Problems with the vestibular apparatus are known to almost every person. Frequent dizziness and nausea in transport most often occur due to the high sensitivity of the organ. But sometimes they can indicate that the patient has a serious illness. Let’s just now try to find out what ailments a disordered vestibular apparatus can “please” us with. Disorders, their treatment with conventional drugs and alternative medicine, the main symptoms and signs - all this is described in the article below.
Vestibular apparatus: what is it?
The proper functioning of this organ is very important to ensure normal human functioning. Any disorder of the vestibular apparatus often leads to loss of balance and poor orientation when performing any tasks. The symptoms are the following: a person cannot walk along a straight line, perform precise movements, in especially severe cases it is even difficult for him to get up from the sofa or have lunch without assistance. He suffers from vomiting, nausea, fainting, high blood pressure, sweating, as well as problems with his eyes, breathing and heart rate.
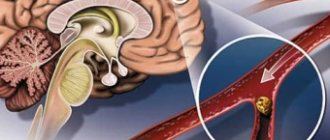
The vestibular apparatus is located in the inner ear. It consists of endolymph, the jelly-like capsules of the semicircular canal and otoliths included in it, as well as a cluster of ciliated cells. But the vestibular center itself is located in the brain of the head: it is here that information about the position of the body, the force of pressure in the organ, data from the visual organ and receptors located in the limbs is collected. Failure in the operation of at least one of the links provokes a violation of the vestibular apparatus. Symptoms may appear immediately in the form of nausea and dizziness.
Symptoms of the disease
Violation of the proper functionality of the organ is associated with symptoms such as: Direct:
- Dizziness.
- Nystagmus (oscillatory eye movements).
Related:
- Nausea accompanied by a gag reflex.
- Pallor or redness of the skin of some areas of the face.
- Loss of support.
- Increased sweating.
- Impaired movement coordination.
- Reduced blood pressure.
- Changes in breathing and heart rates.
The signs of this disorder are variable; they usually arise spontaneously, in most cases they have a paroxysmal appearance. An attack can be triggered at any time by: a strong smell, a loud sound, a change in weather conditions, and so on.
Vestibular neuritis
All diseases of the system are accompanied by loss of orientation, coordination, and headaches. Symptoms can be caused by various diseases. One of the most common is vestibular neuritis. It is diagnosed in patients who lead different lifestyles, in people of all ages and areas of activity. It is most often provoked by the herpes virus and the diseases caused by it - shingles and chicken pox. At first, a person feels dizzy with even the slightest movement. Then he experiences involuntary movements of the eyeballs, vomiting, and nausea.
Such disorders of the vestibular system can lead to serious injuries. Treatment is prescribed only by an experienced doctor - there should be no initiative on your part. If the cause is a herpes bacterium, the doctor prescribes a medicine for the virus: Cycloferon or Valtrex. He also selects anticholinergic drugs, antihistamines and benzodiazepines, which stop attacks of vomiting and dizziness. Doctors also recommend vestibular exercises, the purpose of which is to restore vision and normal functioning of the inner ear.
BPPV
The abbreviation of this dangerous disease stands for: benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. This is another disorder of the vestibular apparatus, the treatment of which consists not only of taking medications, but also special gymnastics. The purpose of physical exercise is to move particles to another part of the ear that irritate the ciliated cells. Most often, BPPV is observed in old age, after severe head trauma, and also in people who have undergone surgery. In addition, it is caused by violations of the hydromechanical principles of the vestibular system and pathology of the inner ear.
The main symptom is dizziness. The attacks are most often short-lived: from a few seconds to five minutes. They occur against the background of changes in body position and sudden jerks of the head. Sometimes they are accompanied by involuntary circling of the eyes - it seems that the person is watching an object moving in a circle. If the case is severe and the attacks are persistent, then the patient is advised to agree to surgery.
Characteristic features of the phenomenon
Vestibular neuritis, also known as acute peripheral vestibulopathy, involves selective damage to the vestibular nerve, occurring against a background of complete well-being. The disease occurs equally often in both women and men.
Characteristic features of this condition are sudden and severe dizziness, which intensifies when trying to change the position of the body, loss of coordination and balance, and a feeling of one’s own body rotating in space.
Typically, vestibular neuronitis is diagnosed in patients aged 30 to 60 years.
There are two forms of pathology – acute and chronic. The first of them is not too dangerous for human health: the symptoms of the disease disappear on their own, without treatment, within six months. As for the chronic form, its peculiarity is the persistence of specific symptoms throughout life, and treatment has no effect.
