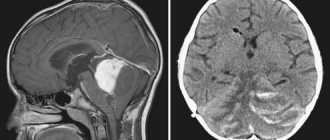
Many people think about the question: “What is a benign brain tumor, symptoms and how long do they live with such a disease?” This disease is an abnormal growth that occurs in the brain. In the process of its development, the formed cells that make up the tissues take part.
A special type of neoplasm is suitable for any type of tissue. For example, a schwannoma is created due to Schwann cells. They form a sheath covering the surface of the nerve; ependyoma is created by the cells lining the ventricle of the brain; meningioma is formed due to the presence of cells that make up the lining of the brain or the tissue surrounding it; adenoma is created due to glandular cells and so on.
There are benign brain tumors that are hereditary:
- Craniopharyngioma chordoma;
- germinoma;
- teratoma;
- dermoid cyst;
- angioma.
Meningioma is a benign neoplasm of the brain characterized by recurrence. Despite its removal.
Meningioma often affects the weakened half of people of different ages. The size of the tumor, the speed of development and the location of detection determine the signs of its manifestation, therapy, as well as the consequences that may arise.
A very large number of benign brain tumors changes his intellectual abilities for the worse. These types of tumors do not contain cancer cells. They are characterized by weak growth, but this is not at all reassuring, since as their size increases, other areas of the brain are compressed, which activates swelling, the growth of inflammation of healthy nerve tissue, and also increases the pressure inside the skull.
Very rarely, a process of transformation of a neoplasm into a malignant one occurs. Then the therapy takes on a completely different character.
What is a benign tumor?
The appearance of a tumor is associated with the uncontrolled division of cells in a particular organ where the tumor is localized. Moreover, the cells, unlike healthy ones, do not develop, that is, the functions that are assigned to them are not performed.
On this topic
- Tumors
13 types of brain tumors
- Natalia Sergeevna Pershina
- June 9, 2020
There are benign and malignant tumors. Distinctive features of benign education are:
- growth to a certain stage;
- no germination into organs;
- does not metastasize to other parts of the body.
These two types of neoplasms have common causes of appearance and manifestation.
To determine the type of formation, various methods are used: MRI, CT, biopsy, puncture, etc.
How to identify the disease
Typically, diagnosing benign tumors does not cause difficulties for doctors. The first step is to examine the patient, interview him and collect the necessary medical history. It is very important to find out whether any family members have tumors.
To confirm the suspected diagnosis, the patient may be prescribed the following tests:
- Ultrasound;
- radiography;
- MRI;
- CT.
In diagnosing brain pathology, an examination by an ophthalmologist and examination of the fundus play an important role. This is the only way to distinguish a tumor from other diseases.
If pathological changes in internal organs are suspected, endoscopic examinations are performed. Using a special device, tissue samples are examined and taken for biopsy.
Why does it appear
There are no clear reasons for the formation of tumor formations. There are certain factors that can have a catalyzing effect on tumor development. But in one case it will work, in another - the person will live his whole life without developing pathology.
Hereditary predisposition
This fact is due to the fact that under the influence of unfavorable factors, genes that are passed on to descendants can be modified (improved or degraded). Such an oncogene can appear even after several generations if a certain impact occurs on it. Therefore, if there was a negative impact on the body now, then the consequences may appear in the future in descendants.
Radiation or chemical effects on the body
This may be an unfavorable region of residence with increased radiation levels or professional activities related to working with lead, mercury, or oil
Consequences of past viral and bacteriological diseases
Exposure to the body of bacteria and viruses, especially the brain and central nervous system, can trigger the formation of tumor formation.
Classification
One of the classifications is the division of tumors into primary and secondary. Primary are those that initially arise in the brain. As a rule, they do not metastasize to other parts of the body. Primary tumors can be either malignant or benign.
The appearance of secondary formations in the brain is caused by metastases from malignant formations in other organs (for example, breast). In other words, a brain tumor in such a situation occurs as a consequence of another formation. Secondary formations are always malignant.
Meningioma
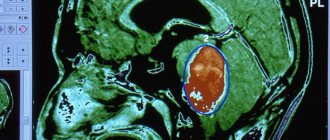
This is one of the common types of benign tumors. The formation is formed from the soft part of the meninges. The tumor is a smooth, dense nodule that is anatomically connected to the soft or hard part of the meninges. Meningioma has a gray-yellow color and sizes from several millimeters to several centimeters.
In most cases, the tumor is benign. The type of tumor is determined by histological examination.
