Features and mechanism of development
First of all, you need to understand what a benign brain tumor is. There are only 2 types of formations that are localized in the skull:
- benign brain tumor;
- cancer formation.
Both types of formations are characterized by abnormal growth of brain tissue cells. What is the difference? There are several features of a benign tumor:
Slow growing (unlike a malignant brain tumor). Sometimes it may stop growing altogether.- Clear boundaries. It does not affect neighboring tissues and organs (does not metastasize).
- After removal it almost never recurs.
- Very rarely, it can transform into a malignant type of tumor, which is also called brain cancer.
There is a special classification of benign formations. Depending on what tissue the tumor consists of, there are several types:
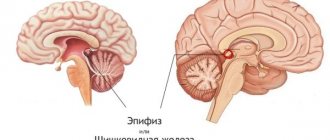
- Meningioma. Formed from the tissues of the spinal cord and brain (its hard shell). Meningiomas are diagnosed most often (about 20% of all head tumors).
- Pituitary tumor. It is the second most common among such formations (15% of cases).
- Schwannoma. This formation consists of cells that cover the brain nerves. They occur in 10% of patients.
- Craniopharyngioma. It consists of pituitary gland cells. Most often it develops in children in a cystic form. It ranks 4th in prevalence (about 3% of cases).
Hemangioblastoma. This formation consists of cerebral vascular tissue. It looks like a cyst. Occurs in 2% of patients.- Papilloma of the choroid plexus. It occurs very rarely, so it has not been studied enough. Appears in children under 3 years of age, disrupting the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
- Cysts. Sometimes dermoid or epidermoid cystic formations arise on the basis of epithelial cells. They are not tumors in the full sense of the word, but are capable of compressing brain structures.
So, a benign brain tumor occurs due to abnormal growth of brain cells, vascular tissue and nerve cells. Such a formation, as a rule, grows slowly, responds well to treatment and does not provoke the appearance of metastases in neighboring organs.
Treatment of tumors
Surgical treatment also does not always help, especially if there is an inoperable type of tumor that has formed in a hard-to-reach area. Removal of a tumor can cause dangerous consequences in the form of involvement of brain tissue in the pathological process and further disruption of the functioning of the central nervous system.
As a rule, pathology can be cured only with the help of radiotherapy (radiation therapy). The tumor formation is exposed to radioactive radiation in the required dosage. In this case, it is possible to achieve maximum survival and stop the uncontrolled growth of pathological cells.
Sometimes a three-stage treatment is carried out: surgical removal of the tumor - taking special medications - radiation exposure. Traditional medicine for brain tumors is ineffective and is applicable only at the first stage of the appearance of the tumor.
Causes, symptoms and consequences
When a brain tumor appears, many people wonder whether it can affect life expectancy, how long they live with it, and what the consequences may be. First you need to figure out why it appears.
There are several reasons for the occurrence of a benign formation in the skull. Among them:
- Hormonal imbalances.
- The action of infections and viruses.
- Pathologies of cerebral vessels.
- Genetic mechanisms.
- Use of mobile communications. The electromagnetic field of phones negatively affects the brain.
- Radioactive exposure. Often this formation is caused by radiation. For example, radiation therapy (radiation) has been used for some diseases of the scalp. The longer the duration of such treatment, the higher the risk of developing a benign tumor.
- Traumatic brain injuries.
- Exposure to chemicals, such as contact with vinyl chloride. This is a special gaseous substance that can be contained in plastic products. Its increased amount in objects used by humans is extremely dangerous.
- Poor nutrition. For example, frequent use of a sugar substitute in food. It contains aspartame (a chemical sweetener), which provokes negative reactions such as brain tumors.
This pathology does not manifest itself in any way at the first stages of development. You can live with it for a long time without even knowing it is there. Only when the size of the brain tumor increases, symptoms appear due to compression of its structures. The presence of pathology can be assumed based on several signs:
- bursting pain in the head (increased by coughing, nodding the head);
- frequent dizziness;
- symptoms of gastrointestinal disorder;
- epileptic seizures;
- convulsions;
- mental disorders;
- personality change;
- presence of hallucinations;
- disturbance of taste, hearing, color sensations;
- lack of coordination;
- memory problems;
- lethargy, apathy, weakness;
- numbness in the arms or legs;
- facial nerve paralysis.
