Perhaps one of the most common injuries among adults is traumatic brain injury. Unfortunately, they have extremely negative consequences for humans.
Despite the fact that everyone has the opportunity to get a traumatic brain injury, statistics show that most often such injuries are suffered by men aged 20 to 50 years on average.
Traumatic brain injuries come in many varieties. Depending on the type and nature of the problem, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment and rehabilitation procedures.
Symptoms of traumatic brain injury can vary, so it is important to differentiate one injury from another. This affects the future state of a person.
How and why post-traumatic headaches occur
Traumatic brain injuries can lead to consequences in the form of prolonged headaches. They have various causes, which include:
- vascular cephalgia;
- cephalalgia of a neuromuscular nature;
- cerebrospinal fluid cephalgia;
- membrane headache;
- neurotic headache .
On this topic
- Shake
7 Facts About Concussions
- Natalia Sergeevna Pershina
- May 26, 2020
Since there can be several causes of headaches after injuries, specialists are not always able to correctly diagnose the patient and prescribe effective treatment.
The occurrence of headaches after a concussion and other traumatic brain injuries is observed in the following cases:
- excessive muscle tension in the neck, which causes a pressing headache spreading over the entire surface of the head;
- increased intracranial pressure - increases when problems arise with the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid;
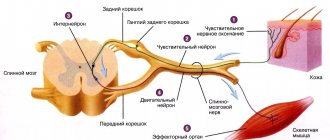
- impaired blood circulation - occurs during a strong blow when blood vessels are damaged, which, in turn, leads to spasms in the arteries and cephalalgia;
- irritation of the nerve endings located on the membrane of the brain;
In order to make a correct diagnosis for a patient, specialists must take into account all possible causes of prolonged headaches, as well as the circumstances under which the injury occurred.
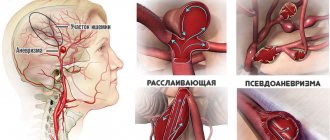
13.1. Etiology and pathophysiology
According to neurosurgeons, most patients experience compression of the trigeminal nerve in the area of its exit from the pons by a large artery (mainly the superior, and sometimes the posterior cerebellar artery, vertebral artery, or anterior inferior cerebellar artery). In rare cases, the nerve is compressed by a vein, arteriovenous malformation, or tumor.
Among patients with trigeminal neuralgia, a small part (0.5-1%) suffers from multiple sclerosis. In this group, the cause of neuralgia may be the formation of a sclerotic plaque in the area of the sensory nucleus of the trigeminal nerve.
Some dentists believe that trigeminal neuralgia is caused by small infectious lesions in the teeth or gums, leading to the spread of excitation along the branches of the trigeminal nerve, but there is no convincing evidence on this matter.
How the possible causes of trigeminal neuralgia (mechanical compression, the formation of a sclerotic plaque, infectious foci in the oral cavity) lead to the development of the disease is not clear.
According to the hypothesis of the central origin of pain, it is considered to be similar to focal epilepsy, with deafferentation playing an important role in the development of neuronal hyperactivity. The peripheral hypothesis considers attacks of pain as a consequence of increased sensitivity of the compressed trigeminal nerve to mechanical or chemical stimuli.
According to the combined hypothesis, the first stage of the disease—damage to the trigeminal nerve—leads to further central synaptic changes with the formation of a pain system in the brain that is stable, highly excitable, and responds to afferent stimuli with paroxysms of pain.
How long does a headache last after a concussion?
For the most part, the duration of headaches depends on the nature of the headaches - chronic or acute, as well as on how correctly the diagnosis was made and how effectively the treatment was carried out.
On average, with injuries of moderate severity, pain can last up to 2-4 weeks, in more severe ones - from 8 weeks or longer. The period of cephalgia depends on the general health of the body at the time of injury, and on the nature and severity of brain damage.