Meningiomas are removed surgically and do not recur. In case of inaccessibility, an operation is performed without opening the skull using a cyber- and gamman knife. After the intervention, chemotherapy and radiation are not required.
Schwannomas
Formed from nerve sheaths. They are whitish nodules enclosed in a capsule. Characterized by hearing loss, trigeminal neuralgia, and dizziness.
Pituitary adenoma
This is a benign formation that causes increased production of certain hormones. So, with an excess of prolactin, infertility occurs, somatotropic hormone - gigantism, thyroid-stimulating hormone - problems with the thyroid gland.
Astrocytoma
It is a benign formation consisting of astrocytic cells that surround the neurons of the brain. It can reach up to 10 cm in diameter. Children are most often affected by the disease. The form of astrocytoma is heterogeneous. Cysts may be found in its structure.
Oligodendroglioma
Formed from neuroglia of the brain. It has a gray-pink color and additional cystic formations in its structure. Located in the white matter of the brain. Most often found in older men.
Ependymoma
It develops from the outer layer of the ventricles of the brain and can be located both on the surface and inside them. The formation also consists of small cysts and necrotic formations. For the most part, ependymoma is a malignant tumor, as it can metastasize. This is due to the close location of the cerebrospinal fluid.
Craniopharyngioma
This is a congenital formation that is formed from embryonic cellular elements of the pituitary duct.
Each type of benign formation under the influence of negative factors can degenerate into a malignant tumor. To prevent severe consequences, timely treatment is required. Observational tactics are not used, since it is unknown at what point the transformation may occur.
Surgery
Modern medicine offers people with this diagnosis many methods for removing benign tumors. The most effective among them is deservedly considered complete excision of the transformed tissue. This way you can prevent further spread of pathological cells. Usually, after such surgery, relapses do not occur. Removal of a benign tumor is carried out using a laser, and the tissue is excised through enucleation.
Another common technique for removing tumors is cryocoagulation. The principle of this procedure is simple: the area affected by the tumor is treated at low temperatures. Modern technology makes it possible to accurately determine the location of the impact, so that only diseased tissues are treated, while healthy structures remain untouched.
Cryocoagulation is most effective in the presence of neoplasms on the following organs:
- shoulder joints;
- spine;
- pelvic bones;
- legs and arms;
- rib cage.
Previously, liquid nitrogen was used for the procedure, which destroyed mutated cells. But today, an innovative device is used for this, which acts on the body more delicately. The use of extremely low procedures has several advantages:
- minimal impact on the body;
- no contraindications;
- minimal damage;
- easy preparatory stage for the procedure;
- preventing relapses.
In general, cryotherapy can easily be used instead of chemotherapy and radiation, which negatively affect the body. After undergoing this procedure, patients do not experience side effects such as nausea, vomiting and excessive hair loss.
Signs
In most cases, many types of tumors are asymptomatic. Moreover, if education is not prone to rapid growth, then a person may not feel its presence for several years. Formations that grow quickly sooner or later begin to make themselves felt. Mostly, patients attribute this to malaise or symptoms of another disease.
You should pay attention to the following symptoms:
- Severe and persistent headaches . Moreover, the pain can be localized in a certain place (in the temple, frontal part, back of the head). This is due to the location of the tumor formation. As it grows, the pain intensifies, as healthy areas of the brain are compressed. Moreover, painkillers do not bring results.
- Impaired coordination of movements. This may be due to both the weakness of the body from debilitating headaches and the impact of the formation on the cerebellum, which is responsible for balance.
- Nausea and vomiting in the absence of gastrointestinal diseases. Symptoms may occur with dizziness and be a sign of increased intracranial pressure.
- Problems with memory and thinking, mood swings.
- Convulsive attacks.
- Depending on the location of the formation, the following may be observed: defects , hearing impairment, numbness of the limbs, and vision problems.
On this topic
- Tumors
11 facts about pituitary microadenoma
- Natalia Sergeevna Pershina
- May 24, 2020
If such symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor for examination.
Also, do not neglect the annual medical examination, as a result of which a pathological condition can be detected in a timely manner.
For large sizes
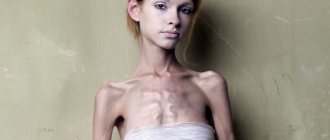
When the tumor reaches a large size, the symptoms become more pronounced. The patient feels heaviness in the stomach, attacks of nausea, and frequent belching occurs. Blood may be found in stool and vomit. Laboratory tests show a decrease in hemoglobin levels. Patients complain of dizziness and general weakness. In this case, weight loss is observed regardless of the presence of a good appetite.