One such symptom or several at once may appear. In any case, consultation with an experienced doctor is necessary, since the pathology can lead to serious consequences. What is the danger of the disease? If treatment is delayed or absent, the following consequences are possible:
- irreversible damage to brain tissue due to compression of brain structures;
- bleeding during or after surgery;
- possible postoperative complications;
- sometimes a transformation of a benign tumor into a malignant cancer occurs. Then the patient's life expectancy decreases sharply.
Specifics of treatment
Many people are interested in how long do patients with benign tumors in the brain live? This depends on the stage at which the pathology is diagnosed, as well as on the effectiveness of its treatment.
Examination methods
If a brain tumor is detected, treatment depends on the results of the study. The following main methods are distinguished:
- Neurological examination. In this case, a fundus examination is mandatory. The condition of its vessels determines the presence of intracranial pressure. Vision, hearing, smell and vestibular functions are also tested.
- Interviewing the patient to identify mental disorders.
- Electroencephalography. It allows you to identify changes in the brain (general and local).
- Radiography. This is a study of the brain using X-rays.
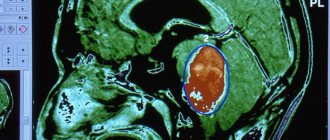
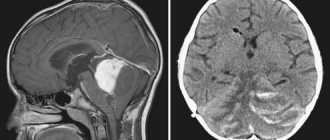
- Computer or magnetic resonance imaging. This is how the nature, location and size of the tumor are revealed.
- Study of cerebrospinal fluid in laboratory conditions.
Choice of therapy
If the diagnosis is confirmed, appropriate therapy is prescribed. For a benign tumor, treatment most often involves its removal. Chemotherapy is not used (unlike with cancer), but drug treatment can be effective.
Let's take a closer look at the main methods of therapy:
- Surgical intervention. For brain tumors, surgery is the most common treatment option. In this case, the skull is opened and the formation is removed using a scalpel. In this case, complications may occur in the form of bleeding or damage to brain structures.
- Radiosurgical. This is the removal of a formation using radio rays without opening the skull (so-called knives: cyber- or gamma-).
- Drug treatment. Corticosteroids (Dexamethasone) are used to stop the growth and shrink the tumor.
As an auxiliary therapy, as well as to prevent the formation of tumors, a special diet is prescribed. Proper nutrition can reduce the risk of relapse, as well as improve the overall physical and mental condition of the body. At the same time, plant foods should predominate in a person’s diet, but the consumption of protein products should be limited. There is a list of products that can stop tumor growth:
- Cabbage. This product deactivates estrogen, the excess of which provokes the appearance of tumors.
- Soy. Soy-based products (soy sauce, tofu, miso) contain substances that have antitumor effects.
- Onion or garlic. These are natural antioxidants that activate the functions of white blood cells that destroy tumor cells.
- Green tea. It prevents tumor cells from dividing.
- Citrus.
- Nuts.
- Seaweed.
- Tomatoes. They have antioxidant abilities.
If you eat a healthy and balanced diet, you can reduce the risk of tumors to a minimum. You should also exclude from the menu foods that negatively affect the nervous system, which contributes to sleep disturbances and the functioning of the nervous system. To do this, you should give up coffee, energy drinks, alcohol, and also do not abuse sweeteners.
So, benign brain tumors are neoplasms localized in the skull that do not metastasize, have clear boundaries and are characterized by slow growth (compared to cancerous tumors).
However, despite their lower danger to the body compared to cancer, such neoplasms also require immediate treatment. If you experience frequent bursting headaches, which are the main symptom of the pathology, you should consult a doctor.
Source: oinsulte.ru
How long do people live with a low-grade brain tumor?
Most often in medicine, the concept of a 5-year survival period differs. A favorable outcome after surgery can be considered if the patient has overcome this indicator. But there are cases when patients lived much longer. When establishing a life period, each statistics is based on the growth of a neoplasm in the human body.
