nervous strain).
Mild cognitive impairment
Moderate cognitive dysfunction refers to disorders that are not typical for a given age norm, but have not reached the state of dementia (memory degradation syndrome). In other words, mild cognitive impairment falls somewhere between aging and dementia.
Symptoms
The symptoms of cognitive impairment are varied and include numerous signs of abnormalities in the functioning of certain brain functions.
The intensity of manifestations depends on the degree of their damage and the presence of concomitant diseases. The first symptoms may resemble specific personality traits of a person, but over time they will become pronounced neurological abnormalities.
Symptoms of cognitive impairment include the following:
- delusions (false conclusions that are persistent),
- eating disorders,
- visual or auditory hallucinations,
- decreased activity of the thought process,
- daytime sleepiness combined with nighttime activity,
- signs of apathy,
- memory impairment,
- motor activity that has no purpose,
- disturbance of orientation in the place where the person is for the first time,
- decreased concentration,
- loss of sense of tact,
- excessive irritability and aggressiveness.
You can learn about the causes and symptoms
Diagnosis of cognitive impairment
Diagnosis of cognitive impairment is carried out using simple tests. For example, “Mini-Cog”, the essence of which is to remember three words said by the doctor, draw a dial where the hands will indicate the exact time, and then say the notorious three words. If the patient cannot draw a dial or does not remember at least one word, it is necessary to contact a specialist, since the disorder has begun to develop.
Another task, the Montreal Cognitive Assessment Scale, involves answering a series of questions. It is advisable to do this in a calm environment so that the person does not get nervous or feel uncomfortable. Questions of the following nature:
- The individual is shown a picture of animals and asked to name each one;
- Tell him the numbers randomly so that he repeats, and then calls them in reverse order;
- In a minute you need to name the maximum number of words per letter of the alphabet (for example, P);
- Ask some simple arithmetic problems, for example, what is 100-3;
- Find the commonality between two slightly similar objects, for example, it could be a watch and a ruler.
In the future, diagnostics are carried out in medical institutions in a more serious atmosphere and with tools.
Classification and types
In medical practice, cognitive impairment is divided into three main groups - mild, moderate and severe.
In the first case, the disturbances will be minor (memory deterioration, excessive fatigue and difficulty in solving any problems may be observed).
The moderate form is accompanied by deterioration of several cognitive functions.
In the severe stage, serious problems arise with the perception of the surrounding world (the patient exhibits most of the characteristic symptoms of cognitive disorders).
Classification of the syndrome depending on the etiology:
- organic disorders (pathological processes become irreversible);
- functional deviations (violations are temporary);
- neurocognitive disorders (characteristic of organic mental disorders).
Cognitive distortions
Cognitive distortion is a person’s irrational thinking and systematic errors in judgment. They arise due to the individual’s strong beliefs and faith in something, stubbornness and inability to give in and admit a mistake. Marketers and psychics readily use this:
- It is human nature to imitate others, that is his nature. If the majority buys a certain product or believes that a black cat brings trouble, an individual with a cognitive distortion will accept these facts on faith.
- The “anchor” effect is also triggered - an association associated with a certain phenomenon.
- The halo effect, when a certain opinion begins to cover everyone around one by one, for example, an approving review of someone by a television star, which will be listened to by tens, hundreds of people.
Correction of thinking errors
In order not to succumb to other people's tricks, you need to distance yourself from the metallic noise, allowing yourself to analyze the situation yourself.
Sometimes it's important to isolate yourself from social noise
In order for someone else’s opinion not to bother a person, to avoid social pressure and emotional reasons, one should consult a specialist. First, he will identify the presence of these ailments and their level. Then he will work through them and teach them to adequately perceive information. The psychologist will select the most convenient time and action options for training cognitive functions and, if necessary, prescribe medications, for example, the familiar glycine.
Concept and definition
In a broad sense, cognitive impairments are deviations in the functions of the human brain responsible for cognition, understanding, perception and awareness of certain information received from the environment.
In some cases, such disorders are observed in the presence of serious diseases of neurological etiology.
Cognitive impairment may be associated with the following brain functions:
- regulation of voluntary activity;
- all types of memory;
- gnosis (assigning objects to a certain category);
- perception of information;
- concentration of attention;
- intelligence;
- speech activity;
- praxis (the ability to apply knowledge in practice);
- psychomotor function.
Prevention
Reading, arithmetic problems in your head, and not with a calculator - all this is daily memory training. In addition, you need to practice fine motor skills: knitting, playing a musical instrument, origami. Foreign languages that train the brain well, as well as poetry by heart, help. Crossword puzzles, checkers, Sudoku and other intellectual logic games that are familiar to many are a big step in delaying cognitive disorders. It is important to disperse the blood throughout the body, where the technique of squeezing and extending the fingers according to the school warm-up principle “we wrote, our fingers were tired” is also considered an exercise in the field of fine motor skills.
Changes in the functioning of the brain of a child, an adult, and people of adolescence and old age negatively affect all areas of an individual’s life. Daily life, social, educational and professional activities suffer. If an individual notices that he is excessively absent-minded, it would not be superfluous to check his mental abilities.