Inflammation of the vestibular nerve causes the patient to suddenly experience a prolonged attack of dizziness. It does not go away within a few hours, and unsteadiness of gait persists for 3-4 days.
Inflammation of the vestibular nerve does not pose a threat to human life. The prognosis of the disease in most cases is favorable, since it does not cause severe complications.
The structure of the vestibular apparatus
Half of the patients experience complete restoration of the functions of the affected nerve within a year, while 30% experience only partial restoration. In the remaining 20% of patients, the symptoms of vestibular neuronitis persist, although this condition does not cause an increase in the severity of symptoms.
The most severe consequence of the pathology is its relapse: in this case, a healthy nerve is also affected. This is observed only in 2% of cases.
The human vestibular system is located in the temporal bone and is represented by the labyrinth of the inner ear - various receptors, calcareous formations (otoliths) that respond to the movement of endolymph. When this fluid “splashes” as the body and head move, it displaces the otoliths, which, in turn, irritate the nerve receptors.
Under the influence of a number of factors, failures may occur in the coordinated operation of the labyrinth system. The most common disorder of the vestibular apparatus is vestibular neuritis (neuronitis) - a lesion of the vestibular nerve, often of infectious etiology, manifested by systemic dizziness, nausea and other symptoms. As a rule, with this disease the upper branch of the nerve is affected, and occasionally pathology of its lower branch is observed.
Vestibular neuritis can occur in people of any age, regardless of their type of activity and lifestyle. However, this disease of the vestibular apparatus is registered at the age of 30-60 years more often, while women and men suffer from the disease with equal frequency. The clinic of vestibular neuritis was first described by E. Ruttin in 1909, but the term was proposed only in 1949 by C. Hallpike.
Meniere's disease
The cause of the disease is an increase in the amount of fluid in one of the structures of the inner ear, the so-called labyrinth, as well as the accompanying increased pressure in this area. The problem can be provoked by congenital disorders of the structure of the auditory organ, allergic reactions, viral infections, vascular pathologies, metabolic and endocrine diseases.
A patient diagnosed with Meniere's disease complains of vomiting, nausea, and prolonged dizziness. The latter occur for no apparent reason and are often accompanied by noise and ringing in the ears. When the disease is advanced, in especially severe forms, a person loses balance and has impaired coordination of movements. Hearing acuity gradually decreases. In some cases, complete deafness becomes a consequence of this disorder of the vestibular apparatus: treatment must be effective and professional. Doctors often prescribe antihistamines, hormonal drugs, and diuretics to patients. They alleviate the patient’s condition and normalize the volume of fluid in the ear labyrinth.
Clinical picture
Vestibular neuronitis manifests itself in symptoms that do not allow an unambiguous diagnosis of this pathology. Its symptoms are similar to such phenomena as ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. Meniere's disease.
The main distinctive manifestation of the pathology is paroxysmal, prolonged dizziness, accompanied by nausea and vomiting. loss of balance. At the same time, the patient has an unusual feeling as if his body and objects around are rotating in space.
The severity of characteristic symptoms increases with rotation of the torso and head, but decreases with concentration of gaze on one point.
Other manifestations of pathology are expressed as follows:
- Coordination disorder;
- Inaccuracy of movements: the patient has difficulty fastening buttons, writing, holding cutlery in his hands and working with them;
- Involuntary eye movements, which are usually directed towards the side on which the undamaged nerve is located;
- Instability of the patient in a position in which his arms are extended forward and his legs are connected. In this position, the person usually deviates to the side on which the affected nerve is located, or even falls.
Dizziness may not go away for several hours or days, involuntary eye movements may not go away for about 4 days. A few days after the attack, the person notices a significant improvement in his condition, although no therapeutic measures were taken.
Since vestibular neuritis is characterized by damage to only one nerve – the vestibular one, the patient’s hearing does not deteriorate. Ringing in the ears and acute pain indicate the presence of diseases of the hearing system.
Also, with this condition, there is no weakness in the limbs, speech impairment, or severe headaches.
Intoxication
Another cause of vestibular disorders. Various medications, industrial and household chemicals have a negative effect on the entire nervous system, including the apparatus responsible for coordination and balance. If the toxin is very aggressive, it can disrupt the function of any nerve that communicates between the brain and the inner ear. At the same time, the person constantly complains of attacks of vomiting and severe dizziness - they are usually tied to the time of taking a poisonous drug or using a harmful drug. Double vision and clouding of consciousness may occur.