Stages of development of a malignant tumor:
- The first stage is a consultation with a specialist at the first symptoms of cancer (nausea, headaches, gait disturbances), which will provide a chance for surgical intervention to remove the tumor completely or partially.
- The second stage, when you see a doctor, the prognosis is not very positive: the affected cells divide and deform neighboring healthy tissues. The operation may no longer be relevant. The characteristics of the body and the age of the patient matter. After 65 years, in operated patients who have undergone chemical and radiation therapy, the survival rate immediately decreases.
- The third stage is an inoperable neoplasm. Survival rate is about 4 years. The tumor is growing rapidly. The patient loses activity and stops fighting the disease. In most cases, after starting therapy, a person lives for about 2-3 months.
- Stage four – the chances of a positive prognosis are almost zero. In this situation, everything depends on the support of relatives and the wishes of the patient himself. In the presence of metastases affecting other organs, life expectancy can be determined by two months or, in exceptional cases, years (only 5% of patients cross this limit).
A low-quality tumor is a brain cancer in which survival depends on the stage of the disease and the timeliness and correctness of treatment; it is diagnosed in 10-15% of patients. At the 4th stage, the only chance to prolong the patient’s life is a cyber knife, irradiation with gamma rays. If it is not possible to completely destroy pathological cells, then it is possible to at least stop their spread.
Medicine has not yet created methods that will prevent the development of cancer, but everyone can minimize the risk of developing the disease by leading a healthy lifestyle, eating right, avoiding exposure to radiation and choosing environmentally friendly places to live with favorable climate conditions.
Causes of tumor formation
Any tumor arises and grows due to the spontaneous growth of abnormal cells resulting from mutation. If the tumor is benign, their growth and division gradually slow down, and they may remain in a “sleep state” for a long period. Malignant cells are characterized by constant activity, a high rate of division and gradual germination into tissues located nearby.
It is impossible to say for sure what triggers the growth of a tumor, but doctors note a number of factors that contribute to their division:
- genetic predisposition. A brain tumor can be diagnosed in a newborn, in rare cases - in an embryo during the prenatal period;
- exposure to electromagnetic waves (including mobile communications);
- infrared and ionizing radiation;
- GMOs in consumed products;
- radioactive exposure is the most common cause of tumors according to medical observations;
- prolonged contact with toxic chemicals: contact with mercury, lead, arsenic, etc.;
- human papillomatosis viruses.
Symptoms of a benign brain tumor
The appearance of a tumor in the brain, regardless of the nature of the formation, manifests itself in different ways. A disruption of the normal structure occurs in any organ during the process of renewal, during the process of cell division. In the body, during the process of division, abnormal cells are destroyed by the immune system, but in the brain everything happens a little differently: it is surrounded by a cellular barrier that does not allow immune cells to enter. Abnormal cells begin to divide unhindered. That is why the symptoms of a tumor appear only when it begins to compress adjacent tissues or its waste products begin to enter the blood.
The gradual growth of cells puts pressure (pressure) on healthy brain cells nearby. Depending on the location, changes occur in one or another area responsible for certain functions - speech, memory, hearing, etc. It is precisely by these signs that in many cases, before research is carried out, it is possible to suggest even the area of the brain in which the tumor has formed.
The initial stage, as a rule, is asymptomatic, which hinders its early diagnosis. The patient may experience minor ailments that are characteristic of a number of other neurological diseases. Primary symptoms include:
- headaches that get worse at night or with exercise;
- decreased level of intelligence, memory problems;
- speech disorders (slurred pronunciation, change in tempo);
- hearing disorders;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- absent-minded attention;
- blurred vision;
- paresis of the face or fingers;
- mental disorders;
- nausea, causing vomiting, independent of food intake;
- muscle spasms, cramps;
- periodic numbness of the limbs;
- drowsiness, fatigue.
All these symptoms may also apply to other diseases, but if their manifestation becomes more frequent and intensified, leading to a deterioration in the general condition, you should consult a doctor. A correct diagnosis and timely treatment provide a chance for a speedy recovery and more favorable prognosis.
