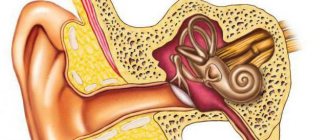
This phenomenon of tinnitus is called “tinnitus” in medicine. In fact, tinnitus is not considered an independent disease, but most often serves as a symptom of serious health problems.
Often patients complain of constant noise in the left ear, which resembles a hum, ringing or an unpleasant grinding sound. Often this phenomenon causes hearing loss because the auditory nerve is damaged. The causes of noise in the left ear are quite varied and can pose a serious danger to human health.
Noise in the right ear - causes
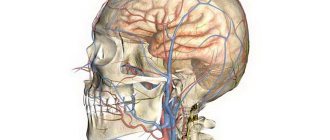
Hearing plays an important role in our life. By influencing various functions, it helps us remember information and navigate space. Therefore, when we hear extraneous sounds, we immediately try to identify the pathology. There can be many reasons, because the organ is located close to the brain, and there are many blood vessels, nerve endings and arteries nearby. It can be difficult for a specialist to find the cause of tinnitus, but we will name the main ones:
- sudden increase in blood pressure;
- sulfur plug;
- concussion;
- atherosclerosis;
- circulatory disorders;
- vascular failure;
- brain tumor;
- neurology;
- osteochondrosis;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- nasal congestion;
- weakness during pregnancy;
- neurosis.
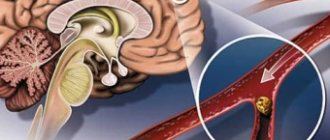
Constant pulsating tinnitus is a sign of atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension or arteriovenous malformation. The most common disease with ear pulsation is arterial hypertension, when high blood pressure contributes to the narrowing of small vessels in the brain. Due to this, the brain does not receive the required amount of oxygen, reacting sharply to these changes.
With arteriovenous malformation, the correct plexus of blood vessels is disrupted, so the blood, bypassing the capillaries, immediately enters the veins, causing the pulsating noise to increase. After a concussion, the ears often hear pulsating sounds and drumming with increasing volume. This condition is a harbinger of vomiting or dizziness, especially when bending over.
If the noise is accompanied by dizziness and headache, then this condition is most likely provoked by one of three factors:
- Auditory nerve disease.
- Atherosclerotic plaques.
- Concussion.
If the headache is accompanied by nausea and vomiting after a blow to the head or a fall, and there is periodic noise in the ears, then this is a concussion and it needs to be treated urgently. When atherosclerosis is detected, the functioning of the vestibular apparatus worsens, and the noise constantly increases, especially in the evening. With such symptoms, it is necessary to urgently examine the blood vessels of the brain.
With dizziness
The noise, which is accompanied by constant dizziness, may occur due to changes in the cervical spine, because over time, thorns or growths appear on it. The normal height of the discs is significantly reduced, so the vertebrae become closer together. The vertebral artery becomes inconsistent with these bone growths.
Idiopathic murmur
A common condition that occurs in 45% of cases when the doctor does not determine a clear cause of tinnitus is called idiopathic tinnitus. Research shows that many patients complaining of tinnitus are people between 40 and 80 years old. This is due to both medications, age-related changes, and normal physiological noise associated with the movement of blood in the inner ear.
Noise in the ear occurs due to irritation of hair-type cells, which are localized in large numbers in the area of the inner ear. Under normal conditions, their functioning occurs synchronously and does not cause any unpleasant sensations.
After their irritation, the movements of the hairs will be unsynchronized, and the order in which electrical excitation impulses enter the brain is quickly disrupted, which is why tinnitus appears.
There is also something called physiological noise. This situation is explained by the noise of blood that passes through the area of the inner ear, hitting the walls of the vessels located there.
The noise occurs in conditions of complete silence and happens on both sides, and only in one ear.
In most cases, tinnitus is a clinical sign of a disease, for example, acute otitis media, sensorineural hearing loss, or Meniere's disease.
Among the reasons leading to tinnitus:
- Changes in blood pressure levels;
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels;
- Traumatic brain injury;
- Brain tumors of a malignant nature;
- Poisoning with various toxic substances.
In fifteen percent of cases, tinnitus is caused by pathology of the hearing aid. In all other situations (with the exception of physiological noise), the etiological factor is associated with a general disease.
Often, severe noise in the right ear is a sign of acute right-sided otitis or acute right-sided tubo-otitis. The noise is accompanied by unpleasant, painful sensations in the ear area and a feeling of stuffiness.
With otitis media, the noise is associated with the accumulation of fluid in the middle ear cavity, called exudate. In the case of Meniere's disease, the noise occurs due to a sharp spasm of the small arteries supplying this area and a violation of blood circulation.