How to treat a vestibular disorder caused by intoxication? This is decided by the doctor depending on the type of toxin and the strength of its effect. First of all, they prescribe cleansing the body with the help of droppers, and prescribe a strict diet and daily routine. Remember: intoxication is the most dangerous cause of vestibular disorders. It not only causes complete hearing loss, but can also be fatal. If at least one symptom appears, you should immediately call an ambulance.
What not to do
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QzNFDi5jiw8
Some actions that can slow down healing and prolong symptoms are prohibited. So, with this pathology you cannot:
- continue to work, allow physical or mental overload;
- eat plenty of fatty, sweet, fried foods;
- do not follow a daily and sleep schedule;
- try to play sports, go to sports training immediately after the clinic of the disease subsides;
- within 1-2 months - play volleyball, badminton.
- How to treat inflammation of the sciatic nerve - drug treatment
- Mustang 2000 laser device purpose
Other causes of violations
Problems arise most often in old age due to vertebrobasilar insufficiency. They are also provoked by diseases of the ear, nose and throat: otosclerosis, otitis, Eustachian tube dysfunction, tonsillitis and even ordinary cerumen. Other causes of vestibular disorders: traumatic brain injury, tumors, epilepsy, migraine, blockage of the internal auditory artery, craniovertebral anomaly, etc.
As you can see, treatment should not be aimed at the vestibular apparatus, but at the pathology or disease that leads to unpleasant consequences. At the first sign of a problem, immediately contact an otolaryngologist. In addition to a routine examination, the doctor may prescribe an ultrasound examination to diagnose the condition of the vertebral arteries, brain tomography for pathological changes, as well as audiometry, which determines the degree of hearing sensitivity. These methods help to uncover the causes of violations. Although, it should be noted that in a third of patients the primary source of diseases of the vestibular zone remains undetected.
Diagnosis of ataxia
First of all, the neurologist examines the patient. The doctor asks the patient to monitor the movements of the hammer in front of the eyes to detect nystagmus.
Then a test is carried out using the Romberg pose. In a standing position, a person keeps his feet together and extends his arms forward, fingers spread out. With static ataxia, the patient loses balance in this position.
Special tests are carried out for coordination of movements. The doctor asks the patient, with his eyes closed, to touch the tip of his nose with his finger. In this case, the accuracy of the hit is assessed.
Additionally, brain function is examined. An encephalogram, echoencephalogram, and MRI are prescribed.
If a neurologist suspects that ataxia is associated with vestibular disorders, then after consulting an otolaryngologist, the following examinations are prescribed:
- vestibulometry;
- MRI or CT scan of the inner ear;
- audiometry (for complaints of hearing loss);
- electrocochleography (examination of the cochlea).
You will be referred for a consultation with an ENT doctor to determine your hearing status. Sometimes a special study is carried out for this - audiography.
If symptoms persist long enough, increase in severity, and do not go away despite treatment, there is a risk that they are caused by other, more serious diseases: stroke, migraine, brain tumor, traumatic brain injury. In this case, the neurologist may prescribe additional studies.
Making a diagnosis of vestibular neuritis is a difficult task. To confirm that the patient actually has this pathology, the specialist needs to conduct a thorough history taking, visual examination, as well as specific examinations:
- Testing of auditory functions;
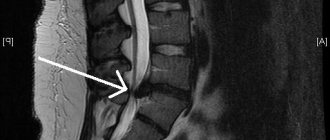
- MRI and CT scan of the brain to differentiate conditions from cerebrovascular accidents;
Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain
- Caloric test, which consists of giving the patient a slight rotation and detecting how pronounced the reflexes are;
- Checking the functions of the inner ear;
- Test of a person's stability in a standing position with arms extended to the sides.
Differential diagnostics such as MRI can be performed using contrast agents.
Diagnosis is carried out in a medical center. The disease is diagnosed after examination by a doctor. The main symptoms that the doctor relies on are long-term dizziness, a recent history of an infectious disease, and rhythmic movement of the eyeballs.
The fact is that the symptoms of vestibular neuritis resemble the symptoms of a brainstem stroke, and therefore, in order to make sure that the diagnosis is correct, doctors send the patient for a CT scan (computed tomography). The caloric test method is often used to confirm or deny the diagnosis of vestibular neuritis.