Headache with brain metastases
Headache with metastases in the brain occurs due to compression by the tumor node and the accumulating fluid of blood vessels, meninges and other connective tissue structures in which there are pain receptors.
Since the tumor constantly presses on the areas bordering it, headaches with metastases to the brain are constant. They do not go away after taking painkillers and vasodilators, and after sleep the headache usually hurts even more.
While the metastases are small and there are not too many of them, patients’ headaches may decrease during the day and even disappear for a while. This happens when a person is in an upright position and moving. In this case, the fluid accumulated overnight in the ventricles of the brain gradually flows into the spinal canal, intracranial pressure decreases and the patient experiences temporary relief.
Types of benign formations
Nerve cells, blood vessels and brain tissue are involved in the formation of benign formations in the brain. Depending on the location of formation and nature, the following types of benign neoplasms are distinguished:
- Meningioma. The most common type of tumor. In most cases, it is diagnosed in women over 40 years of age. Its development involves the hard tissues of the lining of the spinal cord or brain. It can grow both inside and outside the skull, causing thickening of the cranial bones. In later stages, it can degenerate into malignant and metastasize to other organs;
- Pituitary adenoma. It accounts for about 10% of all neoplasms. Most often it occurs in women of reproductive age or in the elderly. Accompanied by abnormal proliferation of glandular cells and an excess of hormones. It is small in size, characterized by slow growth and leads to disruption of the endocrine system;
- Hemangioblastoma. A very rare type of tumor that forms from the vascular tissues of the brain or spinal cord;
- Oligodendroglioma. Localized in the white matter of the brain, consists of multiple cysts;
- Well-differentiated ependyoma. Occurs in 3% of all primary tumors. They are localized in the ventricles of the brain and disrupt their functions. They tend to degenerate into a malignant form. Most often diagnosed in children under 3 years of age;
- Astrocytoma. Develops from astrocyte cells that feed neurons. Can reach large sizes;
- Chondromas. They are formed from cartilaginous tissue in the area of the pituitary gland, at the base of the skull. They can be either single or multiple and reach large sizes. They are characterized by very slow growth. Very rarely diagnosed;
- Schwannoma. Develops from cells of the auditory nerve (Schwann cells), called the acoustic or 8th cranial nerve. Localized in the region of the posterior fossa. Diagnosed in middle-aged women, characterized by very slow growth;
- Glioma. Formed in the brain stem. Diagnosed in children under 5 years of age. The patient has a favorable prognosis, since the tumor responds well to treatment;
- Ependyoma. Affects the ventricles of the brain. Has the ability to degenerate into malignant;
- Cysts. Benign formations, but when located in the departments responsible for the vital functions of the body, can cause serious complications. They have a varied structure depending on the filling: arachnoid (with liquid), colloid (with jelly-like filling), etc.;
- Lipomas. Diagnosed very rarely. Multiple or single, they are located in the area of the corpus callosum.
Prevention and prognosis
Experts divide the prevention of brain tumors into primary and secondary. Primary prevention is the elimination of provoking factors, namely:
- a ban on the consumption of processed meat products (sausages, smoked meats, hams, etc.);
- a ban on the consumption of fried and nitro-containing foods that contain carcinogens;
- limiting smoking and drinking alcohol, including energy drinks;
- restriction of cell phone use.
Secondary prevention is the implementation of measures aimed at excluding other diseases accompanied by the spread of pathological cells to the brain area.
How long can the life of a patient suffering from this disease last? Its duration depends on many factors. That is why it is impossible to accurately answer such a question.
How long do people live with stage 4 brain cancer? Unfortunately, the prognosis is not encouraging. In 70% there is death. Average survival rate is up to 5 years.
Diagnosis of a benign brain tumor
It is important to determine the presence of a tumor at an early stage, as soon as the first warning signs appear. The initial examination and diagnosis is carried out by a neurologist. He assesses the condition of the vestibular apparatus, checks vision, and assesses the condition of the organs of hearing and smell. If necessary, if there are still suspicions, a number of additional examinations are prescribed using special equipment, with the help of which it is possible to accurately identify the lesion, determine its location, boundaries, size and nature.