In parallel with noise, illness, a person will be bothered by dizziness, a sharp loss of balance and a gradual decrease in hearing. If the noise is caused by right-sided tubo-otitis or inflammation of the auditory tube, then along with tinnitus there will be severe congestion in the ear.
Noise in the right ear can occur when taking medications that have an ototoxic effect; this group includes some antibacterial drugs.
A specialist in this area, an ENT specialist, will identify the cause of sound hallucinations by collecting anamnesis:
- Will listen to complaints;
- Ask about the nature of the noise in the ear and its intensity;
- Find out under what circumstances and at what time the sounds appeared.
During the diagnosis, the doctor will examine:
- Outer ear and surrounding area;
- Middle ear;
- Internal;
- Ear canal for the absence of a foreign body;
- Auditory nerve.
Research methods:
- Otoscopy. To perform this, an otoscope is used - a metal ring with a mirror inside, which is placed on the specialist’s head. When using the device, a light beam is directed using a mirror deep into the ear canal, this ensures the study of the eardrum. The use of a fiberoptic otoscope - a stick with a funnel in a perpendicular line with a hole at the end, makes it possible to study the external auditory canal.
- Palpation diagnostics. It is not a finger that is used, but a thin metal rod with curved ends.
- Audiometry. A tuning fork or audiometer is used to determine hearing acuity.
- Vestibulometry. During the research, the specialist will check the vestibular functions for the absence of dizziness, impaired coordination of movements and other symptoms that are associated with dysfunction of the blood supply to the brain and diseases affecting the inner ear and auditory nerve. To identify these pathologies, a finger-nose test is used - the patient must close his eyes and touch the tip of his nose with the index finger of his right or left hand.
- Gas and dehydration testing. Helps identify Meniere's disease. The test is carried out in 2 stages - for the first time, the patient breathes a mixture enriched with carbon dioxide in order to expand the vessel, for the second time, during an attack, the patient takes drugs that reduce the amount of fluid in the body.
- Application of Levy, Valsava, Politzer and others tests. Using air injection, the degree of damage to the eardrum and eustachian tube is examined. In the case of a membrane, a protrusion occurs and a cracking sound is felt in the ear; in the second case, the swollen mucous membrane of the Eustachian tube prevents the penetration of air to the membrane.
- X-ray, MRI, CT. They make it possible to identify pathologies of the internal components of the ear and brain.
- Angiography. This x-ray study uses contrast agents to determine the presence or absence of blockage of blood flow to the cerebral vessels and inner ear.
- Dopplerography. By studying sound waves, the degree of vascular patency is determined.
- General blood analysis. Using this blood sample, the presence of an infectious disease is detected, which becomes clear from the ESR indicators - the erythrocyte sedimentation rate and an increased level of leukocytes in the presence of bacteria.
- Microbiological research. Discharge from the ear is examined for the presence of the type of pathogen, and a test is taken for sensitivity to antibiotics.
It is important to perform a comprehensive examination by a gynecologist, ophthalmologist, therapist, endocrinologist, hematologist, cardiologist, neurosurgeon, neurologist for the presence or absence of possible complications and diseases that are the causes of noise in the ear. Consultation with an audiologist-otorhinolaryngologist is required.
Additional symptoms and diagnostics
Experts identify several types of tinnitus. Thus, it can be objective and subjective, vibrational and non-vibrational. Ringing in the ears is considered subjective if it is only audible to the sick person.
The objectivity of extraneous noise in the ears is indicated by the fact that a strong noise is also heard by the doctor when checking. This form of pathology is less common. When extraneous sounds in the ears are projected directly by the hearing aid and are heard by the doctor and the patient, such noise is called vibrational.
If only the patient hears a buzzing in the ears, then they speak of a non-vibrational form of the disorder. This occurs as a result of irritation of the nerve endings in the hearing aid. In addition, according to prevalence, this symptom is divided into unilateral and bilateral.
In the first case, extraneous sounds are heard only in one ear, and in the second - in both ears. Based on the time of onset of this symptom, it is classified into constant and periodic.
Patients describe the nature of the hum in the ears as the appearance of loud beats, reminiscent of ringing or striking a clock, whistling or squeaking. The severity is also different: sharp, loud or dull sounds.
Ringing in the ears is divided into the following forms:
- Spicy. Extraneous sounds in the ears appear for a short time and suddenly disappear. This condition can last for 3 months.
- Subacute. The hum becomes more pronounced and persists for a long time. If no measures are taken, this condition lasts up to 6 months.
- Chronic. Extraneous sounds in the ears appear for more than 6 months in a row.