The diagnosis is based on the characteristic clinical picture of vestibular neuritis, which is dominated by acute, prolonged dizziness, supplemented by nausea and nystagmus, which indicates existing dysfunction of the labyrinth. Special tests and physical tests are mandatory, for example, a caloric test, assessment of vestibular potentials, and audiometry. Indirectly, the diagnosis of vestibular neuritis can be confirmed by MRI of the brain with contrast. Read more about the symptoms and treatment of labyrinthitis
The disease should be differentiated from labyrinthitis, the consequences of barotrauma, and traumatic brain injury, in which some kind of hearing impairment is always observed (with vestibular neuritis there are none). It is also necessary to distinguish the pathology from a stroke (there are other neurological disorders, brain damage on an MRI image), Meniere’s disease (symptoms are supplemented by noise, fullness in the ear, and hearing loss). Also, vestibular disorders can appear with neurosyphilis, which should be taken into account by a specialist when confirming the diagnosis.
Since vestibular syndrome has many causes, its diagnosis is quite difficult. Patients are examined by a neurologist and an ENT doctor. They listen to complaints, collect anamnesis, examine patients and study symptoms in detail. Then specialists conduct a direct standard examination of the hearing organ and determine the neurological status of the patients.
Special medical techniques include:
- Audiometry allows you to accurately determine disorders in the perception of sounds,
- Electronystagmography is a graphical recording of changes in the biopotentials of the eyeball,
- Ophthalmoscopic examination - examination of the fundus using special instruments,
- Magnetic resonance and computed tomography,
- Vestibulometry is carried out to determine the causes of dizziness and assess the severity of disorders.
How to strengthen the vestibular apparatus?
It's easy to do. Parents are obliged to monitor their child from the first days of life. Having discovered vestibular apparatus disorders in childhood, treatment should be focused on sports and physical exercise. The baby should be immediately enrolled in any club where children jump, run, play active games, and swim. Football and basketball, which develop concentration and coordination, as well as gymnastics, which require balance, are very helpful. If the problem appeared in adulthood, then ordinary attractions will help solve it - ride on the carousel. A swing will also come in handy: you need to swing gradually, increasing the amplitude over time.
Physical exercises are also recommended: rotating the head, bending forward and backward, moving the body in a circle. You can walk through a small section of unfamiliar terrain: first with your eyes open, then with your eyes closed. This exercise should be done daily – 6 times. Only after three months of regular training will you achieve the first results. By the way, it is necessary to strengthen the vestibular apparatus not only for people with disorders, but also for all healthy individuals - for prevention.
How do I know if I have a balance disorder?
Everyone experiences dizziness from time to time, but the term “dizziness” means a different physiological state for each person. For some people, dizziness may be a fleeting sensation of spinning, while for others it is intense and lasts a long time.
To help you decide whether you should seek medical help for your dizziness, ask yourself the following questions. If you answer yes to any of these questions, talk to your doctor.
- Do I feel insecure
- I feel like the room is spinning around me
- Do I feel like I'm moving when I know I'm sitting or standing?
- Do I feel like I'll lose my balance and fall?
- Do I have a feeling of falling
- Do I feel like I might faint?
- Do I see objects "blurry"
- Do I have periods of disorientation in time and place?
Folk remedies
Regular foods and herbs from the pharmacy help overcome any disorder of the vestibular system. Treatment with folk remedies is aimed at dizziness, since this is what patients suffer from in most cases. Hawthorn tincture is recommended - not only internally, but also externally. You can use it to massage your head. For the same purpose, a walnut in the shell is used: in this case, you need to act not on the top of the head, but on the palms, because it is on them that the points responsible for coordination and balance are located.
Infusions of belladonna, clover flowers, parsley seeds, carrot and beet juices will help eliminate disorders of the vestibular apparatus. The treatment is not applicable to pregnant and lactating women - this period is not the best time for experiments. In addition, to get rid of dizziness, you need to enrich your diet with garlic, berries, fruits and vegetables. The fiber that is present in them will cleanse blood vessels of harmful cholesterol and normalize blood pressure. A contrast shower, bathhouse and sauna will ease the patient's condition.
Treatment with decoctions
Some of the best remedies are lemon balm or mint. Fresh leaves (15 g) are poured with half a liter of boiling water, valerian root is added, and simmered for 20 minutes. The mixture is then diluted with a small amount of green tea. The strained and chilled drink should be drunk three times a day - a tablespoon on an empty stomach. For problems with the vestibular system, ginger root is also effective. Grind it into powder and drink a quarter teaspoon three times a day with water.
Oregano also helps. This herb is taken in brewed form - two tablespoons of crushed leaves are poured with boiling water in a thermos and left overnight. In the morning, drink the decoction in four doses.
Herbal mixtures are considered universal folk therapy. It is recommended to use several plants at once for a more effective result. In this case, the drink must be seasoned with honey - it very well helps relieve the discomfort caused by a diseased vestibular apparatus.
Disorders, the treatment of which should be comprehensive, can be easily eliminated if you approach therapy competently and responsibly.