- Encephalography. Allows you to determine the presence of tumors and identify changes in the brain. But this is not a sufficiently informative method for a complete diagnosis;
- MRI or CT scan of the brain. The most informative methods to accurately determine the presence of a tumor and its parameters; they can be used to judge the condition of the blood vessels and tissues of the brain;
- Positron emission tomography (PET) is a study that specifies the size of the tumor;
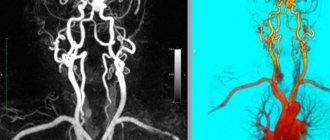
- Magnetic resonance angiography. It is carried out to study the vessels feeding the tumor. To obtain data, a contrasting liquid is used, which makes it possible to accurately determine the boundaries of the tumor.
- Stereotactic biopsy. In order to prescribe treatment and draw up a plan for the operation, a 3D model of the brain with the tumor located in it is built and the area from which material for a biopsy will be taken using a probe is determined.
When the presence of a tumor is confirmed, a number of additional studies are carried out to determine its benignity, a detailed blood test, and a cerebrospinal fluid analysis.
Features of treatment when confirming the diagnosis
The main treatment method for diagnosing a benign tumor is surgery. Its implementation is possible only if there are clear boundaries between the tumor and the meninges. If the tumor has already grown into the membranes of the brain, planned surgical intervention is impossible. But if there is active compression of an area of the brain, and as a result of removing part of the tumor, the patient’s condition may improve, partial removal of the tumor is performed.
If the tumor blocks the flow of cerebrospinal fluid or interferes with the movement of blood through the vessels, bypass surgery can be performed before the operation under MRI guidance - the installation of a system of flexible tubes that will partially compensate for the deficiency of the cerebrospinal fluid pathways.
Removal of a tumor can be carried out in several ways:
- scalpel (craniotomy). Craniotomy and tumor removal are performed, but with this method the chance of damage to nearby brain tissue increases, which can later affect the patient’s reflex functions;
- laser. Using high temperature, it evaporates excess cells without affecting nearby ones;
- ultrasound. High-frequency sound crushes the tumor into small parts and, through suction under negative pressure, removes them from the cranial cavity. This method is used only when the neoplasm is confirmed to be benign;
- radio knife It vaporizes tumor tissue, preventing tissue bleeding, and at the same time irradiates adjacent areas of the brain with gamma rays.
After surgery to remove a tumor, especially in the case of partial removal, active drug support for the patient is required. Sleeping pills, painkillers and sedatives are prescribed. Postoperative cerebral edema can be reduced by taking hormonal drugs.
After removal of a benign tumor, the patient is not prescribed chemotherapy, since it does not metastasize to other organs.
Source: onevrologii.ru
What determines life expectancy?
It’s curious, but for some reason everyone is interested in life expectancy, but few are interested in its quality. Therefore, we will also focus on this important parameter, since a person with brain death, who is on a ventilator in a vegetative state, who is practically preparing to become an organ donor with the consent of relatives, apparently has little comfort in the fact that “life” is not over yet.
Is a benign tumor not dangerous?
The important point is that a benign brain tumor can cause no less harm than a malignant one, and the question of how many people live with such a tumor will become relevant. For example, if we take an acoustic neuroma, then this is a completely benign tumor. The difference between a benign tumor is that it grows slowly and does not destroy, but only pushes aside other tissues and formations, and, in principle, it can always be completely removed without any problems.
But if the situation is neglected, it can cause not only occlusive hydrocephalus, since it will compress the cerebrospinal fluid pathways, but also cause compression of the brain stem, which can result in bulbar syndrome, cerebral edema and death.
Dependence of life span on tumor location
How long does a person live with a brain tumor? If the tumor is located in the anterior cranial fossa, then, other things being equal, the person will live longer than if the tumor is located in the posterior cranial fossa. The thing is that it is in the posterior fossa that the vital sections are located, and in the anterior fossa there are new zones of the cortex that are responsible for the psyche and intellect.
And in the case of tumors in the anterior fossa, a person may experience epileptic seizures, mental disorders, foolishness, decreased intelligence, euphoria, untidiness and decreased criticism of one’s condition. Perhaps his personality will change. But at the same time, a patient with a posterior tumor will experience more serious disorders, directly leading to cerebral edema and which can threaten life much more quickly.