It also happens that in one ear the noise is felt more intensely. For example, noise in the left ear or only the right one can be caused by exudative otitis media. Typically, this disease affects only one ear. The manifestation of unilateral symptoms can also occur with hypertension.
The following symptoms may appear against the background of tinnitus:
- headaches and dizziness;
- temporary hearing loss;
- temperature increase;
- feeling of fullness and pain in the ear;
- nausea and weakness;
- increased sensitivity to sounds;
- feeling of squeezing in the ears;
- intolerance to light.
If tinnitus is accompanied by such symptoms, you should immediately seek medical help. Experts will find out why this symptom appears.
If tinnitus suddenly occurs, or if it persists for quite a long time, you should contact an otolaryngologist. An examination to determine the nature of the occurrence of such a phenomenon includes the following procedures:
- analysis of patient complaints;
- study of anamnesis;
- examination of the ear cavity using special instruments;
- assessment of hearing acuity.
After carrying out the noted manipulations, the doctor, if necessary, will prescribe a blood test and serological test, examination of the thyroid gland. Instrumental procedures are also performed for diagnostic purposes.
These include pure tone threshold audiometry, Weber test, X-ray of the skull and cervical spine, examination of cerebral vessels, computed tomography using contrast.
Common Causes
The brain perceives irritation of the nerve cells of the inner ear as an extraneous sound.
Stress, strong emotional tension, especially when there is adrenaline in the blood. The ears are blocked, a hum is heard.
Fatigue, depression, and neurosis temporarily reduce hearing acuity. Unclear consciousness, confusion of thoughts. To prevent the development of pathology, you need to rest, get enough sleep, and adjust your daily routine.
Other causes of tinnitus.
Sulfur plug is the cause of extraneous hum and tinnitus. Popular home methods for getting rid of a blockage in the ear canal are presented in the corresponding section of this article.
The habit of listening to loud music reduces hearing acuity, one of the causes of ringing in the ears.
Sharp fluctuations in atmospheric pressure cause tinnitus.
Changes in blood pressure are the cause of extraneous noise, hum, and ringing.
Poisoning and allergies cause whistling and squeaking in the hearing organs.
Deficiency of vitamins B3 and E, potassium and manganese is a possible cause of dizziness and tinnitus.
Taking aspirin, chymidine, gentamicin for a long time is a source of tinnitus.
Elimination methods
To begin treatment, you need to find out why there is a buzzing in the ear. The method of getting rid of ringing in the ears depends on what disease provoked such a symptom. Treatment is aimed at eliminating the underlying cause.
If such a manifestation was caused by a circulatory disorder in the brain, medications are prescribed to normalize blood flow. For this purpose, drugs such as Nootropil, Piracetam, Cavinton are prescribed.
These drugs accelerate metabolic processes and activate blood flow in the vessels of the brain. To improve the nutrition of brain tissue in case of problems with blood vessels, the drugs Betaserc and Ateroblock are prescribed. When taking them, the excitability of neurons decreases. These medications are taken for a long time.
What pathologies cause noise and pain in the ears?
Tinnitus, accompanied by painful sensations, can occur with inflammation of the structures of the middle ear, when damage concerns the eardrum, middle ear bone or mastoid process of the temporal bone. Also, pain and noise in the ears sometimes indicate penetration of a foreign object into the structure of the organ. Often such objects are insects that can damage the external auditory canal.
It happens that not one, but several internal structures of the ear are damaged, which causes intense pain.
The following pathologies can be identified that can lead to pain and tinnitus:
- An inflammatory process affecting the structures of the middle ear. At the same time, the vessels expand and begin to pulsate, tissue swelling increases, which leads to increased pressure on the eardrum and provokes the appearance of tinnitus. Painful sensations are a response to damage to the cells of the mucous membrane of the middle ear by pathogenic microorganisms.
- Aerootitis is an inflammatory change in the structure of the middle ear that develops against the background of a difference in atmospheric pressure. Extraneous sounds and pain are symptoms indicating damage to the eardrum and ossicles of the middle ear.
- Injury to the eardrum. The severity of the injury can vary from a mild concussion to a violation of its integrity. At the same time, the person will complain about extraneous noise. In addition, bleeding from the ear is often observed.
- Mastoiditis is an inflammation of the mastoid process of the temporal bone. The pain is localized behind the concha of the ear, or in the ear canal itself. The pulsating noise is caused by the transmission of vibrations from the venous sinus to the labyrinth.
- Myringitis is an inflammation of the eardrum, accompanied by pain and tinnitus. Extraneous sounds appear due to the expansion and pulsation of the vessels supplying the eardrum.
- Foreign bodies entering the ear canal. Insects can irritate the eardrum or damage its integrity, which leads to characteristic symptoms.