Not the least important factor in a complete recovery is compliance with the prescribed rehabilitation measures and the patient’s desire to get well soon. Full recovery of the brain after injury can take from six months to a year.
Bed rest
Does a person feel sick after hitting their head? Most likely he has a concussion. The next point of action is compliance with bed rest. That is, immediately after the blow it is necessary to transfer the “victim” to a horizontal position. But in such a way that after regaining consciousness the person feels comfortable and comfortable.
By the way, for concussions, the absence of brain tension, as well as bed rest, are the main methods of treatment. Therefore, try to provide the person with peace for a while. Just don’t leave the victim alone - maybe he will need your help!
Acute manifestation of cephalgia
Headache can have both acute and chronic manifestations. Acute pain occurs within the first two weeks from the moment the patient receives a traumatic brain injury.
If the patient has a particularly severe brain injury, the pain may last up to 7-8 weeks, depending on the nature of the injury and the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment.
The main causes of headaches after severe head impacts are soft tissue bruises, vascular spasms and tissue swelling in the brain. They are also caused by the presence of hematomas in the epidural, subdural and intracerebral space at the site of impact.
In order to make a correct diagnosis, specialists need to conduct an additional examination of the brain in order to find out the causes, as well as draw up a course of treatment and decide on possible surgical intervention.
Localization of pain
Often, it is the location of the “accumulation” of pain after hitting the head that can indicate a particular injury. True, it is not recommended to diagnose yourself. It is advisable to consult a doctor for a correct diagnosis.
Does your head hurt when you bend over after an impact? Quite normal. But try to concentrate and understand exactly where and what type of pain bothers you. A concussion is usually indicated by a pulsating sound localized in the back of the head.
Additionally, the victim, regardless of age, will experience dizziness. All signs of injury disappear after approximately 2-3 weeks, but sometimes they persist for a longer period of time. What to do if you just hit your head hard? What measures need to be taken immediately? It doesn't matter whether you have a concussion or a simple bruise, you need to understand exactly what to do.
Chronic manifestation of cephalalgia
If acute cephalgia is characterized by a fairly rapid manifestation of post-traumatic headaches, then chronic cephalgia is characterized by a gradual increase in unpleasant sensations and their long duration.
The headache in such cases lasts more than 7-8 weeks and is very difficult for the patient to tolerate. Foci of pain do not have one location; they constantly change their location and can last for several hours or even days. During this time, the patient becomes very irritable, tired and exhausted, incapable of any vigorous activity.
Peace and quiet
The next point is suitable for all cases in which a headache occurs after hitting your head. A person needs to be provided not only with bed rest, but also with silence. Make sure that there are no additional sources of noise around the victim. In this case, the headaches will not be as severe and will pass faster.
It would be good to provide a person with sleep. You can use sleeping pills. Just don't overdo it. In general, doctors do not welcome such a decision. A person must fall asleep on their own.
The last thing to note is that sometimes the pain can be dulled with painkillers. A very good approach, especially if you just hit your head hard, and now you can’t rest, sleep, or just get to the doctor. It is recommended to take tablets available without a doctor's prescription.
Basically, that's all. If you have headaches for a long time after hitting your head, consult a doctor. Usually, drug treatment is not required for concussions or bruises. Only in extreme cases. Performance is also not disrupted too often. So don't panic if you hit yourself!
Treatment
In medical practice, the treatment of head pain that occurs after moderate traumatic brain injury is accompanied, rather, not by a relief of sensations, but, first of all, by the eradication of the very cause of cephalalgia.
On this topic
- Shake
Everything you need to know about concussions
- Natalia Sergeevna Pershina
- March 26, 2020
Doctors have developed several methods that differ in their effectiveness for each individual case of post-traumatic problems:
- If spinal (cerebrospinal fluid) dynamics and with high blood pressure, patients are prescribed drugs that reduce the production of cerebrospinal fluid.