The most dangerous tumors are those of the brainstem and medulla oblongata , especially low-grade glioblastomas. Perhaps this malignant brain tumor, located in the brainstem, gives the most disappointing answer to the question “how long do they live”: from the first symptoms (choking, difficulty swallowing, speech and voice) to death from damage to the vasomotor center and respiratory centers it can take 2- 3 months.
Dependence of the period on the type of tumor
It is important that all neoplasms have varying degrees of malignancy.
Thus, craniopharyngiomas and meningiomas are treated better than astrocytomas, especially poorly differentiated ones, and much better than glioblastomas.
In general, if a histological examination has not been performed, it is difficult to answer the question about the percentage of five-year survival. If the tumor is diagnosed only by MRI, then neurosurgeons can only talk approximately about the timing and prognosis.
They can tell for sure. Only with the data of histological examination in hand. And they, in turn, often receive it only during surgery.
Surgery to remove a brain tumor may result in recurrence. How long do they live after a relapse? Usually, if surgeons decide to remove it, there is a chance of a five-year survival rate, since for tumors with pronounced progression and invasion of brain structures, surgical treatment is refused and chemotherapy and radiation therapy are prescribed.
Peculiarities
A benign brain tumor is an intracranial neoplasm that can be treated. ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases) code – D33.0. The exact name of the disease is a benign neoplasm of the brain above the tentorium.
The neoplasm appears due to chaotic cell division. Unlike a normal cell, a diseased cell is underdeveloped and does not function.
Benign formations:
- develop to a specific stage;
- are formed within one organ;
- do not metastasize.
The reasons for the appearance of various neoplasms are the same. Benign and malignant tumors manifest themselves in the same way.
To identify the type, special examinations are carried out:
- MRI;
- CT scan;
- Submission of biomaterial for research (biopsy).
Causes
No doctor can answer why a brain tumor occurred. But there are factors that provoke development. It is impossible to predict which person will develop a brain tumor in the future.
Heredity
Human genes are modified due to the negative impact of various factors. Changes happen for the better and for the worse. An oncogene can manifest itself even after decades. Therefore, it is not necessary to expect negative consequences in a person under adverse influence. They may occur in the future in children, grandchildren or great-grandchildren.
Chemical exposure and radiation
Living in areas with high levels of radiation provokes the appearance of tumors. If a person’s work involves chemicals (mercury, lead, oil), such risks are likely.
Viral and bacterial infections
Infectious diseases can affect the human body, especially the brain and central nervous system. Against the background of weakened immunity, exposure to viruses or bacteria causes the development of a tumor.
First symptoms of the disease
A malignant neoplasm can begin its development either in one of the parts of the brain or enter it through the bloodstream from any other organ along with metastases.
When cancer is detected, the attending physician predicts the further development of the disease and prescribes the optimal way to combat the disease, based on the following factors:
- patient's medical history;
- type of cancer;
- degree of disease;
- tumor characteristics;
- subtype;
- cell condition (histology);
- size;
- location.
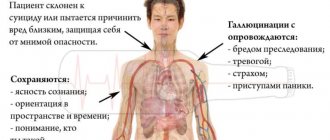
By the location of the tumor, you can notice the first signs of the disease. The symptoms are quite extensive:
- Constant headaches. This is due to the fact that the tumor slowly but surely grows throughout the brain, like a spider’s web. The vessels narrow, intracranial pressure increases. Hence the headache, sometimes even migraine.
- Dizziness. The tumor compresses the structural vessels of the cerebellum, which are responsible for the correct balance of the vestibular apparatus
- Nausea. As a result of intracranial pressure on the middle (gag) center, it causes the gag reflex. The main distinguishing sign of vomiting with a brain tumor is that there is no feeling of relief after it.
- Lethargy and fatigue. The tumor compresses the vessels through which blood and vital microelements enter the brain.
- Changes in hormonal levels. Due to tumor damage to the hypothalamus or pituitary gland, a common symptom is changes in hormonal levels. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland are important parts of the central nervous system, which are responsible for the activity of all endocrine glands.