The ringing problem can only be solved by identifying the source of the problem. One-time congestion and severe noise in the ears can be eliminated by so-called blowing (exhale into a nose pinched with your fingers). This method works when flying in an airplane, climbing mountains or descending below sea level. All other methods of eliminating noise and extraneous sounds, treatment methods are determined only by the disease that provokes the sound effects.
How to treat tinnitus? Drug and manipulative therapy are prescribed only after a clear diagnosis has been made. Self-medication can completely destroy hearing and lead to additional inflammatory processes. For example, otitis media can lead to inflammation of the brain tissue. Therefore, accurate diagnosis is important in order to successfully eliminate the cause and its symptoms. Some common diagnostic cases and their treatment methods for tinnitus:
- wax plug: rinsing to remove excess wax (however, you need to remember that in case of chronic otitis media, the procedure is contraindicated, this can cause an exacerbation);
- external otitis, mesotympanitis: drops as prescribed to calm inflammation (Sofradex, Otipax), antibiotics, painkillers, warming (in acute cases of suppuration, the eardrum is pierced to remove pus);
- pathologies of cerebral vessels: Cavinton, Betasecr, Cinnarizine, and other vascular drugs are prescribed;
- stabilization of blood pressure in case of noise in the ears and head associated with surges in blood pressure (drugs are prescribed by the attending physician);
- traumatic or chemical injuries, damage to the hearing aid (use of aggressive drugs in the treatment of other diseases) are almost not subject to therapy;
- psychosomatic sound symptoms are treated exclusively under the supervision of a psychiatrist and neurologist.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies for the treatment of tinnitus can be divided into those that are aimed at the hearing aid itself, and those that are taken orally. Again, it must be repeated that time-tested grandmother’s remedies can be used only with the consent of the doctor. For example, in case of acute otitis media, you should not instill hydrogen peroxide, and in case of arrhythmia, you should not drink untested decoctions that change blood pressure (you can calculate the required dosage in medications). However, some recipes deserve attention:
- The sulfur plug can be dissolved with oil drops. Regular olive oil is suitable, which should be dripped warm overnight into the problem ear and covered with a cotton swab. In the morning, use a syringe without a needle to rinse with water (you need to carefully adjust the pressure so as not to damage the eardrum).
- For atherosclerotic murmurs, take infusions of rowan bark, clover, and lemon balm. Recipes can be found online in specialized forums. The main thing is that there is no allergy to these herbs.
- For acute headaches and tinnitus caused by overwork, compresses should be made: 2 tablespoons of ammonia per 0.5 liter of water, put a cloth soaked in the solution on the forehead for forty minutes. Alcohol solutions for tinnitus should be used very carefully; they can damage the eardrum.
The main complication to be wary of with constant tinnitus is possible deafness. Moreover, it is not the extraneous sounds themselves that lead to it, but the diseases of which they are symptoms. Therefore, timely accurate diagnosis and treatment are absolutely necessary. In addition, extraneous sound irritates the nervous system, leading to insomnia, stress, and loss of performance. memory disorders.
Preventing ringing and tinnitus consists of two key factors. The first is to observe sound ecology: do not listen to music through headphones at maximum volume, use earplugs in noisy workplaces, keep the ear canals clean, avoid loud sounds that damage the eardrum.
How to get rid of noise in the right ear? To get rid of this problem, you must first find out what caused the noise in the ear.
It is necessary to undergo a set of diagnostic measures, including:
- Visit to an otorhinolaryngologist;
- Vascular ultrasound;
- X-ray of the skull and upper parts of the spinal column;
- Computed tomography of the skull.
After the examinations, the specialist will be able to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment.
Methods for preventing diseases that cause tinnitus are available to anyone. To do this, remember the following precautions:
- Cleaning the ear canal from accumulations of sulfur must be done regularly, using cotton swabs without fanaticism;
- Do not use sharp or hard objects to clean the ear, which can perforate the membrane or disrupt the integrity of the mucous membrane;
- Eliminate aspirin from regular use; it has already been proven to be directly related to the occurrence of noise in the ear.
- Eliminate alcohol and nicotine from consumption - they are pathogens of the nervous system - and the auditory nerve;
- Do not overindulge in fatty foods, as they increase cholesterol levels in the blood, which leads to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques;
- Limit salt intake - it retains fluid in the body, which deforms the inner ear due to a large amount of edema;
- Avoid excessively loud and harsh sounds;
- Take antibiotics only as prescribed by doctors;
- Protect your ears and head from traumatic incidents;
- Protect your head and feet from hypothermia, dress warmly in winter.
Follow these rules to prevent noise phenomena, at the first symptoms of noise, in order to reduce the level of irritation and prevent the development of complications.