- For vascular causes of cephalalgia, specialists prescribe medications that help normalize blood pressure and normalize vascular tone.
- For swelling of the brain tissue, the patient is recommended to take diuretics, otherwise called diuretics.
- For pain caused by excessive overexertion, doctors suggest treatment with analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Doctors, in accordance with the diagnosis, draw up a treatment plan that requires a certain algorithm, and it looks something like this:
- The patient is prescribed analgesic drugs, non-steroidal and anti-inflammatory (example: Nice, Ibuprofen, etc.).
- Further, provided that the patient has increased anxiety and nervousness, he is prescribed sedatives without the effect of a sleeping pill, such as Motherwort Forte, valerian, glycine, etc.
On this topic
- Shake
How to properly provide first aid for a concussion
- Ekaterina Nikolaevna Kislitsyna
- March 26, 2020
Physiotherapy is also considered one of the treatment methods, which may consist of:
- Laser restoration and stimulation of vascular tone.
- Impact of high-frequency current pulses on the head and neck area (carrying out darsonvalization).
- Electrophoresis of the collar zone.
Constant and prolonged headaches should never be taken for granted, especially after traumatic brain injury.
If nausea and vomiting, dizziness, and constant weakness are added to constant unpleasant sensations, you should immediately contact a specialist for consultation and additional examination. This is necessary in order to exclude the possibility of developing other, more dangerous pathologies.
You can’t create a treatment on your own, just as you can’t remain without it at all. If you treat a headache superficially, trying to constantly treat it with painkillers, it becomes chronic and disrupts all the patient’s plans.
What diagnostic methods are needed for a concussion?
At the first manifestation of post-traumatic symptoms, you should immediately seek medical help. In serious condition, the patient is admitted to a hospital. The patient should be examined by a therapist, traumatologist, neurologist and neurosurgeon.
Rarely does the patient's condition improve a few hours after the injury. During this period, hematoma formation is observed.
- Diagnosis of the disease begins with consideration of the patient’s complaints followed by an examination by a neurologist.
- A patient with TBI should undergo radiography. This technique allows you to detect a fracture of the skull bones. The condition of the brain cannot be determined using x-rays, but the procedure allows you to find out the severity of the damage.
- Ultrasound examination (US) evaluates the medulla, visually identifying hematomas. This safe method has no contraindications. Ultrasound echography is prescribed for older people whose skull bones are thick.
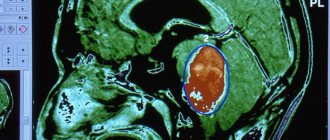
- Using computed tomography, you can diagnose bruises, hematomas, damage to the head bones and foreign bodies. In emergency cases, two methods are used to make the correct diagnosis: MRI and CT scanning.
- A method for recording electrical potential differences (electroencephalography) detects neuronal dysfunction that can lead to epiactivity.
- An invasive examination - brain puncture - is performed in case of bleeding and suspected tumor.
Bed rest and rest for several days or weeks after the injury will reduce the risk of cephalalgia, as a consequence of a concussion. To speed up the recovery process of the central nervous system, the victim is recommended to sleep at least 8-10 hours per night, and stay in a cool and ventilated room.
If a concussion is suspected, patients undergo a diagnosis consisting of an examination, MRI or CT, EEG, X-ray of the head and neck, and ultrasound of the vessels of the skull. This allows you not only to ensure that there are no complications, but also to identify the causes of the headache.
Methods to combat cephalalgia due to head trauma:
- taking medications – depending on the cause of the symptom, the doctor may prescribe different medications. Diuretics will reduce cerebral edema, analgesics will relieve pain, and antispasmodics will alleviate the condition of intracranial hypertension. Sedatives and tranquilizers that relieve tension have a good effect. Additionally, concussion victims are prescribed drugs that stimulate metabolic processes in nerve tissues;
- massage of the collar area in combination with a contrast shower - relaxes tense muscles, stimulates blood flow, helps saturate brain tissue with oxygen;
- physiotherapeutic procedures - the use of laser, electrophoresis and Darsonval eliminates pain, improves cerebral circulation, and relieves muscle spasms.