- Disorders associated with the patient's autonomic system and resulting from constant fatigue. They manifest themselves in the fact that a person is simply unable to get out of bed.
- Impaired memory, attention – psychomotor reactions in the patient’s body.
- Paralysis. It is one of the first symptoms of brain cancer. Impairment of the musculoskeletal system is associated with the same pressure on the blood vessels of the brain. Paralysis can occur in both lower and upper limbs. It happens that the pathology covers the entire body.
- Hearing and speech impairment. Incoherent speech, poor sound recognition. All this indicates that you may have a malignant tumor.
- Sensitivity. The characteristics of this symptom are such that sometimes the patient does not distinguish the pain from the injection given, and does not feel the position of his body in space.
If any of the above symptoms occur, you should consult a doctor. A medical specialist will either refute the terrible diagnosis or confirm it. But it is worth remembering one main thing: stage 1 brain cancer is treatable, and there is a great chance of a full recovery and return to normal life. Operations are performed every day, and as statistics show, after surgical manipulations, after removal of a malignant tumor, the patient lives for many years.
https://youtu.be/Le6T-EEGTr4
Classification
Primary and secondary neoplasms are distinguished. The difference is that the primary ones appear in the brain from the very beginning. They are localized in one place, preventing metastases. There are different types.
Secondary ones arise due to metastases from malignant neoplasms of another organ. The manifestation becomes a consequence of the development of other tumors. Secondary formations can be exclusively malignant.
Meningioma
A common type of neoplasm. Formed from the soft meninges. It is a clearly defined knot of a rounded shape or in the form of a horseshoe. Often adheres to the dura mater of the brain. There are also flat knots. The size of meningioma reaches several centimeters. The tumor tissue is gray-yellow.
Often meningioma is a benign formation. To determine the species, histological examination is used.
Meningiomas are removed surgically. Tumors do not cause relapses. If the tumor is in a hard-to-reach area, use a cyber and gamma knife. Chemotherapy and radiation are not performed.
Neuroma
Also called schwannoma. The diagnosis is common among children. Neuromas make up 8% of tumors that primarily developed in the brain.
Formed from nerve sheaths. It looks like a capsule with light nodules enclosed in it. Symptoms of schwannoma development include:
- hearing loss;
- dizziness;
- trigeminal neuralgia.
Pituitary adenoma
Formed from glandular tissue. Benign tumor. The pathology causes excessive production of hormones. When there is an excess of thyrotropin in the body, the functioning of the thyroid gland is disrupted. Excessive amounts of prolactin cause infertility. Due to an excess of somatotropic hormone, gigantism develops.
Astrocytoma
A benign tumor that forms in the brain from astrocytes - star-shaped neuroglial cells. The diameter of the formation sometimes reaches 10 cm. Children are more susceptible to astrocytoma. The tumor has a pale pink color and is close in density to the brain substance.
Oligodendrocytoma (oligodendroglioma)
Glial tumor, that is, developing in neuroglia. It has a gray-pink color. There are cysts in its structure. Develops slowly in the white matter. Capable of growing to large sizes. Men are more often affected (ratio 3/2).
Ependymoma
Education of the central nervous system. Formed from cells of the ventricles of the brain.
It can be on their surface or inside. It can occur equally among children and adults. Has cystic and necrotic formations. Ependymoma can metastasize. Tumor cells spread along the cerebrospinal fluid outflow tract.
Craniopharyngioma
Present from birth. Develops from embryonic cells of the pituitary tract. Usually benign, but can become malignant. Rarely seen. Causes blurred vision, headaches, hormonal imbalances, and destruction of the nerves of the skull.
A benign formation becomes malignant due to negative influence. To avoid this, it is important to start treatment on time. Observation is excluded; malignancy will occur at any moment.
Classification of tumors
This type of cancer includes both benign and malignant neoplasms, which differ from each other in the cause of development, their distribution, symptoms and prognosis.
To date, there is no unified classification of brain tumors. This can be explained by their diversity and difficulty in diagnosis. The most accurate classification is considered to be one in which oncological tumors are distinguished by histological structure and degree of maturity.