Doctor:
Shishkina Olga ✓ Article checked by doctor
What diseases cause tinnitus?
There is noise in the ears due to ENT diseases, damage to the inner ear, to the nerves that transmit impulses to the brain. Eliminating ear ringing requires precise localization of the pathology.
The cause of spasm of the posterior ear artery and extraneous sounds is hypertension, as well as anemia (anemia), low level of hemoglobin in the blood.
In case of anemia, there is ringing or noise in the ears, weakness, dizziness, “floaters” before the eyes.
High blood pressure is the cause of pulsating ear noise. The arteries are narrowed, so there is insufficient supply of oxygenated blood to the brain. Rings from one or both sides in time with the pulse.
There is noise in the ears due to spasm of the blood vessels in the brain.
In Meniere's disease, there is an excess amount of fluid in the inner ear cavity. Rumble, ringing. Increased pressure on the cells of the vestibular apparatus disrupts the sense of balance. It is difficult to stand and sit, dizziness, nausea, poor coordination of movements, cold sweat, decreased blood pressure.
Cholesterol plaques inside the arteries of the brain are dangerous for stroke and intracranial bleeding. Irregularities and turbulence in the blood flow are the causes of tinnitus.
Thyroid diseases associated with iodine deficiency cause ringing, dizziness, and extraneous sounds in the hearing organs.
Disruption of the production of the hormones adrenaline and norepinephrine by the adrenal medulla, which are responsible for increased blood pressure, intense work of the heart muscle, and increased blood glucose levels, is the cause of noise and congestion.
Those suffering from diabetes mellitus experience ringing in the ears and an extraneous hum.
Periodic sounds and hums signal pathology of the vessels of the neck or the vessels of the brain, especially in the absence of injuries and inflammation of the ENT organs.
For example, the cause of tinnitus in osteochondrosis of the cervical vertebrae is compressed arteries, deterioration in the blood supply to the brain.
Labyrinth syndromes
A hum in the right ear or on the left side may appear when:
- Lermoyer's syndrome;
- peripheral tympanogenic labyrinthine syndrome.
Lermoyer's syndrome belongs to the Meniere-like syndromes. The etiology is unknown; researchers consider the most likely cause to be a spasm of the vessels responsible for the blood supply to the structures of the inner ear. The noise appears suddenly and persists from several days to several weeks. Patients describe it as extremely intense - often the noise complaint is dominant among the rest.
The development of peripheral tympanogenic labyrinthine syndrome is associated with exposure to toxins when the patient has acute or chronic purulent inflammatory processes in the middle ear.
The murmur in tympanogenic labyrinthine syndrome disappears if the inflammation is eliminated.
“Background noise” in this pathology is a solvable problem. Timely comprehensive treatment of the underlying disease allows the patient to get rid of all manifestations.
Effective Treatments
Treatment for tinnitus depends on the cause. Tinnitus is not just a noise in the head, but a large collection of social, mental and emotional problems. About 5% of the world's population suffers from chronic tinnitus, which leads to stress, fear, and impaired concentration. Tinnitus itself is not an independent disease, but rather a symptom of another disease or hearing loss.
Tinnitus often occurs with diabetes or kidney disease. When examining a patient, an ENT doctor should pay attention to his general condition, find out whether he is taking medications and, first of all, identify the presence of cerumen plugs that cause noise and ringing in the ears. If tinnitus is caused by age-related changes, there is no cure.
Drug treatment for noise that sometimes occurs in the ears is not indicated in all cases. Tinnitus often appears and disappears suddenly, and if it happens for a short time and once, then doctors say that there is no need to worry. You need to contact a specialist if:
- noise and ringing in the ears is regular;
- discomfort from ringing is significant and interferes with work;
- you know about the disease that causes tinnitus.
There are certain medications that reduce tinnitus, but the results depend on the cause of the discomfort. Tricyclic antidepressants help some, but these medications sometimes cause side effects such as dry mouth, blurred vision, or heart rhythm problems.
List of the most common antibiotics that cause painful tinnitus:
- antimalarial drugs;
- some cancer drugs Vincristine or Mechlorethamine;
- diuretics: Furosemide, Ethacrynic acid, Bumetanide;
- in large doses “Aspirin”;
- some antidepressants;
- antibiotics: Erythromycin, Polymyxin B, Neomycin, Vancomycin.
Folk remedies
To do this, you need to grate 2 small onions on a fine grater, squeeze out the juice through gauze and put 2-3 drops in your ear. The procedure should be repeated 2 times daily until the ringing stops. If the child has a problem, then the onion juice should be diluted with water 1:1.