Traditional medicine can help in the fight against headaches caused by a concussion. Decoctions based on lemon balm, peppermint, yarrow, as well as chamomile tea have a beneficial effect on the nervous system and the body as a whole. The use of such drugs must be agreed with a doctor.
In order to provide medical assistance, first of all, it is necessary to lay the person horizontally on a flat surface and, if possible, fix the head with a loose tourniquet in an elevated position. Under no circumstances should you throw your head back. If a person faints and does not come to his senses, then until the ambulance arrives, you can lay him on his side, bend his right arm and leg at an angle of 90 degrees and raise his head, this will make it easier for air to enter the lungs and nourish the brain.
During inpatient treatment, doctors must take an x-ray, which shows whether there are injuries in the skull itself, prescribe medications and bed rest, and recovery occurs under the supervision of specialists.
Difficulties in diagnosis and treatment can only arise if a person does not see a doctor on time. This happens most often with mild concussions, when the victim does not go to the hospital with complaints in time, and they begin to manifest themselves only after a certain time. In this case, treatment may be delayed, and determining the severity of the concussion may be completely impossible.
After the treatment ends and the brain is restored, it is worth remembering that over the course of several years it is necessary to visit a neurologist and, at the slightest manifestation of symptoms, ask to prescribe treatment with a description of the trauma suffered. In this case, drug treatment is prescribed to restore the body after an injury associated with a concussion.
This is a serious injury that requires a differential. diagnosis, especially if you feel dizzy, there is no relief.
The first stage is a consultation with a traumatologist, neurologist, a study of your medical history (the method of injury, location, severity of the injury), as well as complaints (dizzy, blurred vision, etc.) will complete the picture and help correctly diagnose injuries.
Differential methods examinations:
- CT (computed tomography);
- MRI (magnetic resonance therapy);
- X-ray;
- Biochemical analysis of a cerebrospinal fluid sample if a serious pathology is suspected.
What people are interested in: “What is the diagnosis of MRI or CT?” MRI better reflects the condition of soft tissues and blood vessels, and CT better reflects the condition of the bone structure. If there is any doubt about a concussion, both types of testing are required. They significantly complement each other and will help to correctly diagnose any changes.
Both diagnostics are based on scanning and transmitting a visual image to a computer monitor. If a person has suffered from a severe concussion, time ticks by in minutes, so the doctor prefers a CT scan - the execution time is only a few minutes.
In addition to concussion, MRI will also reveal other pathologies - coronary artery disease, pre-stroke condition, blood clot formation, narrowing of cerebral vessels, which will help adjust treatment.
Even if after the impact you do not feel any serious changes, it is best to go through the differential. diagnosis, some changes may not be felt at first, but gradually develop. Trauma has many consequences, which the differential will help identify and eliminate. diagnostics.
Why does my head hurt after an MRI? Some patients feel dizzy and feel worse – this has nothing to do with the examination. This condition is explained by the body’s delayed reaction to mechanical impact, which can be suppressed or become stronger.
A neurologist and a traumatologist diagnose and treat a concussion; if necessary, a consultation with a neurosurgeon is also required.
These research methods are necessary in order to distinguish a concussion from a brain contusion - a more severe traumatic brain injury, and to exclude hemorrhages in the brain and its swelling. All of the above can also cause headaches.
In general, a concussion is diagnosed based on external functional signs, because it is impossible to detect this injury at the laboratory level using modern means.
Headache
With a severe concussion, even convulsive seizures, similar to epileptic ones, may appear, but later they stop and do not return again.
But headaches due to this injury can bother the victim for many years to come. This pain can develop into a migraine over time, and can be excruciating. At the same time, the victim may periodically feel dizzy and feel motion sick in transport.