Based on the degree of maturity, there are 2 types of neoplasms:
- malignant (glioblastoma, etc.);
- benign (gliomas, etc.).
Considering the area of the brain in which the tumor developed, neoplasms are distinguished:
- inside the brain;
- inside the ventricle;
- outside the brain;
- in the intermediate zone: embryonic, teratomas;
- according to the type of metastatic nodes, cysts (in the frontal and other lobes).
Taking into account histogenesis, experts distinguish the following types of neoplasms:
- neuroepithelial, which are formed from the medulla;
- meningovascular, which are formed from the membranes of the brain;
- pituitary adenomas;
- neoplasms, derivatives of mesenchyme;
- neoplasms from the nerves of the skull;
- teratomas that form as a result of impaired embryogenesis;
- metastatic neoplasms (the so-called tumors that develop from malignant cells spread from another primary focus).
The most common benign tumor is meningioma, which is formed from cerebral vessels. If such a neoplasm is diagnosed at the initial stage of its development, one can hope for a favorable prognosis. The only exception is the localization of meningioma in the trunk. Even with a small tumor size, compression of nerve tissue can occur and serious disorders can develop.
Common malignant neoplasms are glioblastoma and medulloblastoma. Medulloblastoma has a high level of malignancy, as it is formed from the least immature cells - medulloblasts. The main source of formation is the development of dysgenetic changes.
Glyblastomas in most cases form in people after 40 years of age. The tumor is characterized by rapid progression, has no clear boundaries, and is prone to secondary changes (even with timely treatment) - necrosis, hemorrhages, cysts.
Metastatic tumors can be classified as a separate group of brain tumors. Pathogenic cells most often spread to the brain from a neoplasm located in the mammary gland, lung or kidneys.
Symptoms of tumor development
It is often difficult to suspect the presence of a neoplasm. And given the slow development, a person does not feel its presence after years. Rapidly growing formations make themselves felt earlier. A person does not immediately think about a tumor. Often ailments are written off as signs of another disease.
The following should be taken seriously:
- Continuous headaches. Felt at a specific point or part of the head. For example, in the temporal, occipital, frontal region, depending on the location of the tumor. As it grows, the symptom intensifies due to compression of other areas. Painkillers do not have the desired effect.
- Uncoordination of movements. It occurs due to constant acute headache or under the influence of a tumor on the vestibular apparatus located in the cerebellum.
- Nausea or vomiting in the absence of gastrointestinal problems. May occur due to dizziness.
- Deterioration of memory and mental activity, sudden changes in mood.
- The appearance of seizures.
- Also, depending on the location of the tumor, speech is impaired, hearing is reduced, limbs become numb, and vision deteriorates.
If you have such symptoms, you should undergo a medical examination.
Medical examinations are carried out regularly to allow timely detection of developing tumors.
Metastases in the brain - how quickly do they grow?
The rate of growth of brain metastases varies depending on the type of maternal tumor that has spread to this part of the central nervous system.
Most often, cancers of the lung, breast, colon and kidneys metastasize here. In addition to cancer cells, melanoma cells often migrate to the brain.
In most cases, metastases are found in the upper parts of the brain, but some may grow at the base of the brain.
Secondary tumors are single (less often) and multiple (more often). If they can be detected and neutralized in time, or at least weakened, the growth of metastases slows down. Sometimes doctors manage to achieve complete regression, and the cancerous nodes disappear.
Diagnostic methods
To make a diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct several surveys and studies:
- During the interview with the patient, the existing symptoms are identified and the duration of poor health is determined. Tests are ordered if necessary. But they cannot detect a tumor. You can learn about the inflammatory process or other pathologies associated with the development of the tumor.
- Magnetic resonance imaging can determine the presence of a tumor. During this examination, images of the brain are taken from all sides. This way you can see the location of the tumor and its size.
- Computed tomography, electrical activity of the brain, angiography, craniography - these examinations provide detailed information about the tumor and allow you to determine the right direction of treatment.
- A biopsy (removal of tumor cells from the patient) determines whether the tumor is benign or not.