For this medicine, take 3 tbsp. fresh viburnum, add water and put on fire. After boiling for 5 minutes, drain the water, and add 3 tbsp to the berries mashed with a spoon. l. honey, stirring the mixture thoroughly. Make 2 knots from the bandage, fill them with the prepared mixture and insert them into your ears at night before bed. Repeat the procedure every night until complete recovery.
Pour boiling water over three teaspoons of fresh dill, then leave for 1 hour. You should drink the infusion 100 ml daily 3 times before meals until complete recovery.
The method of treating ear noise depends on the cause that caused it. Often, therapy for this condition is complex and consists of taking a course of medications with metabolic, sedative, vascular and anti-inflammatory effects.
In case of circulatory disorders, drugs that stimulate blood flow through the vessels have a good effect, these are Cavinton, Betahistine and others.
In case of otitis development, the doctor prescribes antibacterial agents taking into account the sensitivity of the microorganism that caused this process, antihistamines designed to relieve swelling and reduce the amount of exudative fluid in the middle ear.
This group includes:
- Promethazine;
- Hydroxyzine;
- Fenkarol.
Nootropic drugs have a good effect on tinnitus:
- Cortexin;
- Phezam;
- Mexidol.
In parallel with drug therapy, the doctor may prescribe a visit to the physiotherapy room, where the following medical procedures can have a good effect:
- Electrophoresis;
- Laser therapy;
- Pneumomassage of the eardrum.
From alternative medicine, we can separately mention anti-stress therapy, hydrotherapy or psychocorrection sessions.
Preventive actions
If there are hearing problems, a person is recommended to:
- avoid noisy places,
- listen to music not at full volume and always without headphones,
- go to bed no later than 11 pm,
- If you feel tired, put things aside and rest for a few minutes,
- stop smoking. Tobacco is one of the causes of oxygen starvation in the body,
- take long walks in the fresh air.
If chronic otitis media or other hearing diseases are to blame, you should take care of the condition of the nose. Often, it is a prolonged runny nose that leads to exacerbation of otitis media. You should not sniffle, as such actions lead to mucus from the nose getting into the middle ear and the development of an inflammatory process. Swelling of nearby tissues develops, compression and narrowing of the lumen of the ear canal occurs.
It is important to pay attention to any changes in your health. There is no need to be embarrassed to come to see a doctor and talk about your concerns. Sometimes the patient's understatement about his problems makes diagnosis difficult.
Remember, noise in the head does not occur on its own. This is not a separate disease and treatment, first of all, should be aimed at eliminating the underlying pathology that led to such consequences.
Age reasons
In old age, the ears ringing due to otosclerosis. In the early stages of the disease, enlargement of the bone in the middle ear reduces the perception of low-frequency sounds. In the later stages – high-frequency range. First, the disease affects one side, then the other.
Age-related destruction of the auditory nerve is the reason why there is noise and ringing in the head.
Insufficient blood circulation in a diseased heart impairs the supply of oxygen, nutrition, and disposal of waste to the internal organs. In old age, this condition is the cause of ringing and noise in the ears.
Prevention
Tinnitus does not require any specific preventive measures. To avoid its occurrence, you only need to:
- follow safety rules when working with toxic substances and heavy metals;
- take medications only as prescribed by your doctor and strictly adhere to the dosage;
- avoid physical and nervous stress;
- completely eliminate or minimize the impact of loud sounds on the ears;
- make sure that water does not get into your ears;
- Clean your ear canals regularly with cotton swabs.
Since a large number of different diseases can cause a buzzing sound in the ears and head, the main preventive recommendation is to regularly undergo a full medical examination.
Folk remedies
- A decoction of lemon balm has a good effect. You need to take a small bunch of fresh or dried lemon balm and fill it with one glass of hot water. After an hour, the broth should be strained and cooled. You need to drink half a glass 2 times a day.
- Traditional medicine recommends using ear drops made from vegetable juice:
- Grate the boiled beets and squeeze out the juice from the resulting mass, instill it 3 times a day, 2 drops;
- Bake a small onion in the oven until half cooked and squeeze out all the juice, instill it 2 times a day, one drop at a time.
- Bay leaf effectively helps fight tinnitus. To make the product, you need to take about ten grams of laurel leaf and pour 50 milliliters of warm sunflower oil into it. The mixture should sit for several hours. Then it can be instilled 3 drops every six hours.
- For noise in the ear, a decoction made from fresh dill works well. To do this, pour boiling water over a small bunch of dill and let it brew for about 2-3 hours. This remedy should be taken half a glass orally thirty minutes before meals.
Melissa has a sedative effect and relieves shortness of breath and tachycardia in case of heart disease. Useful for dizziness, noise in the head, insomnia.
- Brew 1-2 tablespoons of boiling water. lemon balm, leave for an hour, strain.