There are more than one hundred varieties of benign neoplasms. Their course and clinical signs can vary greatly. The intensity of symptoms depends on the size and growth rate of the tumor, as well as its location. Bleeding is considered a classic sign of the presence of a neoplasm, especially if it is accompanied by disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made after a series of studies:
- Survey . The doctor asks the patient about the existing symptoms and the duration of the painful condition. If necessary, prescribes tests (general, biochemical, tumor markers, etc.). Although tests cannot determine the presence of a tumor, the data obtained can indicate inflammatory processes in the body, as well as other pathologies that are associated with the tumor.
- MRI is one of the reliable ways to obtain information about a tumor. MRI takes pictures of the brain from different angles. This allows you to determine the location of the formation and its size.
- CT , angiography, craniography, electroencephalography - all these methods allow you to study the tumor in more detail and choose the right method of further treatment.
- A biopsy is the process of obtaining material (tumor cells) to determine whether they are malignant or benign.
Main varieties
The main types of non-epithelial type gastric tumors are:
- Fibroids that form from muscle tissue.
- Neuromas are formed from cells that enter the myelin sheath of nerve fibers.
- Fibroids arising from fatty tissues.
- Lymphangiomas, when tumor cells arise from the walls of the lymph nodes.
- Hemangiomas originating from cells found in lymphatic and blood vessels.
- Mixed variants of nonepithelial neoplasms.
If the appearance of polyps is typical for men, then non-epithelial tumors are more typical for females. All neoplasms of this type have a number of specific features, including clear contours, a smooth surface and a round shape. The growth of a neoplasm in the stomach can occur to quite significant sizes.
Treatment
The most effective way is surgical removal of the formation.
On this topic
- Tumors
Everything you need to know about brain tumor surgery
- Ekaterina Nikolaevna Kislitsyna
- March 26, 2020
The operation can be performed in the following ways:
- Trepanation of the skull. The skull is opened and the tumor is removed.
- Application of ultrasonic waves. With this operation, the impact occurs without opening the skull.
- Endoscopic surgery. It is also carried out without opening the skull using endoscopic instruments.
- Stereotactic radiosurgery . It is one of the effective methods, since direct access to the brain is not required. Gamma and cyberknife are used. The impact is carried out in a targeted manner, which prevents trauma to healthy areas of the brain.
After surgery, radiation therapy is prescribed if necessary. To relieve some symptoms, medications are used: corticosteroids, which relieve swelling, and painkillers.
Consequences and complications
Consequences include:
- growth that puts pressure on healthy areas of the brain. Depending on the location, the pressure exerted can affect some body functions: speech, vision, hearing, coordination of movements. After removal of the formation, the symptoms disappear. In rare cases, problems remain.
- Convulsive conditions, which are also associated with damage to brain tissue.
- Bleeding , which may occur during or after surgery.
- Brain swelling
- Cystic formations that sometimes appear at the site where there was previously a tumor.
- Consequences associated with the operation (headaches, dizziness, nausea).
Almost all benign tumors are treatable.
Pathologies
A benign neoplasm in the brain is characterized by certain risks and pathologies, as a result of which, like any other disease, it requires appropriate therapy, which cannot be delayed. An operation performed at the wrong time can cause compression of certain areas of the brain, which can deform vital or functionally significant tissues. Then the pathologies can be fatal.
The presence of unexpected seizures can be a factor in damage to brain tissue. The operation process may be accompanied by the appearance of bleeding, which has negative signs and pathologies after surgery.
The growth of a tumor can be stopped in various ways. All types of these tumors are amenable to surgery and are therefore safe. Their unpleasant feature is the likelihood of a benign neoplasm changing into a malignant one.
Preventive measures
There is no specific list of preventive measures to prevent the formation of a brain tumor. This is due to the fact that there are no exact reasons provoking the growth of pathological cells.
General recommendations:
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle (walking in the fresh air, exercise or gymnastics).
- Quitting smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Reduce consumption of coffee and energy drinks.
- Normal sleep (8 hours).
- If there is a hereditary predisposition to the disease, then undergo annual examinations.
- Exclusion from the diet of carcinogenic foods.
Following these rules can reduce the risk of developing the disease.
Thus, a benign tumor is a formation of rapidly dividing cells. Distinctive features of benignity are the inability to metastasize and cessation of growth at a certain stage. A tumor of this type does not poison the body, so death does not occur.
Treatment includes surgical removal of the mass, radiation therapy and medication aimed at eliminating symptoms (headache, swelling, blood flow problems, etc.).