To prevent this from happening, you need to consistently carry out the right measures, the goal of which is complete restoration of the brain and the disappearance of pain in the head.
As prescribed by the doctor, the patient should take:
- painkillers;
- sedatives;
- sedatives and other drugs.
If necessary, the doctor may prescribe tranquilizers. But under no circumstances should you abuse these medications; take them strictly in the dosage indicated by your treating neurologist.
It is very important that concussion treatment is carried out in an inpatient neurological department to ensure the necessary rest and proper monitoring of the patient's condition by medical personnel. This is especially true for young children.
The problem of treating a concussion arises when the symptoms, in particular headaches, appear mildly and only a few days after the injury. In this case, you can simply start this pathology.
Also, for a year it is necessary to completely give up alcohol, nicotine, energy drinks, active work and recreation, attending public events, prolonged surfing on the Internet and everything else that can have a stimulating effect on the still immature brain.
It is very useful to move to the countryside, away from the rumbling city and lead a moderate lifestyle. All this will allow you to completely heal the concussion and not suffer in the future from the negative consequences and complications of this injury.
specialist
Concussion Clinic
After a concussion, a headache is one of the components of the clinical picture of such an injury. People of retirement age often experience loss of consciousness and even mild amnesia. An interesting fact is that loss of consciousness is never observed in old people and infants. Elderly people sometimes experience a short-term loss of spatial and temporal orientation, but this has nothing to do with loss of consciousness.
The severity of a concussion is determined by a neurologist based on the following clinical manifestations:
- Dizziness and pain.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Coordination violations.
- Intermittent sleep.
- Nervous overexcitation.
- Dysfunctions of the respiratory and visual systems.
If treatment was prescribed and started in a timely manner, and then all the rules of behavior during the rehabilitation period were followed, then the symptoms of a concussion go away fairly quickly. But it becomes harder to cope with the headache. This symptom can “linger” for quite a long period.
In particular, people of advanced age have headaches for a long time after a concussion, who are diagnosed with hypertension, vascular atherosclerosis and other pathologies one way or another related to the brain.
Possible complications and prevention
Headache always accompanies a concussion, regardless of the degree of organ damage. For this reason, it is considered a symptom of the condition rather than a possible complication. A negative consequence is the long-term persistence of a symptom or its transition to a chronic form. In addition, doctors identify several other conditions that can develop against the background of TBI.
Possible complications after a concussion:
- neuroses and neurotic conditions;
- increased risk of developing epilepsy, Parkinson's disease, hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke;
- changes in emotional background, irritability, mood swings;
- sleep problems;
- weakened immunity;
- exacerbation of the body's reaction to alcohol, tobacco, strong odors, sounds, bright light;
- memory impairment, decreased learning;
- chronic vascular diseases against the background of a decrease in their functionality.
The best prevention of the listed conditions is timely seeking help from a doctor and following his prescriptions. Not a single head injury that causes neurological symptoms leaves its mark on the brain. Attentive attention to health will at least minimize the likelihood of complications for the victim.
The situation when you have a headache for 2-4 weeks after a concussion is normal. This does not mean that unpleasant sensations must be endured. Modern medicine has a number of methods that can alleviate the patient’s condition until recovery.
What to do at home
Of course, if the concussion is severe, then treatment should be carried out in a hospital setting.
Well, a mild form can be treated at home only with strict adherence to all procedures prescribed by the doctor:
- The patient should be provided with complete rest.
- Minimize communication with the patient.
- If necessary, dim the light in the room with the patient.
- Taking sedatives and antidepressants prescribed by a doctor is carried out in the dosage indicated in the prescription.
- Reduce mental activity to a minimum.
- Eliminate irritating factors from the victim’s life for a time: computer and TV.
- Provide a diet based on a dairy-vegetable diet for the period of treatment.
- Sleep is the best medicine in this case.