Take half a glass several times a day.
Melissa is contraindicated in cases of low blood pressure and low heart rate (bradycardia).
Hawthorn infusion is taken if the cause of noise and buzzing in the ears is high blood pressure.
Dill infusion helps with tinnitus:
- Finely chop the seeds, stems, leaves, brew with boiling water, leave for an hour.
Take 1/2 cup half an hour before meals for two months.
Garlic and propolis:
- Finely chop 2-3 cloves of garlic, pour in 2 tbsp. propolis tincture, strain after 5 days.
Rub behind the ears several times a day.
Dandelion:
- In May, collect yellow dandelion flowers.
- Add 2 parts granulated sugar, mix and compact.
- Place in a cool, dark place for 2 days.
- Drain the juice, carefully squeeze out the plant mass, and strain.
Dilute 1 tsp. syrup in 1/4 cup warm water. Take four times a day.
Beetroot to eliminate noise and ringing. Ear drops:
- Boil the beets, grate and squeeze out the juice.
Place 3 drops into the ear canals twice a day.
- Bake the onion in the oven, squeeze out the juice.
Instill 3 drops 2 times a day for a week.
Potatoes, honey:
- Mix finely chopped raw potato particles and a little honey.
Wrap in gauze and place in the ear canal overnight.
Instill 3 drops.
Endolymphatic hydrops
Endolymphatic hydrops refers to an increase in pressure in the endolymphatic system. These include:
- Cochlear passage.
- vestibular sacs.
- Endolymphatic duct.
- Endolymphatic sac.
- Membranous semicircular canals.
Endolymphatic hydrops cannot be isolated as a separate disease. A constant buzzing in the ears associated with it occurs with such pathologies as:
- traumatic damage to the labyrinth;
- chronic purulent otitis media;
- acute sensorineural hearing loss;
- vertebrobasilar insufficiency;
- otosclerosis.
It is worth noting that noise can occur with syphilitic lesions of the temporal bone.
Sulfur plug
The occurrence of a traffic jam is explained by various reasons. The key role, as a rule, is played by an increase in the secretory activity of the glands located in the external auditory canal. The consistency of the sulfur produced and the presence of skin damage are also important. The intensity of secretion depends on many factors - including taking medications, wearing a hearing aid, and frequent use of headphones (especially “vacuum” and “in-ear”).
The presence of wax plug cannot be called a life-threatening condition. In general, many patients may not notice it until water gets into the ear. This happens because:
- the plug does not always completely block the ear canal;
- water entering the ear closes the remaining free lumen of the ear canal;
- When the plug comes into contact with water, it swells and clogs the ear canal.
Traffic jams on both sides are rare, so if you suddenly have noise in your ears, you should think not only about this reason for the “background sound”. However, when the noise is one-sided - for example, buzzing in the right ear, and immediately before the onset of the symptom, liquid entered the ear canal - there is a high probability of detecting an accumulation of earwax.
In the presence of a traffic jam, not only a subjective sound occurs, but also autophony.
Earwax is a common cause of decreased hearing acuity and tinnitus. Under the influence of moisture after a shower or diving, it swells and causes congestion.
To prevent and remove sulfur, instill 3% hydrogen peroxide, 1 drop, several times a day. Soon lumps of sulfur come out.
Using Remo-Vax ear drops 2-3 times a month softens, moisturizes the ear canal, and removes wax. The A-cerumen solution cleanses the ear canal of wax plugs.
Old sulfur is softened by instilling a mixture of sunflower oil heated to 37C and 3% hydrogen peroxide.
The wax plug is removed with a heating pad - lie on it with your stuffy ear. The heat softens the plug and it frees the ear canal.
Dense, old wax plugs are removed in a medical facility.
Why is there a buzzing in the ear and how to get rid of extraneous sounds and hum?
A fairly common situation: the patient has a buzzing in the ear. The patient, as well as the treating specialist, in such circumstances will be primarily interested in: why this happens and what to do to eliminate the manifestations that have arisen. First of all, you need to understand that noise is created inside the body.
In this case, the patient can hear not only a hum, but also other irritating sounds: humming, whistling, hissing, squeaking, clicking, etc. in both the left and right ears. Even in the absence of pain and other aggravating factors, a patient who is faced with the problem in question must definitely consult a doctor. The specialist will use the necessary diagnostic methods, determine the causes of third-party sounds and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Loud noises on the right
Noise in the ear can appear on either side, it does not need to be on the right, it often occurs in both ears at the same time. This phenomenon is not always a consequence of pathologies. This annoying manifestation occurs due to the huge number of hair cells located in the inner ear, and their synchronous activity does not cause discomfort. Failure and pain occur as a result of erratic flow of electrical impulses into the brain.
On the right side, strong noise in the ear is a consequence of:
- Right-sided otitis - discharge and fluid fill the middle ear, creating pressure on the eardrum, which leads to noise effects;
- Acute tubo-otitis - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the Eustachian tube simultaneously with the eardrum; this complication causes severe pain and a feeling of congestion;
- Meniere's disease is an inflammation of the inner ear with fluid accumulation. The disease is complicated by poor circulation due to compression of the blood arteries, which results in decreased hearing, dizziness and loss of balance;
- Abuse of a certain type of antibacterial drugs, which leads to an ototoxic effect and noise in the ear on the right side of the head;
- Other reasons - cerumen plug, foreign body, malignant and benign formations, injuries, bruises and other problems on the right side of the head;
- Cardiovascular problems.
Noises come in different forms and appear as:
- Pulsations, for example, with otitis media, Meniere's disease, arterial aneurysm, the appearance of a tumor, eustachitis;
- Clicking sounds, the soft palate and middle ear contract sharply and actively by clicking;
- Simple sounds - hissing, clicking, whistling, buzzing;
- Complex - the sound of music and voices, which can sometimes indicate mental disorders.
All these phenomena cause unbearable suffering to the patient, worsening hearing abilities, providing insomnia, irritation and other neurotic complications.
The appearance of a strong sound effect is an undeniable reason to visit a doctor, who will conduct the necessary research and, based on the results obtained, prescribe effective therapy.
Meniere's disease
Meniere's disease belongs to the pathologies of the inner ear and is rare - according to statistical studies, there are from 2 to 20 cases per 100,000 population.
At the same time, the disease has a high socio-economic significance, since it usually begins at working age (from 30 to 50 years) and, if affected bilaterally, can lead to severe impairments up to and including disability of the patient. The exact etiology of Meniere's disease is unknown. It has been established that infectious diseases, in particular ARVI, as well as neuro-emotional stress can be provoking factors. Various theories have been proposed, the study of which is still ongoing. Ear buzzing in Meniere's disease has the following features:
- At first one-sided, it later becomes two-sided.
- Intensifies before and during an attack of dizziness, can be considered as a “harbinger”.
- In the initial stage it appears periodically.
During the height of the disease, ringing in the ears becomes a constant symptom.
Endolymphatic hydrops is important in the pathogenesis of Meniere's disease. The intensity of the hum that the patient notes may vary, but the possibility of debilitating constant noise cannot be ruled out.
If the cause of ear noise is atherosclerosis
For atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels, the following composition helps relieve noise or congestion:
- Brew 0.5 liters of boiling water and 200 g of rowan bark, simmer for 2 hours in a water bath, let cool.
Take 2-3 tbsp. half an hour before meals. Treat in courses of 1 month 2-3 times a year.
If atherosclerosis is accompanied by headaches and tinnitus, prepare a clover infusion:
- Brew 1.5 cups of boiling water 2 tbsp. clover, insist, do not remove the petals.
Take 1/2 cup of strained infusion half an hour before breakfast. Before lunch, take the next 1/2 glass. An hour or two before bedtime, squeeze out the petals, strain and drink the last 1/2 glass. Treat decreased hearing acuity for 1-2 months.
Diagnostics and treatment methods
First of all, the patient should contact an otolaryngologist (ENT) and determine the cause of extraneous sounds. Among the diagnostic measures, the following procedures are often used:
- X-ray of the cervical spine and brain;
- Dopplerography of cerebral vessels;
- ultrasound examination of blood vessels;
- rheoencephalography (REG) - allows you to determine the elasticity and tone of blood vessels by influencing them with weak high-frequency currents.
The treatment order is determined in accordance with the identified disorders.
If necessary, medications are prescribed to improve cerebral circulation. Neurometabolic stimulants that improve memory and concentration may be recommended. Various physiotherapeutic procedures are used.
Respond in a timely manner to uncharacteristic changes in your body’s condition, follow your doctor’s recommendations and be healthy!
Possible complications
The types of complications and consequences of noise phenomena depend on the causes of their occurrence, but they have a bad effect on health and pose a great threat to a full life.
Right-sided noise disrupts a person’s mental state, causing headaches, disrupting night’s rest, and as a result the person becomes distracted, irritable, and restless. All these reasons generally lead the patient to a depressive state.
If you refuse the help of a specialist, a person with similar symptoms risks becoming disabled - partially or completely losing hearing, and an infection that affects the ear can spread to neighboring organs and the brain. If the cause of the noise is a tumor, then the situation generally ends in death.
- Subchondral endplate sclerosis what does it mean?
- What does the heart on the tonometer mean - Pressure and everything about it